Conjunctiva Disorders
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
follicles
lymphoid tissue
reactive hyperplasia w/in stroma
conjunctival lymphoma
appearance: multiple, elevated, lumpy/grain of rice appearance
large ones can be common in children w/ no clinical significance
papilla
non-specific finding
inflammatory cells
appearance:
vascular core that branches out over the surface
velvety
chemosis
severe inflammation of the conjunctiva
transudation of fibrin & protein fluid through the walls of leaky blood vessels
usually associated with an immediate allergic rxn
appearance:
translucent swelling
can protrude through closed lids & impact lid closure
jelly-like appearance
conjunctivochalasis
etiology:
aging (most common)
allergies
post-op
venous congestion
angioneurotic edema
myxedema
appearance:
presence of excess folds in conjunctiva
slack/sagging of the conjunctiva, bunched up appearance
tx: surgical resection
pseudomembrane
etiology:
severe adenoviral infections (EKC, SJS, gonococcal herpes, allergic & bacterial conjunctivitis)
combo of fibrin & proteinaceous coagulated exudates
loosely attached to the inflamed conjunctival epithelium
appearance:
wet scab
can be seen on upper or lower lid
removal may cause bleeding & scaring but not usually
very uncomfortable & can cause corneal issues
tx: usually can be easily peeled off w/ a wet swab
true membrane
etiology:
severe infections (strep)
SJS
chemical burns
forms when inflammatory exudate secreted by invading microorganisms or ocular tissues permeates the superficial layers of the conjunctival epithelium & vascularity
appearance:
bleed when removal is attempted
firmly attached
will scar
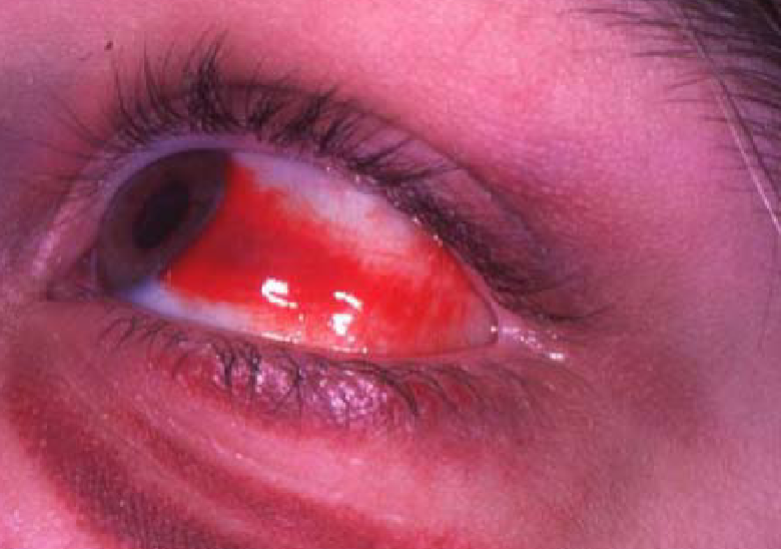
subconjunctival hemorrhage
etiology:
valsalva maneuver
trauma
surgical
HTN
bleeding disorders
blood thinners
post-op
severe infections
idiopathic
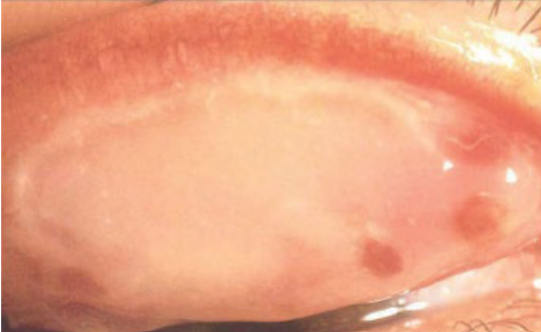
