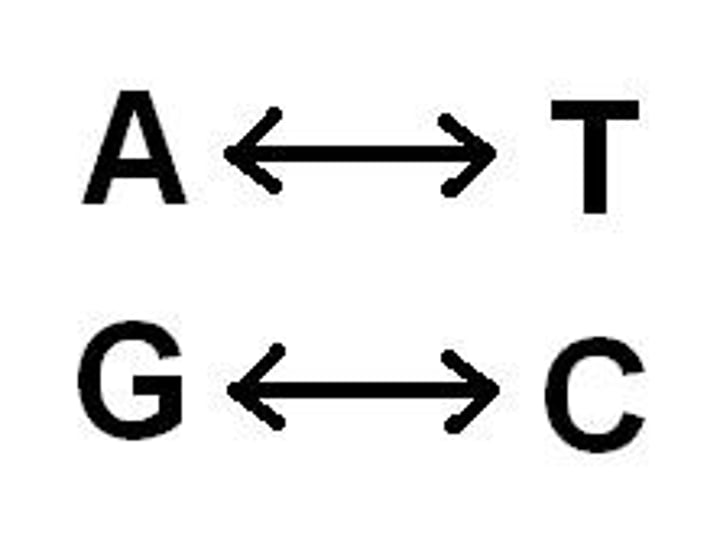Nucleotides: Cell level systems: Biology: GCSE (9:1)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
DNA
Chemical molecules found in every living organism that hold instructions for growth and development
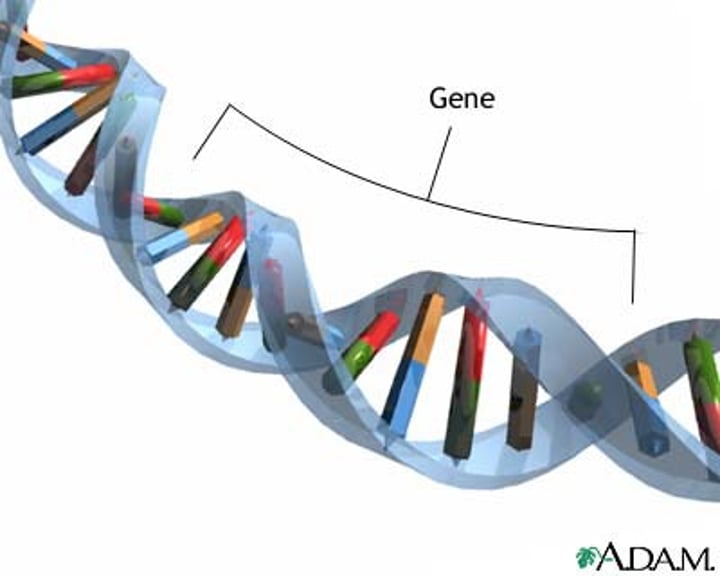
Gene
A small section of DNA that controls a specific characteristic by coding for a specific protein
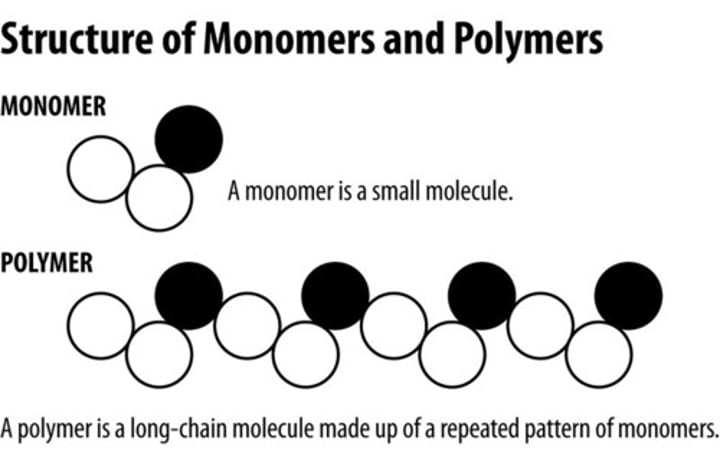
Polymer
A material such as DNA that is made of very large molecules that are composed of many smaller repeating subunits
