Quiz 5 Control Plane
1/21
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Which of the following statements correctly identify the differences between routing and forwarding. Select one or more statements.
Forwarding refers to moving packets from a router’s input to appropriate router output, and is implemented in the data plane.
Forwarding refers to determining the route taken by packets from source to destination, and is implemented in the control plane.
Routing refers to moving packets from a router’s input to appropriate router output, and is implemented in the data plane.
Routing refers to moving packets from a router’s input to appropriate router output, and is implemented in the control plane.
Routing refers to determining the route taken by packets from source to destination, and is implemented in the data plane.
Forwarding refers to determining the route taken by packets from source to destination, and is implemented in the data plane.
Forwarding refers to moving packets from a router’s input to appropriate router output, and is implemented in the control plane.
Routing refers to determining the route taken by packets from source to destination, and is implemented in the control plane.
Forwarding refers to moving packets from a router’s input to appropriate router output, and is implemented in the data plane.
Routing refers to determining the route taken by packets from source to destination, and is implemented in the control plane.
Fowarding
the router-local action of transferring a packet from an input link interface to the appropriate output link interface
Routing
the network-wide process that determines the end-to-end paths that packets take from source to destination
Centralized, global routing
All routers have complete topology, and link cost information.
Decentralized routing
An iterative process of computation, exchange of information with neighbors. Routers may initially only know link costs to directly-attached neighbors.
Static routing
Routes change slowly over time.
Dynamic routing
Routing changes quickly over time.
What is the definition of a “good” path for a routing protocol? Chose the best single answer.
A path that has little or no congestion.
A path that has a minimum number of hops.
Routing algorithms typically work with abstract link weights that could represent any of, or combinations of, all of the other answers.
A high bandwidth path.
A low delay path.
Routing algorithms typically work with abstract link weights that could represent any of, or combinations of, all of the other answers.
“Good” path
BGP may use Multi-Exit-Discriminator (MED) values as part of cost metric
BGP can include Weight, Local_Pref, AS-Path Length, Origin, policies and can learn from RIP, IGP or OSPF advertisements
OSPF calculates metric cost with a reference bandwidth of 100 Mbps for cost calculation divided by the outgoing interface bandwidth.
EIGRP uses the minimum bandwidth on the path to a destination network and the total delay to compute routing metrics with values configured on the interfaces of routers in the path to the destination network.
Consider Dijkstra’s link-state routing algorithm that is computing a least-cost path from node a to other nodes b, c, d, e, f. Which of the following statements is true?
In the initialization step, the initial cost from a to each of these destinations is initialized to either the cost of a link directly connecting a to a direct neighbor, or infinity otherwise.
The values computed in the vector D(v), the currently known least cost of a path from a to any node v, will never increase following an iteration.
Following the initialization step, if nodes b and c are directly connected to a, then the least cost path to b and c will never change from this initial cost.
The values computed in the vector D(v), the currently known least cost of a path from a to any node v, will always decrease following an iteration.
Suppose nodes b, c, and d are in the set N’. These nodes will remain in N’ for the rest of the algorithm, since the least-cost paths from a to b, c, and d are known.
In the initialization step, the initial cost from a to each of these destinations is initialized to either the cost of a link directly connecting a to a direct neighbor, or infinity otherwise.
The values computed in the vector D(v), the currently known least cost of a path from a to any node v, will never increase following an iteration.
Suppose nodes b, c, and d are in the set N’. These nodes will remain in N’ for the rest of the algorithm, since the least-cost paths from a to b, c, and d are known.