appearance:
blood underneath the conjunctiva
often sectoral
can obstruct the entire view of the episclera & sclera
tx:
may take 2wks to resolve
no tx needed, like a bruise
AT PRN
monitor BP & NSAID usage
concretions
etiology:
idiopathic
chronic conjunctival infections
just trapped cellular debris that calcifies
appearance:
small, hard, yellow-white, crystal-like deposits w/in palpebral conjunctiva
usually 1-2mm in size
sx:
usually asymptomatic
FB sensation
FB tracking if superior
associations:
inclusion cysts
tx:
none if asymptomatic
can remove if symptomatic (cotton swab, needle, forceps)
inclusion (lymphatic) retension cysts
etiology: blockage of ducts of glands of Krause
appearance:
clear, fluid filled cysts on palpebral, bulbar, or canthal areas
conjunctival blood vessels pass over
tx:
none usually
if large, can be excised or punctured w/ needle
symblepharon
etiology:
EKC
post-op
trauma
burns
long-standing inflammation
atopic
ocular cicatricial pemphigoid
SJS
radiation
congenital
fusion of the palpebral conjunctiva w/ the bulbar conjunctiva
conjunctival degenerations
usually seen in people over 30
etiology:
exposure to noxious environmental stimuli & UV light
age-related or environmental
chronic exposure to wind/dust/sun
altered collagen & elastic tissues
appearance
usually in interpalpebral (exposed) conjunctival area
rarely produces any serious effects on ocular functioning
pinguecula
extremely common
usually seen in pt over 30yo
etiology: elastic degeneration of the collagen tissue of conjunctival stroma (age related or environmental)
appearance:
yellow-white elevation on bulbar conjunctiva adjacent to nasal or temporal aspect of the limbus
can be highly vascularized & injected
usually in 3/9 oclock positions
signs/sx:
irritation
redness
asymptomatic
associations:
can become inflammed
SPK
dellen
CL
can progress to a pterygium
tx:
cosmetic concern
