Subsection of Unit 2 - Cell Junctions & Epithelial Tissues
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Covers everything in the Google Slide show from slides 5 to 41.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
How do cells “join together” into tissues?
They can fit together by shape, chemical attraction or special junctions.
What is interstitial/extracellular fluid?
It is the fluid where joints can fit together to form tissues. It is also fluid on the exterior of the cell that contains nutriends, hormones, neurotransmitters, salts, waste products.
What is interstitial fluid on the inside of a cell called?
Cytoplasm
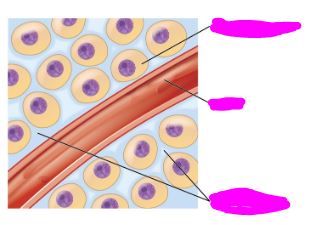
Label the three covered things :)
Top to bottom: Intracellular Fluid (cytoplasm), Plasma, Interstitial fluid.
What is histology?
The study of cells and tissues.
What are the three ways that cells can be held together?
Through glycoproteins, wavy countours, or special cell junctions.
What are glycoproteins?
They stick out the cell and act like glue, causing cell to cell recognition and causes cells to “stick together” chemically.
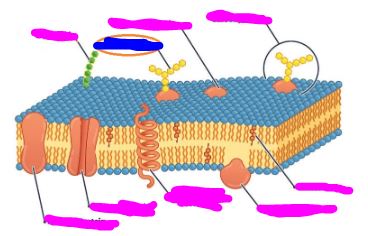
What is the BLUE colored box? (ignore the pink)
Glycoprotein
What are wavy countours?
They are cells that can have a “tongue and groove” / “lock and key” shape fit with adjacent cells.
Looks like a bunch of puzzle pieces put together.
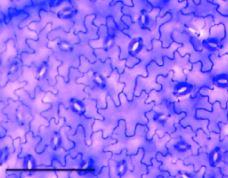
What is this an example of?
Wavy countours!
What are the three types of special cell junctions?
Tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junction.
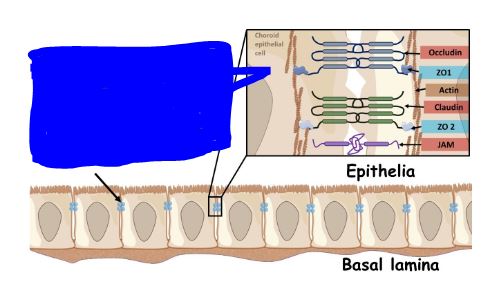
What are tight junctions? Where are they commonly found?
They are impermeable junctions (bind together and become water tight).
Found in stomach, bladder, other organs that need a water tight seal.
What are desmosomes? Where are they found?
They look like buttons and are created by two different plasma membranes anchoring together. Materials move between those connected cells in the interstitial fluid.
Found in the skin and heart muscles or any tissue subjected to mechanical stress.
What is this an image of?
A tight junction.
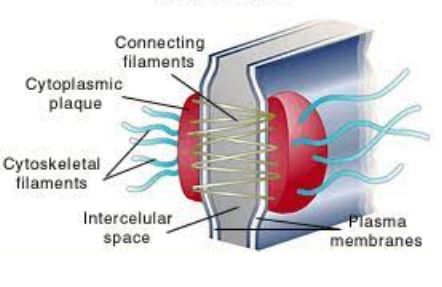
What is this an image of?
Desmosome.
What are gap junctions? Where are they found?
It is a gap between cells to allow for cell to cell communication (these gaps are called connexons).
They are typically found in any tissue that needs to get electrical messages (muscles, heart, stomach).
What are connexons? What is their purpose?
They are hollow cylinders of proteins that span the width of two cells.
Their purpose is to allow molecules to travel directly from one cell to another.
