OCHEM 2 Lab Final Study Guide
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
IR of O-H
3600-3200 (strong, broad)
IR N-H
3300-3500 (sharp)
IR C-H (sp3)
3000-2850
IR C-H (sp2)
3100-3000
IR C-H (sp)
3300
IR C-C triple bond
2200-2100
IR C-N triple bond
2300-2200
IR C=O
1850-1650
IR C=C
1700-1600
IR Aromatic Ring
1450-1600
1650-2000
C NMR C sp3
0-50
C NMR C sp2
100-150
C NMR C=O
150-200 ppm
C NMR C sp
50-100
H NMR H on C sp3
0-2
H NMR H on C sp
2-3
H NMR H on C sp2
4-5
H NMR H on Aromatic
6-8
H NMR H in Aldehyde
9-10
H NMR H in Carboxylic Acid
10-12
How do you determine organic and aqueous layers?
The organic and aqueous layers can be determined by adding water to the solution. Whichever layer has increased volume because of the water will be the aqueous layer.
What is the role of anhydrous sodium sulfate in Williamson ether synthesis experiment?
The function of anhydrous sodium sulfate was to dry the organic layer in order to ensure that there is no more water in the product that could give us incorrect IR signals, such as a broad OH curve.
What is the role of tetrabutylammonium bromide in the Williamson ether synthesis experiment?
The role of TBAB in the experiment was to speed up the reaction by allowing the organic and aqueous layers to mix faster than they would have on their own.
Why do you wash the diethyl ether layer containing the product with 5% NaOH during the extraction procedure?
The diethyl ether organic layer containing the product is washed with 5% NaOH during the extraction procedure in order to eliminate any acidic compounds that could be dissolved within the organic layer. The NaOH serves as a base causing an acid-base reaction to occur with any acidic compounds, thereby neutralizing any acid in the product.
Explain one reason why dichloromethane was chosen over the other two organic solvents.
We used dichloromethane in this experiment because it is more polar than ethyl acetate and diethyl ether, meaning that the organic and aqueous layers can be seen easier. Furthermore, dichloromethane has a lower melting point than ethyl acetate and diethyl ether, so it evaporates faster.
NaBH4 is a less powerful reducing reagent compared to LiAlH4. In what ways do these two reagents differ?
NaBH4 is different from LiAlH4 because NaBH4 is less reactive, so it allows us to use any polar solvent. If we used LiAlH4 instead of NaBH4, then we would not be able to use any polar solvent because that would risk producing hydrogen gas, which is highly flammable and thereby dangerous.
What is the role of 3 M HCl in the first step of the extraction process in this experiment?
The role of 3M HCl in the first step of the extraction process would be to protonate a ketone, so the broad alcohol curve in the product could be easily seen.
What is the identity of the bubbles formed during the question #3 step?
The identity of the bubbles formed during question #3 is H2, which is hydrogen gas.
Why is it very important to use moisture free glassware and a moisture free environment during the preparation of Grignard reagent?
It is important to avoid moisture when producing a Grignard reagent because Grignard reagents are strong bases, meaning that in the presence of water, which is weakly acidic, Grignard reagents will produce side products and react violently with water, causing a potentially dangerous exothermic reaction due to the generation of a lot of heat.
Why is it important to add bromobenzene dropwise and slowly to the Magnesium/Ether mixture?
If the bromobenzene is added at a fast rate, it could react with some of the phenyl magnesium bromide. This could cause the formation of biphenyl side products and magnesium bromide, which reduces the amount of Grignard that is available to be retrieved.
State two purposes of adding 3.0M HCl.
One reason for adding 3.0M HCl was to protonate trimethyl phenoxide to triphenylmethanol. Another reason for adding 3.0M of HCl was to ensure that any excess Grignard reagent was deactivated through protonation, so the extra Grignard reagent could not cause any further reactions that could change the final product.
What is the definition of a good recrystallization solvent?
A good recrystallization solvent is one that has a low solubility at low temperatures and a higher solubility and higher temperatures because this allows for the compounds in the solution to be separated and mixed when needed through the manipulation of temperature.
Fischer esterification does not work well with most tertiary alcohols. What would be the major product of the reaction if t-butyl alcohol was combined with acetic acid in the presence of H2SO4?
Tertiary alcohols like t-butyl alcohol are sterically hindered, so they do not usually react in Fischer esterification reactions. However, reacting t-butyl alcohol will react with acetic acid and sulfuric acid, not to form an ester, but to form a carbocation that undergoes elimination to produce isobutene, also known as 2-methylpropene. Therefore, the major product of a reaction between t-butyl alcohol, acetic acid, and sulfuric acid would be isobutene, not an ester.