protection from UV light
surgical excision is rarely necessary
important to R/O other pathologies
pingueculitis
inflammation of a pinguecula
sx:
irritation
redness
tearing
can be asymptomatic
tx:
may not require
mild soft steroids
pterygium
etiology:
age-related
environmental
increased incidence in hot, dusty regions
chronic inflammation
seen in those over 20
more common in males
damages limbal stem cells
appearance:
raised, triangular, white, fibrovascular overgrowth of bulbar conjunctiva onto the cornea
early on: small, gray opacities near limbus
bilateral
nasal > temporal
interpaplebral area
Stocker’s line
signs/sx:
blurry vision if overgrows visual axis or K’s get distorted
red, scratchy, inflamed eye
dry eye complaints
cosmetic concern
tx:
AT
soft steroids
surgery (excision)
protection from UV
Stocker’s line
iron deposition line at the leading edge of pterygium
yellow, golden/reddish brown, brown
pseudopterygium
adhesion of a fold of conjunctiva to a peripheral ulcer, fixed only at the apex
ex: ocular cicatricial pemphigoid
ocular cicatricial pemphigoid
rare
etiology: chronic autoimmune sub-epithelial blistering
affects basement membrane
appearance:
erosive skin lesions of mucous membranes
scars
affects all mucous membranes of the body
dermoid cyst
etiology:
congenital choristoma
appearance:
mass of collagen tissue containing hair, follicles, & glands covered by keratinized epithelium
choristoma
congenital overgrowth of normal tissue in an abnormal location, composed of tissue not normally found in the region
limbal dermoid cyst
etiology:
congenital
appearance:
smooth, soft, yellowish-white, solid, oval, conjunctival mass at the limbus
usually at lower temporal limbus & involves cornea, conjunctiva & sclera
can enlarge (puberty)
signs/sx:
DES
irritation
lagophthalmos
associations:
eyelid colobomas
preauricular accessory skin tags
vertebral abnormalities
mal-development of the jaw
