(4.7.2)(Reactions of alkenes and alcohols)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What bond do alkenes have?
Double carbon carbon bond.
What is the equation for alkenes?
CnH2n
Why are alkenes unsaturated?
Alkene molecules are unsaturated because they contain two fewer hydrogen atoms than the alkane with the same number of carbon atoms.
What are the first 4 alkenes?
Ethene, Propene, Butene, Pentene. ( EPBP )
What are the two ways alkenes can be represented as?
WRITTEN C3H6
OR
DIAGRAM
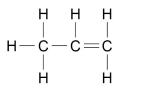
What is the functional group of alkenes?
C=C
Why is alkenes reaction with oxygen different?
They tend to burn in the air with smoky flames due to incomplete combustion.
What happens to the their bonds when alkenes react with hydrogen, water and the halogens?
The double carbon bond becomes single carbon bond.
What functional group is alcohols?
-OH
What are the first 4 alcohols?
Methanol, Ethanol, Propanol, Butanol. (MEPB)(Monkeys Eat Peanut Butter)
What are the two ways alcohols can be represented as?
WRITTEN CH3CH2OH
OR
DIAGRAM
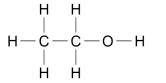
What happens when any of the four alcohols react with sodium?
A redox reaction occurs.
What happens when any of the four alcohols combust in the air?
It produces carbon dioxide and water.
What happens when any of the four alcohols react with water?
They dissolve.
What happens when any of the four alcohols react with an oxidising agent?
Forms a carboxylic acid.
What happens when sugar solutions are fermented using yeast.
Aqueous solutions of ethanol are produced.
What are the conditions for fermentation of sugar using yeast.
Anaerobic conditions and 25-35 degrees Celsius.
What is the functional group of carboxylic acids?
-COOH.
What are the first four carboxylic acids?
Methanoic acid, ethanoic acid, propanoic acid, butanoic acid. (MEPB)(Monkeys Eat Peanut Butter)
What are the two ways carboxylic acids can be represented?
WRITTEN CH3COOH
OR
DIAGRAM
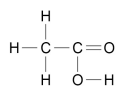
What happens when a carboxylic acid reacts with carbonates?
Carboxylic acids react with carbonates to produce carbon dioxide gas, water, and a salt.
What happens when a carboxylic react with water?
When dissolved in water the carboxylic acid releases H+ ions into the water. Stronger acids release more ions than weaker acids.
What happens when a carboxylic react with alcohols?
Carboxylic acids can react with alcohols in the presence of an acid catalyst (usually concentrated sulfuric acid) to form esters and water. This reaction is reversible.
Why are carboxylic acids weaker than other acids?
Because they only partially ionise in the solution so there is less hydrogen ions compared to a stronger acid at the same concentration and that means that the pH of the solution will be higher than a stronger acids.