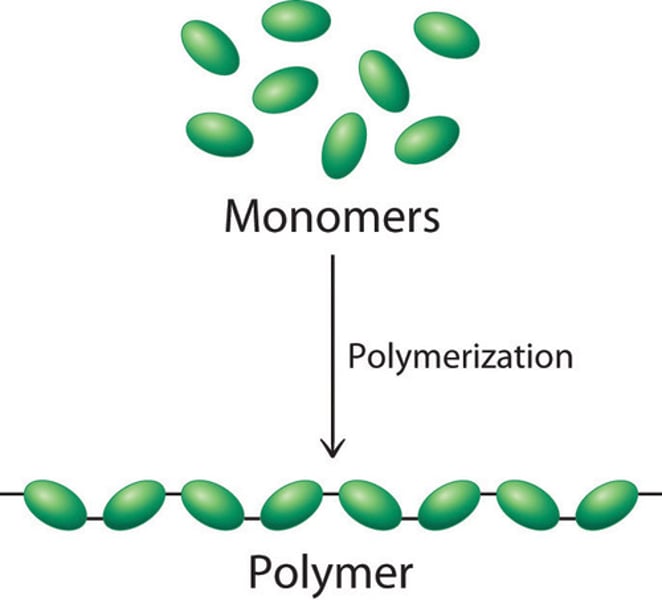
Monomer
A small repeating unit of a polymer such as the nucleotides that make up a DNA polymer
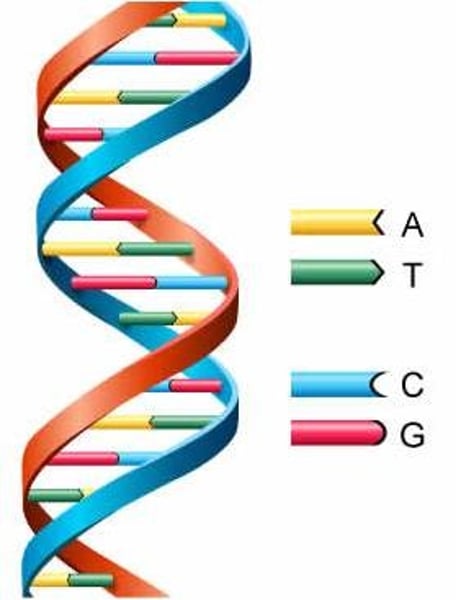
Double helix
The structure of DNA where two strands of DNA wind around each other like a twisted ladder
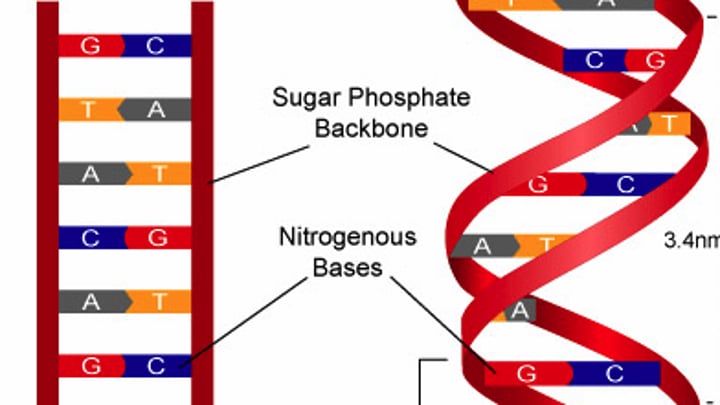
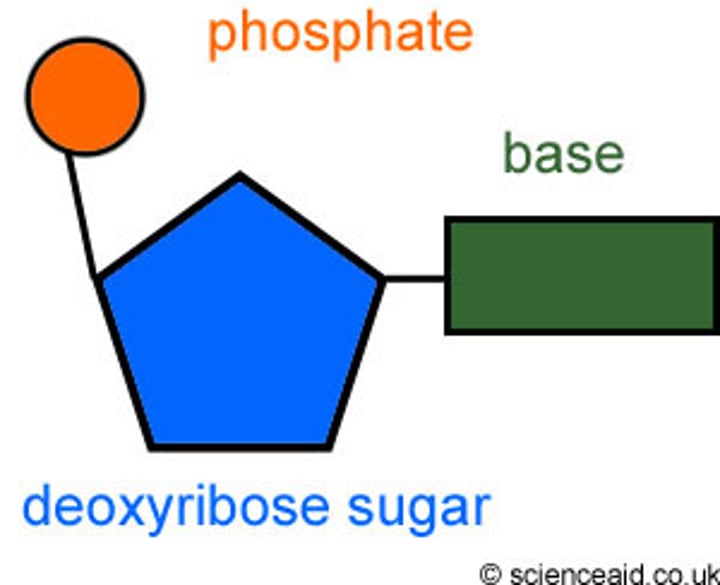
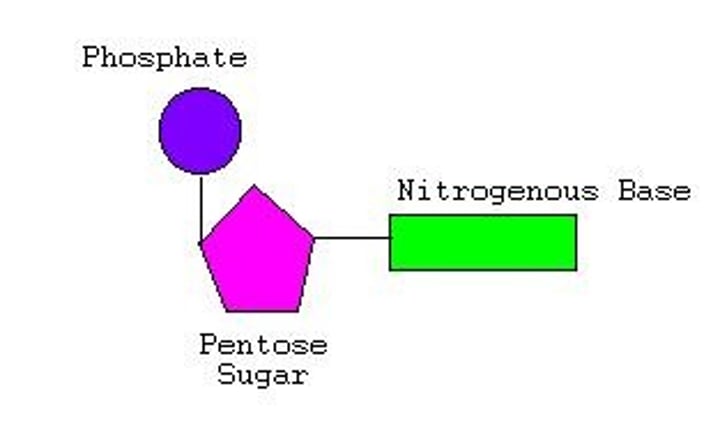
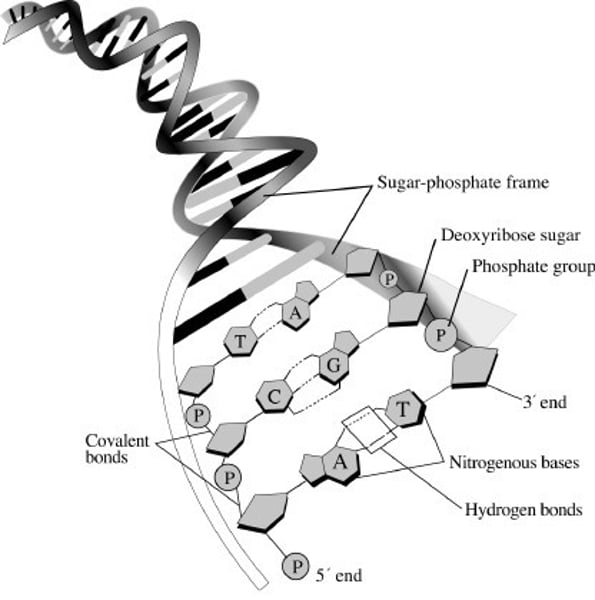
Nucleotide