hearing loss (Goldenhar’s syndrome)
systemic abnormalities
amblyopia
astigmatism
tx:
removal for cosmetic & visual reasons near school age
sclerokeratectomy w/ excisional biopsy
leaves a scar & underlying tissue can be very thin
Goldenhar’s syndrome
includes accessory auricles, limbal & ocular dermoids, & sometimes jaw malformation
dermatolipoma
etiology:
congenital
can be part of Goldenhar’s syndrome or separate
appearance:
firm, elevated, movable, yellowish, subconjunctival mass
outer canthal angle of eye
usually obscured in primary gaze (pt must look in a different gaze to be able to see it)
usually a smooth surface but can contain hair follicles, glands, or fatty tissue
tx:
none unless cosmetic concern
lymphangiectasia
etiology:
blockage of lymphatic channels
more common in pt w/ chronic irritation
appearance:
clear, yellowish, serous cyst w/ dilated, tortuous clear or yellowish tubules
2-10mm
round or linear
can fill with blood
typically resolve on their own
conjunctival lymphoma
etiology:
Hodgkin disease
variety of benign & malignant lymphoid lesions
affects young to middle aged adults
appearance:
salmon colored, subconjunctival lesion
fleshy
may grow rapidly
often arise from the fornix & extend to the cornea
tx:
radiotherapy
systemic chemotherapy
pyogenic granuloma
etiology: overgrowth of tissue due to irritation or physical trauma/infection/inflammation
appearance:
vascular lesion
red/pink or purple & smooth or lobulated
can grow & bleed
papilloma
etiology:
HPV
viral infection
appearance:
soft, pink, strawberry red, elevated lesion w/ a slightly irregular surface
multiple cores of corkscrew blood vessels
may grow rapidly
most commonly at the caruncle, fornices, lid margin, & limbus
pedunculated or sessile
signs/sx:
asymptomatic
FB sensation
itching
tearing
improper lid closure
tx:
if viral, often left untreated due to frequent recurrence