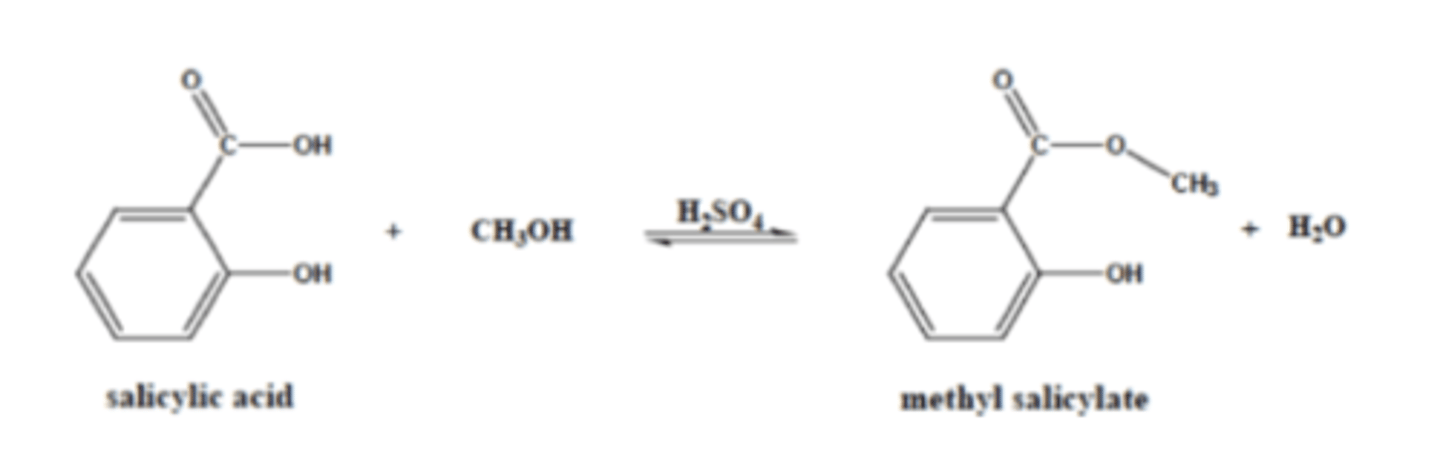
Methyl salicylate exhibits a pleasant wintergreen odor. This ester can be prepared from salicylic acid and methanol via Fischer esterification. Which one of these reagents would you use in excess in order to drive the reaction to the product? Explain how you would isolate the ester product from the reaction mixture for full credit.
Based on Le Chatelier's Principle that increasing the reactants leads to an increase in products, using excess methanol should shift the equilibrium toward the ester product. To isolate the ester, the reaction mixture needs to be washed with water so the ester, which is nonpolar, can separate from the water, allowing it to be extracted as the organic layer. The mixture must then be dried over an anhydrous salt like magnesium sulfate, and the solvent must be evaporated to yield the purified ester.
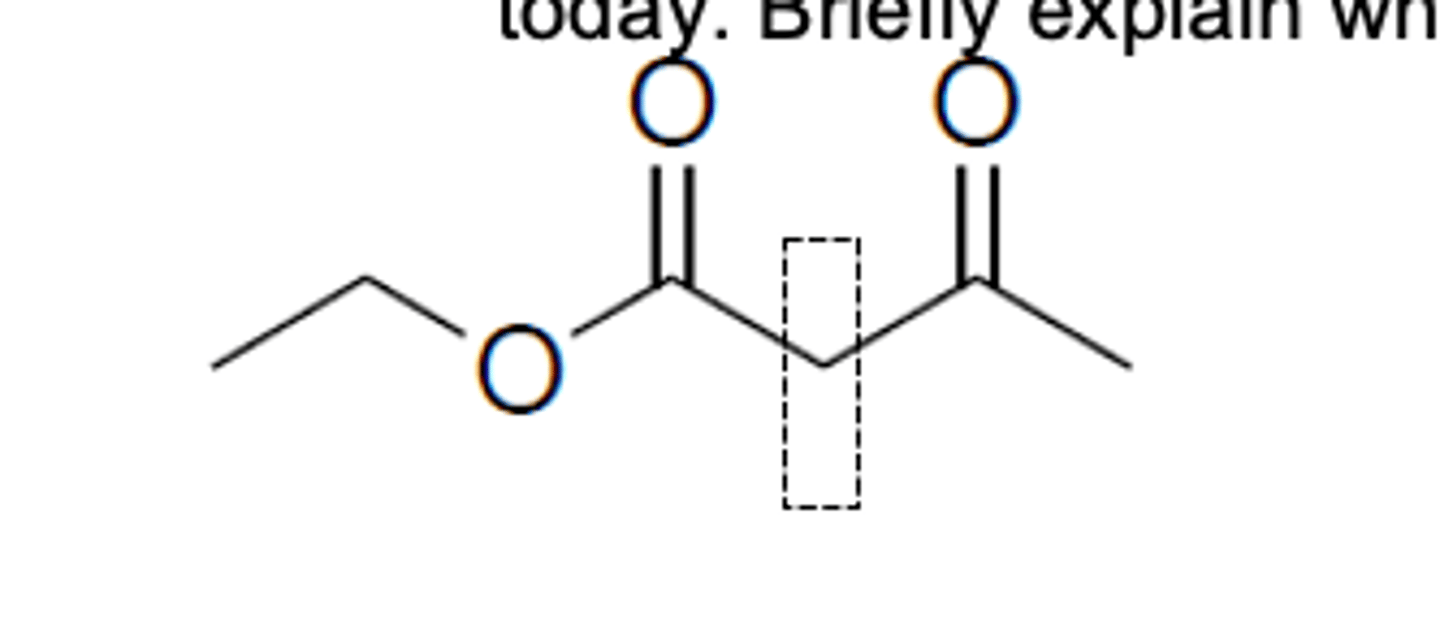
Briefly explain why the H on the boxed carbon atom are highly acidic.
