Chapter 17: Endocrine System
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
What is the Endocrine System?
A system of ductless glands
secrete messenger molecules called hormones
interact with nervous system
controls and integrates the functions of other organs systems
How do hormones travel?
Hormones travel to distant body cells and signal characteristic physiological responses
What does the endorcrine system maintain?
Maintains homeostasis, controls growth, metabolism, stress defenses, blood chemistry, etc
Which endocrine organs are PURE
Pituitary
Pineal
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Adrenal Glands
Which endocrine organs are REGULAR (not pure)
Hypothalamus, thymus, pancreas, and gonads
True or False, are endocrrine organs richly vascularized?
true
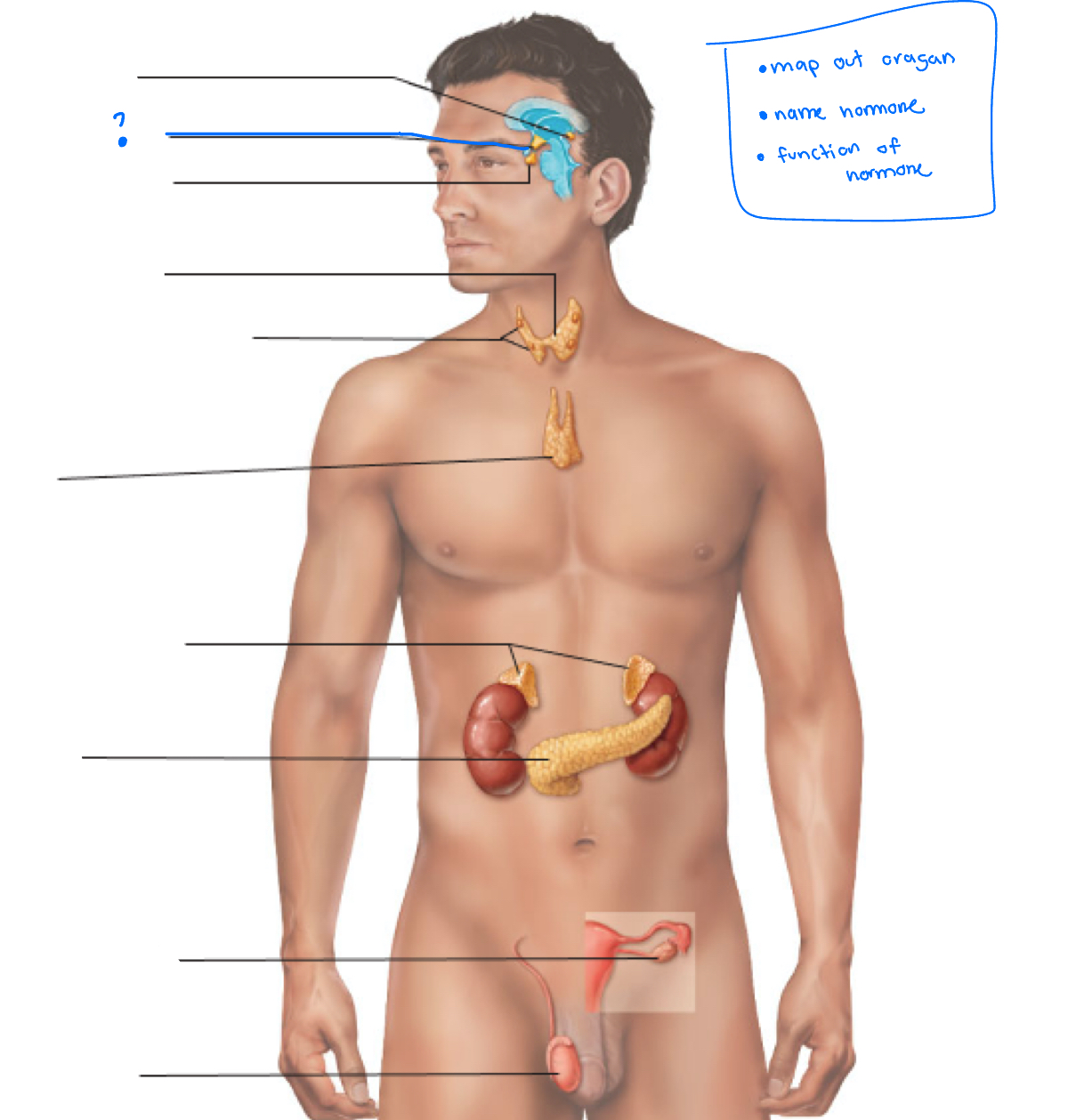
Hypothalamus
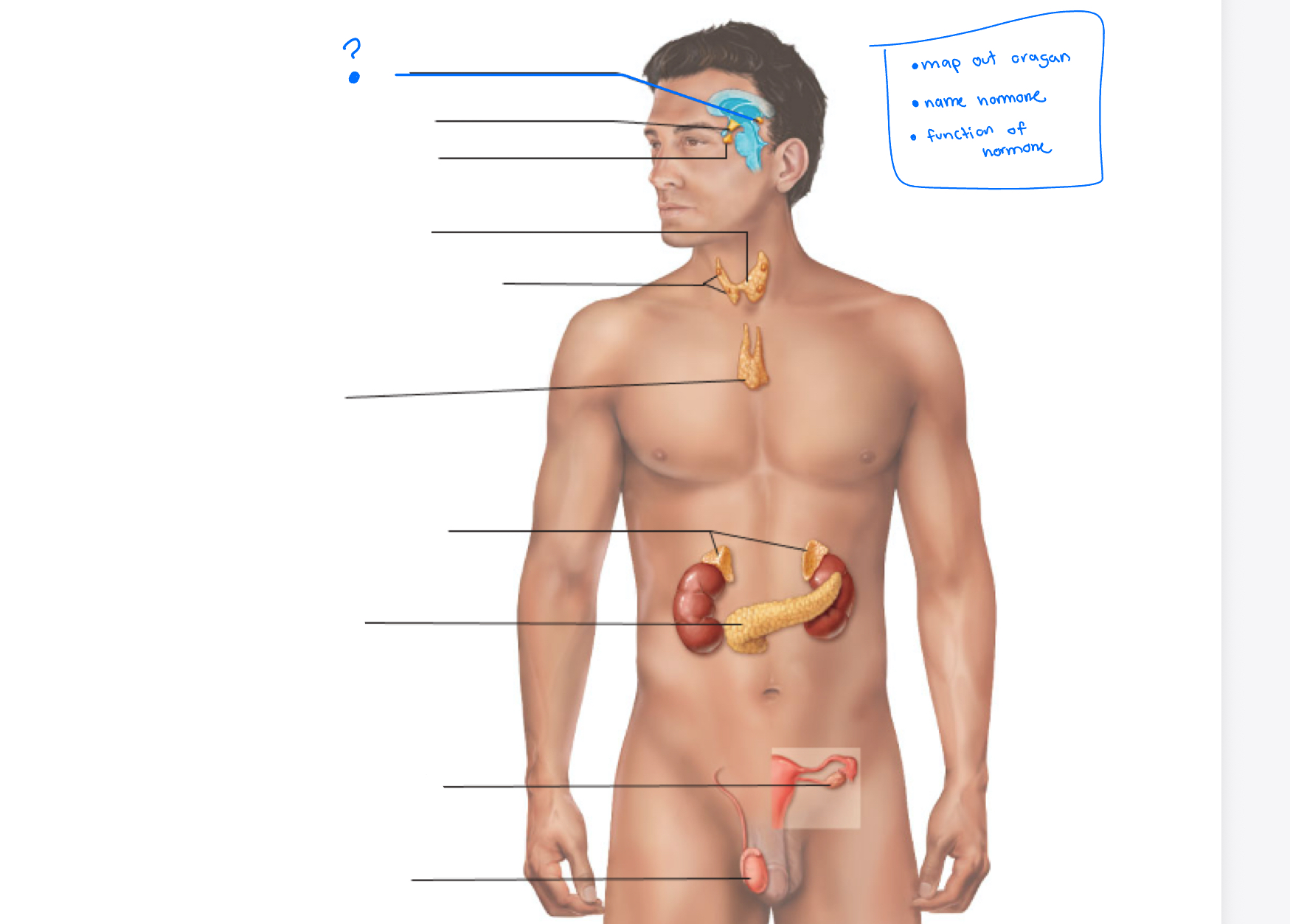
Pineal gland
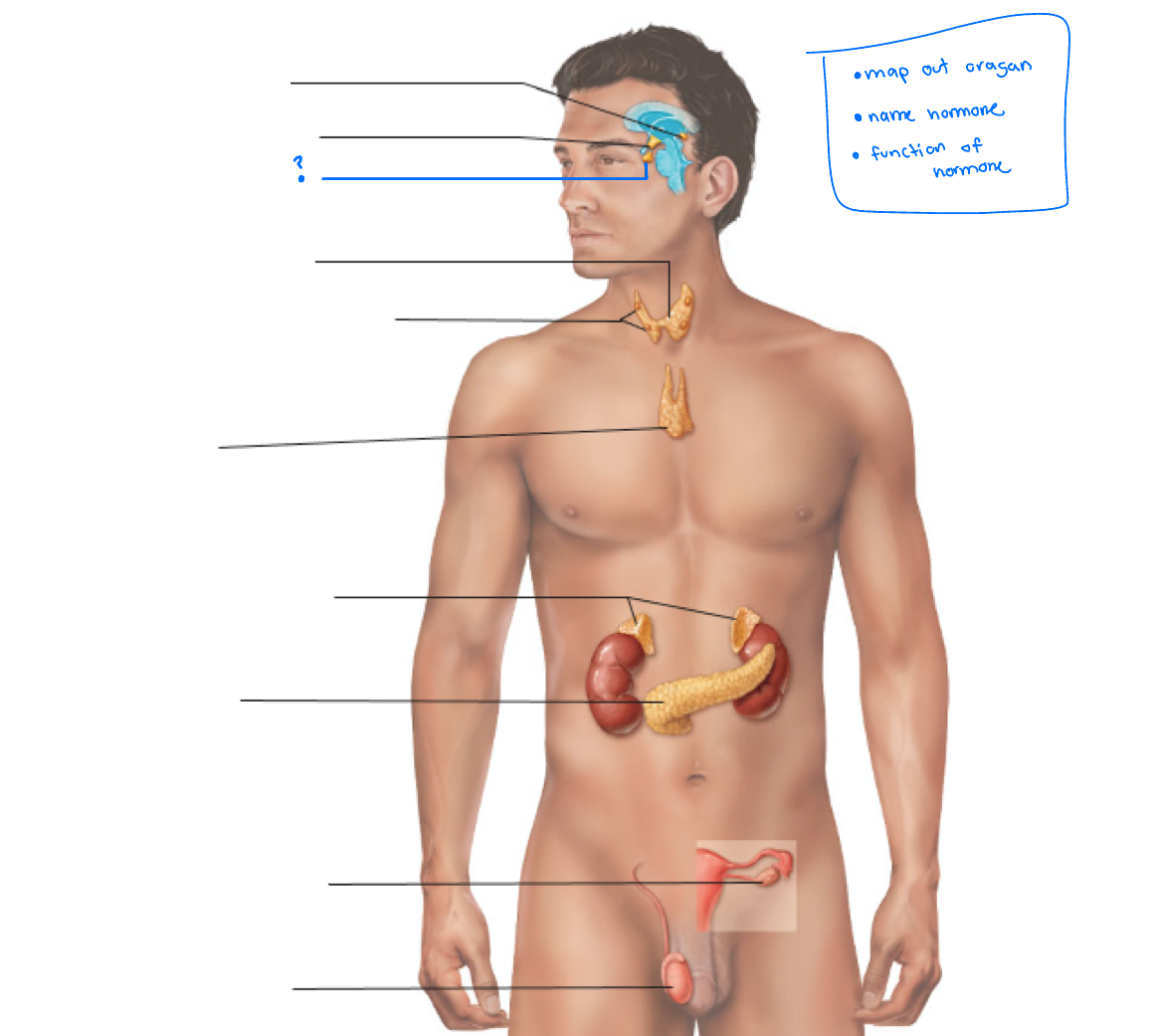
pituitary gland
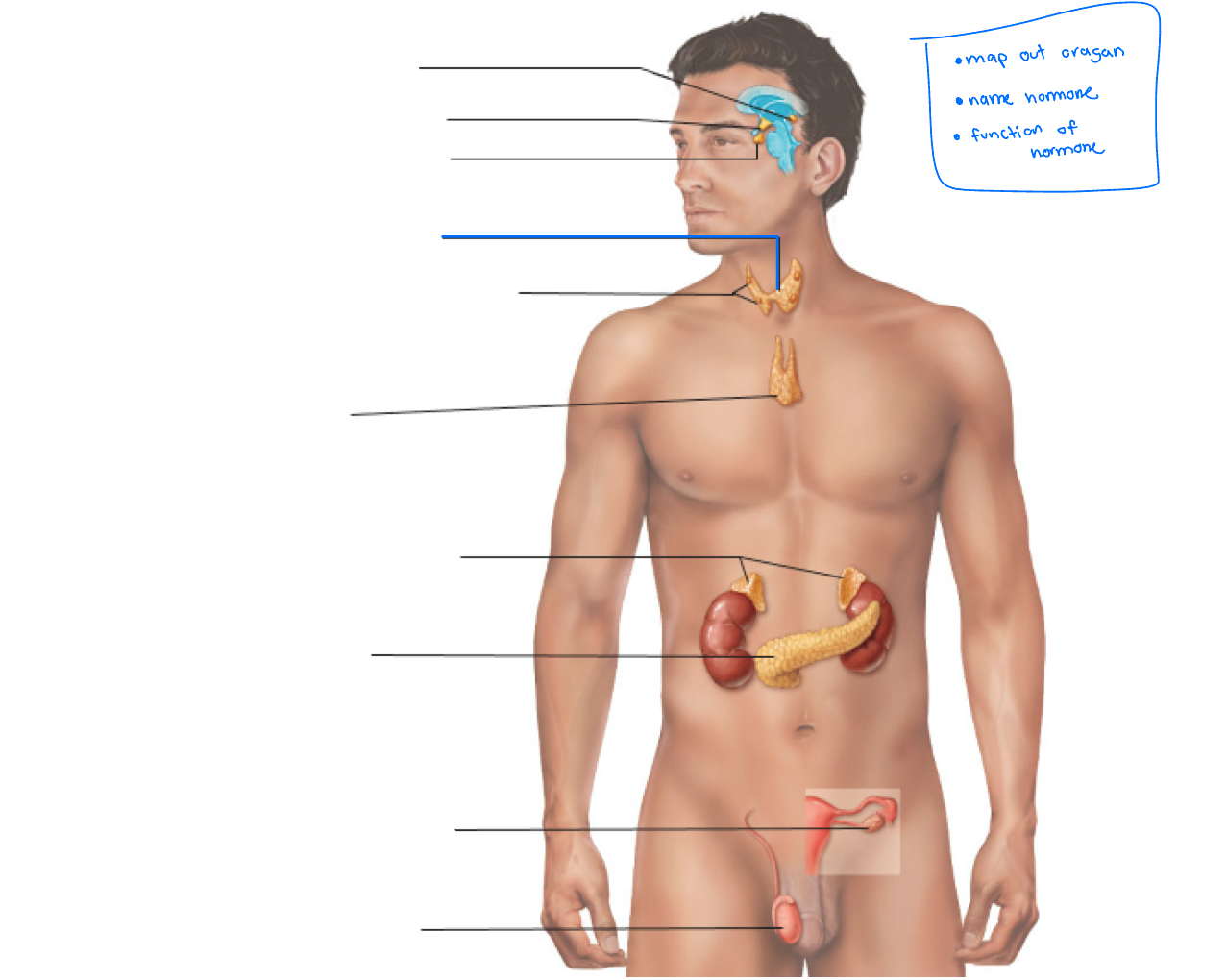
thyroid