if non-viral (sessile), usually excisional biopsy
Kaposi sarcoma
etiology: occurs in pt w/ AIDS
appearance:
bright red, purplish, vascular, nodular, subconjunctival mass
usually in inferior cul-de-sac
often combined with subconjunctival heme
may also involve skin of the lid, lid margins, & orbit
conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)
etiology:
UV
HPV
AIDS
usually occurs in late adulthood, in fair-skinned people
rare
appearance:
begins near limbus
can spread over the cornea
leukoplakic (gray-white), elevated, gelatinous or highly vascularized, ameboid shaped, fleshy lesion
RB or LG staining
movable
can metastasize
can evolve to SCC
tx:
local excision
biopsy
squamous cell carcinoma
rare
typically seen in white pt 50+ that have had significant UV exposure
appearance:
starts as small, elevated, fleshy, pink, gray nodule
becomes almond shaped as it extends around the limbus
large feeder vessels
flaky placoid white area over the surface
hemangioma
etiology:
usually present at birth but can appear up to 10y
appearance:
can enlarge w/ time
mass of fine, tortuous blood vessels
slowly progressive
bright red patch
rounded, nodular, lobulated
capillary (mass of fine vessels) or cavernous (broad base)
associations:
Sturge Weber
racial/congenital melanosis
etiology:
congenital
can increase w/ age
greater in darkly pigmented races
no/little malignancy
appearance:
flat, pigmented brown patches
usually near the limbus or around perforating vessels
bilateral
can extend into the cornea
acquired melanosis
can be benign, precancerous, or cancerous
more common in those 30-40+
almost always in Caucasians
higher risk of developing into melanoma
unilateral
primary acquired melanosis (PAM)
appearance:
development of irregular, diffuse, flat, grayish-black, brown, or tan bulbar pigmentation
may extend into palpebral conjunctiva
w/o cysts
suspect malignancy when elevation, nodules, or increase in vascularity occurs
