Functional anatomy Lecture 1 (shammy)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Which of the following ligaments is the strongest and helps prevent hyperextension of the hip joint?
A) Ischiofemoral ligament
B) Pubofemoral ligament
C) Iliofemoral ligament
D) Ligamentum teres
C) Iliofemoral ligament
Which structure deepens the acetabulum to enhance joint stability?
Acetabular labrum
Which nerve supplies the gluteus maximus muscle?
B) Inferior gluteal nerve
A positive Trendelenburg sign indicates weakness in which muscles?
Gluteus medius and minimus
What is the primary action of the gluteus maximus muscle?
Hip extension
Which artery is the main blood supply to the femoral head in adults?
Medial circumflex femoral artery
Which nerve is most at risk during a posterior dislocation of the hip?
A) Femoral nerve
B) Obturator nerve
C) Sciatic nerve
D) Superior gluteal nerve
C) Sciatic nerve
(this is becoz sciatic nerve lies posterior to the hip joint )
The angle between the neck and shaft of the femur is termed the:
A) Q angle
B) Carrying angle
C) Angle of inclination
D) Angle of anteversion
C) Angle of inclination
which is the primary muscle responsible for hip abduction?
Gluteus Medius
(It plays a key role in stabilizing the pelvis duing walking and standing on one leg.
Damage to the superior gluteal nerve would most likely cause:
A) Loss of hip extension
B) Loss of hip adduction
C) Positive Trendelenburg sign
D) Loss of hip flexion
C) Positive Trendelenburg sign
The femoral triangle does NOT contain:
A) Femoral artery
B) Femoral nerve
C) Femoral vein
D) Obturator nerve
D) Obturator nerve
What is the originating site of a femoral hernia?
A) Inguinal canal
B) Femoral ring
C) Umbilical ring
D) Epigastric region
B) Femoral ring
What typically protrudes through the femoral ring in a femoral hernia?
A) Stomach
B) Liver
C) Loop of small intestine
D) Kidney
C) Loop of small intestine
Which of the following structures are compressed by the hernia sac in a femoral hernia?
A) Blood vessels and nerves
B) Loose connective tissue, fat, and lymphatics
C) Muscles and tendons
D) Bones and cartilage
B) Loose connective tissue, fat, and lymphatics
What is a common symptom of a femoral hernia?
A) Headache
B) Tender or painful lump in the groin
C) Chest pain
D) Blurred vision
B) Tender or painful lump in the groin
What is the clinical significance of the femoral ring?
A) Site of femoral artery pulse
B) Site of femoral hernia
C) Attachment for inguinal ligament
D) Site for sciatic nerve block
B) Site of femoral hernia
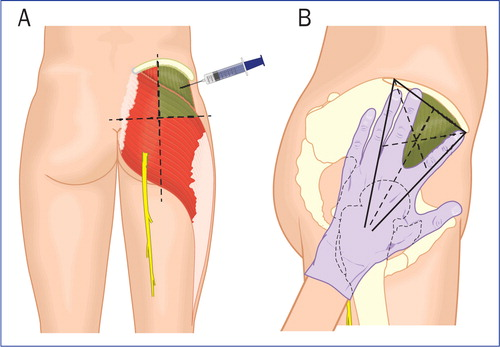
Which quadrant is considered SAFE for intragluteal injections?
