chem test 2
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Which of the following has a higher boiling point? Explain your answer
Oleic acid
Palmitic acid
Elaidic acid
Palmitic acid If you look at the images of palmitic acid, you’ll see that it is a saturated fatty acid. Saturated fatty acids have the highest melting and boiling point because it is a linear and straight structure, therefore, they would make a substance solid, making the MP and BP significantly higher than the rest.
Which of the following above would you recommend for a patient with coronary heart disease? Explain your answer.
Oleic acid because it is an unsaturated fatty acid, therefore, it would form a kink in its structure. This kinky structure does not accumulate as plaque in the body.
Remember omega values are…
Remember omega values are the first double bonds from the end of the fatty acid tail. The ratio is the number of carbons to the number of double bonds.
Arachidonic acid
20:4; omega 6
Oleic acid
18:1; omega 9
Describe the production of prostaglandin. Start with the first precursor.
Linoleic acid (essential fatty acid) → Arachidonic acid→ prostaglandin
Explain what prostaglandin causes.
Inflammation, pain, and fever
What decreases prostaglandins? What is the process of this inhibition?
NSAIDs (nonsteroid antiinflammatory drugs) stop the production of prostaglandins by inhibiting the enzyme (cyclooxygenase) from cleaving the arachidonic acid.
More saturated fatty acids
Solid; fat
More unsaturated fatty acids
Liquid; oil
Saponification
is also referred to as base hydrolysis. It involves heat and a strong base such as KOH or NaOH to form glycerol and salts of fatty acids. The salts of fatty acids are the actual soap. There must be a charge within the salts of fatty acids. For example, K+ and O- just like the picture shows.
What structure is this?
Phosphoglycerides
Where can phosphoglycerides be found in the body?
Cell membranes
Name each component of the phosphoglycerides.
Two fatty acids, glycerol, phosphoric acid, and amino alcohol
Male sex hormones:
testosterone and androsterone promote muscle and facial hair, and the maturation of the male sex organs and sperm
(cholesterol precursor)
Female sex hormones:
Estrogen–direct development of female sexual characteristics
Progesterone prepares the uterus for the implantation of fertilized eggs (ovulation)
(cholesterol precursor)
What is cholesterol the precursor to? Name the function and location of each substance.
Bile salt, vitamin D, steroid hormones
Name the function and location of each substance. Bile salt, vitamin D, steroid hormones
Bile salt is responsible for breaking down large globules of fats into smaller droplets for lipases to digest. Vitamin D is responsible for absorption of calcium and phosphorus within the bone (bone health). Steroid hormones are a category of hormones responsible for being chemical messenger and initiating bodily function.
Look at the following packages. List the melting point in ascending order.
b<c<a. Nutrient fact A shows more saturated fats, therefore, it has the highest melting point. Nutrient fact b shows more unsaturated fats in the form of polyunsaturated and monounsaturated, therefore, it has the lowest melting point. Nutrient fact C shows it has trans fats, therefore, it is in-between.
(the more saturated fats the higher the melting point)
Draw a glycerol molecule.
Where is the alpha carbon and the omega carbon
alpha carbon is with functional group -cooh and omega is at other end
Describe the similarities and differences between hydrogenation and hydrolysis.
Both hydrogenation and hydrolysis break bonds.
The difference is that hydrolysis involves water-breaking bonds, while hydrogenation involves using hydrogen to break double bonds into single bonds
What are the components of sphingomyelin? Does it have a glycerol?
Sphingosine, amino alcohol, phosphoric acid; it does NOT have a glycerol.
