Energy storage
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is glycogenesis?
Synthesis of glycogen
What is Gluconeogenesis?
Synthesis is glucose from non-carbs
What is Glycogenolysis?
Breakdown of glycogen
What are the normal and diabetic levels of fasting plasma glucose ?
Normal:
<5.6 mmol/l and <7.8 mmol/l 2 hours after the test
Diabetic:
>7 mmol/l and >11.1 mmol/l after 2 hrs
Properties of glycogen
Alpha 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bond
Large branched molecule
Low osmotic effect
Stored in nucleus and live
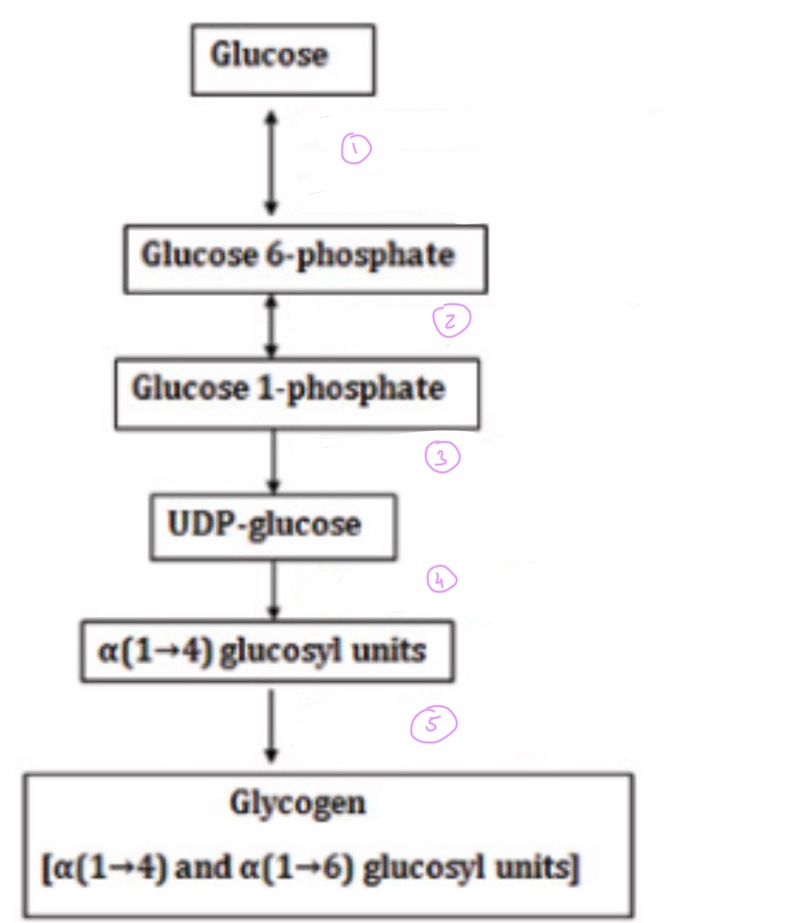
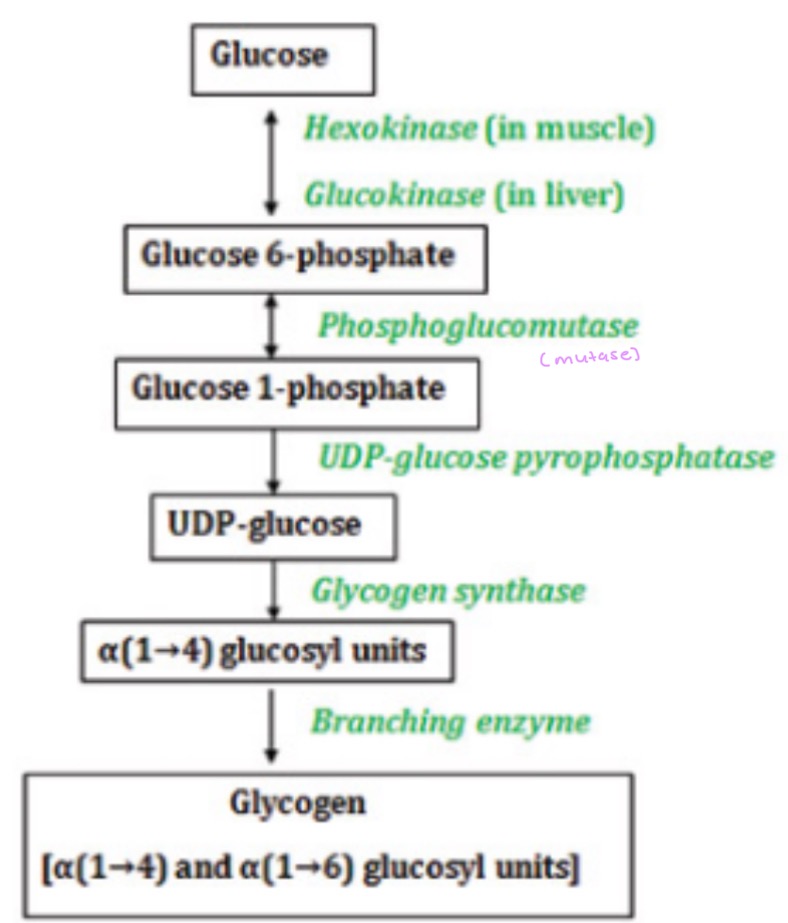
Glycogenolysis pathway
(Glycogen phosphorylase) (Mutase)
Muscle glycogen → glucose-1-phophate → glucose-6-phosphate → glycolysis → ATP, CO2, lactate
(Glycogen phosphorylase) (Mutase) (Glucose-6-phosphatase)
Liver glycogen → glucose-1-phophate → glucose-6-phosphate → blood glucose
What is Von Gierke disease (glycogen storage disease) and what are the symptoms?
The body cannot breakdown glycogen due to deficiency in glucose-6-phosphatase → accumulation of glucose-6-phosphate
** autosomal recessive
Symptoms: hypoglycemia + lactic acidosis → seizures, hepatomegaly (distended abdomen) cerebral damage, doll like face
Where does gluconeogenesis occur?
In the liver and the kidney cortex
Occurs due to stress (fasting, exercise£
What are the importance enzymes in gluconeogenesis and what can stimulate and inhibit them?
PEPCK + fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
Stimulate: glucagon
Inhibit: insulin
Where does the body get energy after eating?
<2 hrs: glucose
8-10hrs: glycogenolysis
>10 hrs: gluconeogenesis
How does insulin stimulate glycolysis?
increases the rate of glucose transport across the membrane
Increases Hexokinase and 6-Phosphofructokinase activity
Stimulates the rate of glycogen synthesis and decreases the rate of glycogen breakdown
What promotes and inhibits lipid storage?
Promote: insulin (inhibit HSL)
Inhibit: glucagon, adrenaline cortisol, GH (activate HSL)
How many molecules of ATP are produced in fatty acid oxidation ?
4 ATP per round
** occurs in mitochondria
Where and from what are lipids synthesised from ? (Lipogenesis)
In the cytoplasm of liver cells
Acetyl CoA from mitochondria is used
Requires ATP + NADPH
Lipogenesis vs lipolysis
