Blood Typing / Paternity / Transfusions
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
genetics
The scientific study of heredity
paternity
fatherhood

synthetic
not naturally produced; made by artificial processes

antigen
substance that triggers an immune response
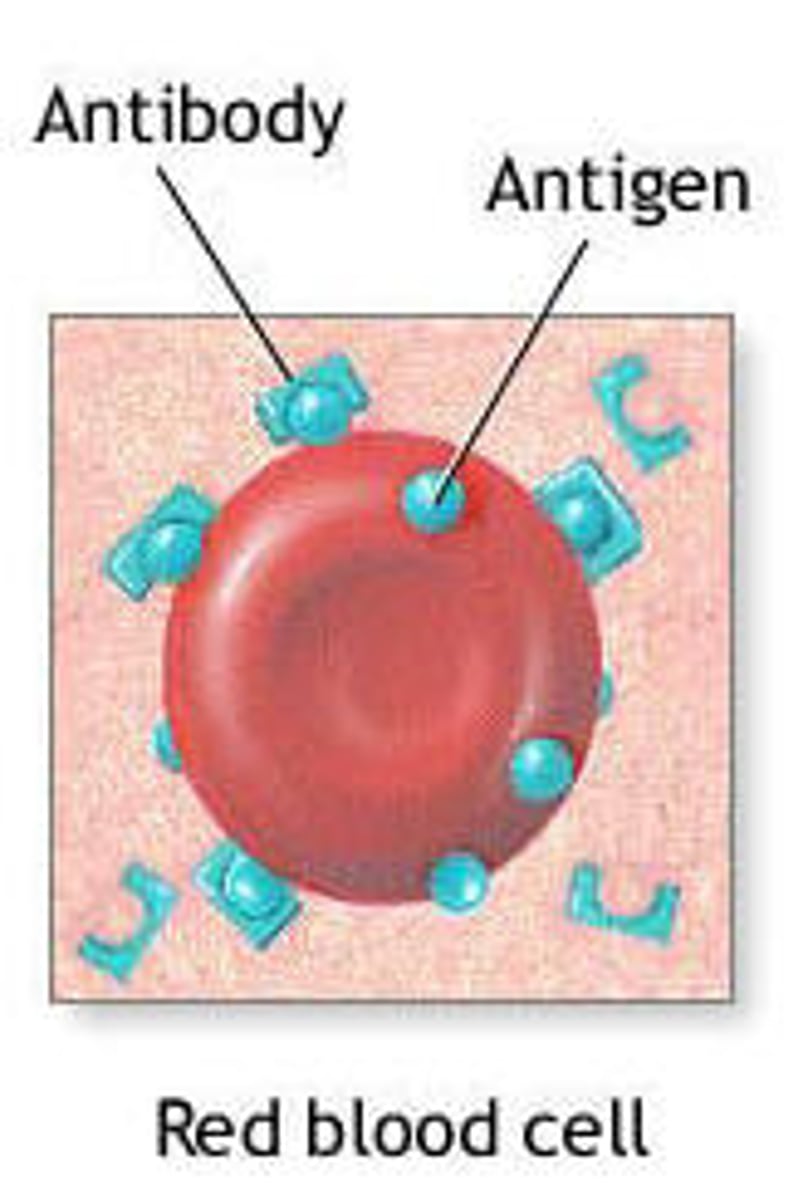