A small structural unit of DNA, composed of a common sugar and phosphate group with one of four different bases attached to the sugar
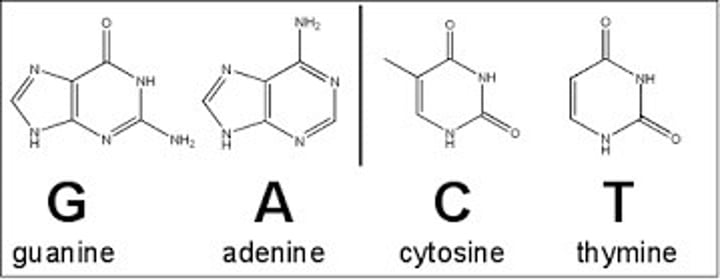
Bases
A specific organic section of a nucleotide that contains nitrogen, there are four different types of bases in a DNA polymer
C, G, A and T
The letters that represent the four different types of bases found on a strand of DNA
Sugar in DNA
Also called deoxyribose sugar, the sugar joins with a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group to make a nucleotide
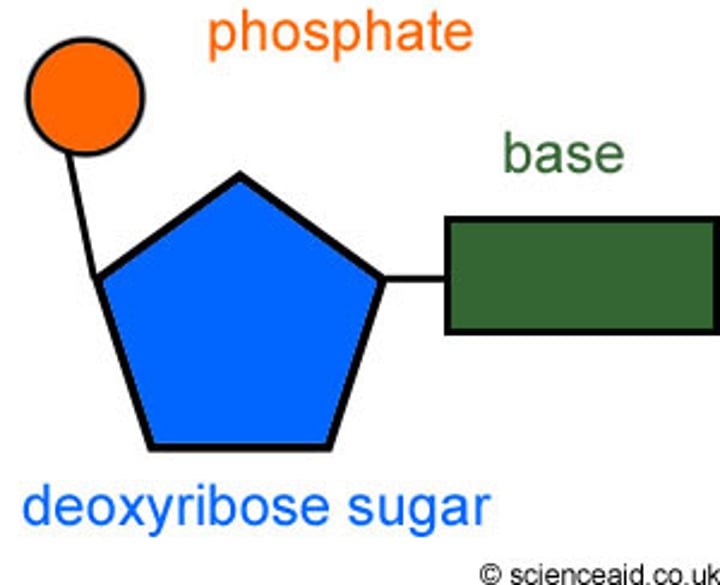