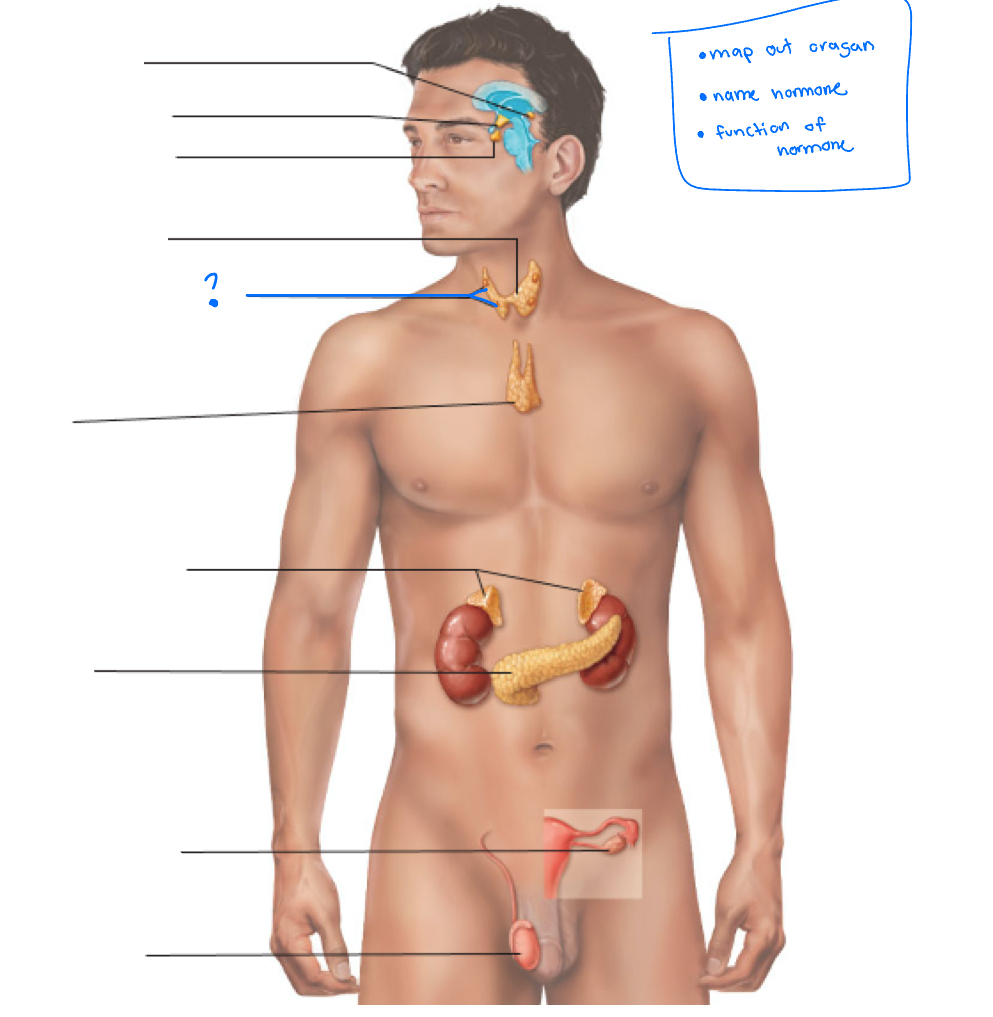
Parathyroid glands
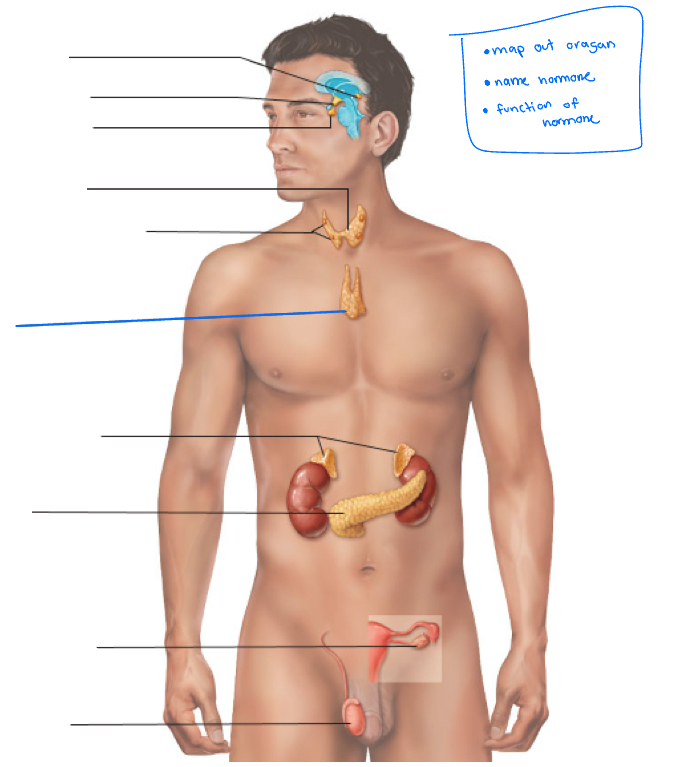
Thymus
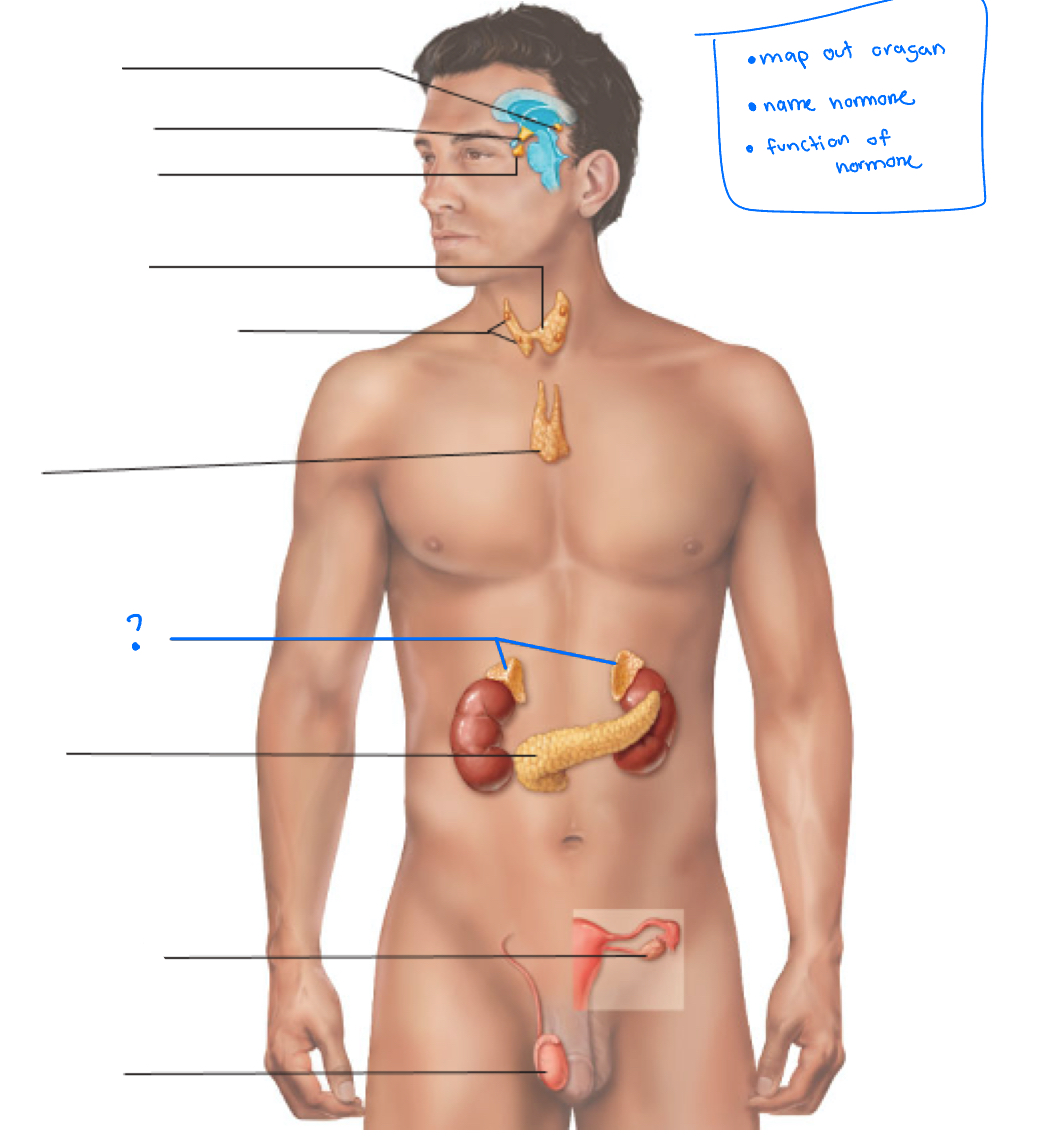
adrenal glands
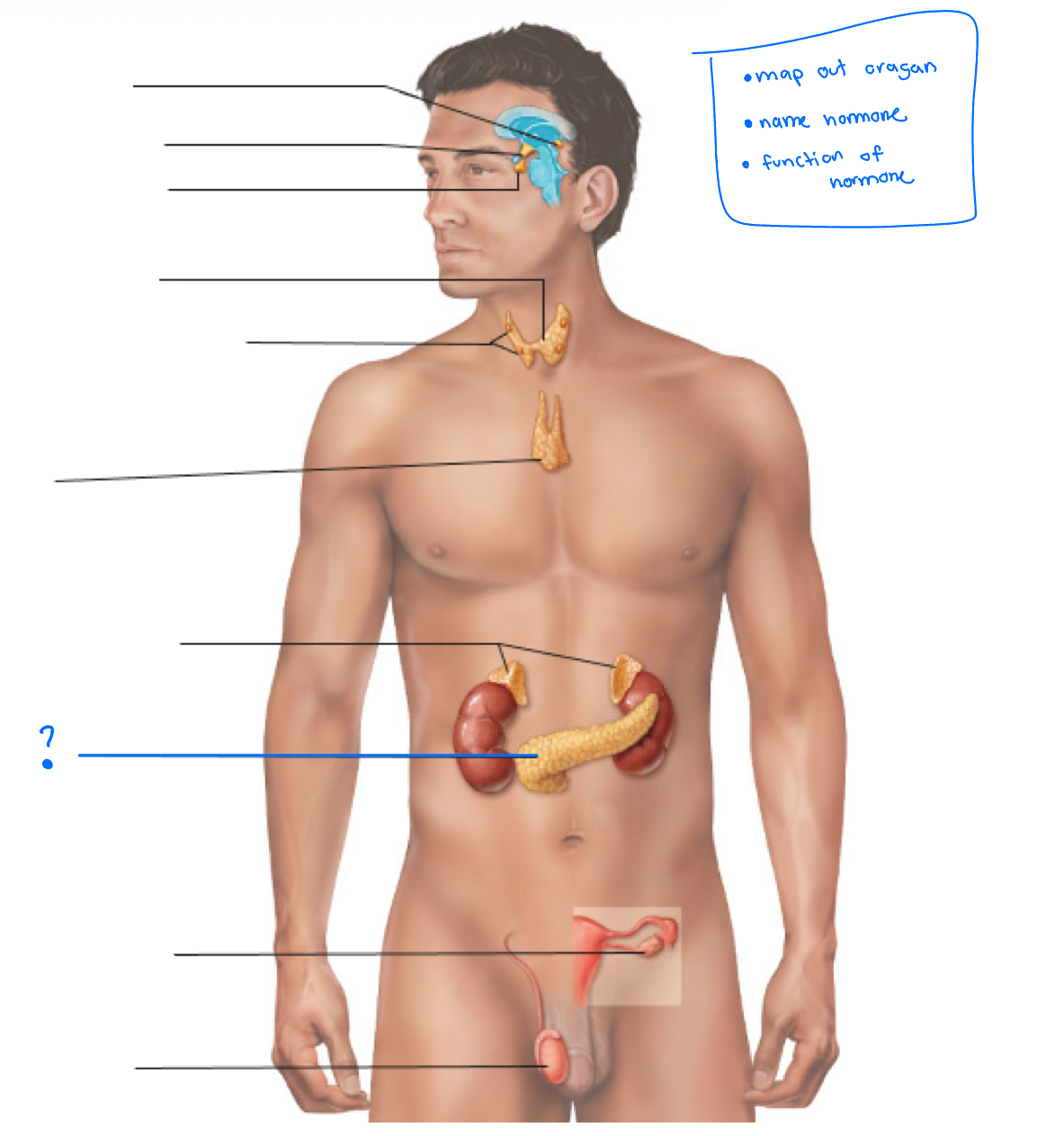
pancreas
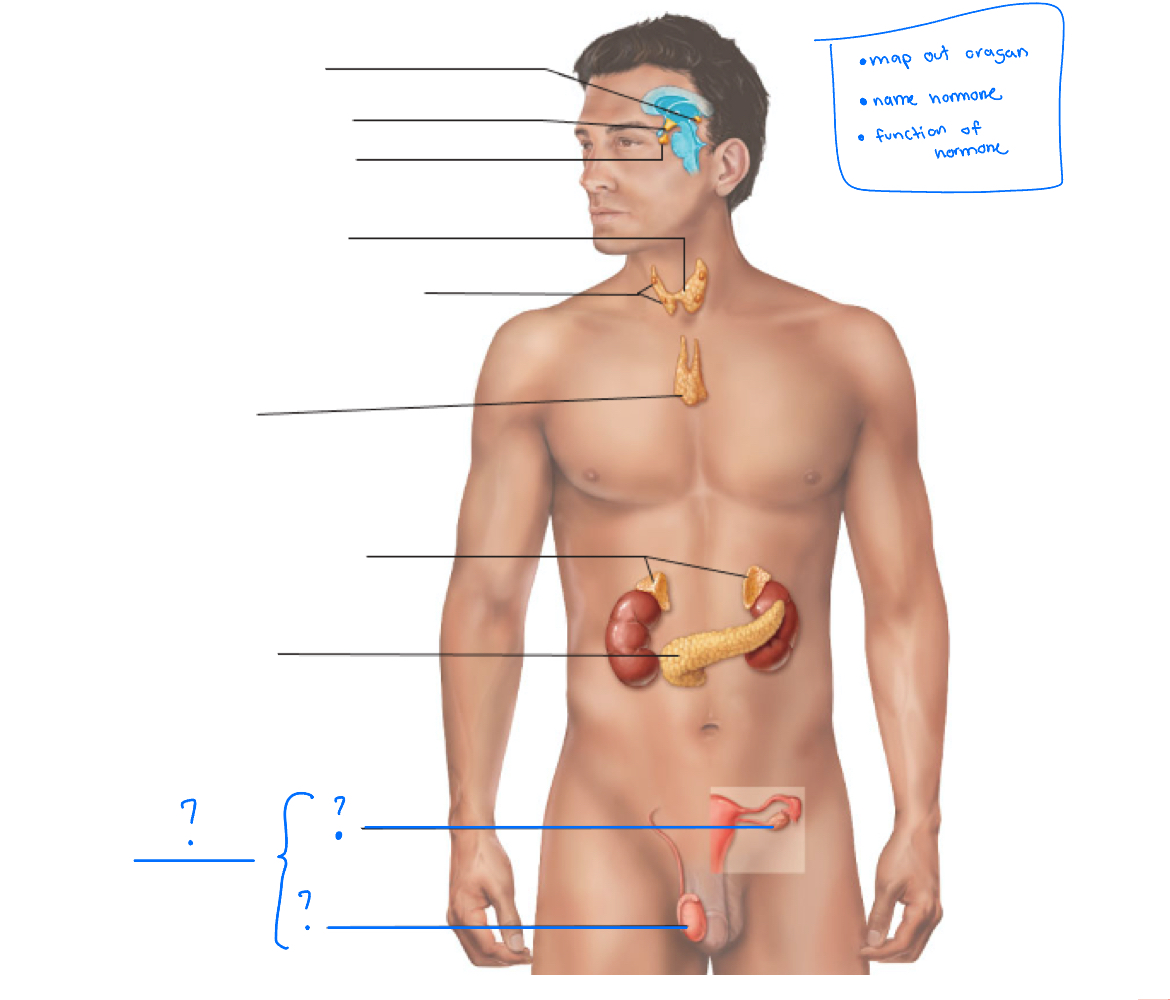
Gonads (ovaries and testes)
What are steroid hormones
Steroid hormones are a class of hormones derived from cholesterol, which is a type of lipid
Examples include estrogen, progesterone, androgens, cortisol, and aldosterone
What are non-steroidal hormones?