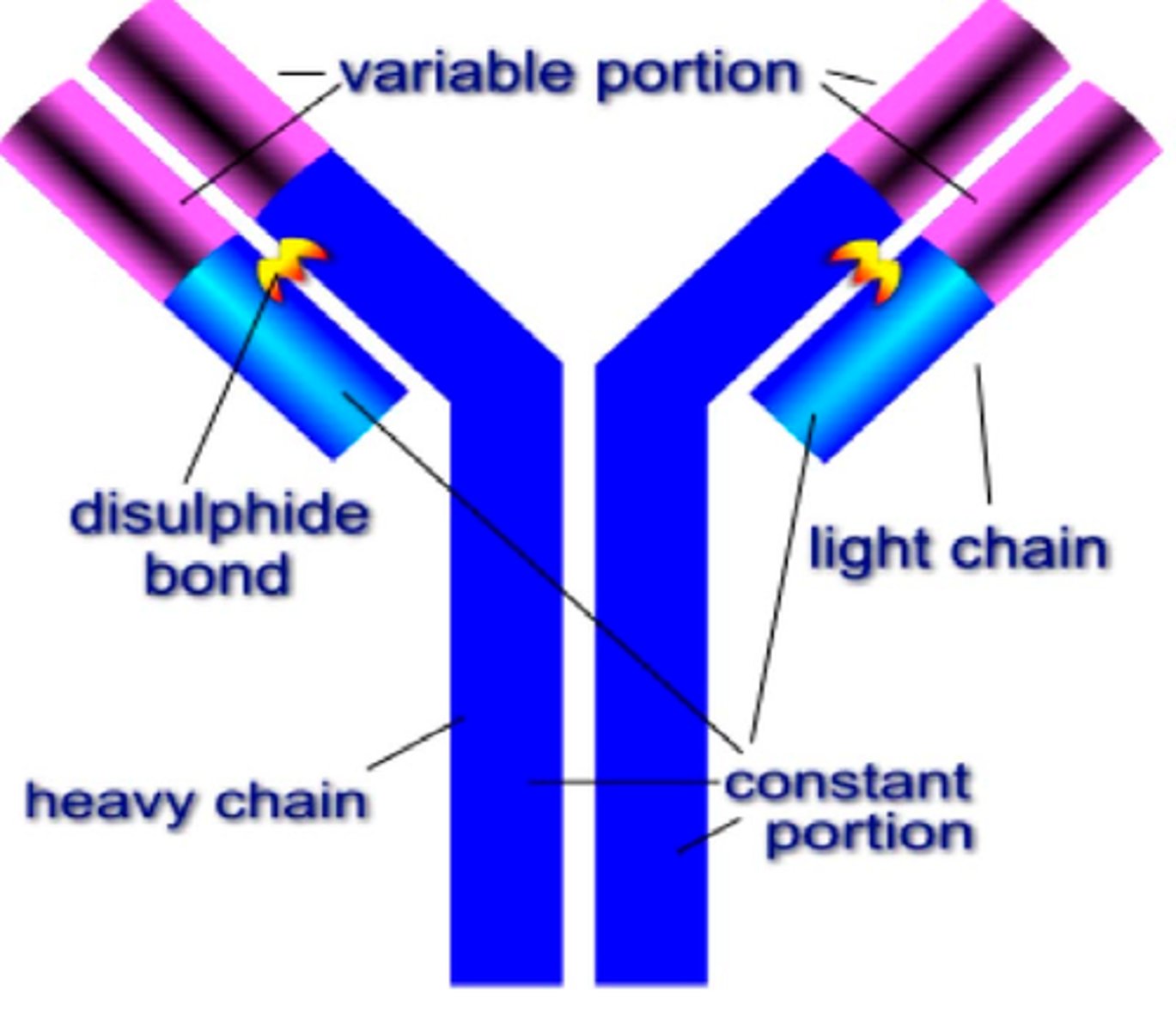
antibody
A protein that acts against a specific antigen
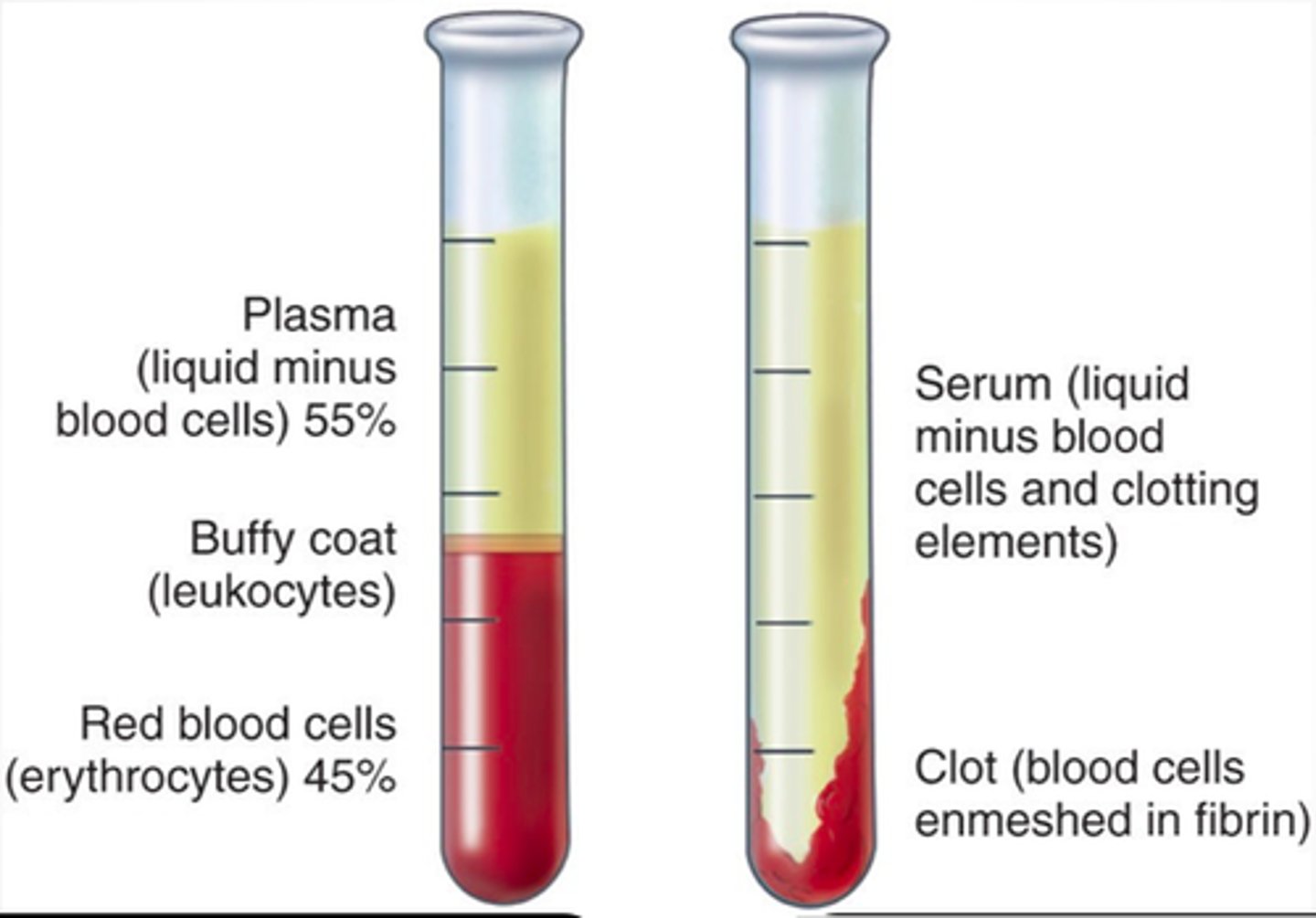
serum
plasma without clotting factors
agglutination
Clumping of microorganisms or blood cells, typically due to an antigen-antibody interaction.
