Plant Physiology
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Cell division
The process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells.
Cell enlargement
The process by which a cell increases in size.
Cell differentiation
The process by which a cell changes from one cell type to another.
Shoot apical meristem
Region at the tip of a shoot responsible for the growth of stems and leaves.
Root apical meristem
Region at the tip of a root responsible for the growth of the root.
Lateral bud meristem
Meristematic tissue located at the nodes of the shoot that gives rise to branches.
Internode
The section of stem between two nodes.
Lateral root meristem
Meristematic tissue located along the length of the root that produces lateral roots.
Primary growth
Growth that results in the lengthening of plants.
Embryophytes
Land plants that have adaptations for survival on land.
Bryophytes
Nonvascular plants, commonly known as mosses.
Tracheophytes
Vascular plants, which include seed and non-seed plants.
Alternation of generations
A life cycle that alternates between diploid (sporophyte) and haploid (gametophyte) stages.
Megaspores
Spores that develop into female gametophytes.
Microspores
Spores that develop into male gametophytes.
Angiosperms
Flowering plants that produce seeds. Monocots & Eudicots. About 370 000 known species, 17 000 unknown species.
Monocotyledons
Plants with one seed leaf in the embryo.
Eudicotyledons
Plants with two seed leaves in the embryo.
Secondary growth
Growth that results in an increase in the girth of plants. Gymnosperms go through this.
Indeterminate growth
Growth that occurs continuously throughout a plant's life.
Determinate growth
Growth that ends at a certain point.
Monoecious
Plant species that have both male and female reproductive structures on a single individual.
Dioecious
Plant species that have male and female reproductive structures on separate individuals.
Conifers
A group of gymnosperms that produce cones.
Primary cell wall
The outermost layer of a plant cell that allows growth and flexibility. All plant cells have.
Secondary cell wall
A thicker cell wall found in some plants that provides additional strength. Contains lignin (provides greater strength). No further cell growth can occur once this is present.
Plasmodesmata
Microscopic channels that connect plant cells, allowing for communication and transport. Tubular structures. Intercellular movement of proteins, nucleic acid and macromolecules.
Symplast
Region of the plant body enclosed by plasma membrane (interior of plant cells). Includes plasma membrane and cytosolic connections (plasmodesmata) between adjacent cells. Movement through plasmodesmata is called ____mic transport.
Apoplast
consists of the region outside the plasma membrane (intercellular air space). Transport through the permeable cell wall space outside the cells is called _____ic transport
Parenchyma tissue
Thin primary wall and large central vacuole. Wide range of functions in the plant, depending on their location, from food storage to carrying out photosynthesis.
Collenchyma tissue
Often present in young actively growing parts of the plant requiring mechanical support. Parenchyma-like cells, often more elongated and thicker which provides mechanical support while still allowing for cell expansion in these growing parts
Sclerenchyma tissue
This tissue is found in mature plant parts and also provides mechanical support. Thick secondary cell wall. Dead at maturity. Two types of cells. Fibers (elongate cells, vascular tissue), and Sclereids (more variously shaped cells, common in seed coats).
Xylem tissue
Vascular tissue responsible for water and nutrient conduction from root to shoot. In gymnosperms → tracheid. In angiosperm → vessel elements. Both withstand extreme negative pressure (tension).
Tracheid
Elongate, hollow, dead cells in xylem. The plasma membrane, nucleus, and cytosolic contents have been lost. Has pits in their walls - movement from one cell to another
Vessel elements
Hollow dead cell at maturity. form a continuous hollow tube for efficient water conduction. Larger over evolutionary time. Lower water resistance, breaking down walls
Phloem tissue
Vascular tissue responsible for transporting the products of photosynthesis. From leaves to stems, roots, flowers, and fruits. Major conducting cells are the sieve tube elements. Cells form long tubes (sieve tubes) for conduction of substance. Contain cytosol and some organelles but lack nucleus. Movement is aided by pores in the end walls between cells.