Non-steroidal hormones are derived from protein/peptides, amino acids, or fatty acid derivatives
Examples of non-steroidal hormones include:
Glycoproteins like follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG)
Polypeptides such as prolactin, growth hormones, insulin, and glucagon
Monoamines like epinephrine and norepinephrine
Eicosanoids, which are fatty acid derivatives, such as prostaglandin
Which non-steroidal hormones is dervied from protein/peptides?
1. Glycoproteins: Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH), Luteinzing Hormone (LH), and Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
2.Polypeptides: Prolactin, Growth Hormone (GH), Insulin, and Glucagon
Which non-steroidal hormones is dervied from amino acids?
Monoamines: epinephrine, norepinephrine
Which non-steroidal hormones is dervied from fatty acids derivatives?
Eicosanoids: prostaglandin
Basic Hormone Actions
Travel in the blood
Affect only target cells with matching receptors
Can cause different effects in different cells
Act as triggers, not instructions — cells are preprogrammed
Control Hormone Secretion; name the 3 main types of triggers
Humoral
Neural
Hormonal
What is humoral hormone control? w/ example
Hormones released due to changes in blood levels of ions/nutrients
Example: If calcium levels drop, it releases parathyroid hormone (PTH) to raise calcium levels.
What is neural hormone control? w/ example
Hormones released by nerve signals
During stress, the sympathetic nervous system signals the adrenal medulla to release epinephrine (adrenaline) for the "fight or flight" response.
What is hormonal hormone control? w/ example
One hormone triggers another hormone to be released
Hypothalamus releases TRH
TRH signals pituitary to release TSH
TSH signals thyroid gland to release thyroid hormones
How is hormone secretion controlled?
Controlled by feedback loops
If hormone level drops below minimum, secretion increases
If hormone level exceeds maximum, secretion stops
How does the hypothalamus control the anterior pituitary?
Hypothalamus controls hormone release from the anterior pituitary which includes the releasing hormones and inhibiting hormones
What are releasing hormones?
Hormones from the hypothalamus that stimulate the anterior pituitary to release its hormones
What are inhibiting hormones?
Hormones from the hypothalamus that stop or reduce hormone release from the anterior pituitary
How many major hormones does the pituitary gland secrete?
The pituitary gland secretes nine major hormones.
Where is the pituitary gland located?
Located in the hypophyseal fossa, a depression in the Sella turcica of the sphenoid bone.
What are the two basic divisions of the pituitary gland?
Adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary)
Neurohypophysis (posterior pituitary)
What are the anterior lobe hormones (adenohypophysis)
Growth Hormone (GH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Prolactin (PRL)
What are the effects of hyposecretion and hypersecretion AND regular function in Growth Hormone
Low Levels: dwarfism in children
High Levels: giantism in children; acromegaly in adults
Function: promotes growth of bones, muscles and tissues
What are the effects of hyposecretion and hypersecretion AND regular function in Thyroid-stimulating hormone
Low levels: cretinism in children; myxedema in adults
High levels: hyperthyroidism; effects similar to those of Graves’ disease, in which antibodies mimic TSH
Function: Thyroid gland: stimulates thyroid gland to release thyroid hormones
What are the effects of hyposecretion and hypersecretion AND regular function in Adrenocorticotropic hormones (ACTH)
Low levels: rare
High levels: Cushing’s disease
Function: Stimulates the adrenal cortex to release cortisol and other glucocorticoids
What are the effects of hyposecretion and hypersecretion AND regular function in Follicle-stimulating hormone
Low: failure of sexual maturation
High: No important effects
Function: women: helps eggs mature (inside follicles); men: help make sperm (follicle and sperm helper)
What are the effects of hyposecretion and hypersecretion AND regular function in Luteinizing hormone
Low levels: Failure of sexual maturation
High levels: no important effects
Function: women: triggers ovulation (release of eggs) and makes the body produce progesterone; men: tells the testes to make testosterone
What are the effects of hyposecretion and hypersecretion AND regular function in Prolactin
Low levels: poor milk production in nursing women
High Levels: inappropriate milk production; cessation of menses in females; impotence in males
Function: prolactin makes breast milk after birth
What is the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis), and is it part of the brain?
The posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) is structurally part of the brain.
It does not make hormones, but stores and releases hormones made by the hypothalamus.
What is the role of the posterior pituitary in hormone production?
The posterior pituitary does not produce hormones.