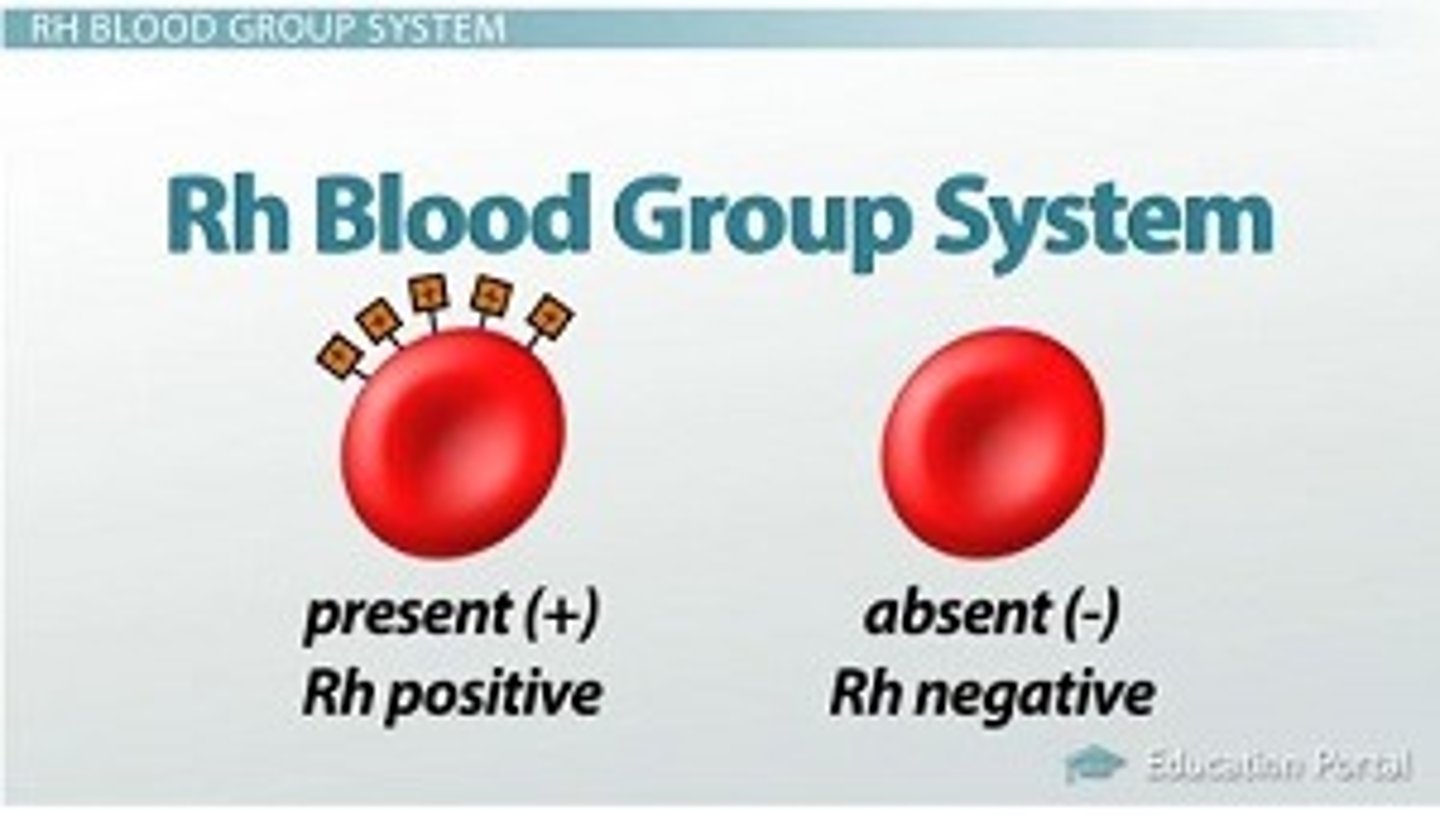
Rh factor
Refers to the presence or absence of the Rh antigen on red blood cells.
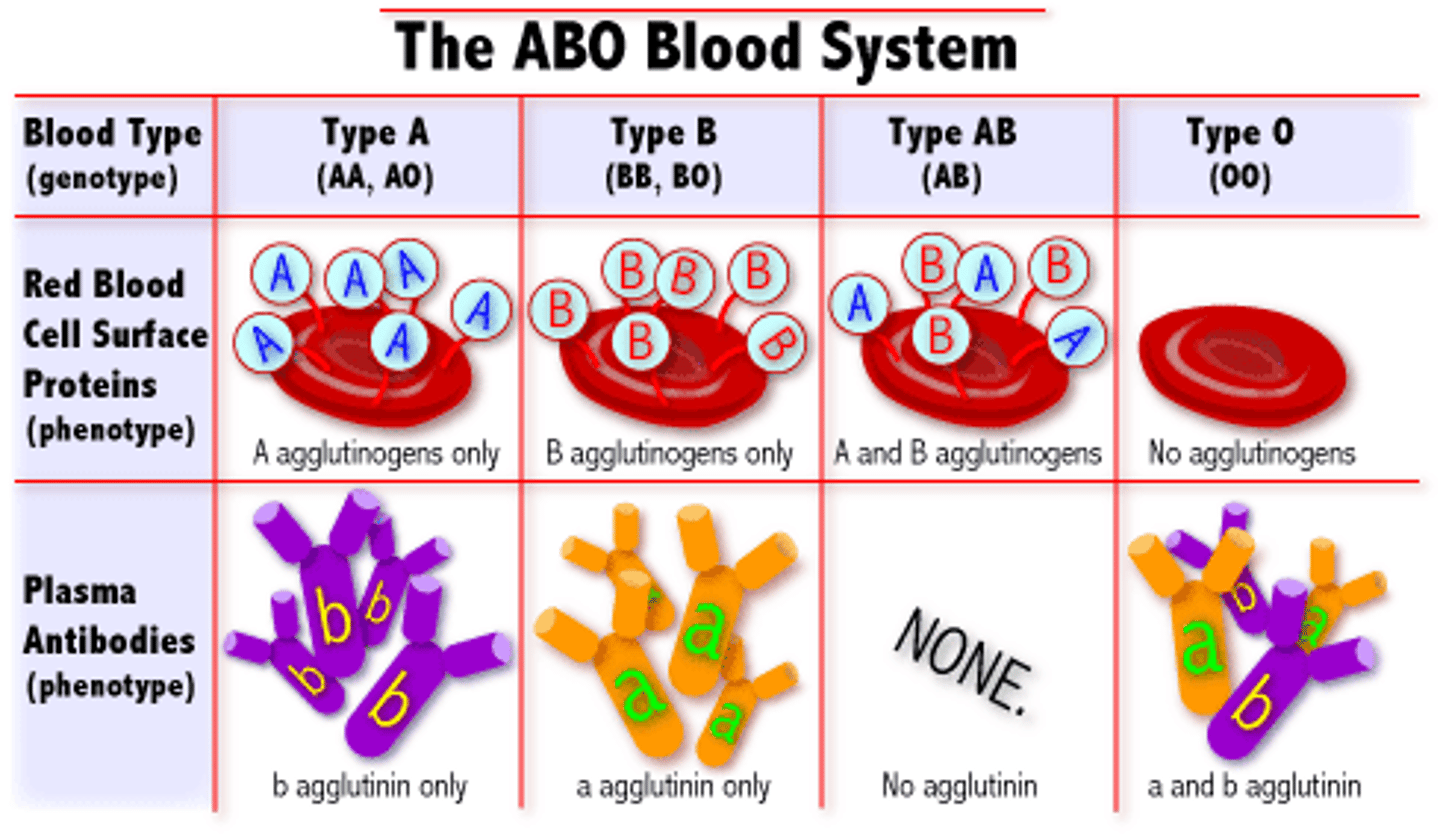
Type A
A antigens and anti-B antibodies
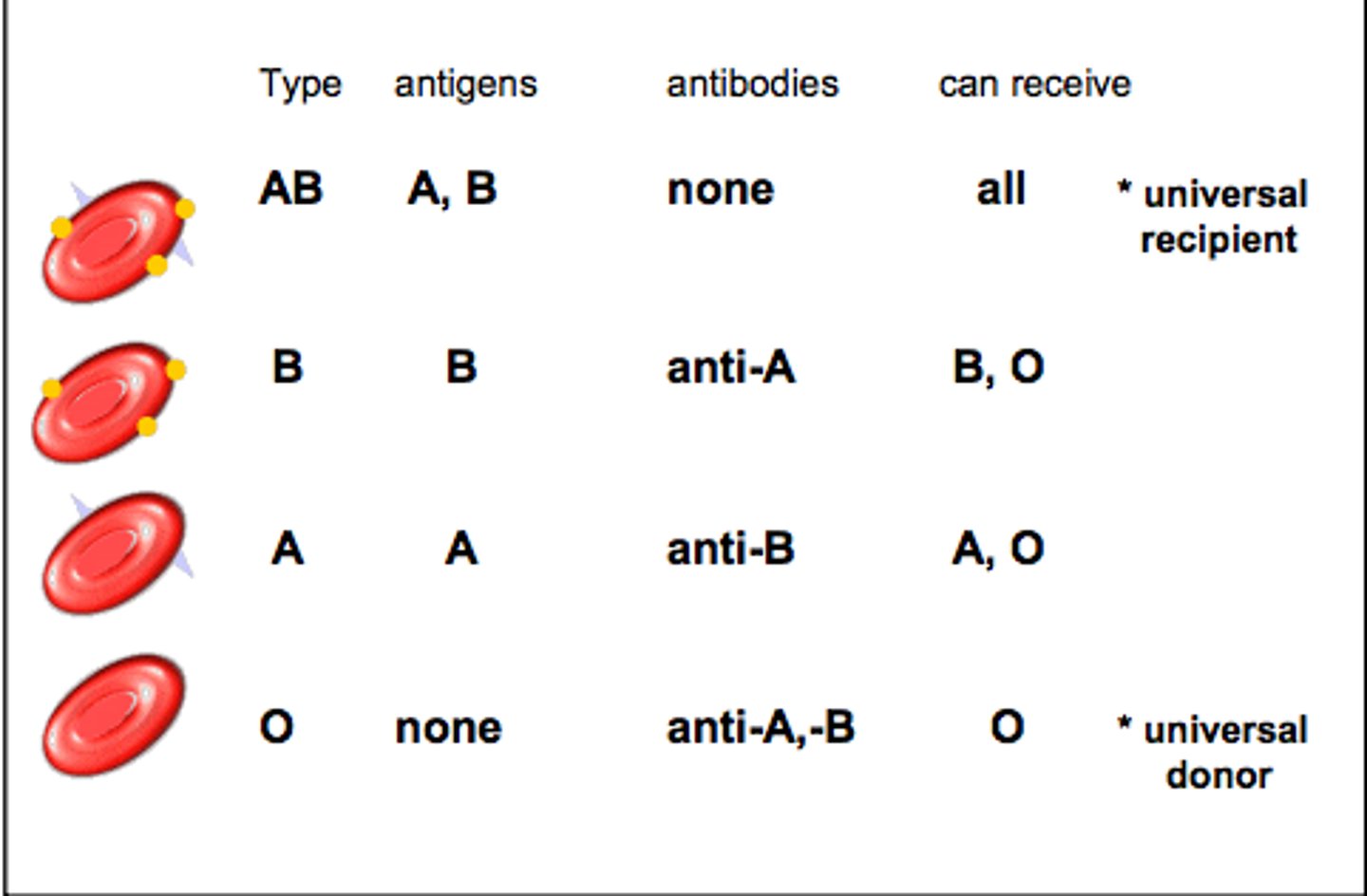
Type B