sphingosine
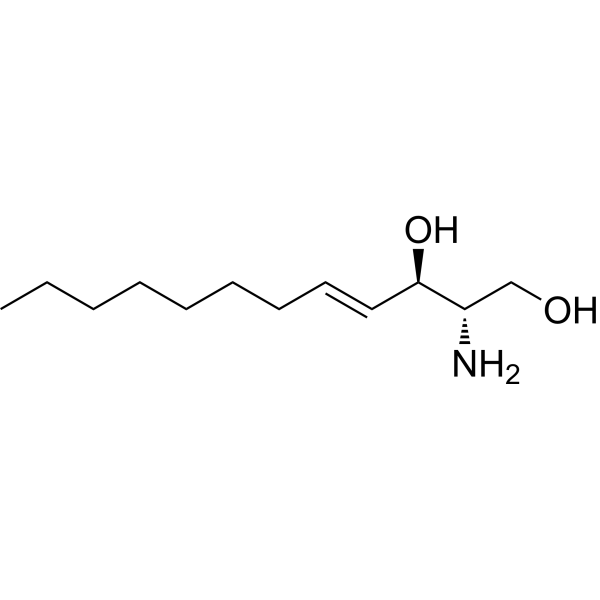
ceramide
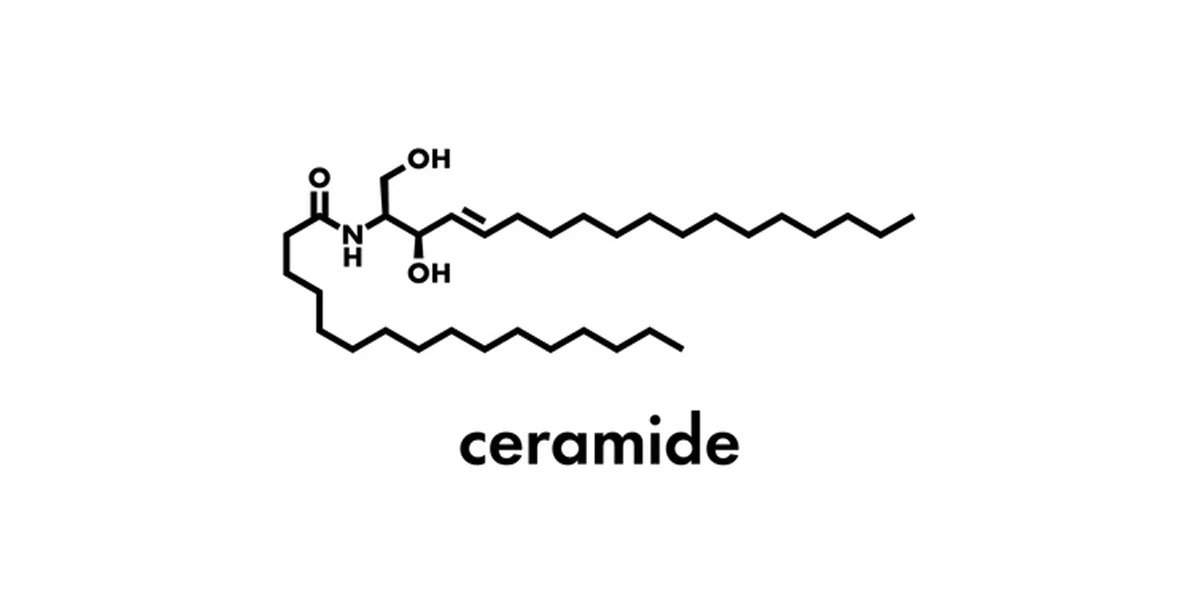
sphingomyelin
What is a lipoprotein?
A lipid and protein membrane structure that transports fats such as cholesterol and triglycerides through the blood bloodstream. Acts as a water-soluble carrier.
What are the two main cholesterols?
High-Desnsity Lipoprotein (HDL) and Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL).
What structure of these two lipoproteins (HDL and LDL) makes them different from each other ? State the function.
HDL has higher protein content and lower cholesterol content. Function: removes excess cholesterol from tissue and blood vessels and transport them to the liver for elimination.
LDL has a low protein content and high cholesterol content. The function is to deliver cholesterol to the cells from the liver.
What happens when there is too much cholesterol? What does it cause (medical term for a certain buildup?
LDL would deposit cholesterol onto the walls of blood vessel, causing atherosclerosis.
Which is the “good” and “bad” cholesterol.
HDL is the “good” cholesterol because it takes away cholesterol from tissue to liver to be eliminated. LDL is the “bad” prteoin because it can deposit cholesterol if there is too much of it.
List the cell membrane structures.
A–phosphoglycerides, C–peripheral protein, D–carbohydrates E–cholesterol, F–peripheral protein, G–integral protein, H–I–lipid bilayer.
For A, what is this called?
