Exam 3
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Micro Bio 251 CSN
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Contributions of Ignaz Semmelweis & Joseph Lister
Ignaz Semmelweis
Established Handwashing practice used today
Joseph Lister
Established techniques of aseptic surgery that were widely adopted around the world, creating a path towards safe surgery

Antisepsis vs. Disinfection
Antisepsis
Used to reduce microbes numbers on living tissue ( like on skin)
ex: Alcohol, Hydrogen Peroxide etc.
Disinfection
Reduced microbes numbers on non-living surface or material
ex: Bleach, ammonia
Purpose:
Control growth of microorganisms outside the body
Prevent the spread of infections disease by cleaning environment
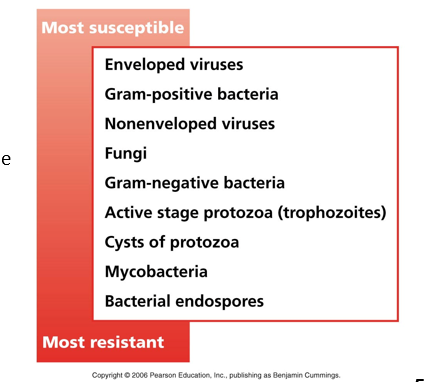
Most Susceptible vs. Most Resistant
Some types of microbes are more susceptible than others to antiseptics and disinfectants
Bacteria endospores vs. Nonenveloped viruses
Witch would be more easier to kill? - nonenveloped
Which will be the hardest to sterilize kill and removing all the microorganism - endospore
Sterilization meaning
The removal or destruction of all living microorganisms (including spores and endospores)
Common methods:
Heating
Filtration
Sterilization gases

Disinfection
Destroy most microorganisms, particularly pathogens on a non-living surface
Disinfectant

Antisepsis
Destroy most microorganisms, particularly pathogens on a living surface ( like skin)
antiseptic
**Preventing of infection or sepsis by removing and decrease bacteria on skin and mucous membrane.
Sanitization
Decrease number of microorganisms that meets specific public health standards
Sanitizer

Degerming
Degerming - Process of removing microorganisms by mechanical means rather than killing the microbes outright
Handwashing is a common and effective degerming technique

Bacteriostatic
Inhibits the growth of bacteria but does not kill bacteria, If a bacteriostatic agent is removed, the bacteria may begin growing again
Bactericidal
Kills bacteria
* (Suicide)
Biocidal / Germicidal
Kills microorganisms ( general term)

Targets of antimicrobial agents
Targets:
Cell walls
Cell Membrane or viral envelope
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Factors that affect death rate of Microbes
Number of microorganisms
Type of microorganisms
pH and temperature
Concentration of agents
Presence of organic matter/chemicals
What are the things to considered for choosing the correct method agent to use?
What is desired result?
What type of material?
What will the material be used for?
Cost-effective?
Safe?

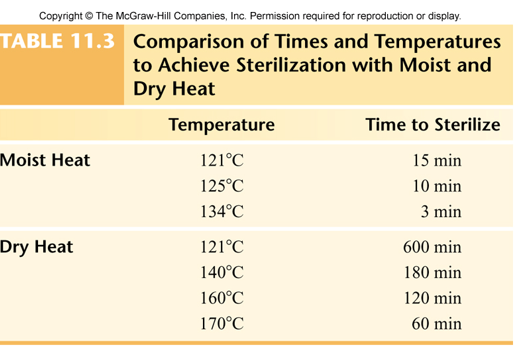
Moist Heat
Lower temperatures and shorter exposure time, coagulation and denaturation of proteins

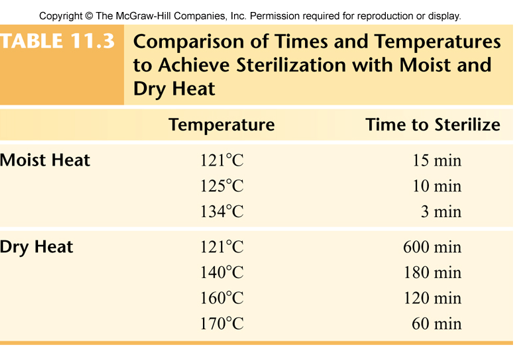
Dry Heat
Moderate to high temperatures dehydration, denaturation of protein, oxidation of cellular components, incineration

Autoclaving
Preferred method of sterilization with moist heat in the healthcare field
Related to moist heat

Boiling
Needs much more time to destroy endospores so not very reliable
-sanitation
Moist Heat Related

Pasteurization
Must be sufficient without altering the taste of foods
Quick method
Related to Moist Heat*
Prevents spoilage