A) Inferomedial
B) Superolateral
C) Superomedial
D) Inferolateral
B) Superolateral
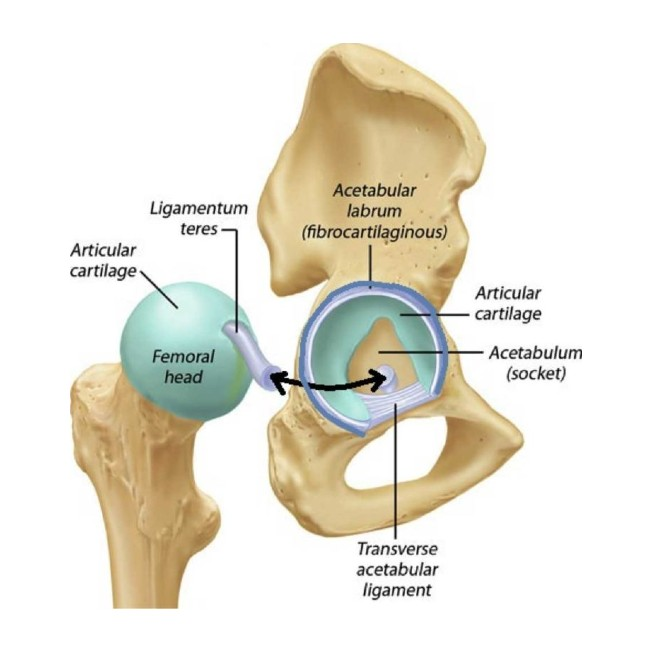
The acetabular notch is converted into a tunnel by the:
A) Acetabular labrum
B) Ligamentum teres
C) Ischiofemoral ligament
D) Transverse acetabular ligament
D) Transverse acetabular ligament
Which structure is most commonly fractured in elderly patients leading to "hip fracture"?
A) Acetabulum
B) Shaft of femur
C) Neck of femur
D) Greater trochanter
C) Neck of femur
During locomotion, which muscle is most responsible for rising from a sitting position?
A) Gluteus medius
B) Gluteus minimus
C) Gluteus maximus
D) Tensor fasciae latae
C) Gluteus maximus
The obturator nerve innervates which compartment of the thigh?
A) Anterior
B) Medial
C) Posterior
D) Lateral
B) Medial
The ligamentum teres attaches the femoral head to the:
A) Ischial spine
B) Acetabular notch
C) Fovea capitis
D) Iliac crest
Fovea capitis
Which of the following is a function of the acetabular labrum?
A) Lubrication only
B) Shock absorption only
C) Deepening the acetabulum and providing stability
D) Attachment for gluteus maximus
C) Deepening the acetabulum and providing stability
A patient with paralysis of the hamstring muscles and sensory loss over the posterolateral leg likely suffered injury to the:
Sciatic nerve
Which is NOT a boundary of the femoral triangle?
A) Sartorius
B) Adductor longus
C) Inguinal ligament
D) Rectus femoris
D) Rectus femoris
The primary function of the hip joint capsule is to:
Hold the femoral head in the acetabulum
Which artery is often used for cannulation during coronary angiography due to its accessibility?
A) Popliteal artery
B) Femoral artery
C) Profunda femoris artery
D) Obturator artery
B) Femoral artery
The femoral artery is commonly accessed for coronary angiography because it is large and easily palpated, providing a convenient route for catheter insertion.
What is the clinical importance of the saphenous opening?