tx:
monitor very closely
DFE
PAM w/o atypia
benign proliferation of normal melanocytes confined to the basal layers of the conjunctiva
PAM w/ atypia
pre-malignant condition w/ a 50% chance of malignant transformation w/in 5y
characterized by melanocytes involving all layers of the conjunctiva
nevus
benign
etiology:
usually appear during 1st 2 decades of life
increase in pigment during puberty or pregnancy
appearance:
usually unilateral
most commonly juxtalimbal, at plica or caruncle
70% are pigmented
amelanotic/pink
multiple cysts w/in on histology
associations:
25% of conjunctival melanomas arise from this
tx:
monitor
cosmetic concern or suspicious - excisional biopsy
malignant melanoma
most common b/t 40-60y in Caucasians
etiology:
can arise spontaneously from nevus or acquired melanosis
2% of all eye malignancies
appearance:
commonly at limbus
higher concern if at upper tarsal plate or lower fornix
nodular brown or solitary black or gray nodule
fixed to episclera
can be pink
smooth, fish-flesh appearance
dilated feeder vessels
signs/sx:
ABCDEs
bleeding/ulceration
tx:
prognosis is generally good, small risk of metastasis if caught early
excision
conjunctival laceration
etiology: trauma
appearance:
red eye w/ subconj heme, torn edges retracted, revealing underlying sclera
NaFl staining & pooling
signs/sx:
less symptomatic than corneal abrasion
mild pain/scratchy/FBS
tx:
broad spectrum antibiotic sol or ointment
if larger than 2cm, suture
acid (sulphuric, acetic, solvents, detergents, irritants)
_______ chemical burns cause rapid denaturation & coagulation of tissue proteins, may produce a physical barrier than prevents further penetration, more often confined to superficial tissues
alkali (lye, ammonia, lime, NaOH, cements, plastics)
______ chemical burns cause dissolving of tissue proteins & allow for deep & rapid penetration through tissues
mild to moderate burn