Phosphoglyceride.
hydrophilic head (attracted to H2O) hydrophobic tail (repelled by H2O)
What makes the hydrophobic parts and hydrophilic parts (think the component of phosphoglycerides)?
Hydrophobic molecules are molecules that are non-polar and do not mix with water. Water in contrast is a polar molecule and mixes with other polar molecules, called hydrophilic molecules.
What is passive transport? List what goes under passive transport.
Passive transport is the movement of molecules down the concentration gradient (high concentration to low concentration) without energy (ATP)
Simple difficulties:
molecules move directly across the lipid bilayer (small molecules and nonpolar molecules)
Facilitated diffusion–
larger and charged molecules pass through integral proteins (glucose or ions).
What is active transport? What does it involve? Down or against the gradient.
Active transport is the movement of polar molecules, large molecules, and ions across the cell membrane against the concentration (low concentration to high concentration). This requires energy (ATP).
What are the hydrolyzable lipids and the nonhydrolyzable lipids?
Hydrolyzable lipids are triglycerides (glycerol and 3 fatty acids), waxes (long-chain esters), and phospholipids (lipids with a phosphoric acid group). Nonhydrolyzable lipids are steroids such as cholesterol and vitamins (coenzymes).
Niemann-Pick–
a rare condition recessive hereditary disease that affects lipid metabolism, causing an accumulation of sphingomyelin in the brain and harmful substances in the liver, spleen bone marrow, and lungs.
Gaucher's disease–
a recessive genetic disorder that is a result of a deficiency in the enzyme glucocerebrosidase, leading to fats building up in bone tissue, liver, and spleen.
Tay-Sachs–
a recessive neurodegenerative disorder affecting infants and young chig children, causing a lipid storage disease and cause a buildup of fatty substance in the brain and spinal cord and affects function of the nerves due to the lack of enzyme hexosaminidase A.
Fabry’s disease–
a recessive genetic lysosomal storage disorder. Not enough enzymes to break down fats. Causes tingling toes and fingers (onsets in age 20s)
Draw out an amine.
What are the adrenal corticosteroids? Location and function.
Corticosteroids: cortisones increase the blood glucose level and stimulate the synthesis of glycogen in the liver.
Cortisol is released during stages to increase blood sugar and regulate carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism. Aldosterone is a mineralocorticoid, which regulates electrolytes.
What are the two amino alcohols that you must memorize? Draw both.
Cephalin and lecithin
What are the functions of lipids?
Long-term energy, protection, insulation, hormones, structural components
What are the components of glucocerebroside? List the location.
Ceramide–sphingosine and fatty acid and glucose. Located in the brain
What is the name of this ester?
Ethyl hexanoate
What reaction breaks down this structure (ester)? State the definition of the reaction.
Hydrolysis–the action of breaking bonds with water
What are the products of the reaction (ester)? State the general term.
Carboxylic acid and alcohol
What are the names of the products (be specific)?
Ethanol and hexanoic acid
What are chiral atoms?
A carbon atom that is attached to four different groups or atoms
Which of the following molecules has a chiral center?
CH3-CH2-CH3
CH3-CH(Br)-CH2-CH3
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2OH
CH3-CH2-COOH
CH3-CH(Br)-CH2-CH3
What would the bond angle be in a tetrahedral molecule?
109.5
What would the bond angle be in a trigonal planar molecule?
120
What functional groups are found in lipids
Carboxyl, ester
What organic chem reactions can be done to these functional groups? (carboxyl and ester)
Esterification, hydrolysis, and hydrogenation
Which of the following would lipids be soluble in?
Water
Ethanol
Hexane
Acetic acid
Hexane
Hexane is a nonpolar molecule, because it consists of only carbons and hydrogens.
Since it lacks a F, O, N atom(s) and strongly electronegative molecules, it can’t have hydrogen bonding or dipole-dipole interactions.
Identify the different classes of lipids
Fatty acids, triacylglycerides, phospholipids, steroids, waxes, eicosanoids, glycolipids, lipoproteins
Which isomer is naturally occurring?
cis
How is the other isomer made if its not natural?
Made via a hydrogenation reaction. This reaction forces the natural “bent” (cis) bond to straighten out → trans
Where is vitamin D synthesized and stored?