A) Site for venous cannulation
B) Entry point for femoral hernia
C) Attachment for inguinal ligament
D) Passage for sciatic nerve
B) Entry point for femoral hernia
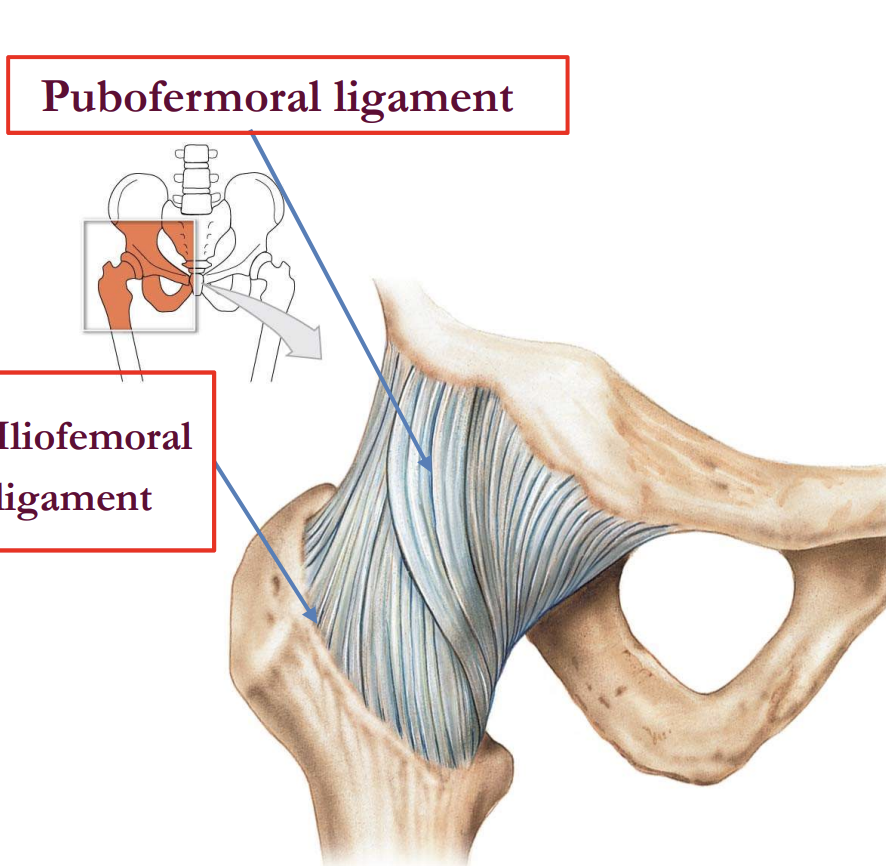
Which ligament limits hyperextension of the hip and helps maintain upright posture?
A) Ischiofemoral ligament
B) Pubofemoral ligament
C) Iliofemoral ligament
D) Ligamentum teres
C) Iliofemoral ligament
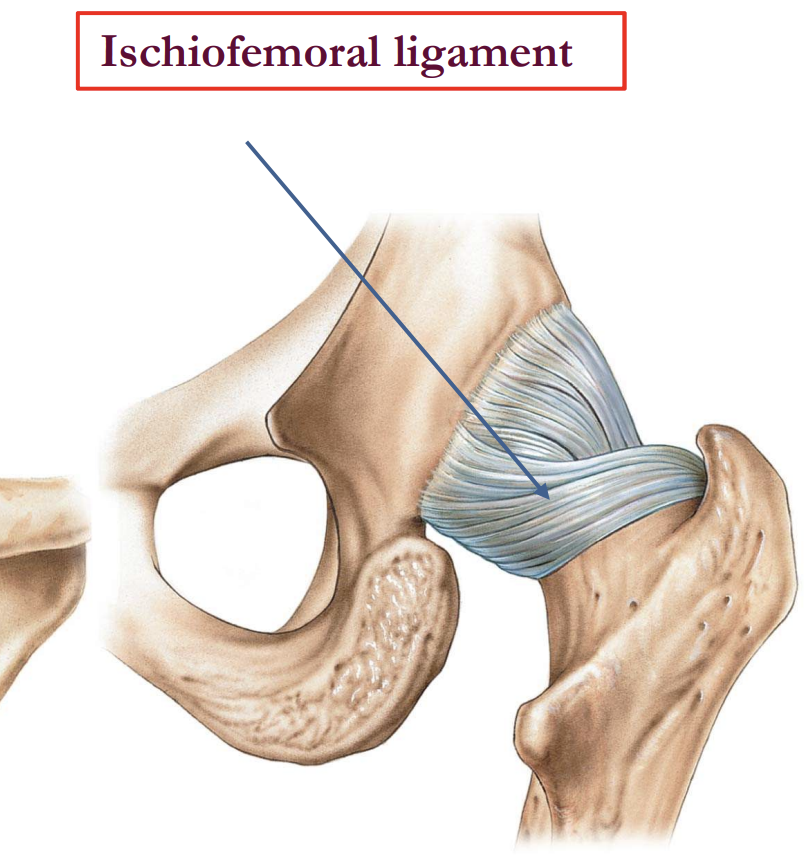
Which ligament stabilizes the hip during internal rotation and extension?
