aquatic systems and niche
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
freshwater
1% of water on earth
lentic or lotic,
lotic systems
ecology of running water - rivers and streams
divided into various sections horizontally and vertically
lentic systems
ecology of still water - lakes, ponds, wetlands
limnology
the study of inland aquatic systems
aquatic zones
broad, vertical divisions in both ocean and other zones
pelagic, benthic
pelagic zone
in the water, off the bottom of the aquatic environment
(epipelagic → bathypelagic)
benthic zone
on the bottom of aquatic environments
(abyssal → hadal in oceans)
epipelagic layer
from the surface to 200 m depth
photic zone - most sun rays can penetrate, photosynthesis occurs, phytoplankton
coastal upwellings
nutrient rich water from the deep comes up and replaces water that moves away from shore on the surface
imp for marine food webs, but can cause eutrophication
phytoplankton blooms of the coasts with incoming nutrients
mesopelagic layer
200 m to 1000 m depth, light can still penetrate, decreasing temp
bathypelagic layer
1000m to 4000m depth
light can’t really penetrate anymore, temp is decreasing a lot
abyssal layer
4000 - 6000m depth
dark and cold
hadal layer
>6000 m depth
the bottom layer of the ocean
wetted channel
water remains all year round
horizontal river division
active channel
will be flooded once per year
horizontal river division
riparian zone
transition to terrestrial, roots of trees, etc
horizontal river division
water column
water from the surface to the floor
vertical river division
hyporheic zone
where surface water meets groundwater
increased nutrient content
hyporheos
elongated, streamlined organisms living in the hyporheic zone
vertical river division
phreatic zone
ground water
vertical river division
phreatobites
small amphipods adapted to living in groundwater
no eyes, no light, lack pigmentation
can also be very small snails
littoral zone
along lake edge
limnetic zone
open lake, anything not along the edge
lake stratification
epilimnion, metalimnion, hypolimnion
(limnetic zone)
epilimnion layer
warm layer at the top of lakes, high O2, photosynthesis
has phytoplankton, fish and birds
metalimnion
rapid decrease in temperature, it is the thermocline between the other layers
hypolimnion
dark, cold, low O2 due to decomp of organic matter
bottom layer of lakes
thermal stratification/thermocline
summer and winter have thermally divided lakes , but the hypolimnion remains at 4 degrees while the surface temps are either warmer (28) or frozen (0)
in spring/water vertical mixing maintains uniform temps and it is 4 degrees throughout
oligotrophic
low nutrients (N, P), clear water, high O2, low primary productivity (plants)
different organisms will be adapted
eutrophic lakes
can be natural or cultural
increased N and P, decreased O2, more plants (primary productivity), dark water,
can cause algae bloom - even less O2 and even hypoxia
different organisms will be adapted
dystrophic
humic lakes
organic and humic acids, decreased pH (acidic), brown water, decreased primary productivity compared to oligo
different organisms will be adapted - but little survives here
wetlands
semi aquatic, changes with seasonality
two forms, bogs and fens
bogs
rainwater as the source → acidic, lumpy/patchy topography,
plant diversity - mosses and carnivorous plants, many shrubs and hardy tree species - requires specialized organisms
fens
groundwater reservoir as the source, variable pH - dependent on soil, flat topography
plant diversity: grasses, sedges, mosses, vascular plants
niche
environmental factors - abiotic and biotic factors, in which an organism can survive, grow and reproduce
this is abstract - any factors of interest can be apart
fundamental niche
physical conditions under which a species might live in the absence of interactions with other species → only abiotic factors are present
the full, idealized range of a species
realized niche
a subset of fundamental niche
environmental conditions under which a species might live when restricted by interactions with other species → includes biotic factors/competition
this is the real niche where a species resides
niche concept
Grinnell - abiotic factors, Elton - biotic factors
Hutchinsonian niche
n-dimensional hypervolume
when n is the number of environmental factors important to survival and reproduction, all the things which influence where something lives
for ex can include temp, pH, humidity and so on and so on
why characterize niche?
allows us to predict species range, where it travels, or how it moves during climate change
can be characterized by climate modelling (temp, precipitation, seasonality) and GIS
competitive exclusion principle
no two species can occupy the same realized niche, eventually one will out compete another
ex MacArthur’s warblers - timing or location on trees was different even tho they appeared to live on same trees
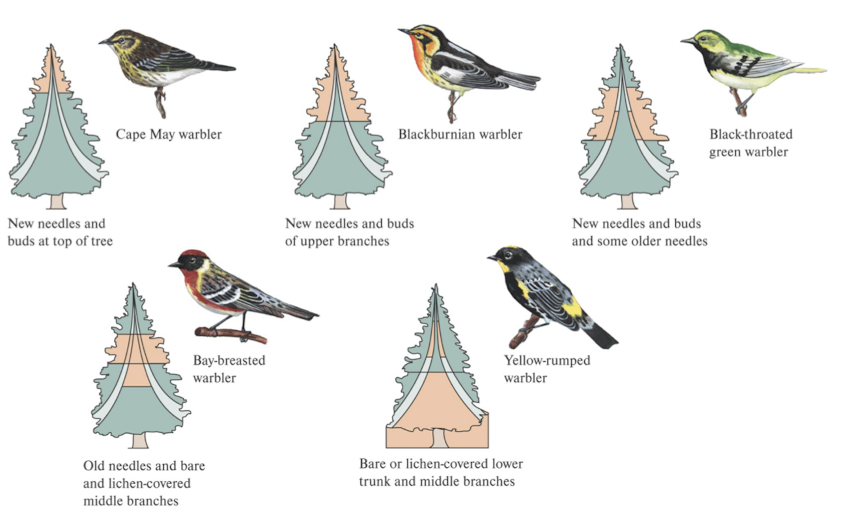
niche partitioning
when species in a community use resources (limiting factors) in different ways they are occupying different realized niches and coexists
ex cat tail species and water depth changes to limit overlaps