Exam 3 Study Material for Systems Pathology - Prostate (Pages 47-77)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
area that surrounds the ejaculatory duct
central zone
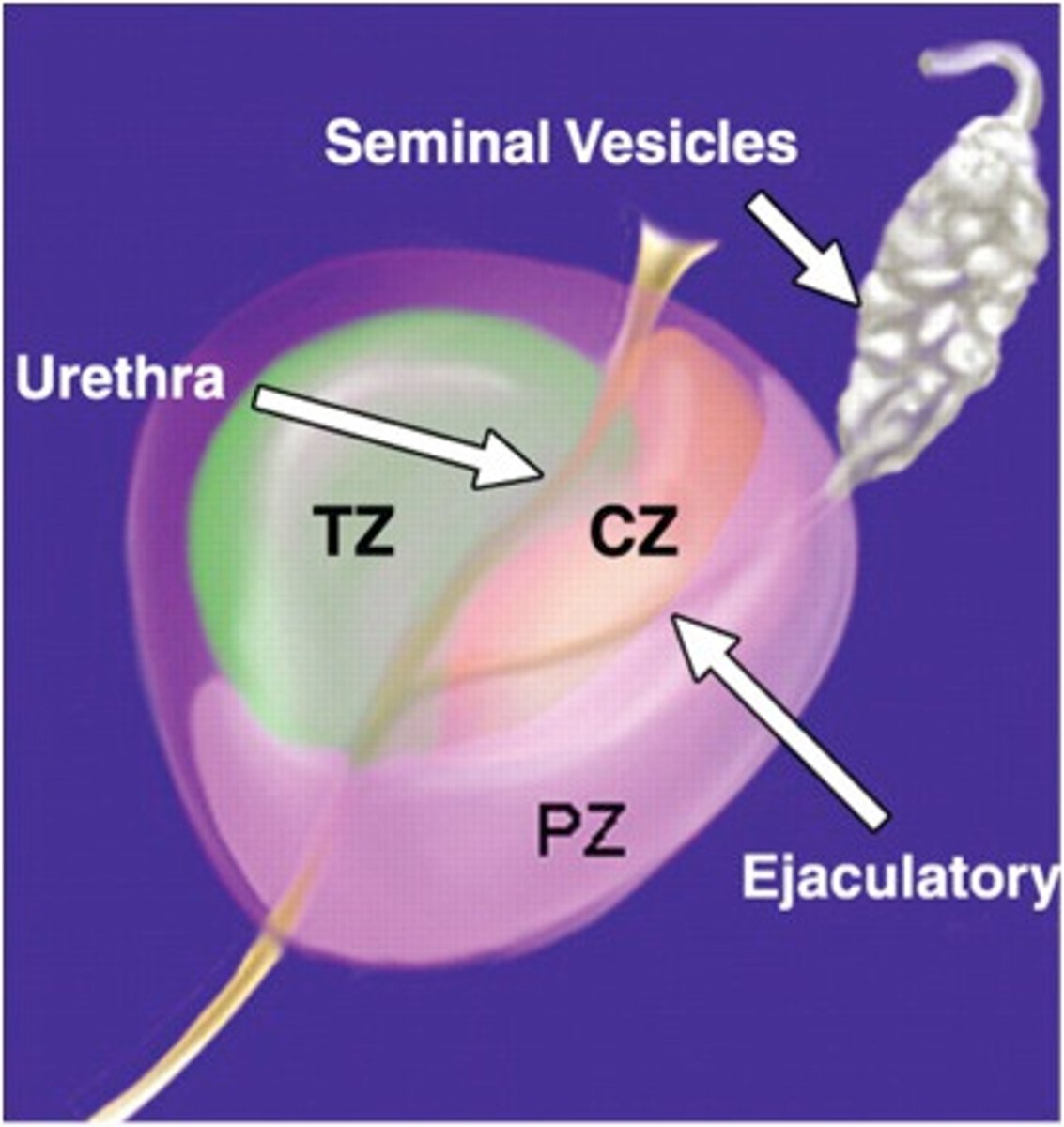
largest area of the prostate, easily felt by doctor during digital rectal exam, location where most prostate cancers start
peripheral zone
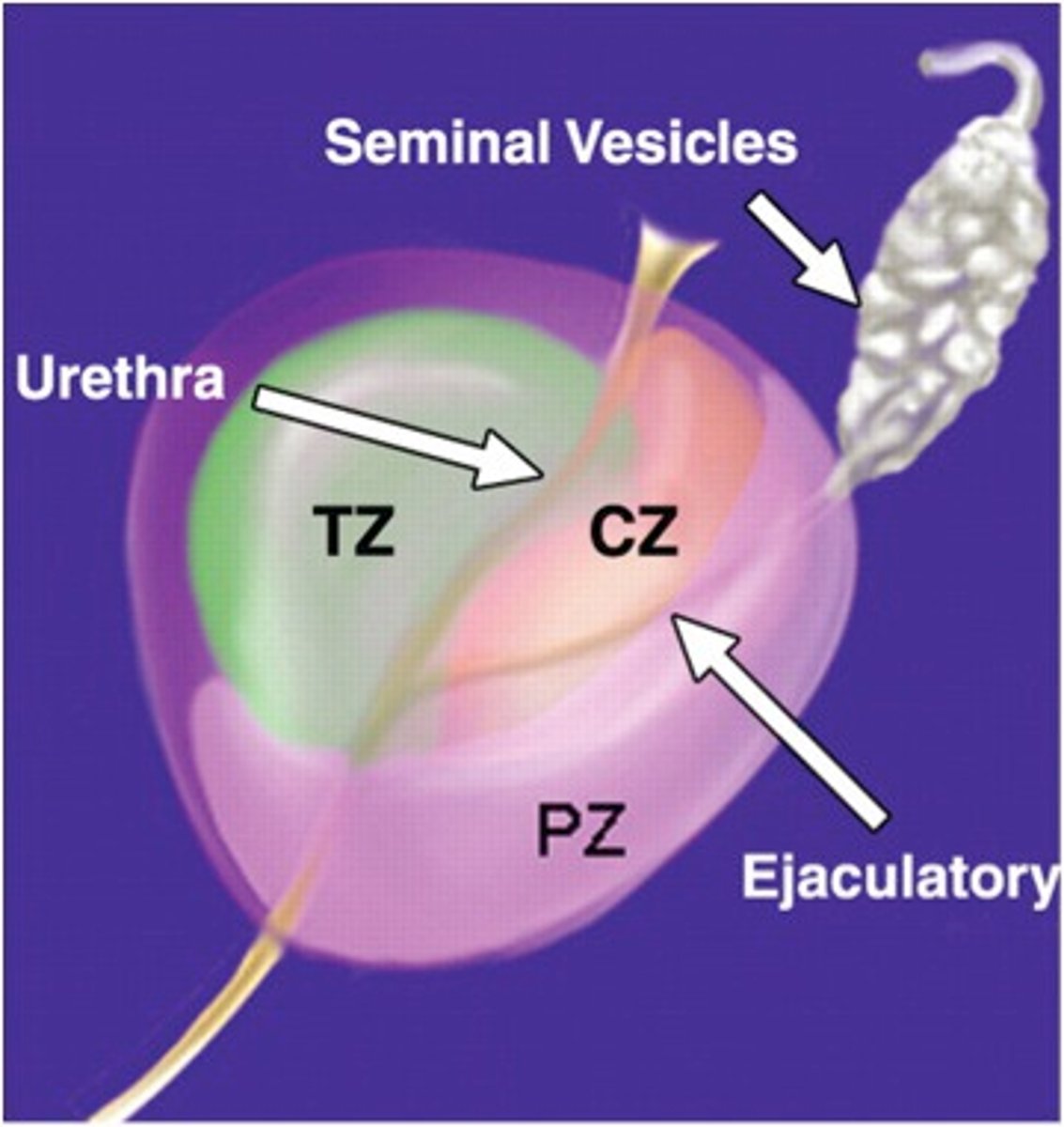
area that surrounds the urethra as it enters the prostate gland
transitional zone
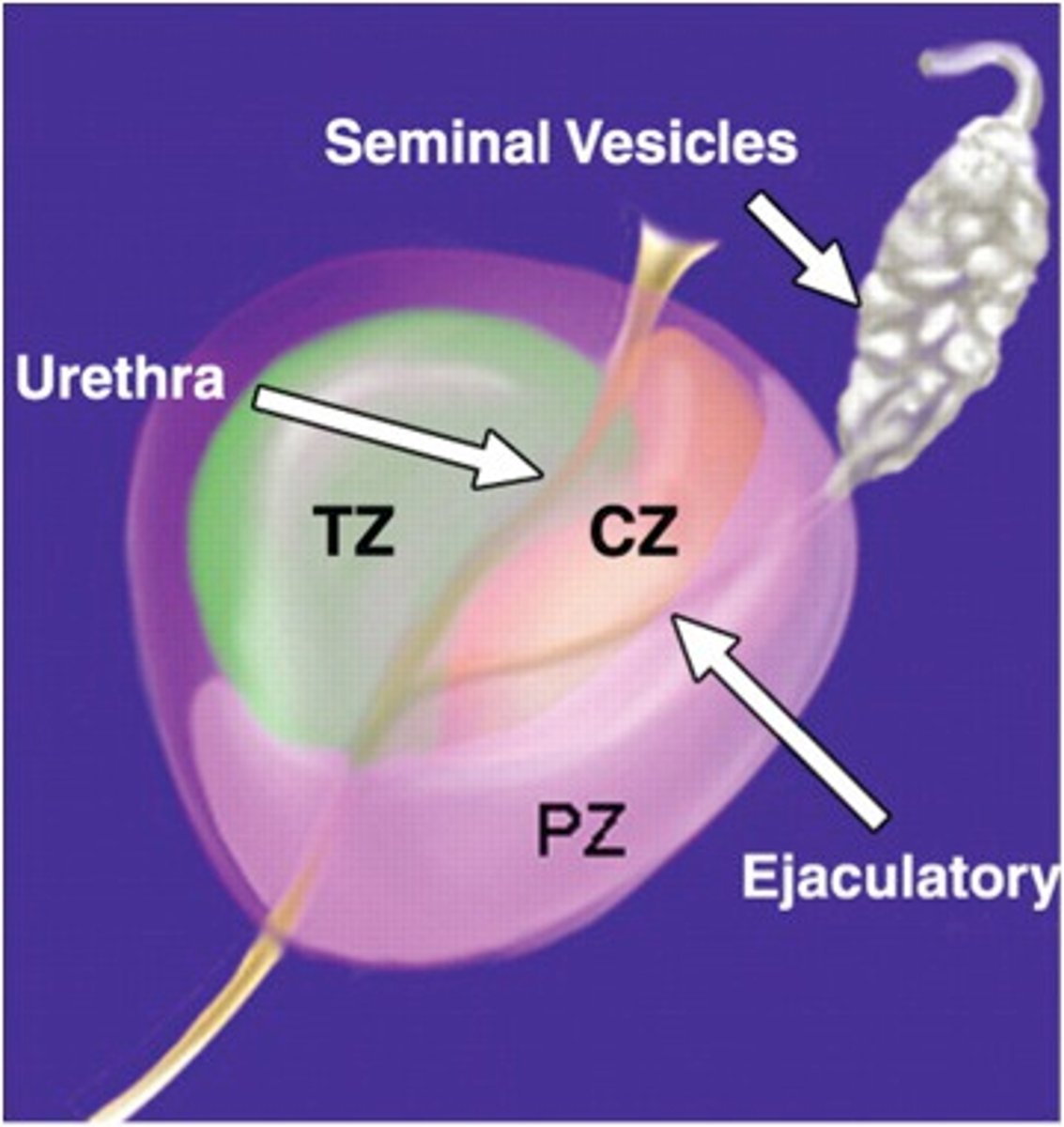
finger palpation through the anal canal and rectum to examine the prostate gland
digital rectal exam (DRE)
swelling and inflammation of the prostate gland
prostatitis
Who is prostatitis common in?
50 years ad younger
signs/symptoms of prostatitis (depending on cause) include:
dysuria, difficulty urinating, frequent urination (night)
Acute bacterial prostatitis/chronic bacterial prostatitis account for what % of prostatitis (each)?
2-5%
MC cause of bacterial prostatitis
E. coli (or other uropathogens)
how can bacteria enter the prostate to induce bacterial prostatitis?
hematogenous, descending (bladder/kidneys), ascending (urethra), lymph, rectum
signs/symptoms of bacterial prostatitis
LBP, pelvic pain, dysuria, fever, chills, tender DRE
what accounts for 90-95% of prostatitis?