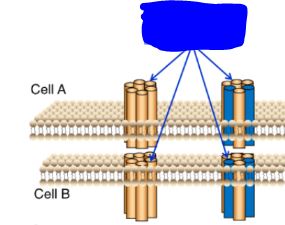
What is this? (two answers)
Hemichannel (Connexon)/Gap junction
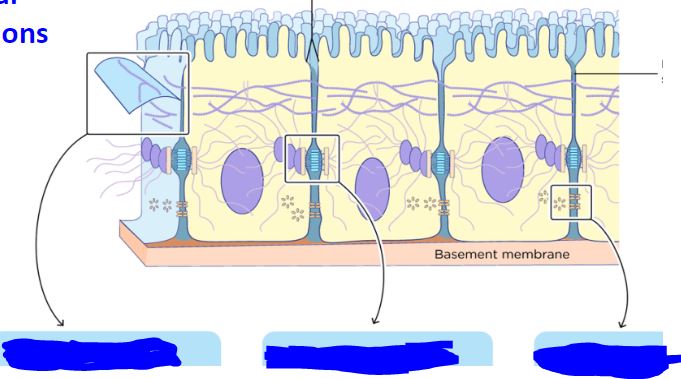
Label these going from left to right.
Tight Junction, Desmosome, Gap Junction.
What are the four types of tissues?
Epithlial, Nervous, connective, muscle.
What do epithelial tissues cover?
They cover the boundary between our body and the external environment.
What are the functions of epithelial tissue?
Protection, Absorption, Filtration, and Secretion (sweat, mucus, hormones).
What is the free/apical surface?
The top part of an epithelial tissue.
What is the basal surface?
The bottom of the cell
What is the basement membrane?
The membrane underneath the basal surface. (Very bottom)
All epithelial tissues (are avascular/are not avascular)…
are avascular (no blood vessels).
How are epithelial tissues classified?
They are classified by the number of layers and the shape of the cells.
What does simple epithelial tissue mean?
One layer of cells.
What does stratified epithelial tissue mean?
More than one layer of cells.
What are the three shapes of epithelial cells AND their descriptions?
Squamous: Flattened, like fish scales.
Cuboidal: Cube-shaped, like dice.
Columnar: Column-like.
What is the function of simple squamous epithelium? Where is it found?
It is for the rapid diffusion of materials.
Found in blood vessles, lung tissues, and serous membranes that surround organs.
What is the function of simple cuboidal epithelium? Where is it found?
It is for secretion and absorption of substances.
Found in the tissues of the kidney.
What is the function of simple columnar epithelium? Where is it found?
It is for secretes mucus for protection and absorbs substances.
Found in the lining of the digestive tract.
What is the function of stratified squamous epithelium? Where is it found?
It provides protection for the underlying layers of the body (usually the skin).
Found in the epidermal layer of the skin (outer layer).
What is the function of stratified cubodial epithelium? Where is it found?
It provides protection to the salivary and mammary glands. (rare in the body).
Found in the salvary and mammary glands
Where is stratified columnar epithelium found? What is the free/apical surface lined with?
The free surface (apical) is lined with columnar cells. This is rare in the body and found in the larynx and male urethra.
What is the function of psuedo-stratified epithelium and where are the nuclei found? Where is it found?
It provides secretion and absoption. The nuclei are found at different levels.
It is found in most of he upper respiratory tract.
Where is transitional epithelium found? What makes this tissue special (hint: it can take on two different looks)?
Found in the lining of the urinary bladder.
The apical surface cells can vary in appearance based on the stretching of the tissue.
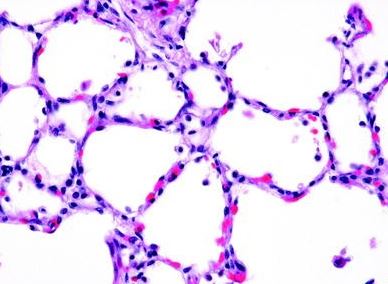
What epithelial tissue is this?
Simple squamous epithelial tissue.
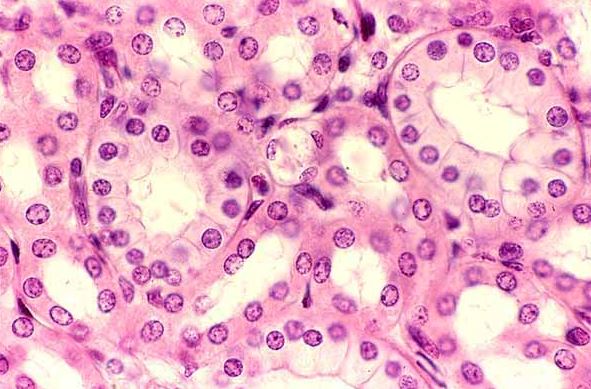
What epithelial tissue is this?