Thermoduric Microbes
Can survive pasteurization
Certain microbes are thermoduric ( survive high temps for short times) & survive the pasteurization process

Hot Air Sterilization | Dry Heat
items to be sterilized are placed in an oven 350 F
Flaming: Heat item ( like inoculation loop) over direct flame or in an incinerator

Incineration
Materials ( like biohazard waste) undergo combustion and become ash
Temperatures can reach up too 9032 F

Ionizing Radiation
Wavelength shorter ( less than 1 nm) More energy
Gamma - Nuclear Reaction
XRAY
Wavelength Short
More Energy
Strong
Penetrate through materials
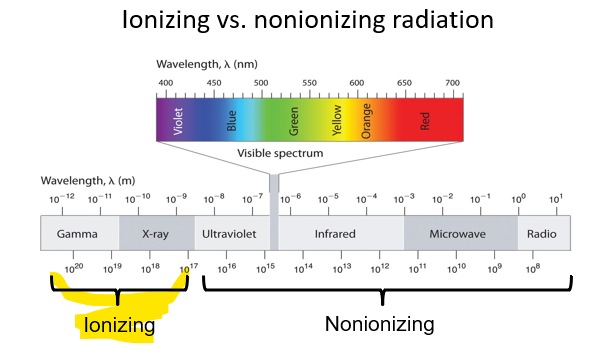
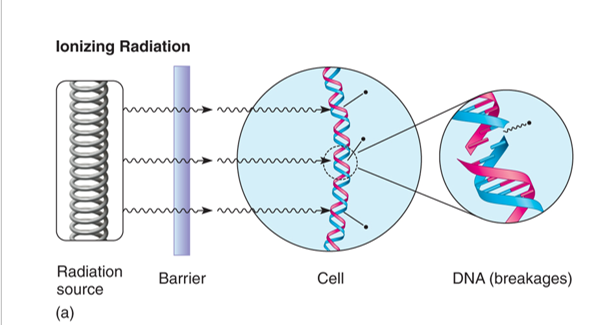
Ionizing radiation can penetrate barriers
Cause lethal double stranded DNA Breaks
Can break DNA molecules apart
Ionize water to form (ROS) oxidative damage to cell
Ionize the water in the cell to create reactive oxygen species (ROS) that then damage the cell’s components.
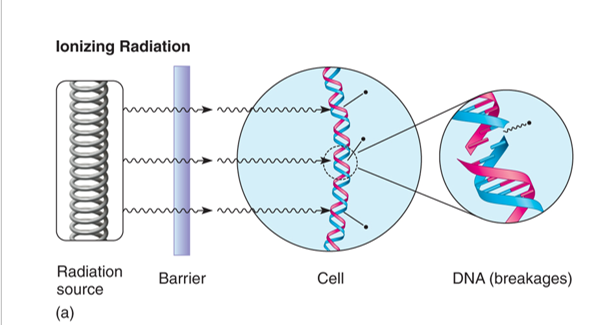
Nonionizing Radiation
Wavelength longer ( greater than 1 nm) Less energy
Large wavelength
Less energy
Weak
Does NOT penetrate through materials
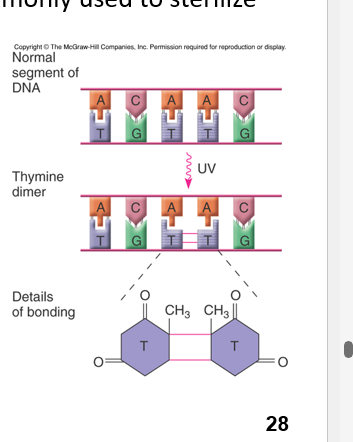
Kills cells by inducing formation of pyrimidine dimers in DNA
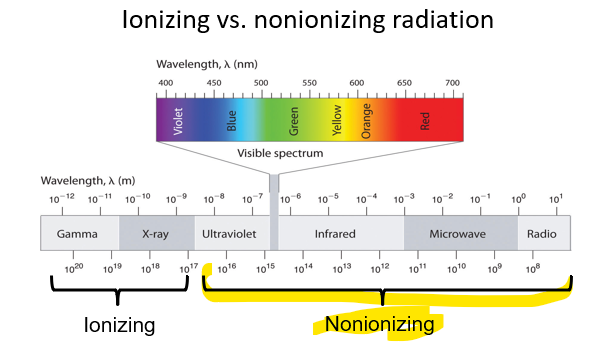
UV Radiation for Sterilize
Ultraviolet Radiation
Nonionizing radiation
Commonly used to disinfect/sterilize medical and scientific equipment
Cause molecular lesions in DNA
Poor Penetration
Filtration
Physical
Level of disinfection
or sterility based on pore
size of filter
Filtration - Filter Liquid
Air Filter - FIlter Air
Chemical agents used for Control Growth
Chemical agents are commonly used to disinfect or sanitize surface, in laboratories and home
Chemical agents do not sterilize, mostly only reduce the number of microbes ( microbial load) by sanitization
Levels of Chemical Decontamination
High-Level Germicides - kill endospores; can sterilize if used correctly
Intermediate- Level - Kills all organisms except endospores ( and fungal spores)
Low- Level - Eliminate only vegetative bacteria, vegetative fungal cells, and some viruses.
Degerming
Most common and easiest ways to degerm is to wash our hands with soap, which allows mechanical removal of microbes
Microbes do not die from determine with soap
Levels of chemical decontamination