Phosphate group
Makes up the backbone of the DNA structure by joining with the sugar group in an alternating sequence
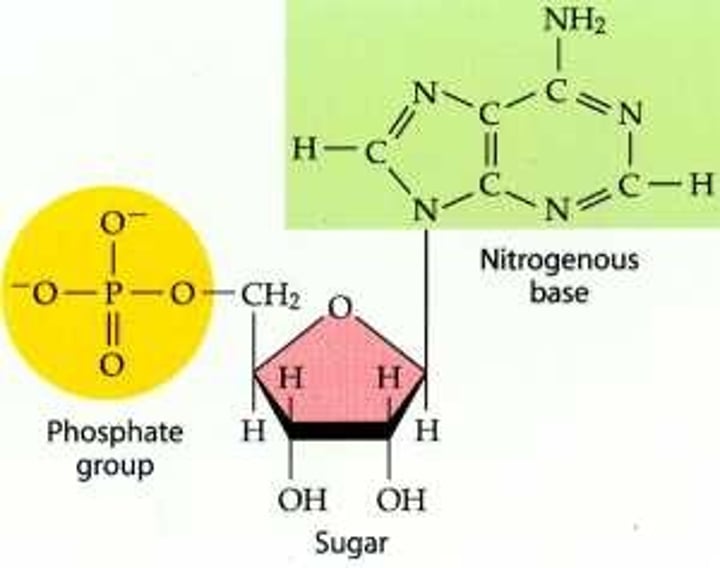
Repeating nucleotides
The DNA polymer is made up of repeating nucleotide units with different arrangements of the bases C, G, A and T
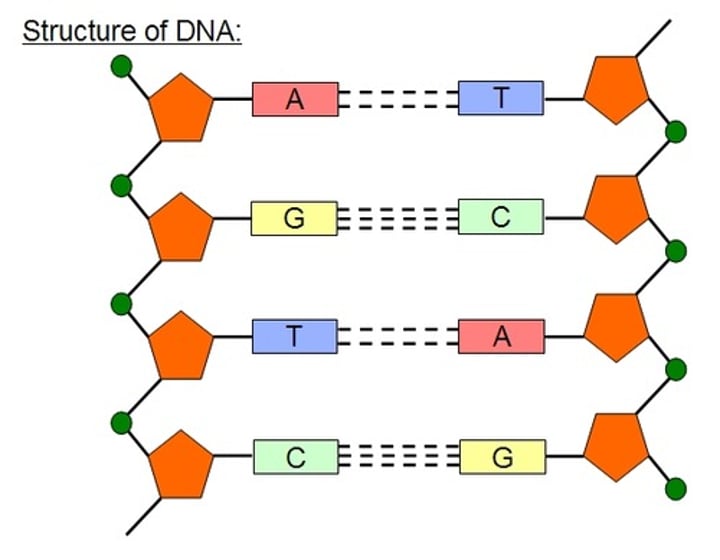
Sugar-phosphate backbone
An important structural component of the DNA strands, made up of alternating sugar and phosphate sections
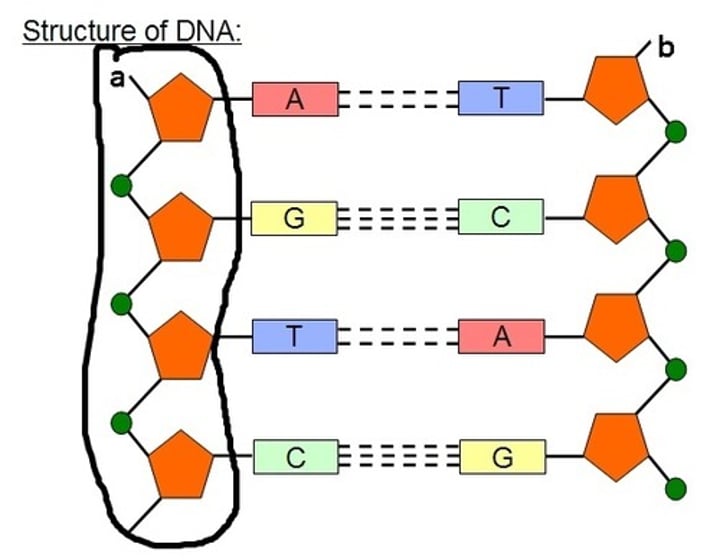
Complementary base pairs