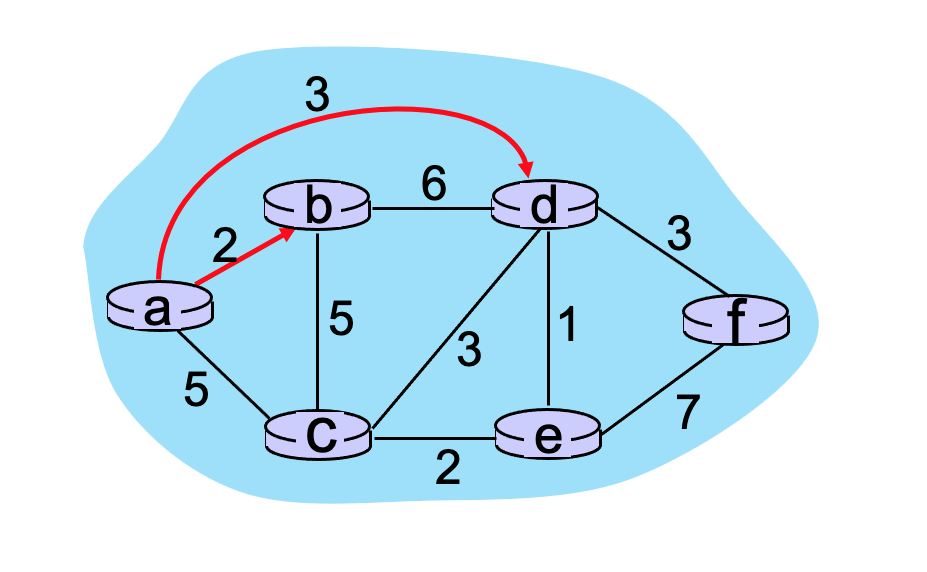
Consider the graph shown below and the use of Dijkstra’s algorithm to compute a least cost path from a to all destinations. Suppose that nodes b and d have already been added to N’. What is the next node to be added to N'?
node e
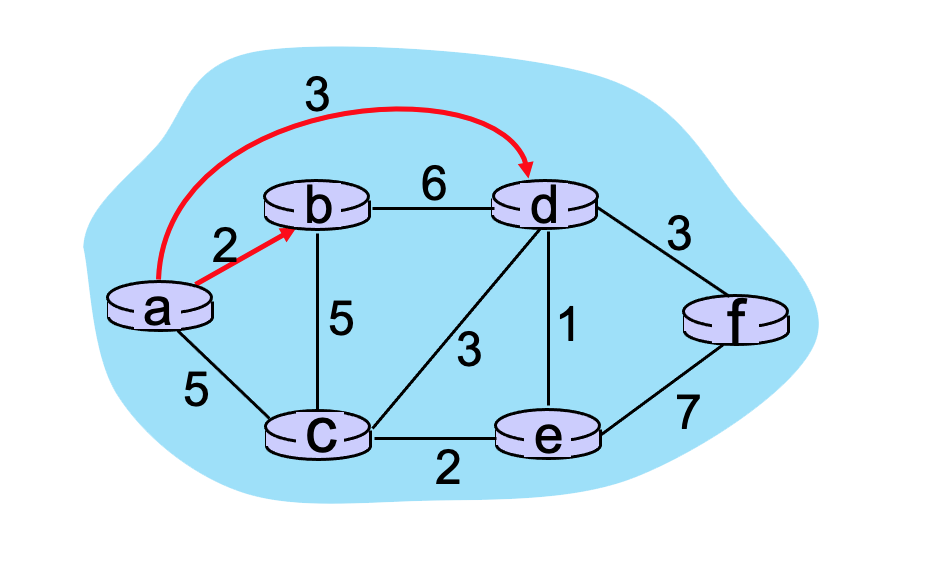
Consider the graph shown below and the use of Dijkstra’s algorithm to compute a least cost path from a to all destinations. Suppose that nodes b and d have already been added to N’. What is the path cost to the next node to be added to N'?
4

Use Dijkstra’s algorithm to compute a least cost path from u to all other destinations. Suppose that nodes x and y have already been added to N’. What is the next node to be added to N’? Fill out the table.