B antigens and anti-A antibodies
Type O
no antigens, A and B antibodies
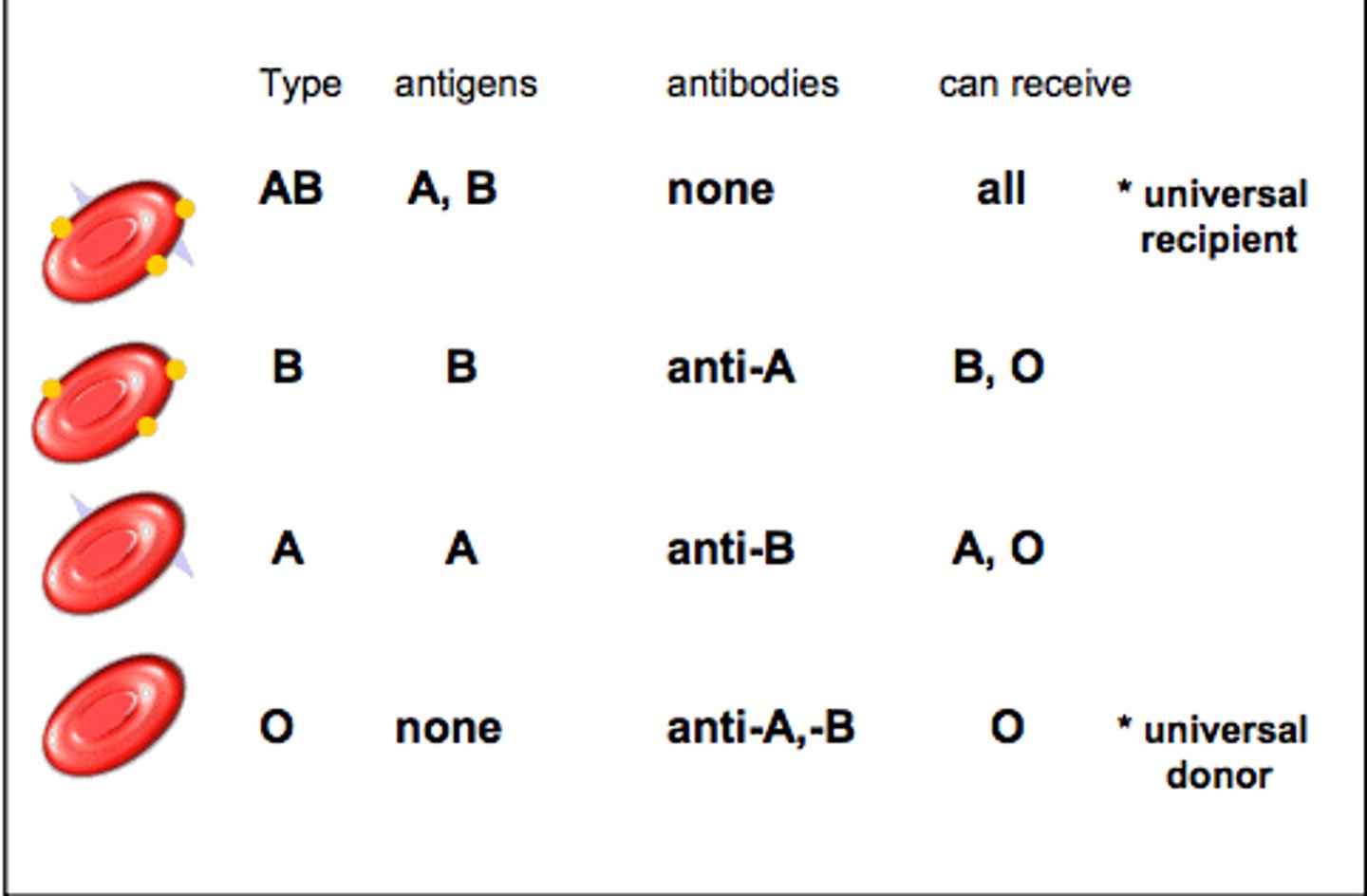
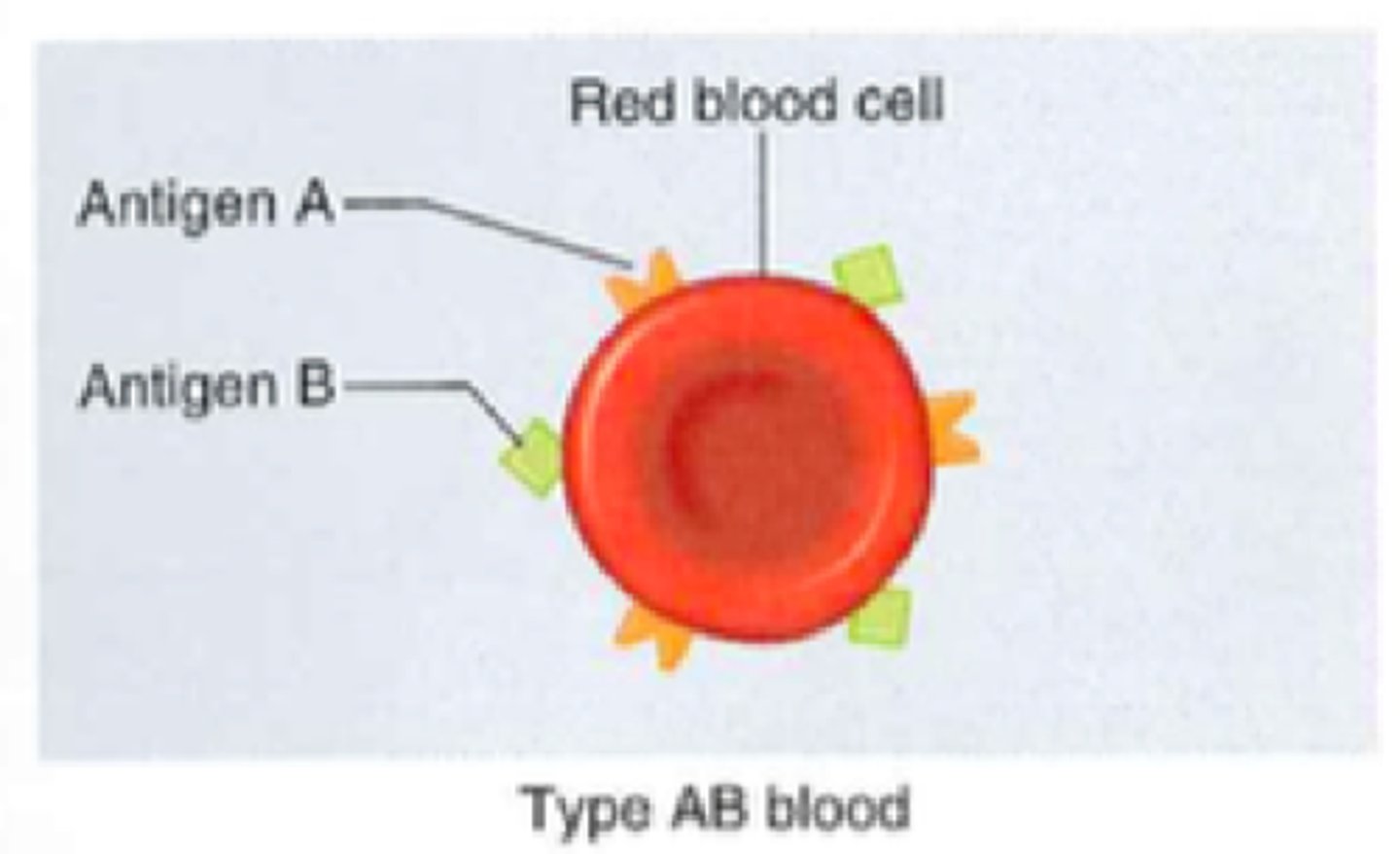
Type AB
A and B antigens, no antibodies
accurate
correct in all details; exact.

alleles
Different forms of a gene

ABO blood group
Genetically determined classes of human blood that are based on the presence or absence of carbohydrates A and B on the surface of red blood cells. The phenotypes, also called blood types, are A, B, AB, and O.
