ESCI 204 - Topics in Ocean Science
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/203
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
204 Terms
1
New cards
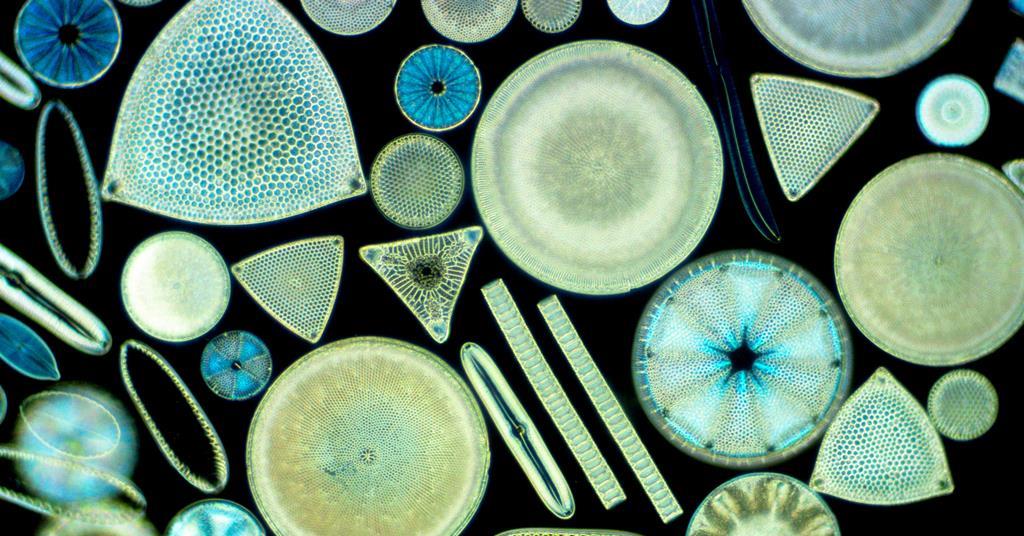

Centric (circle shaped) or Pennate (pen shaped)
Large Cells
May Form Long Chains
Large Cells
May Form Long Chains
Diatoms
2
New cards