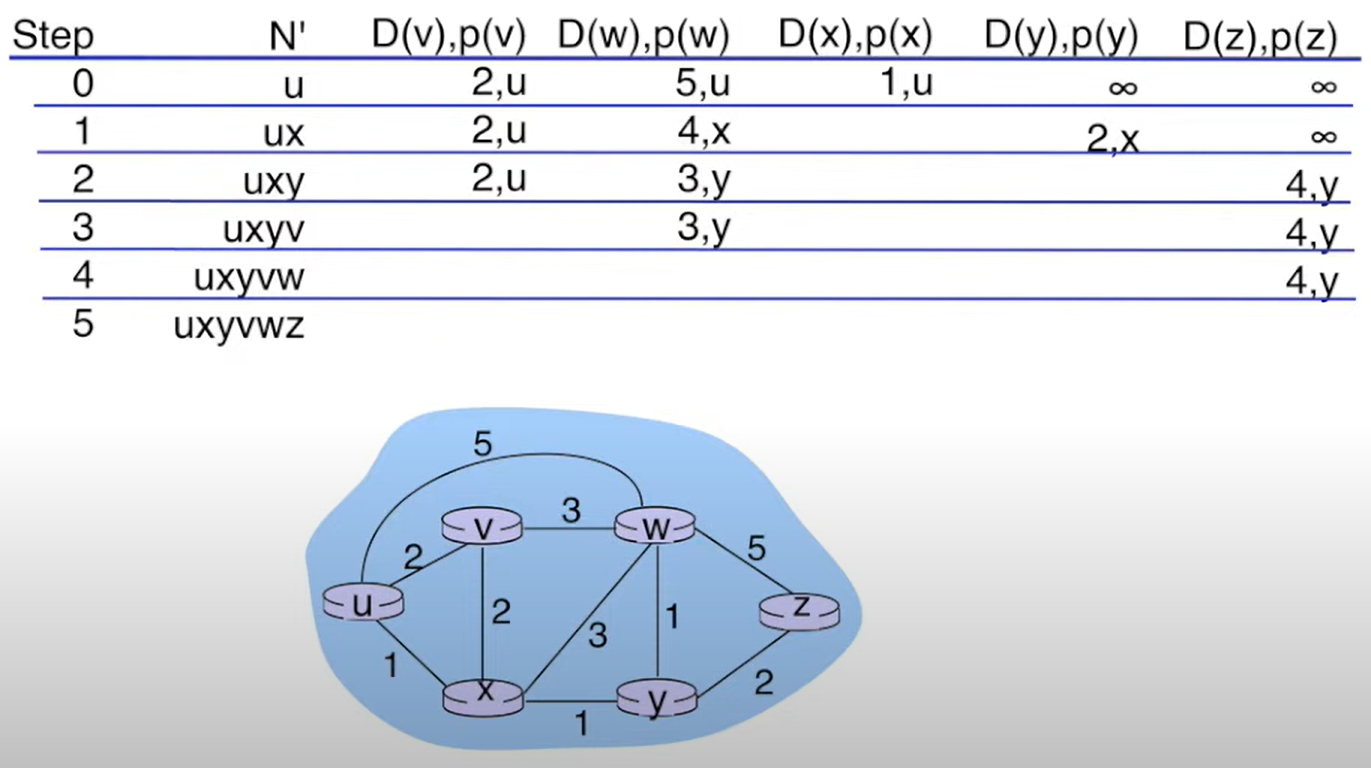
Consider the 6-node network shown below, with the given link costs. Write your answer as n,p.
What is the shortest distance to node x and what node is its predecessor?
What is the shortest distance to node y and what node is its predecessor?
What is the shortest distance to node v and what node is its predecessor?
4,v
5,w
3,u
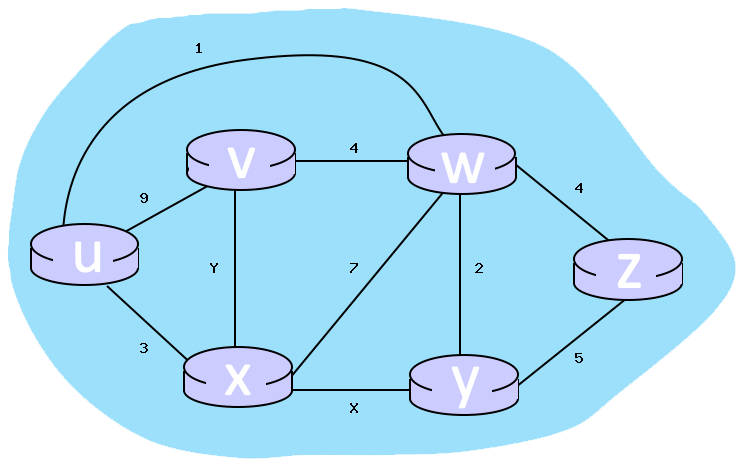
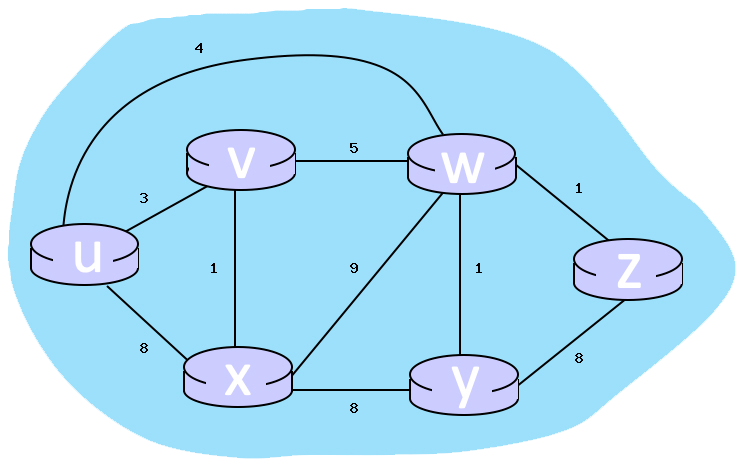
Consider the incomplete 6-node network shown below, with the given link costs.