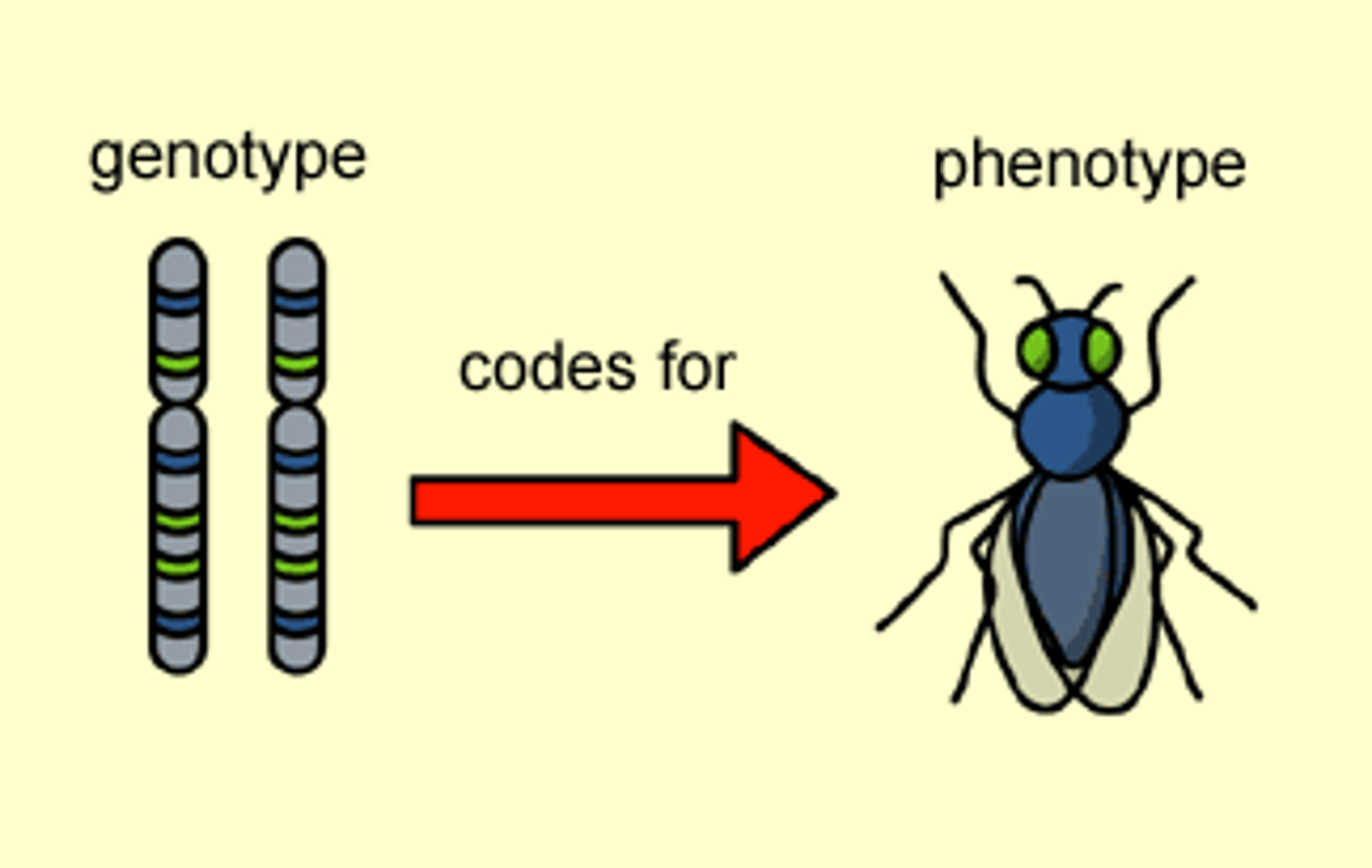
genotype
An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations.
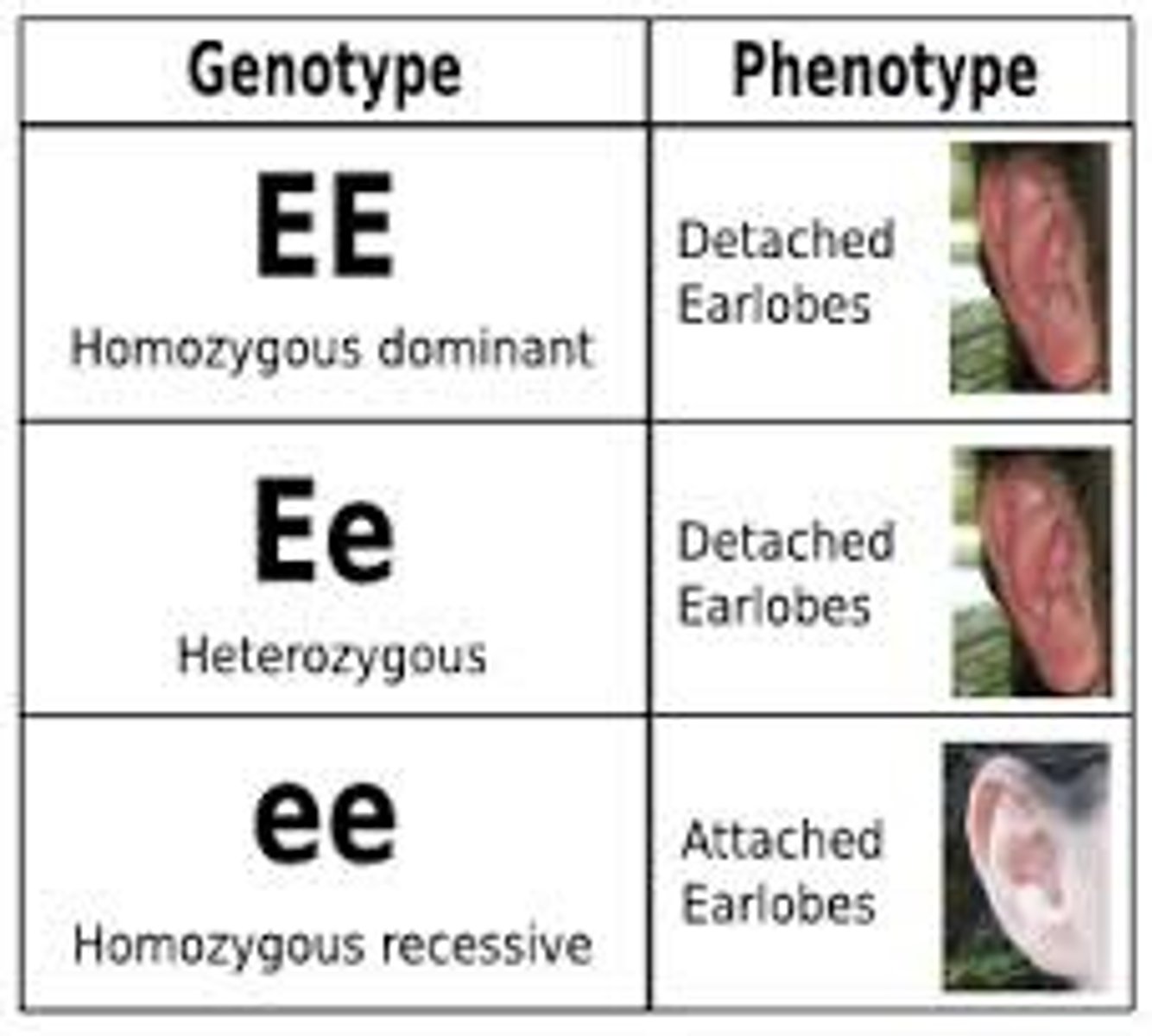
phenotype
An organism's physical traits.
dominant allele
An allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present.