Dermal tissue system
Outer protective layer of the plant (epidermal or corky tissue)
Vascular tissue system
Tissue system specialized for the transport of substances from one part of the plant to another (xylem and phloem). Conducting, parenchyma cells. Thick-walled fibers.
Ground tissue system
Tissue system that fills the spaces between dermal and vascular tissues. Includes pith and cortex of primary stems and roots, and the mesophyll in leaves.
Root cap
Structure that protects the root apical meristem as it grows.
Zone of cell division
Root apical meristem and the cells immediately behind it undergo rapid cell division. Can begin to see blocking out of dermal, vascular and ground tissue → mature epidermis, xylem and phloem, and the cortex and pith
Zone of cell elongation
In this zone, cells produced by the root apical meristem undergo a period of rapid growth in length
Zone of cell differentiation
Now fully expanded cells differentiate into particular cell types. Proceeding from the outside toward the middle of the root there are different parts
Epidermis
Outer layer of cells, dermal tissue system of the root. Many epidermal cells grow long extensions called root hairs. They increase the absorptive surface of the root, aiding uptake of water and minerals
Cortex
Region usually made up of thin-walled parenchyma cells often involved in the storage of food within the root
Endodermis
Single layer of cells, the cell walls of which contain suberin (called the casparian strip), which provides a barrier preventing any further movement of water or solute within the apoplast.
Sieve cells (gymnosperm), and sieve tube elements stack and create sieve tubes (angiosperms). Made in phloem cells
Stele
Central region of the root that contains vascular tissues.
Pericycle
Layer of cells that can produce lateral roots in plant roots.
Axillary buds
Meristems developed at the nodes of leaves that can form branches.
Rays of parenchyma cells
Within xylem and phloem tissues are arranged like the spokes of a tire.
Cork cambium
Layer of cells that produces cork, providing protection.
Palisade mesophyll
Layer of elongated cells in leaves where photosynthesis primarily occurs.
Spongy mesophyll
Layer of loosely packed cells in leaves that facilitates gas exchange.
Stomata
Pores in the leaf surface that allow for gas exchange.
Vacuoles
Organelles that store substances and help maintain turgor pressure in plant cells.
Chloroplast
Plant cell organelle responsible for photosynthesis.
Middle Lamella
Region “cementing” one cell wall to its neighbour. Pectin holding in place. Staple, don’t move around.
Primary plasmodesmata
forms during cytokinesis, connections between clonally related cells.
Secondary plasmodesmata
Form after cell wall deposition, requires localized digestion of existing wall between cells, allows communication between clonally unrelated cells. Cell walls are too difficult to get through. Cell really needs to locally digest cell wall
Pit fields
Depressions in the primary cell walls where numerous plasmodesmata cluster. Secondary wall does not form over these fields, leaving pits in the secondary wall.
Vacuoles
Single membrane bound (one bilayer), tonoplast membrane. Store water, inorganic ions, organic acids, sugars, enzymes, secondary metabolites (diverse functions)
Peroxisomes
Involved in photorespiration in mesophyll cells. glycolate oxidation in this pathway produces hydrogen peroxide, a reactive oxygen species (reactive, potentially damaging). High levels of catalase breaking down H2O2. Single membrane. Uses rubisco to react with oxygen rather than CO2 which then uses CO2 to make sugar (3-PGA)
Glyoxysomes
Lipid-storing seeds, enzymes for glyoxylate cycle which converts triacylglycerols to sugar during germination.
Microtubules and actin filaments
Components of the plant cytoskeleton that provide structural support and facilitate transport.
Polymerization
Building up the highway. Sheet-like positive end, curling into a tubule as the GTP is hydrolyzed.
Depolymerization
Taking down the highway. Frayed positive end, with individual protofilaments separating and curling
Specific heat capacity
Heat energy required to raise the temperature of one unit of mass by one unit of temperature
Latent heat of vaporization
Energy needed to separate molecules from the liquid phase and move to a gas phase. Occurs during transpiration. Latent heat the energy released.
Hydraulic conductivity
The ease of water movement through plant membranes.
Turgor pressure
Pressure exerted by water in the vacuole against the cell wall.