It stores and releases hormones that are made by the hypothalamus.
Which two hormones does the Posterior Lobe store and secrete?
Antidiuretic hormone and Oxytocin
What is Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH), and what are its functions?
ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone), also called vasopressin, is secreted by the posterior pituitary.
It targets the kidneys and arterioles to:
Help retain water
Regulate fluid volume
Increase blood pressure
Low levels: Diabetes insipidus
High levels: Syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion
What is oxytocin and what are its effects?
Oxytocin is secreted by the posterior pituitary.
It causes:
Uterine contractions during labor
Milk ejection during breastfeeding
Low and High Levels: unknown
What are the functions of the thyroid gland and the hormones it produces?
The thyroid gland produces two hormones with distinct functions:
Thyroid Hormone (TH):
Regulates metabolic rate
Affects energy use, growth, and development
Calcitonin:
Lowers blood calcium levels
Inhibits osteoclasts (bone breakdown)
Enhances calcium excretion by kidneys
What is the difference between follicular cells and parafollicular cells in the thyroid gland?
Follicular Cells:
Produce Thyroid Hormone (TH)
Function: Regulate metabolic rate
Parafollicular Cells (C cells):
Produce Calcitonin
Function: Lower blood calcium levels by inhibiting osteoclasts and increasing calcium excretion by the kidneys
Disorders of Thyroid
Low Levels: person always cold, gains weight, but doesn’t feel hungry
High Levels: Person is “hot”, loses weight, very hungry, anxious. Must ablate thyroid
Goiter appears on the neck and it is unknown if it due to hyper or hypo- thyroidism
What is the function of the parathyroid gland and its main hormone?
he parathyroid gland contains chief cells that produce parathyroid hormone (PTH). And also contains oxyphil cells
Function of PTH:
Increases blood calcium (Ca²⁺) levels by:
Stimulating osteoclasts to break down bone
Enhancing calcium reabsorption in kidneys
Promoting calcium absorption in the intestines (via vitamin D activation)
What are chief cells in the parathyroid gland and what is their function
Chief cells are the main functional cells of the parathyroid gland.
They produce parathyroid hormone (PTH)
What are oxyphil cells in the parathyroid gland and what is their function?
Oxyphil cells are larger, less numerous cells in the parathyroid gland.
Their exact function is unknown
What are the main functions of the pancreas?
Exocrine function:
Acini cells secrete digestive enzymes into the small intestine to help break down food.
Endocrine function:
Pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) secrete hormones (like insulin and glucagon) that regulate blood sugar levels.
What are the endocrine cell types?
Alpha cells and beta cells
What is the function of Alpha cells in the pancreas?
Secrete glucagon: signals the liver to release glucose from glycogen which raises blood sugar
(in other words, the glucagon (hormone) goes to the liver to break glycogen (sugar) back to glucose (sugar), and it happens when sugar levels are low and alpha cells send signals to receive the glucose that is stored to be used)
What is the function of Beta cells in the pancreas?
Secrete insulin: signals most body cells to take up glucose from the blood which lowers blood sugar
(in other words, beta cells tell the glucose to go get stored in the liver which then gets transformed into glycogen)
What causes diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus is caused by:
Insufficient secretion of insulin, or
Resistance of body cells to the effects of insulin
What is Type I Diabetes Mellitus?
Develops suddenly, usually before age 15
Caused by a T cell-mediated autoimmune response
Destroys beta cells in the pancreas
Leads to little or no insulin production
What is Type II Diabetes Mellitus?
Known as adult-onset diabetes
Usually occurs after age 40
Body cells have lowered sensitivity to insulin
Can be controlled by dietary changes and regular exercise
What are the two main parts of the adrenal glands?
Adrenal medulla: a knot of nervous tissue
Adrenal cortex: bulk of the gland, composed of three layers:
Zona glomerulosa
Zona fasciculata
Zona reticularis
What cells make up the adrenal medulla and what do they secrete?
Chromaffin cells: modified postganglionic sympathetic neurons
Secrete catecholamines: norepinephrine and epinephrine
Active in the fight, flight, and fright response
What hormones are secreted by the adrenal cortex and their functions?
All hormones are steroids and grouped into:
Mineralocorticoids:
Aldosterone (zona glomerulosa)
Glucocorticoids:
Cortisol (zona fasciculata and zona reticularis) — helps deal with stress
Androgens:
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) (zona reticularis) — converted to testosterone and estrogen; may help with stress, immune system, and mood
What are the Gonads
Main source of sex hormone- testes and ovaries
What do the male gonads secrete and what are their functions?
Interstitial cells secrete androgens, primarily testosterone
Testosterone:
Promotes sperm formation
Maintains secondary sex characteristics (like facial hair, deep voice, muscle mass)
What hormones do the female gonads secrete and what are their functions?
Ovaries secrete:
Estrogen:
Maintains secondary sex characteristics
Signals uterine mucosa to repair after menstruation
Progesterone:
Produced by follicular granulosa cells and corpus luteum
Prepares the uterus for pregnancy
What is the function of the thymus gland and what happens to it after puberty?
Produces and secretes thymosin, a hormone essential for T cell development and production
Largest in children
Shrinks and is replaced by fat after puberty
What hormone does the pineal gland secrete and when?
Secretes melatonin
Mainly produced in the absence of light (at night)
Helps regulate sleep-wake cycles (circadian rhythm