Consider the completed table below, which calculates the shortest distance to all nodes from W:
Node | Shortest distance from W | Previous Node
W 0 n/a
U 1 W
Y 2 W
V 4 W
X 4 U
Z 4 W
For links X and Y, what are the costs associated?
cannot determine value of X and Y so n/a
Per-router control plane
Individual routing algorithm components interact in the control plane
Routing algorithm runs in each and every router
Both a forwarding and a routing function are contained within each router
Each router has a routing component that communicates with the routing components in other routers to compute the values for its forwarding table
Software-defined networking (SDN)
A (typically) remote controller gathers information from routers, and then computes and installs the forwarding tables in routers
A logically centralized controller computes and distributes the forwarding tables to be used by each and every router
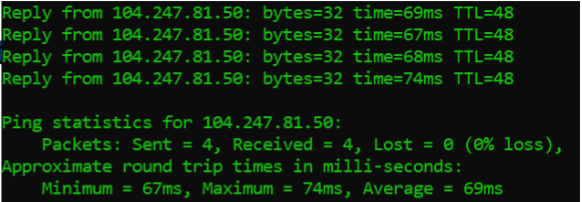
ping
verify whether a network data packet can reach an address without errors or not
used to check for network errors
used in video games to estimate latency
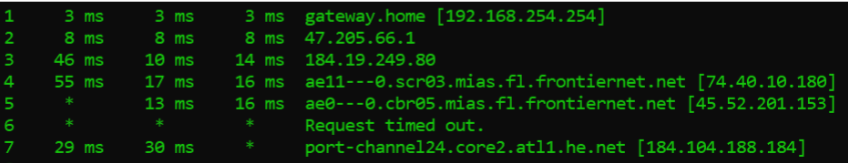
traceroute (tracert → windows)
provides a map of data on the internet from its source to its destination
helps in the packet capture
troubleshoot the hop delays during video conferences
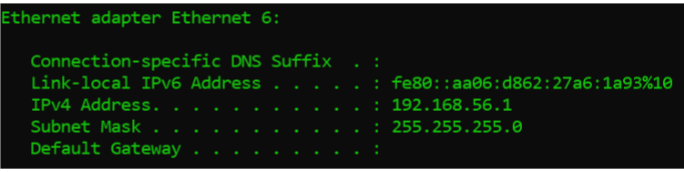
ifconfig vs ipconfig
ifconfig:
used in Linux / macOS
displays IP configuration details of network interfaces
provides packet statistics, error counters, and interface status
doesn't have a built-in command for releasing IP addresses
ipconfig:
used in Windows
displays IP configuration details of network adapters
displays MAC address, DNS suffix, and IPv6 status
can release currently assigned IP address of a network adapter
What is the fastest and still effective utility to determine from Host A if the Webserver is running?
ping because it sends ICMP packets
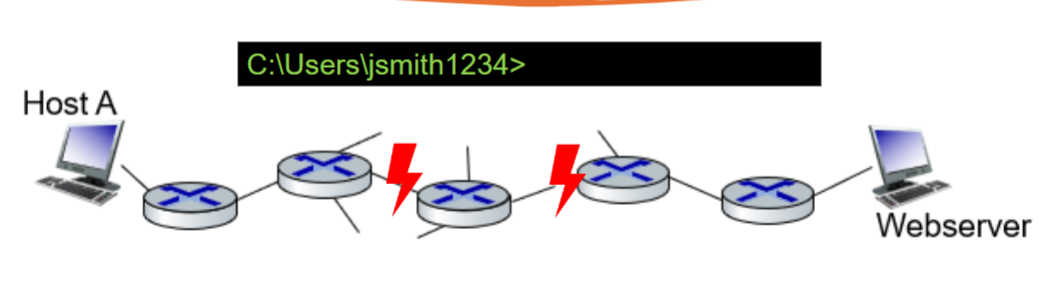
If a ping test fails from Host A to Webserver, what is the most effective utility to determine (from Host A) where the possible fault is located in the network?
traceroute