The bases found on one strand of DNA must pair with specific bases on the other DNA strand, so that the strands can be held together
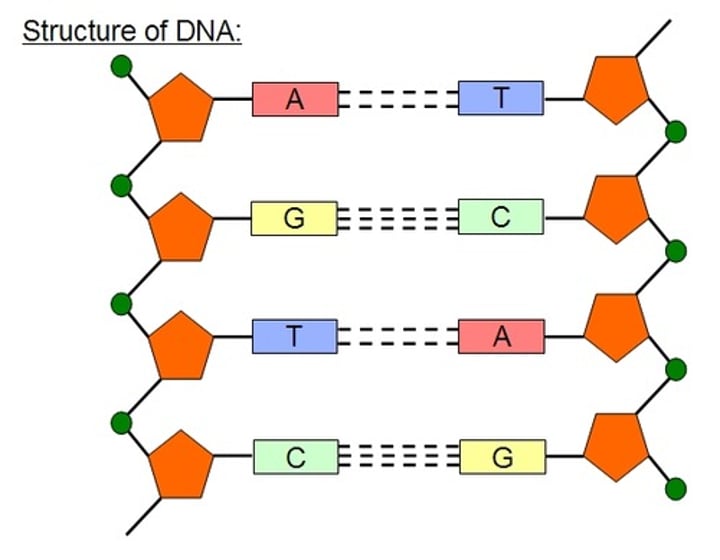
Complementary strands
A DNA molecule is made of two strands that are held together by the bonds between complementary base pairs
C
A base that is complementary to G, it will not pair up with A or T on the complementary strand
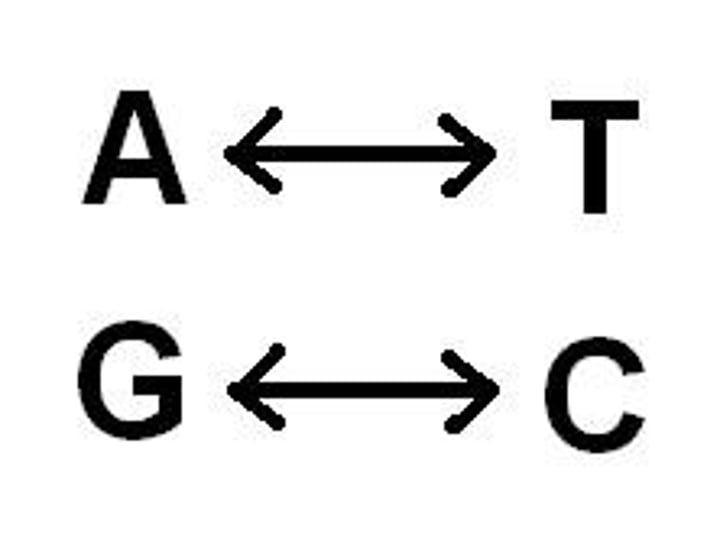
A
A base that is complementary to T, it will not pair up with a C or G on the complementary strand