Simple cubodial epithelial tissue.
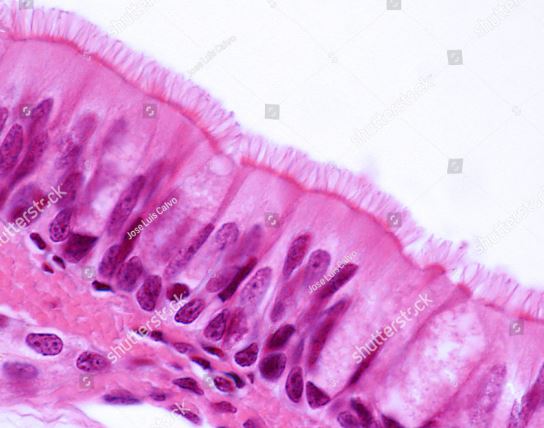
What epithelial tissue is this?
Simple columnar epithelial tissue.
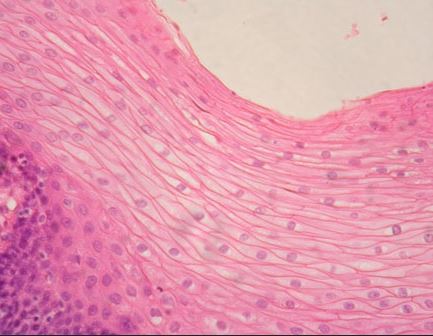
What epithelial tissue is this?
Stratified squamous epithelial tissue.
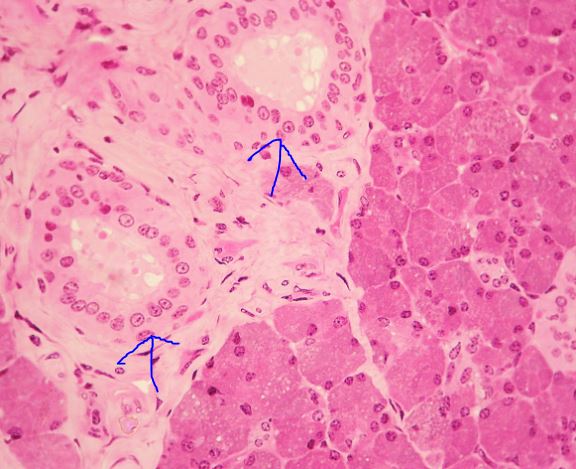
What epithelial tissue is this?
Stratified cubodial epithelial tissue.
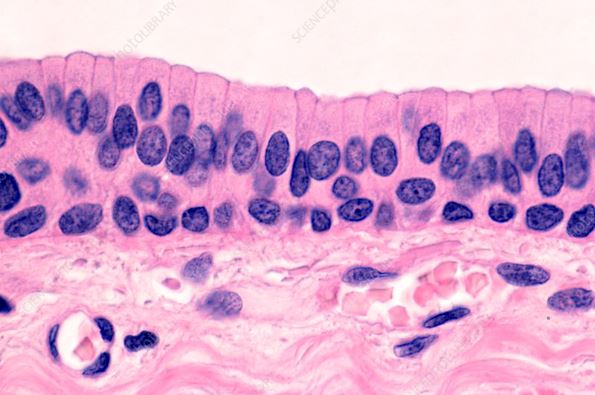
What epithelial tissue is this?
Stratified columnar epithelial tissue.
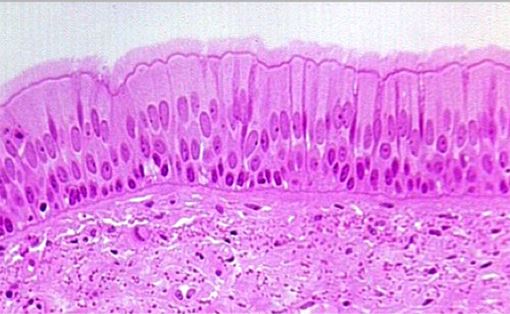
What epithelial tissue is this?
Psuedostratified epithelial tissue.
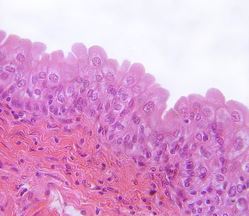
What epithelial tissue is this?
Transitional epithelial tissue.