Soaps and detergents - are amphipathic
contains both a polar and nonpolar end
Mechanism of action soap
Soap doesn’t kill microbes - just helps dislodge them from the surface
Micelle “lifts” bacteria away from the surface
4 Types of Antimicrobial drugs
Antimicrobial drugs: Synthetic substances that interfere with the growth of microbes
Antibacterial drugs (antibiotics)
Antiviral drugs
Antifungal drugs
Antiprotozoan & Antihelminthic
Antibiotics
An antimicrobial agent used to treat bacterial infections
Natural antibiotic
Antibiotic that is produced by a microorganisms ( from nature)
ex: Penecillin
Semi Synthetic Antibiotic
Natural antibiotic that has been altered in the lab
Synthetic Antibiotic
Antibiotic that is used completely synthesized in a lab ( found naturally at all)
Selective Toxicity
Selective destroying pathogens without damaging the host
High Selective Toxicity: Highly specific for microorganisms ( little toxicity to humans)
Low Selective Toxicity: Not very specific for microorganisms and cause toxicity and adverse side effects in humans
Who discovered Penicillin
Ernest Duchesne (1896)
Narrow spectrum antibiotics
Affects a narrow range of microbial types
Broad-Spectrum Antibiotics
Affects a broad range of gram-positive and gram- negative bacteria
Superinfection
secondary infection occurring during or immediately after the initial infection by microorganism that is not sensitive to previous antibiotic use for treatment
*when you don’t finish your antibiotics cause reinfection
Bactericidal
Kill bacteria directly
Bacteriostatic
Prevent bacteria from growing
immune system usually destroy microbes
How exactly do antibiotics affect bacteria?
5 Different types
Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
Inhibition of protein synthesis
Inhibition of nucleic acid replication and transcription
Disruption of cellular ( plasma) membrane
Inhibition of essential metabolite synthesis
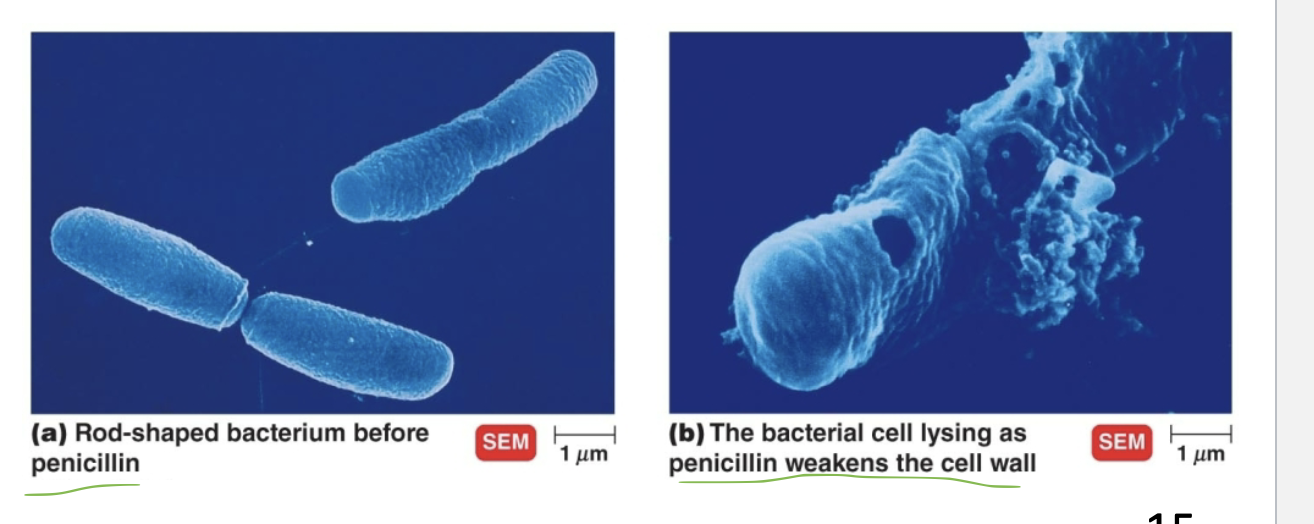
Inhibiting cell wall
Antibiotics prevent the synthesis of intact peptidoglycan weakening the cell wall, and causing the cell to lyse apart
PBP = Penecillin- Binding Protein
(Protein that synthesize or modify cell wall)
Inhibit cell wall synthesis, modification result in cell lyse due to osmotic stress.
Cell wall inhibition : inactive enzyme