signs:
corneal epithelial defects
mild stromal haze
no significant area of perilimbal ischemia
focal areas of conjunctival chemosis/hypermeia/hemorrhages
mild eyelid edema
mild AC rxn
1st/2nd degree burns of periocular skin
severe burns
signs:
pronounced chemosis & conjunctival blanching
limbal ischemia
corneal edema
dense stromal haze & opacification
poor/no view of AC, iris, lens
moderate to severe AC rxn
increased IOP
2nd/3rd degree burns of periocular skin n
necrosis of conjunctiva/cornea
loss of limbal stem cells
sterile corneal ulcers
neovascularization
OSD
symblepharon
entropion
severe stromal opacification
iris/lens damage
hypotony
phthisis bulbi
what are some ocular complications of burns? (11)
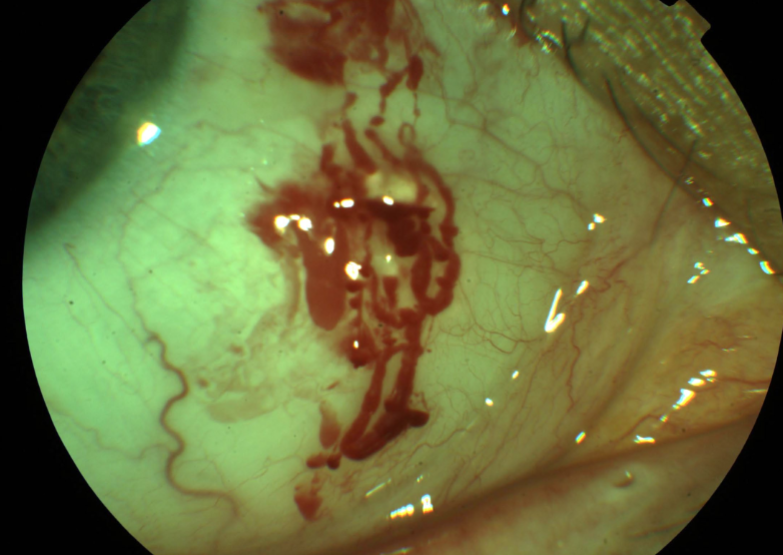
follicles
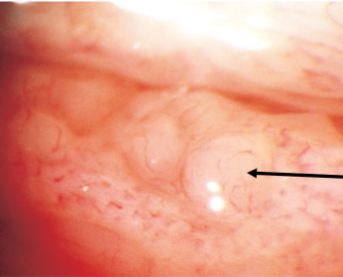
papilla
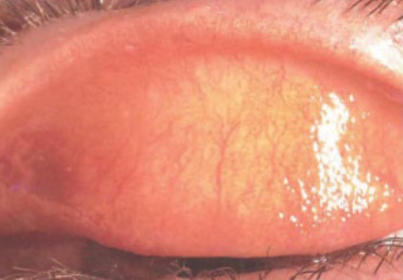
edema
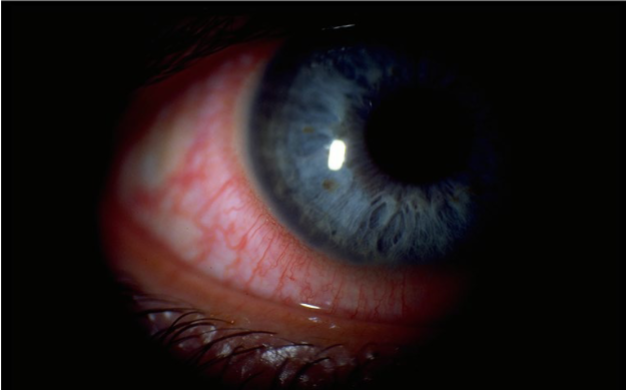
chemosis
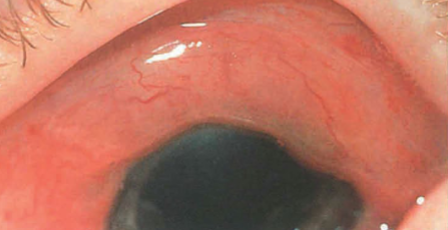
conjunctivochalasis
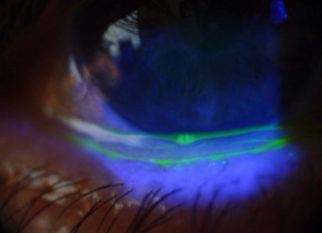
conjunctivochalasis
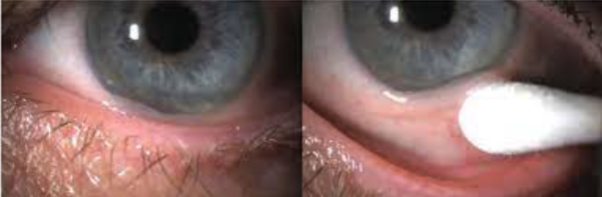
pseudomembrane
pseudomembrane
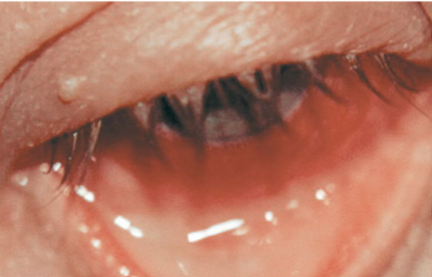
symblepharon
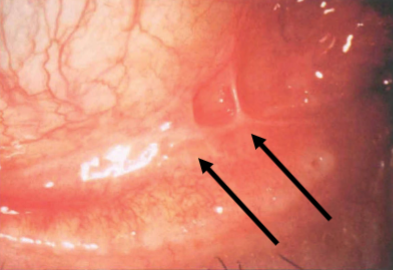
true membrane
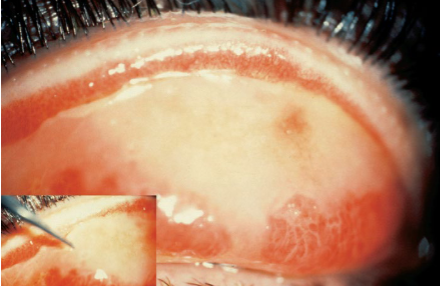
scarring
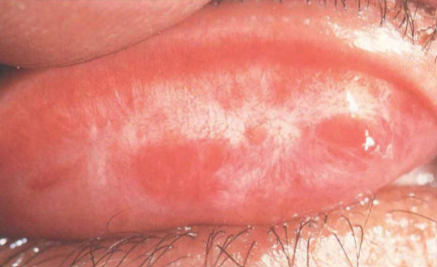
subconjunctival hemorrhage
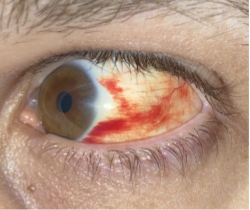
subconjunctival hemorrhage
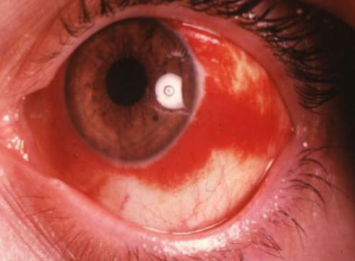
subconjunctival hemorrhage
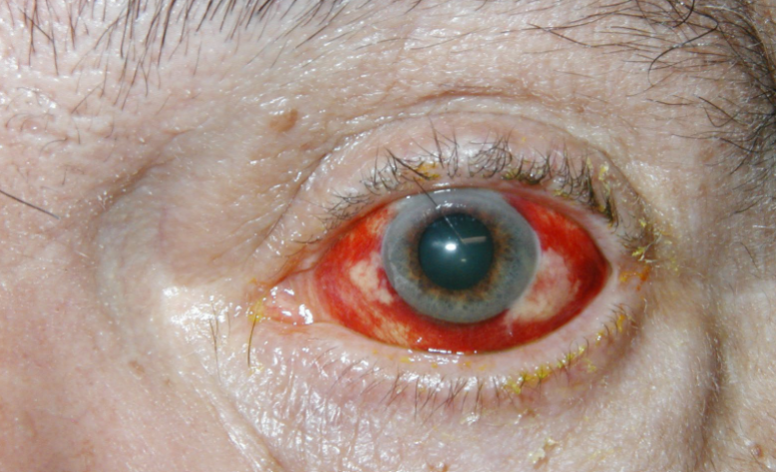
subconjunctival hemorrhage
concretions
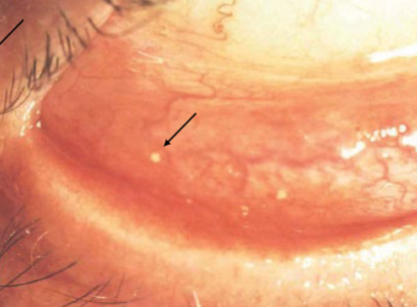
concretions
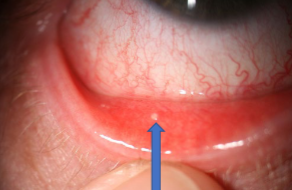
concretions
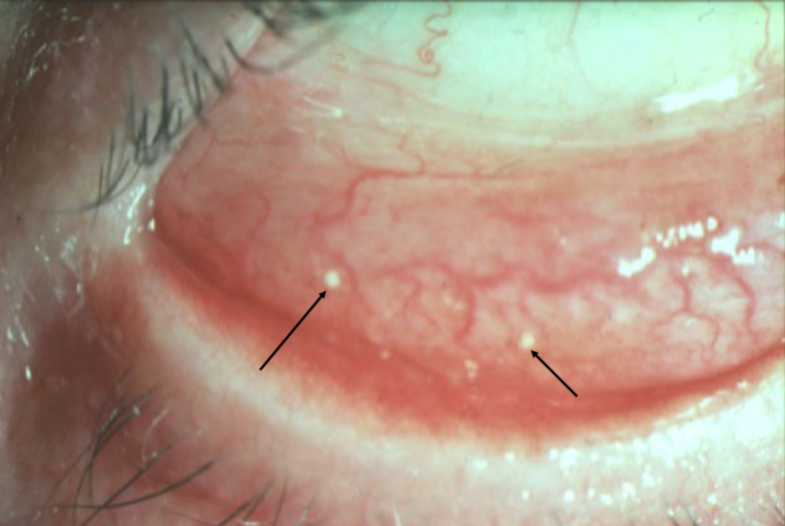
concretions
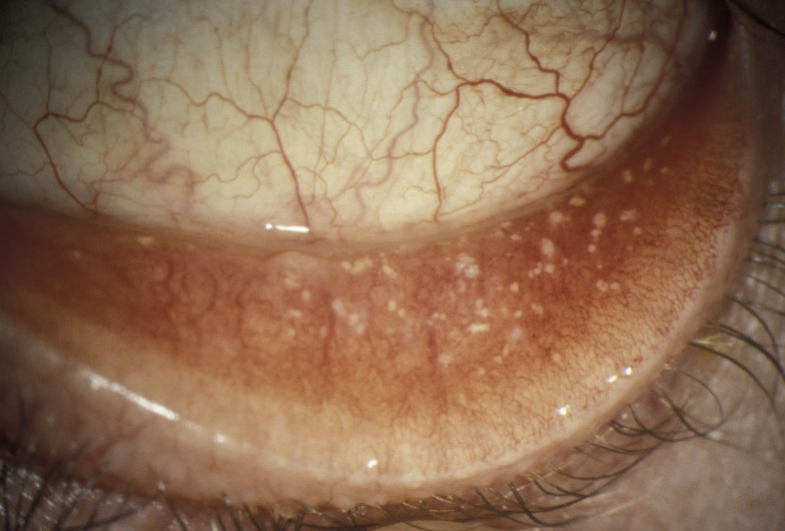
conjunctival cyst
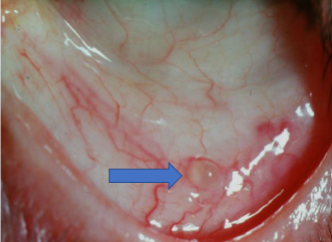
inclusion retention (lymphatic) cysts
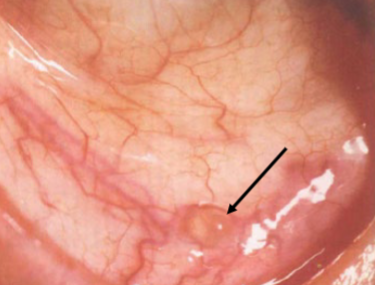