Ischiofemoral Ligament
Which muscle is a major hip flexor and inserts onto the lesser trochanter?
Iliopsoas
Dislocation of the hip most commonly occurs in which direction?
A) Anterior
B) Posterior
C) Superior
D) Inferior
B) Posterior
Which nerve is responsible for the sensory innervation of the skin over the lower lateral aspect of the thigh?
A) Inferior gluteal nerve
B) Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
C) Obturator nerve
D) Pudendal nerve
B) Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
A 75-year-old woman falls and sustains a hip fracture. Which anatomical feature makes the femoral neck especially vulnerable in elderly individuals?
A) High vascularity
B) Increased bone density
C) Narrow diameter and angle of inclination
D) Proximity to the acetabular labrum
Narrow diameter and angle of inclination
A patient displays a positive Trendelenburg sign. Which nerve lesion is most likely responsible?
A) Inferior gluteal nerve
B) Obturator nerve
C) Superior gluteal nerve
D) Femoral nerve
C) Superior gluteal nerve
During hip replacement surgery, which artery must be preserved to prevent avascular necrosis of the femoral head?
A) Obturator artery
B) Medial circumflex femoral artery
C) Inferior gluteal artery
D) Lateral femoral circumflex artery
B) Medial circumflex femoral artery
The medial circumflex femoral artery is vital for supplying blood to the femoral head; preservation during hip replacement surgery is crucial to avoid avascular necrosis.
Which of the following muscles is NOT a lateral rotator of the hip?
A) Piriformis
B) Obturator internus
C) Quadratus femoris
D) Pectineus
D) Pectineus
Which clinical landmark is used to safely administer an intragluteal injection?
A) Ischial tuberosity
B) Inferomedial quadrant of buttock
C) Superolateral quadrant of buttock
D) Sacral promontory
)Superolateral quadrant of buttock
Which ligament prevents excessive abduction and extension at the hip joint?
A) Iliofemoral
B) Ischiofemoral
C) Pubofemoral
D) Ligamentum teres
C) Pubofemoral
Which of the following structures is NOT contained within the femoral sheath?
A) Femoral artery
B) Femoral vein
C) Femoral nerve
D) Femoral canal
Femoral nerve
A 55-year-old woman is diagnosed with a femoral hernia. Through which structure does the hernia pass?
A) Femoral ring
B) Saphenous opening
C) Inguinal ligament
D) Obturator canal
A) Femoral ring
The blood supply to the ligamentum teres in adults is:
A) The main supply to the femoral head
B) Absent
C) A minor contribution from the obturator artery
D) From the inferior gluteal artery
C) A minor contribution from the obturator artery
Which of the following best describes coxa vara?
A) Increased angle of inclination (>135°)
B) Decreased angle of inclination (<120°)
C) Normal angle of inclination (125°)
D) Fracture of the femoral shaft
B) Decreased angle of inclination (<120°)
Palpation of the femoral artery is best performed at which anatomical landmark?
A) Midway between the ASIS and pubic symphysis
B) At the inguinal crease
C) Lateral to the sartorius
D) Over the greater trochanter
A) Midway between the ASIS and pubic symphysis
Boundaries of the Femoral Triangle
Superior: Inguinal ligament
Lateral: Sartorius
Medial: Adductor longus
Contents of the Femoral Triangle (medial to lateral)
femoral vein, femoral artery, femoral nerve
why the superolateral quadrant of the gluteal region is the preferred site for intramuscular injection. What are the risks of injecting in other quadrants?
The superolateral quadrant avoids major nerves and vessels (especially the sciatic nerve and superior gluteal vessels).
Injecting into other quadrants risks injury to the sciatic nerve (inferomedial), superior gluteal nerve, or large blood vessels, which can result in neuropathy, hematoma, or muscle paralysis.