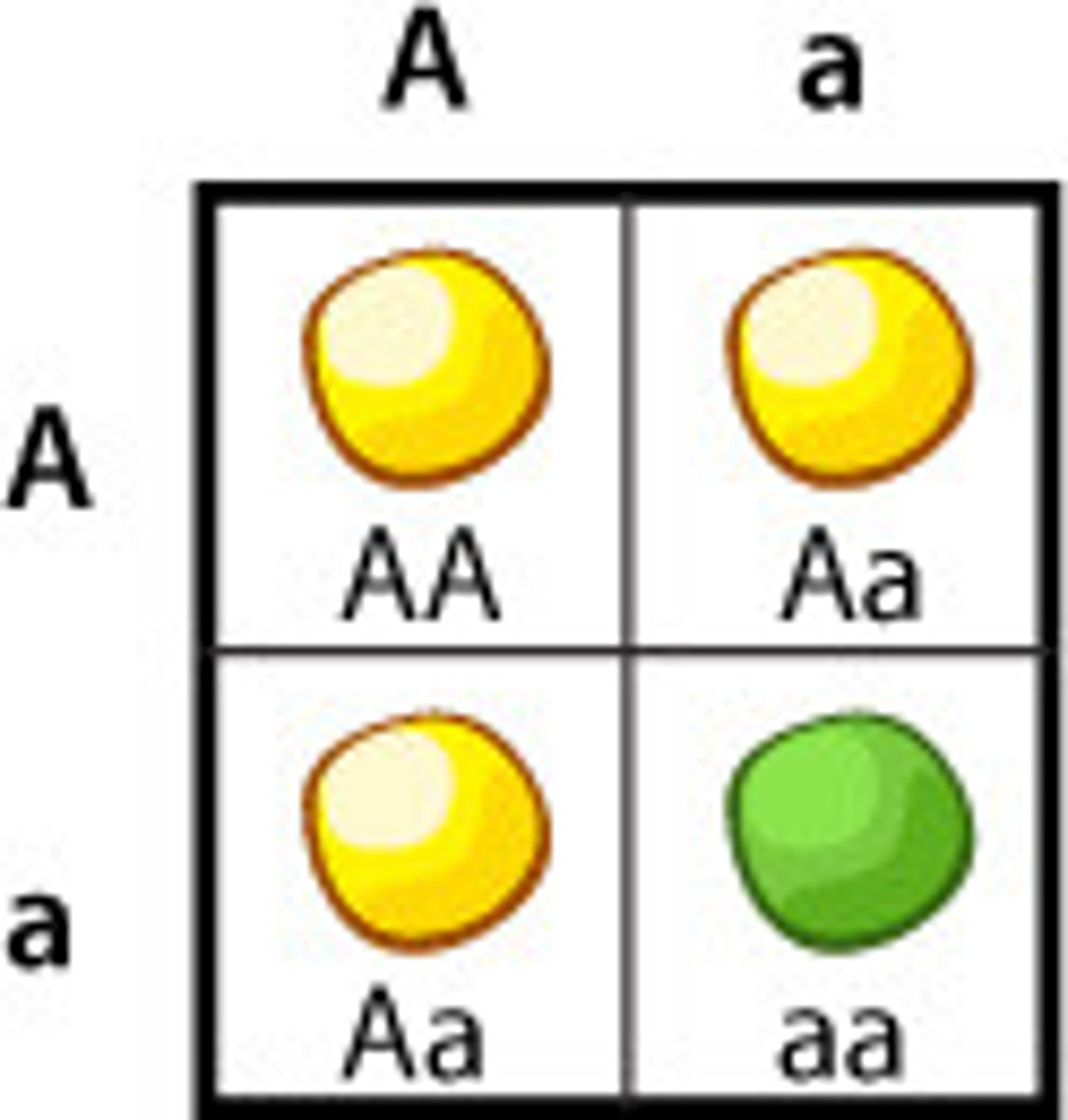
recessive allele
An allele whose phenotypic effect is not observed in a heterozygote.