Antibiotics ( Penicillin) block enzymes such as PBP that are responsible for cross linking the layers of peptidoglycan
The antibiotic binds the active site of PBP enzyme and prevents the enzyme from functioning properly
Effects of Compromised cell walls
The bacteria cell wall is weakened and unable to provide rigid support for the cell wall
Ultimately growing the cell lyse and dies
weakens the cell wall till burst
Inhibition of protein synthesis
antibiotics can inhibit the synthesis of proteins by binding to different sites of the ribosome, preventing the ribosome from doing it’s job
Cell can not maintain it’s self without new proteins
Antibiotics bind to large or small subunit of ribosomes (70s)
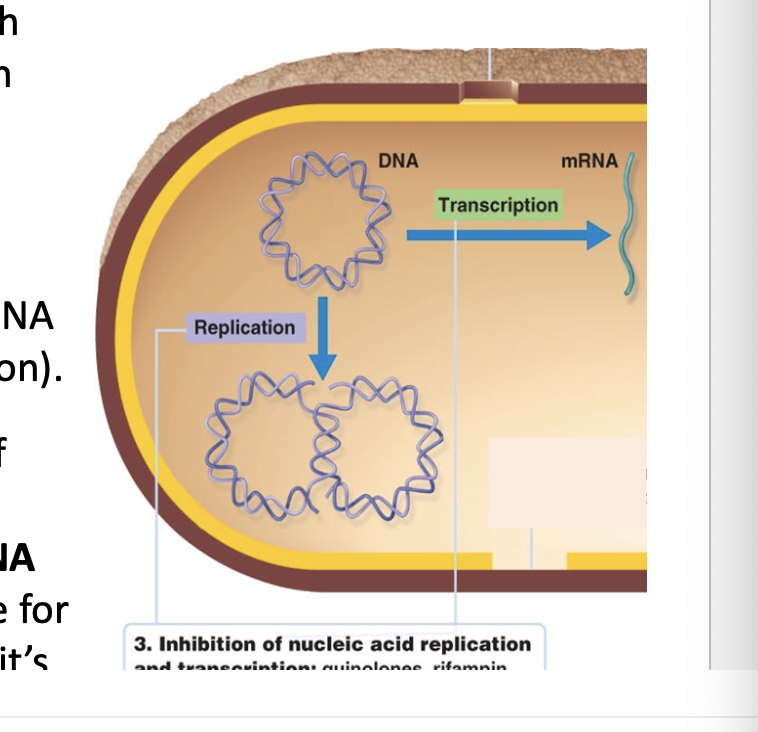
Inhibition of nucleic acid, & replication & transcription
Some antibiotics interfere with the process of DNA replication and transcription
No RNA synthesis ( transcription inhibited)
No DNA synthesis ( DNA replication inhibited)
Antibiotics bind to enzymes inhibit activity
Plasma membrane Disruption
Antibiotics inserted into membrane can cause it to fall apart
leak important metabolites
Commonly low selective toxicity
Inhibit essentials metabolite synthesis
These antibiotics inhibit the activities of important enzymes by competitively binding to the enzyme - blocking substrates
ex: Sulfa Drugs ( inhibit the folic acid which is necessary making proteins and DNA and RNA
antibiotics bind and inhibit enzymes in metabolic pathways needed by bacteria
Antifungals
Funny are Eukaryotic
Difficult to find drugs that selectively kill or inhibit the growth of fungi
Not many available
Mechanisms of Acton
How they can destroy them
Disruption of cell membrane (Ergosterol)
Inhibit synthesis of fungal cell wall ( Chitin & Glucans)
Inhibit synthesis of nucleic acids
Antivirals
Viruses are difficult to target because they use the host own cellular machinery to replicate themselves
Difficult to develop drugs against viruses
Mechanisms to prevent (infection)
Prevent Entry/ Penetration
Block Nucleic acid synthesis - replication
Block Assembly maturation
Antiprotozoan & Antihelminthic
Protozoan parasites and helminths are most difficult to treat
Helminths are parasitic worms, like flukes, tapeworms, and round worms
Difficult to target because they are eukaryotic (like animals)
To much like humans