AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Unit 1-5
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering basic economic concepts for AP Macroeconomics.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Economics
The study of how people satisfy their unlimited wants with scarce resources.
Scarcity
Limited goods and services available for an unlimited amount of wants; leads to choices in satisfying the most important wants.
Macroeconomics
The study of the economy as a whole, including inflation, price levels, GDP, economic growth, national income, and unemployment.
Opportunity Cost
The loss of potential gain from other alternatives when one alternative is chosen.
Trade-offs
Involve losing all other options when a choice is made.
Factors of Production
Land, Labor, Capital, and Entrepreneurship
Capital Goods
Goods made not directly for consumption, used in production (e.g., oven to bake cookies for sale).
Human Capital
Human skills and knowledge that enhance production (e.g., education, training).
Production Possibility Frontier (PPF)
A curve illustrating the possible quantities that can be produced of two products if there is limited resources.
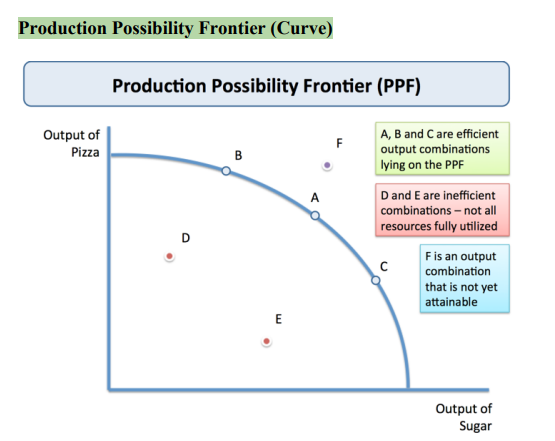
Comparative Advantage
The ability to produce a product at a lower opportunity cost compared to another producer.
Absolute Advantage
The ability to produce more of a product than another producer, using the same amount of resources.
Law of Demand
The inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded; as price increases, quantity demanded decreases.
Law of Supply
The direct relationship between price and quantity supplied; as price increases, quantity supplied increases.
Shifters of Supply
Cost of inputs, change in productivity/technology, number of sellers, government actions (taxes, subsidies, regulations), expectations of future profit.
Shifters of Demand
Number of consumers, change in tastes & preferences, change in income, change in price of substitute goods, change in the price of complementary goods, future expectations.
Equilibrium
The point where market supply and demand balance each other, resulting in stable prices.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
Monetary total value of all final goods and services produced in one country in a period of time.
Expenditures Approach to GDP

Types of Approaches to GDP
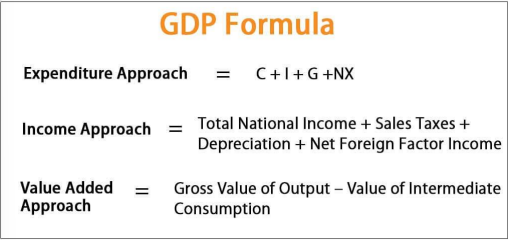
Not Counted in GDP
The sale of something that is not new or does not produce a new product; Intermediate products; illegal activities. (ex: stock and used products and flour used in bakeries)
Circular Flow Model
How many and transactions travel and form our society
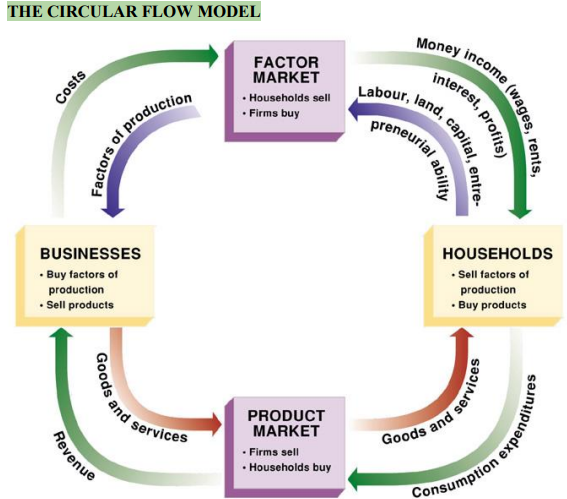
Factor Market
Buy labor from households, sell resources to businesses
Households
Sell labor to factor market, buy products from product market
Product Market
Buy product from businesses, sell product to households
Businesses
Buy factors of production from factor market, sells product to product market
Unemployment
A person capable of working and searching for work, but unable to find a job
Types of Unemployment
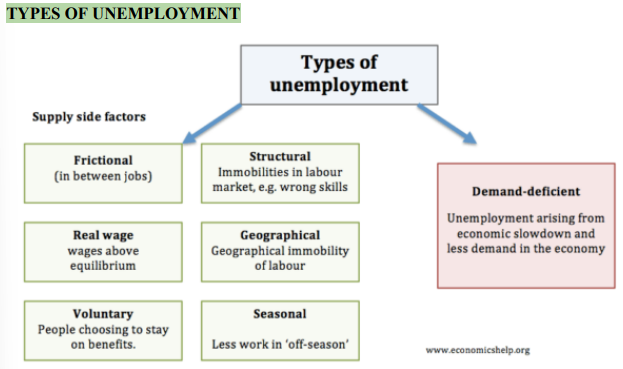
Frictional Unemployment
In between jobs
Structural Unemployment
Replaced by advancement in tech and can’t convert skills into other work
Seasonal Unemployment
Unemployment based on time of year (like lobster fishermen in the winter seaso)
Unemployment Rate Formula
Unemployed (able and looking for work); Labor force (working + unemployed)

Consumer Price Index (CPI)
How the price of a specific product changes over a period of time
CPI Formula

Inflation
General increase of a product’s price; When the price increases, the purchasing power decreases
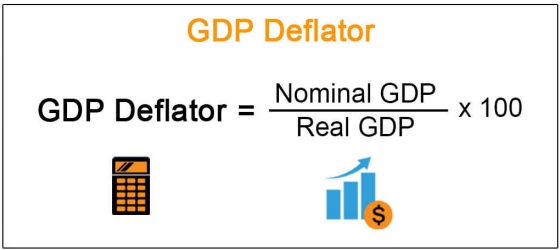
GDP Deflator
Measure of the Economy’s prices of final goods in a period of time
GDP Deflator Formula
Real GDP
Market value of the final production of goods and services within a country in a given period adjusted for price changes that may have occurred over time.
Nominal GDP
Market value of the final production of goods and services within a country in a given period evaluated at current market prices
Aggregate Demand Curve
Shows relationship between aggregate price level and quantity of aggregate demand
Why is Aggregate Demand Downward Sloping
Real balance effect (increase price level decreases purchasing power); Interest rate effect (increase in interest rate decreases borrowing and spending); Open economy effect (higher price levels decreases net exports
Aggregate Demand Shifters
Changes in expectations, changes in wealth, size of existing physical capital
Fiscal Policy
Government spending increase or tax cuts increase demand
Monetary Policy
Quantity of money increases demand