Diffusion
Net movement of particles down concentration gradient (driving force). Comes to equilibrium (no more net movement) Initial → intermediate → equilibrium. Rate of ____ (Fick’s 1st Law) = -____ coefficient (total concentration / total distance).
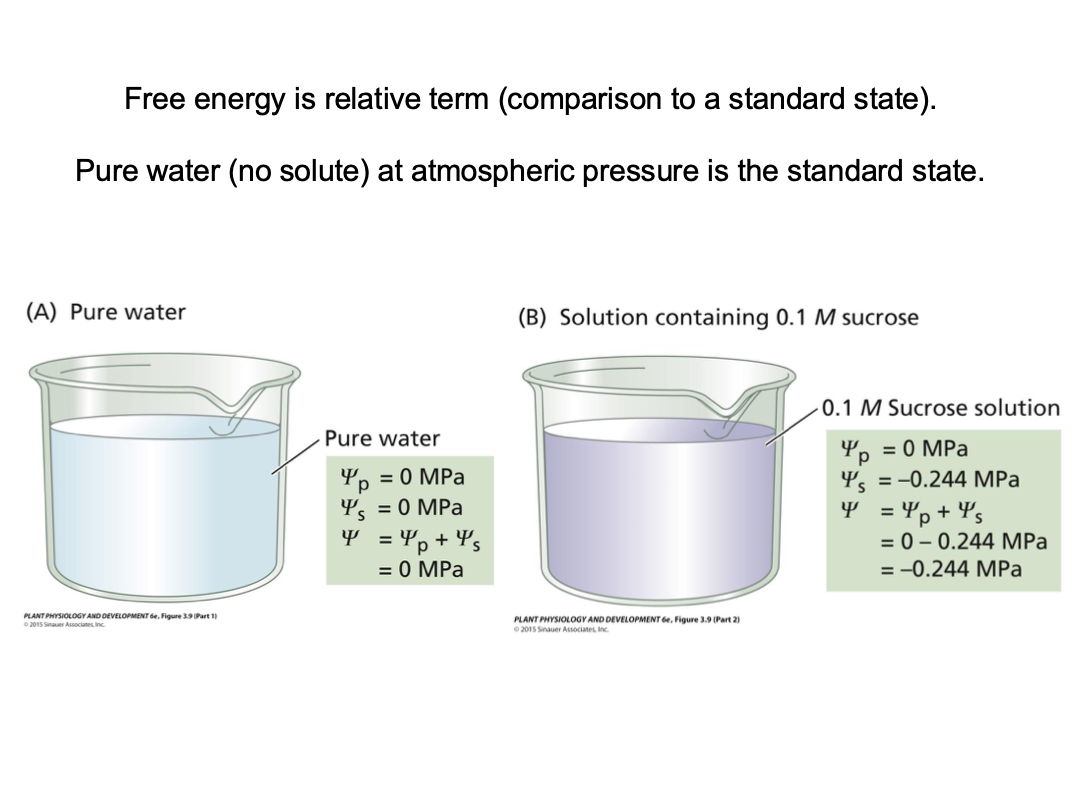
Osmosis
The diffusion of solvent (water) across a selectively permeable membrane (ie. a membrane where solutes can’t readily cross). The driving force is a difference in water potential. Movement across the membrane is facilitated by integral membrane proteins (aquaporins)
Flux density
rate of transport = (diffusion coefficient)(concentration gradient / distance or size)
Photosynthesis
Process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy.
Light reactions
Phase of photosynthesis that captures energy from sunlight.
Calvin cycle
Phase of photosynthesis that synthesizes glucose from carbon dioxide.
Photosystems
Clusters of chlorophyll and proteins involved in the light reactions of photosynthesis.
Photon
A particle of light that carries energy.
Fluorescence
Emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light.
Emerson enhancement effect
The rate of photosynthesis when red and far-red light are given together is greater than the sum of their rates when given separately. More effective light use when both wavelengths were given. Two photosystems cooperate and work more efficiently.
700 nm and 600 nm then add = photosynthetic rate is higher than just the sum.