chronic nonbacterial prostatitis (prostatodynia/chronic pelvic pain syndrome)
3 types of symptoms of chronic nonbacterial prostatitis
pain upon urination, urinary voiding difficulties, sexual dysfunction
what will show up on a urinary sample of someone with the bacterial form of prostatitis?
bacteria and WBC
what will show up on a urinary sample of someone with the nonbacterial form of prostatitis?
WBC only
NIH outcome measures or chronic nonbacterial prostatitis?
pain, urinary symptoms, quality of life impact
tx for chronic nonbacterial prostatitis
antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, alpha blockers (3 A's)
what area of the prostate does benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) typically occur?
transitional zone
cause of BPH
idiopathic, androgen related increase in estrogens (expresses DHT and encourages prostatic growth)
onset of BPH is usually ____ years but around 90% of males > ____ years have it
40 ; 70
only 10% of BPH is symptomatic and symptoms usually consist of:
urethral obstruction (difficulty starting/maintaining stream, increase frequency, nocturia)
1st round of tests to diagnose your patient with BPH
digital rectal exam, urine and blood test, PSA test (will be increased)
treatment for BPH is dependent on what factors?
size of prostate, age, overall health, discomfort
most common treatment for mild to moderate symptoms of prostate enlargement
medication (alpha blockers, 5-a reductase inhibitors, both)
does the size of your prostate determine severity of your symptoms?
no
MC type of surgical therapy for BPH
TURP
consequences of surgical intervention for BPH
incontinence, erectile dysfunction
most common cancer in American men ; second leading cause of cancer death among American men
prostate
who is prostate cancer more likely to develop in?
older men, non-hispanic black men, usually 65+
most common prostate cancer which forms in glandular tissue, is a firm mass with ill-defined borders, and may be palpable
adenocarcinoma
most common location for prostate cancer
peripheral zone
risk factors for developing CA of the prostate
>50 years (MC 65-75), African Americans, family Hx, obesity, African Americans
symptoms of CA of the prostate (usually only s/s when advanced)
trouble urinating, blood in urine/semen, bone pain, losing weight without trying, erectile dysfunction
Where does prostate cancer metastasize to?
spine (bright white)
Increased PSA indicates
prostate cancer, BPH
Does the USPSTF recommend PSA-based screening for cancer in men age 70+?
no
regular or repeated inability to obtain or maintain an erection firm enough for sex
erectile dysfunction