Plant Anatomy
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Epidermis
Protects against drying out
Pith
Stores excess water and starch
Cortex
facilitates transfer of water, minerals, nutrients, sugars, and hormones
Root Cap
layer of dead cells at very tip of root
Region of cell divsion
is where new cells are constantly dividing
Region of cell elongation
is where cells get longer and most of lengthening happens
Region of maturation
where root hairs begin to develop
Root Hairs
use capillary action to pull water out
Guttation is the release of excess water at tip of leaves
Meristems
are regions of plant where cells are constantly dividing and growing
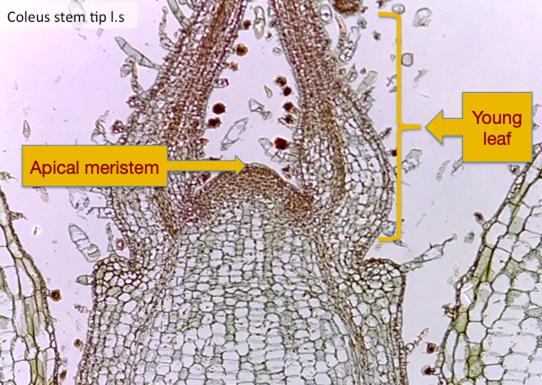
shoot apical meristem
responsible for primary upward growth of the plants
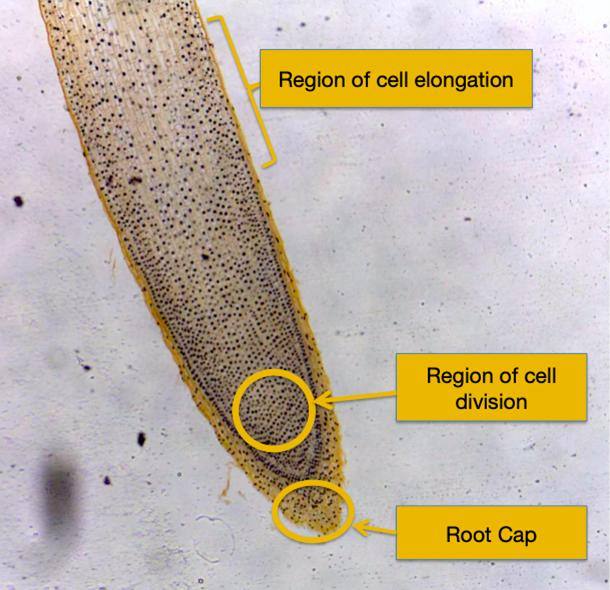
Root apical meristem
responsible for primary downward growth of plant
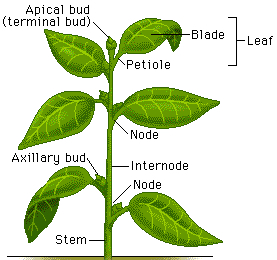
Axillary meristem
can develop into branches and define the overall shape of the plant
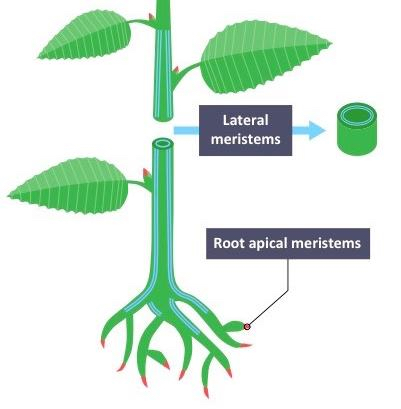
Lateral Meristem
responsible for stem thickening, sometimes called secondary growth, origin of bark and wood