inclusion retention (lymphatic) cysts
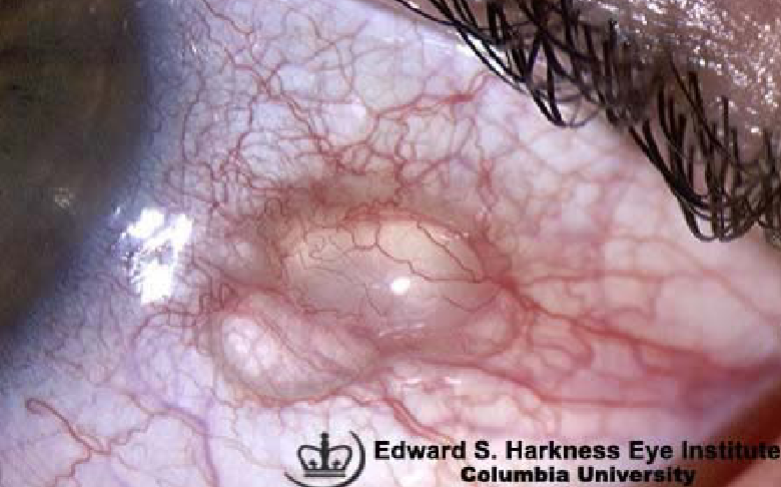
conjunctivochalasis
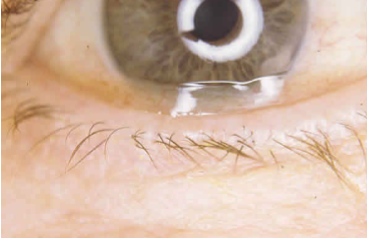
symblepharon
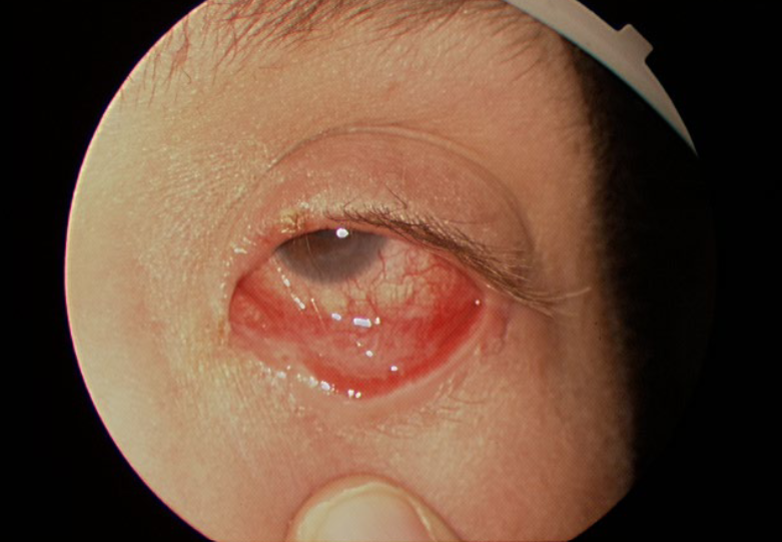
pinguecula
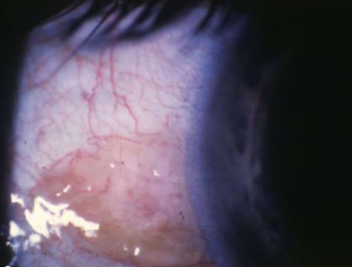
pinguecula
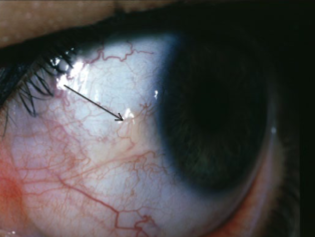
pinguecula
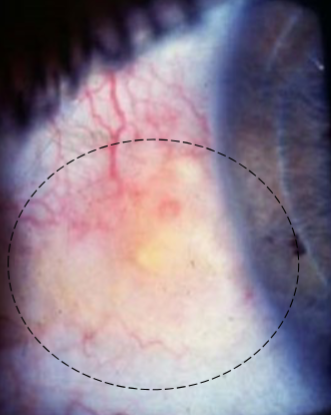
pinguecula
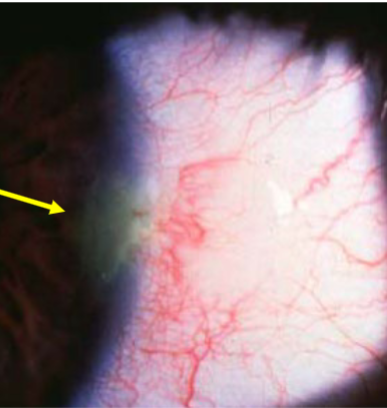
pingueculitis
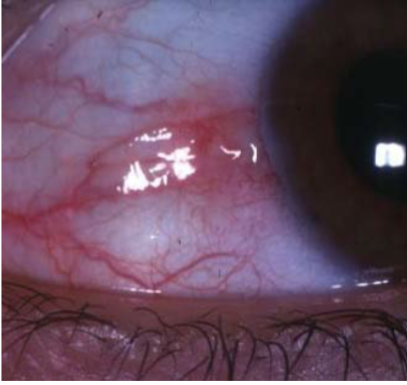
pterygium
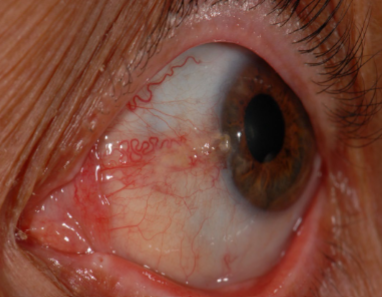
pterygium
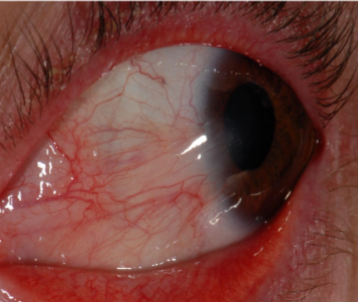
pterygium

pterygium
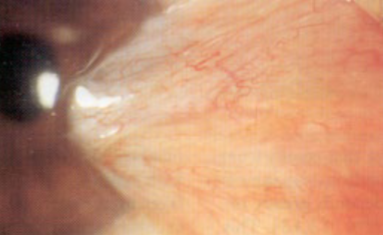
Stocker’s line
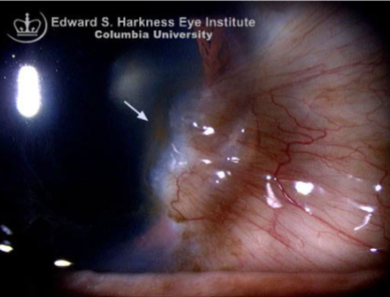
pterygium
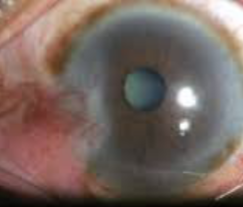
pterygium

pterygium
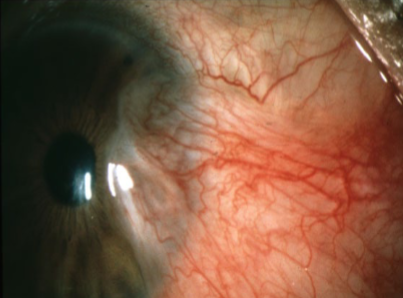
pterygium
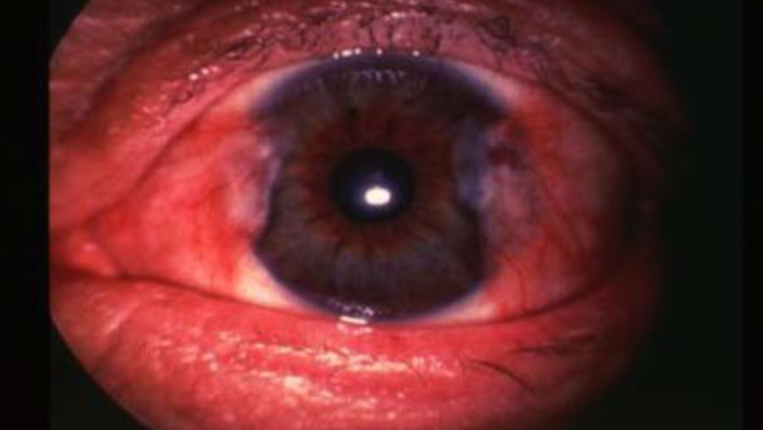
pterygium
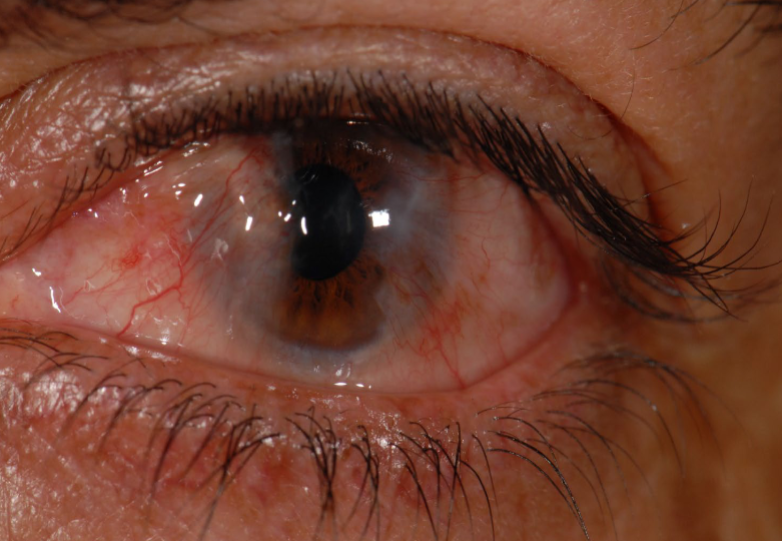
pseudopterygium
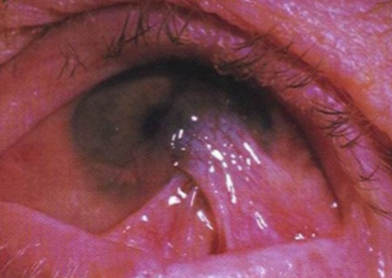
choristoma
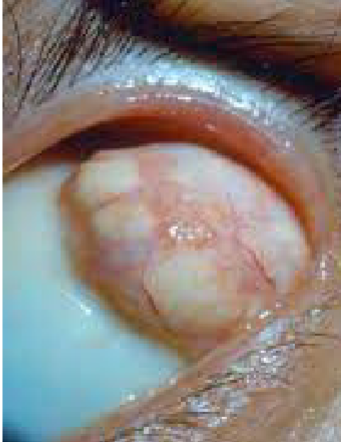
dermoid
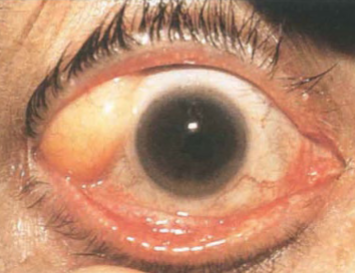
limbal dermoid cyst
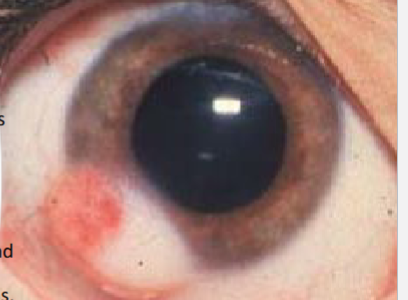
limbal dermoid cyst
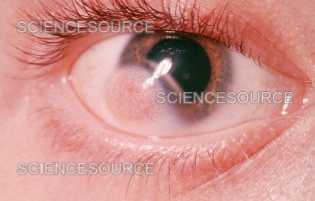
dermoid
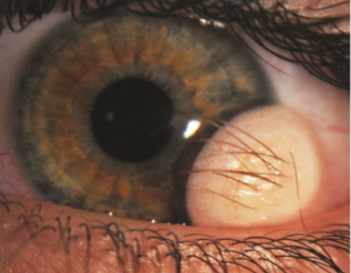
Goldenhar’s syndrome
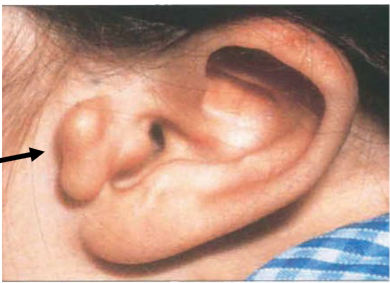
Goldenhar’s syndrome
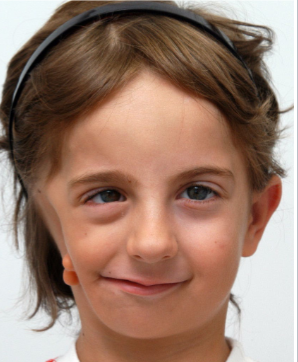
limbal dermoid cyst
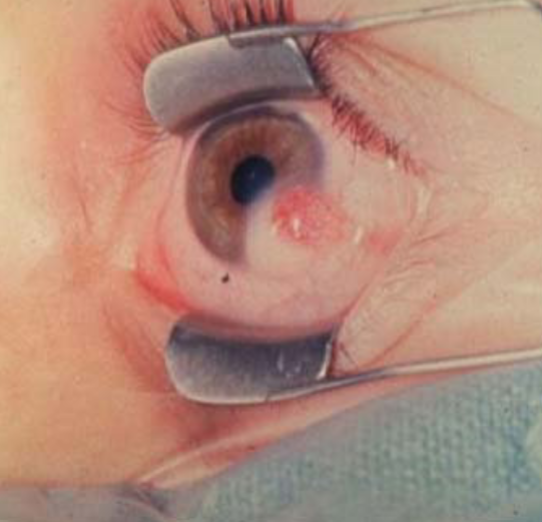
limbal dermoid cyst
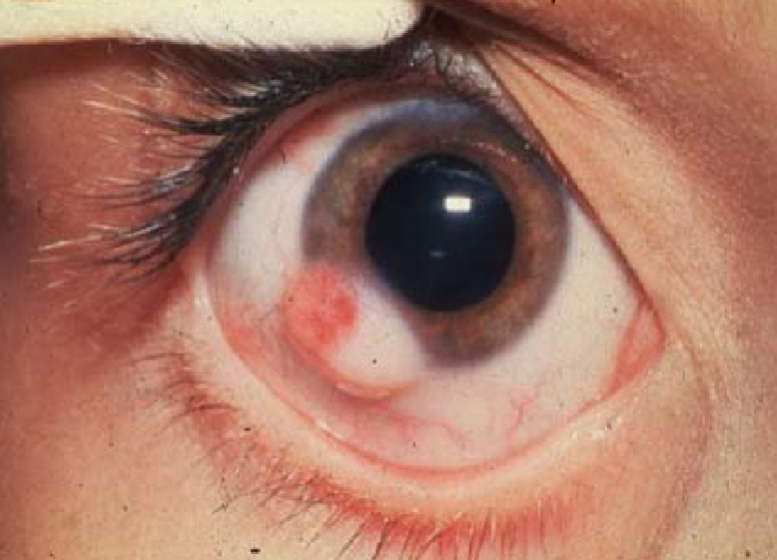
limbal dermoid cyst
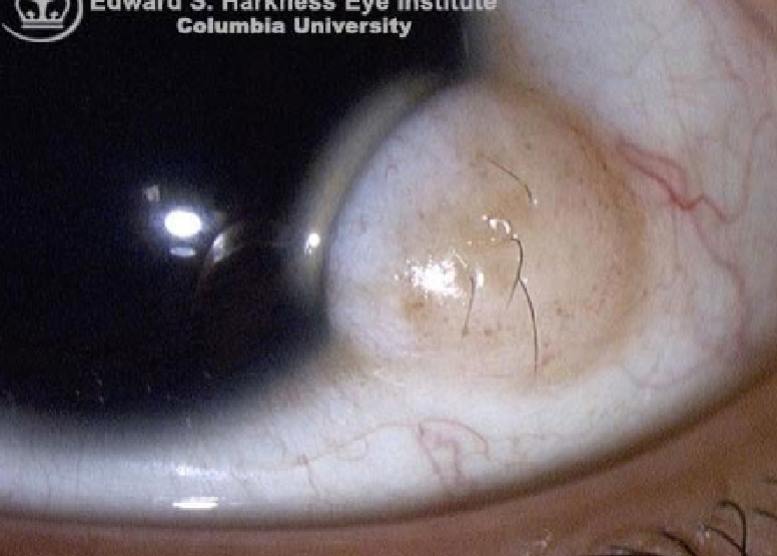
dermatolipoma
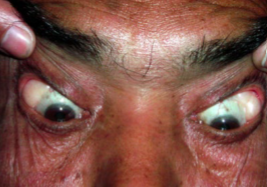
dermatolipoma
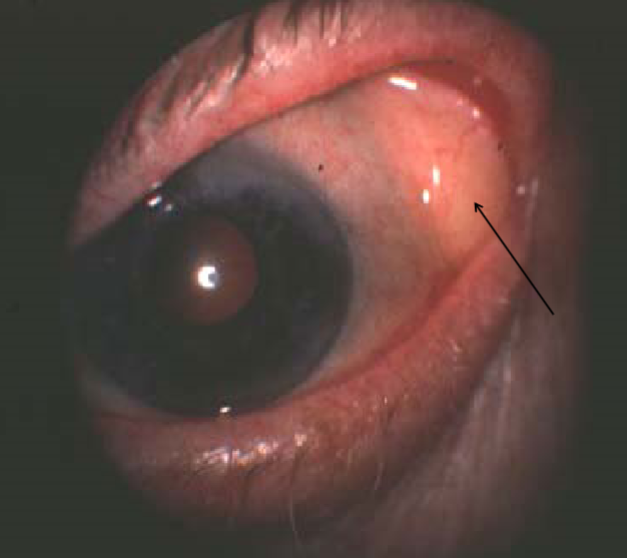
dermatolipoma
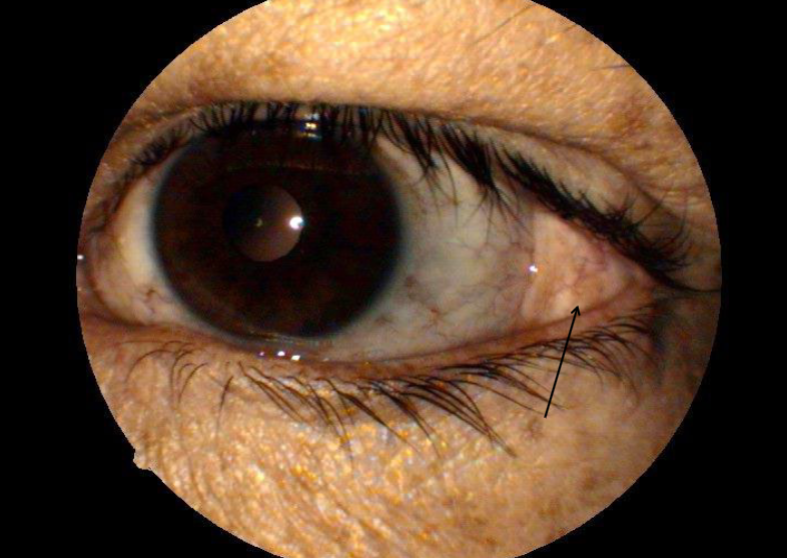
dermatolipoma
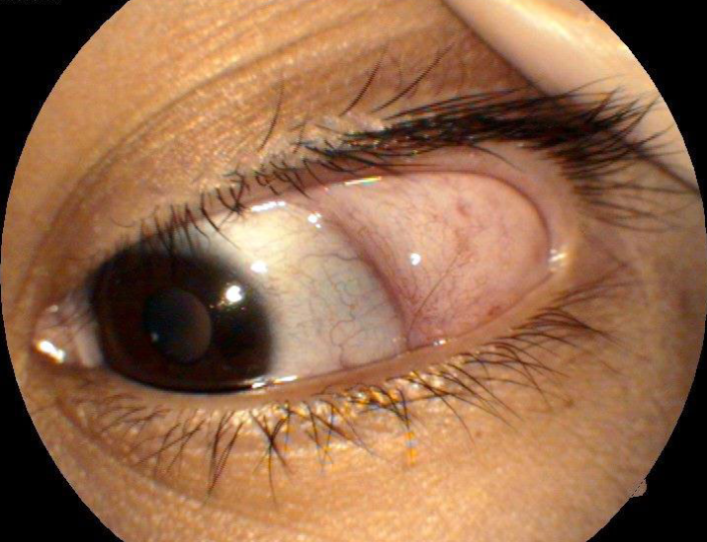
lymphangiectasia
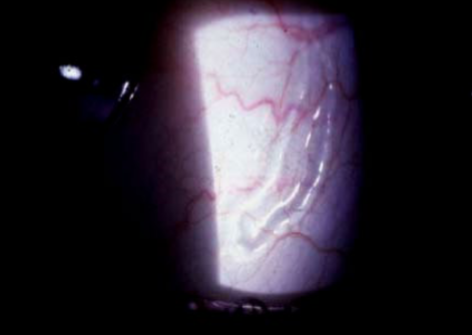
lymphangiectasia
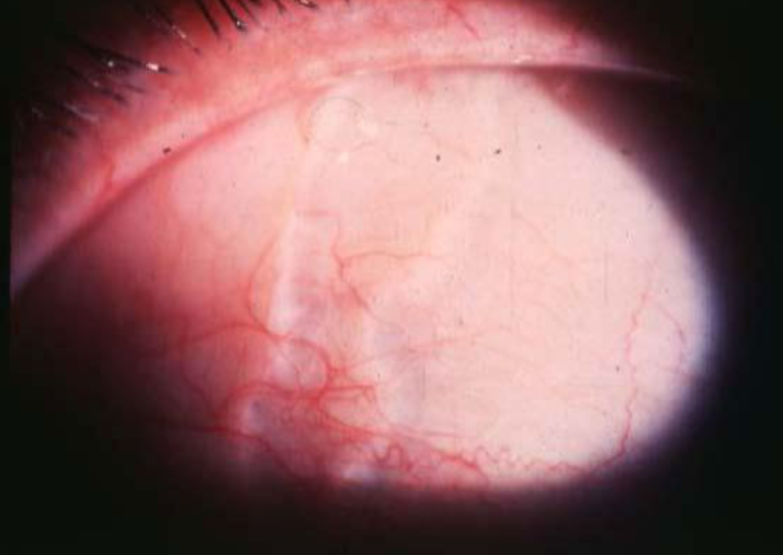
lymphangiectasia