Made in the skin when exposed to sunlight (then sent to the liver to be converted into a form that the body can use). Stored in fat tissues and liver
Why do unsaturated lipids have lower melting points than saturated lipids?
Saturated fats have no double bonds; they are linear. The bends in the fatty acid chains of unsaturated lipids dont allow for close packing, and gives them a lower melting point
Bile salts are derived from which lipid molecule?
Cholesterol
What is the relationship between cholesterol and bile salts?
Bile salts are derived from cholesterol when the liver modifies its structure.
Bile salts help emulsify fat and regulate cholesterol levels
Excreting bile salts removes excess cholesterol
Are bile salts soluble in water?
They are both hydrophilic and hydrophobic, making them partially soluble in water.
What does cholesterol help with regarding cell membranes?
Maintains structure and function of cell
What are the functions of cholesterol?
Regulating membrane fluidity, providing structural support between the phospholipid bilayer, precursor to steroid hormones/vitamin D, needed for myelin sheath formation
Explain the storage and release of bile salts
Bile salts are made in the liver and stored/released from the gallbladder.
Roles of calcium
bone/teeth health, muscle function, nerve transmission, hormonal secretion, cellular functions
Roles of phosphorus
Energy metabolism, dna/rna synthesis, cell membrane, muscle function, bone remodeling and mineralization
Why is the liver important for the synthesis of vitamin D?
If the liver isn’t functioning properly, it would struggle to convert vitamin D into its active form, possibly leading to rickets
What is the main function of glucocorticoids?
Regulate metabolism and help body’s response to stress
What is the main function of mineral corticoids?
Ion balance, blood pressure
What is the primary glucocorticoid and what does it assist with?
Cortisol, commonly known as the “stress hormone” and helps the body respond to stress by increasing glucose levels & breakdown of fats/proteins
What is the primary mineral corticoid and what does it assist with?
Aldosterone, assists in maintaining electrolyte/fluid balance, and blood pressure
Estrogen:
regulation of menstrual cycles, reproductive tissue development, cognitive, bone, cardiovascular health
Testosterone:
development of male reproductive tissues, muscle growth, fat distribution, bone health
Vitamin D:
bone health, calcium & phosphate regulation, immune system activity, muscle function, made in skin moves to liver and throughout body
List the water soluble & in-soluble vitamins
Water soluble:
Fat soluble:
Water soluble: Vitamin C and B
Fat soluble: Vitamin A, D, E, and K
What does a lipid lack if it cannot be hydrolyzed?
Lack an ester, amide, or glycosidic bond
List the hydrolyzable lipids
Triglycerides, phospholipids, glycolipids, sphingolipids, waxes
List the non-hydrolyzable lipids
Sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, lipid-soluble hormones
What is the structure of sphingomyelin composed of?
Sphingosine backbone, fatty acid, phosphate group, choline (*or other group) attached to phosphate
List the hydrolyzable bond(s) on sphingomyelin
Amide, phosphodiester
Whats the relationship between ceramide and sphingolipids?
Ceramide is a building block of sphingolipids, serves as a precursor
What would the product be if you hydrated ethene?
Ethanol
What happens if you hydrogenate an unsaturated fatty acid?
You get a saturated fatty acid
Explain saponification
Chem reaction when a fat reacts with a strong base (such as NaOH), and the result is soap and glycerol
Explain what the saponification of vegetable oil would produce
Soap and glycerol
essential fatty acids
linoleic and linolenic turn into arachidonic
How do soap molecules emulsify oils?
Emulsify via their (both) hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts. The hydrophobic tails of soap molecules bind to oil, and the hydrophilic heads interact with water. This allows the oil to be washed away from surfaces.
Arachidonic acid is a carbon, omega- fatty acid
20, 6
What is arachidonic acid involved in?
Precursor to eicosanoids, inflammatory response
What food(s) have omega-3 fatty acids?
Fortified foods, fatty fish
Functions of omega-3 fatty acids
Reduce inflammation, improves heart health, brain function, eye health, skin
What food(s) have omega-6 fatty acids?
vegetable oils, nuts, processed foods
Functions of omega-6 fatty acids
Inflammatory response, brain function, skin health
List the common diseases linked to omega-3 & omega-6 fatty acid imbalance
Heart disease, inflammatory conditions, mental health disorders