Physics- End of Year 10 Mocks
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
kinetic energy
joules
mass
kg
speed
metres/second
elastic potential energy
joules
gravitational field strength
Newtons per kilogram
height
metres
change in thermal energy
joules
specific heat capacity
joules per kilogram per degree Celsius
temperature change
degrees Celsius
power
watts
energy transferred
joules
work done
joules
current
amps
potential difference
volts
resistance
ohms
time
seconds
density
kilograms per meter cubed
specific latent heat
joules per kilogram
pressure
pascals
volume
metres cubed
force
newtons
spring constant
newtons per metre
acceleration
meters per second squared
period
seconds
wave speed
meters per second
frequency
hertz
live wire
brown wire, 230volts that provides alternative potential difference from the mains electricity supply
neutral wire
blue, 0 volts that completes the circuit by carrying current away from the appliance.
earth wire
green and yellow stripes, only carried current if there is a fault so stops appliance becoming live
power supply energy transfer
energy in the chemical store is decreased and transferred away by electricity
surroundings energy transfer
energy in the thermal store increases and is transferred by sound and heating
walking speed
1.5m/s
running speed
3m/s
cycling speed
6m/s
car speed
25m/s
train speed
55m/s
plane speed
250m/s
sound in air speed
330m/s
state newtons first law
an object at rest will stay at rest and a moving object will continue to move at a constant velocity if there is no external resultant force acting on the object
state newtons second law
an object with a resultant force applied to it will undergo a change in speed or a change in direction, if it is in the direction of motion it will accelerate, if it is in the opposite direction it will decelerate
current in a parallel circuit
total current in the circuit is the sum of the currents in each separate branch
potential difference in a parallel circuit
potential difference across all component is the same
resistance in a parallel circuit
total resistance of components is less than individual resistances
current in series circuit
current is the same through all components
potential difference in series circuit
total potential difference is the sum of potential difference in each cell
resistance in series circuit
total resistance of components is the sum of resistance of each component
thermistor
hot- low resistance, cold-high resistance
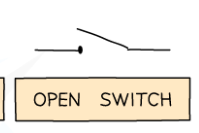
LDR
bright- low resistance, dark-high resistance
diode
only lets current go in one direction