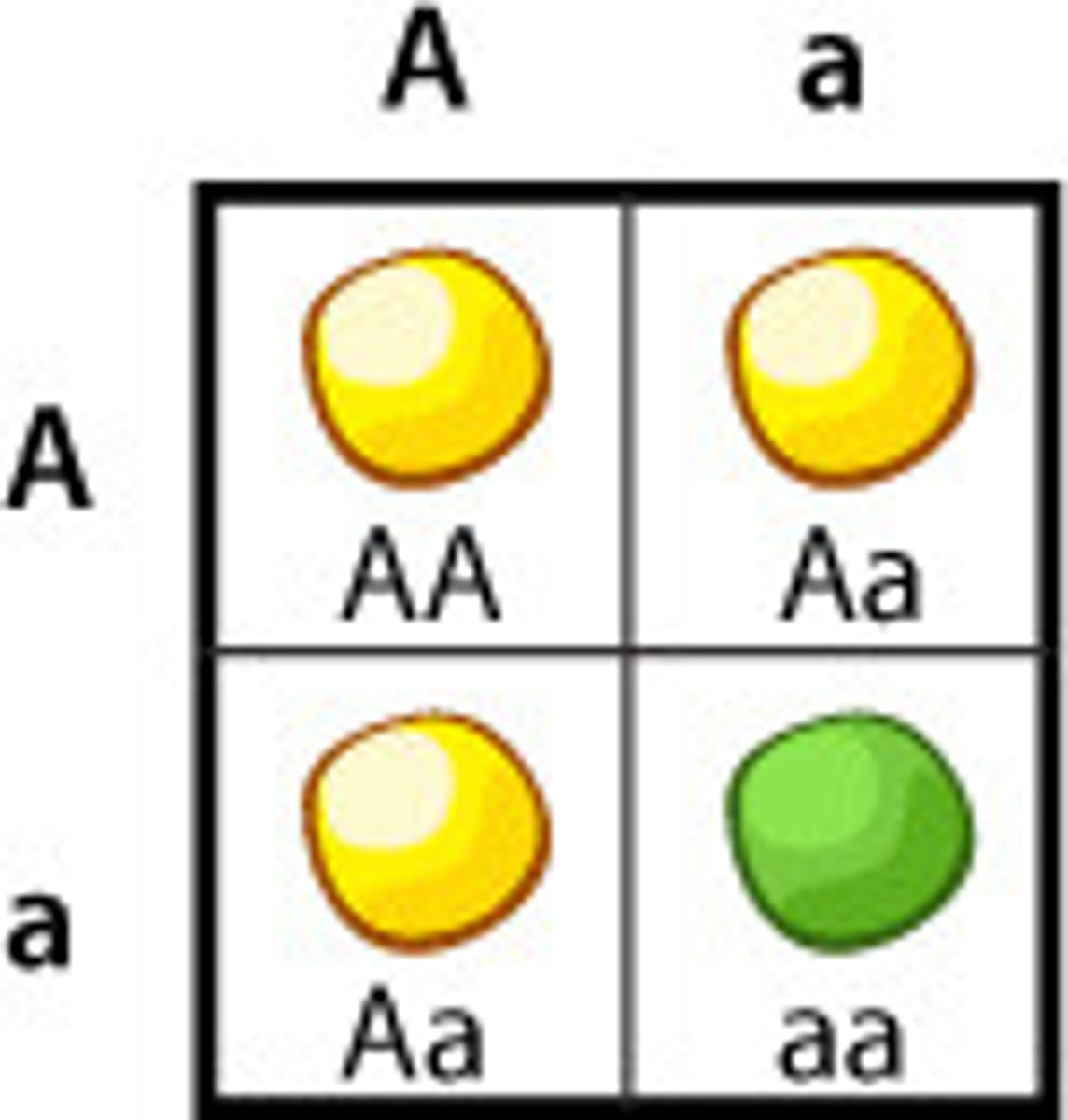
heterozygote
organism that inherits two different alleles for a given gene
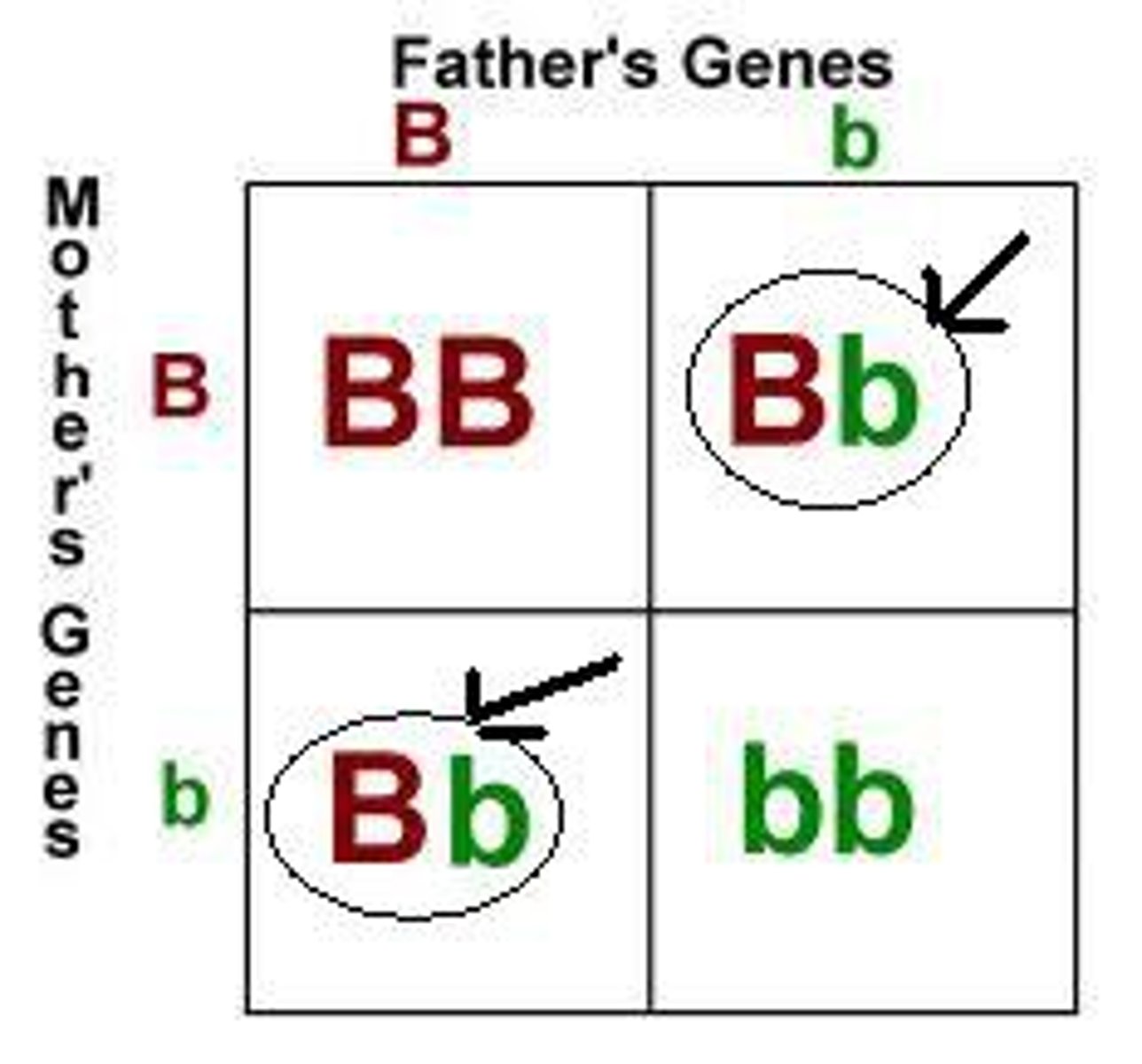
homozygous
An organism that has two identical alleles for a trait

exclude
to leave out

candidate
a person or thing regarded as suitable for or likely to receive a particular fate, treatment, or position

paternity test
A test to identify an individual's father

homozygous dominant
Both alleles (factors) for a trait are the same and dominant (AA)

homozygous recessive
Both alleles (factors) for a trait are the same and recessive (aa)