The H in the box is highly acidic because it is surrounded by both the ketone and the ester, instead of just one. This allows for the possibility of more resonance structures when this H is taken away compared to other H's, and allows more electron density to be taken away from the H compared to other H's, rendering the H in the box highly acidic.
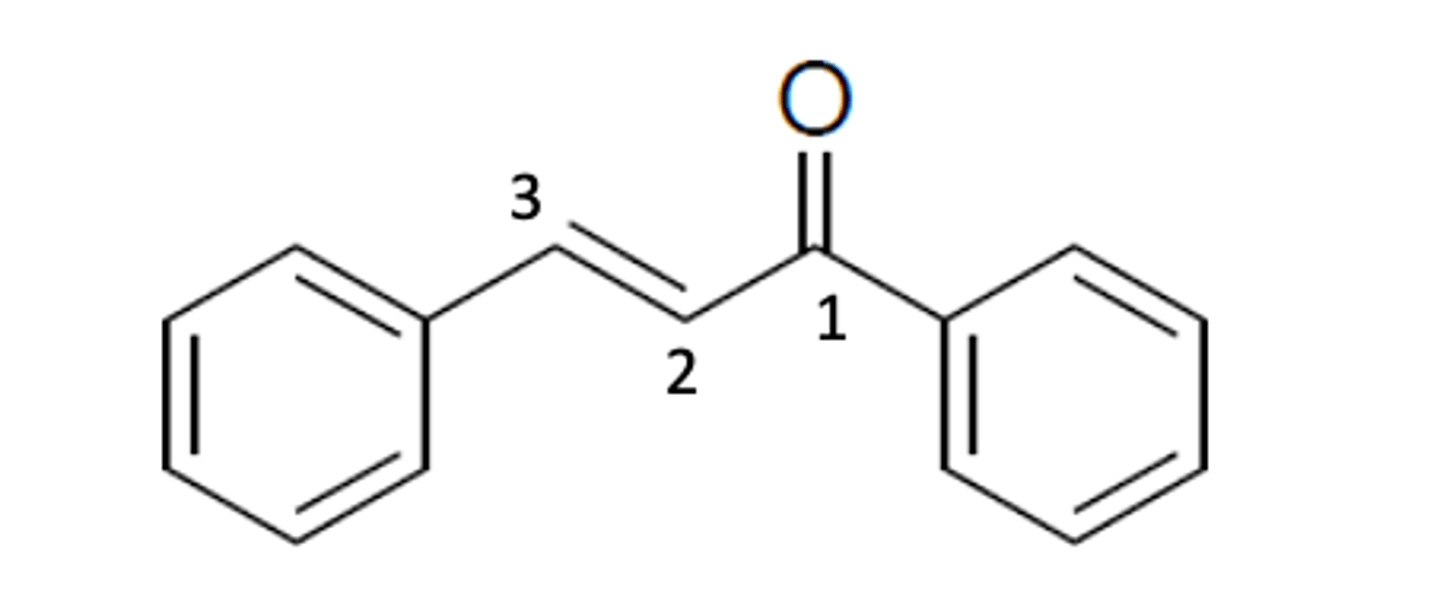
Identify the α and β unsaturated carbons on the ketone.
The α-unsaturated carbon is the carbon in position 2 because it is the carbon next to the carbonyl bond. The β-unsaturated carbon is the carbon in position 3 because it is two carbons away from the carbonyl bond.
Recrystallization
purifies solids by dissolving in hot solvents and allowing mixture to cool slowly
Extraction
separates compounds by using immiscible solvents and an acid/base strategy
Distillation
separates liquids with different boiling points
TLC (thin layer chromatography)
Rf = spot distance / solvent front distance
Column Chromatography
purifies compounds because polar compounds are washed away from the solvent slower
Vacuum Filtration
isolates solids from liquids using a hirsch funnel
Melting Point
checks purity
Pure: higher BP and narrow range
Impure: lower BP and wider range
Grignard Reagent
RMgBr adds to carbonyl → alcohol; dry ether required
Aldol Condensation
Enolate + carbonyl → β-hydroxy ketone → α,β-unsaturated ketone
Diels-Alder
Diene + dienophile → cyclohexene ring; concerted, stereospecific
E1
2 step, weak nucleophile, weak base, tertiary,
(is made with Sn1)
E2
1 step,
strong base, weak nucleophile, primary, secondary, and tertiary
or
strong base, strong nucleophile, primary (minor), secondary (major), tertiary (only product)
Sn1
2 step
weak nucleophile, weak base, tertiary,
(is made with E1)
or
strong nucleophile, weak base, tertiary
Sn2
1 step,
strong nucleophile, weak base, primary and secondary
or
strong base, strong nucleophile, primary (major), secondary (minor)