Possess two flagella
Very large cells
Hetero- or phototrophic
Very large cells
Hetero- or phototrophic
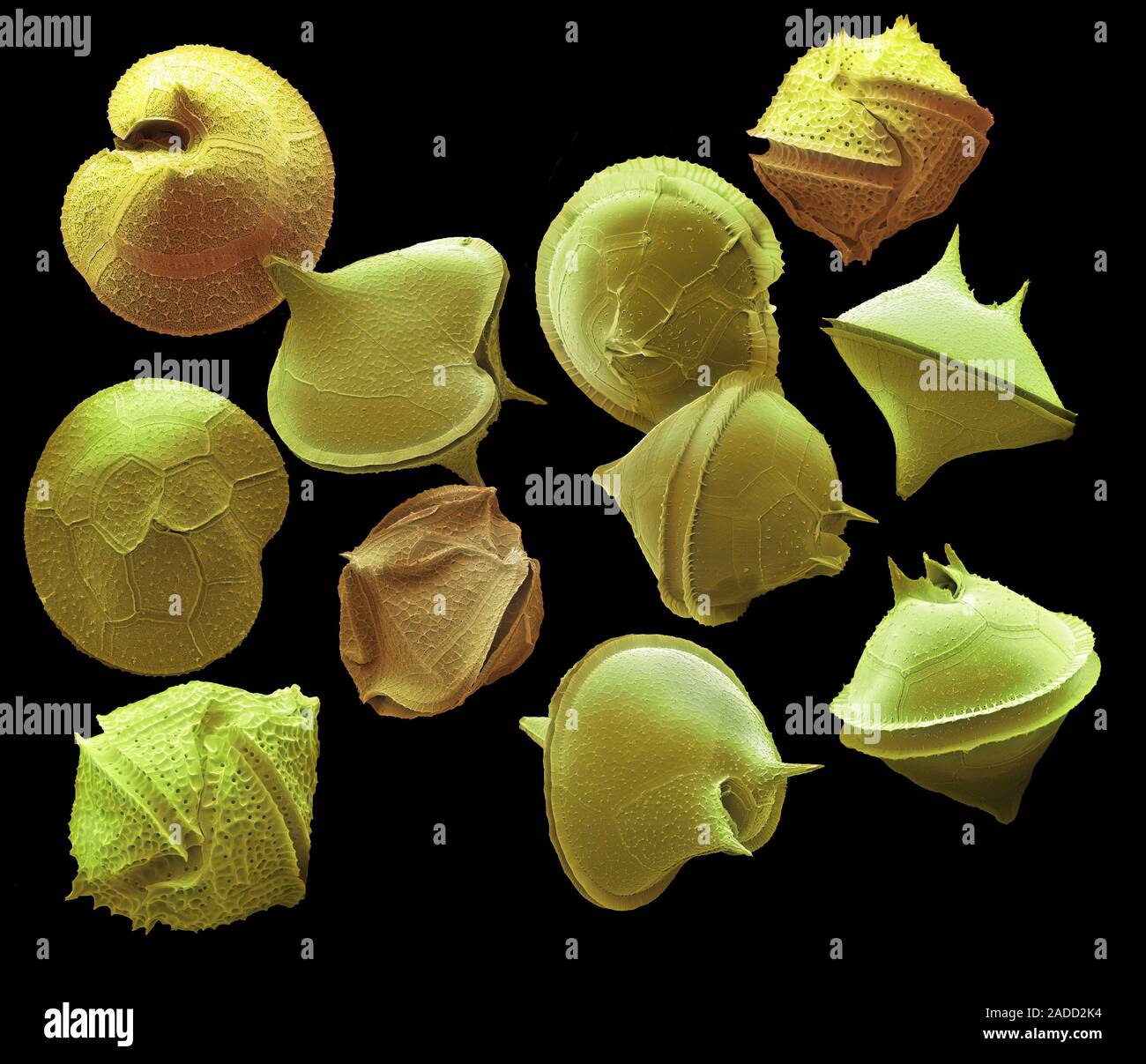
Dinoflagellates
3
New cards
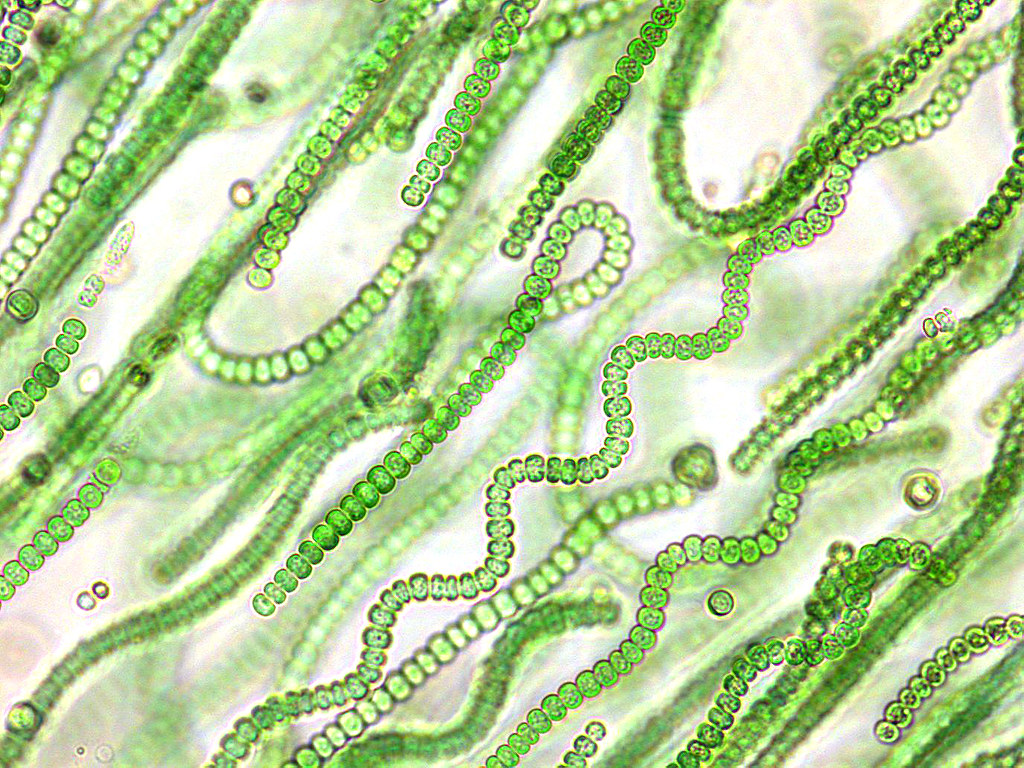
Very small cell size
Majority of phytoplankton biomass
Primitive species
Majority of phytoplankton biomass
Primitive species
Cyanobacteria
4
New cards
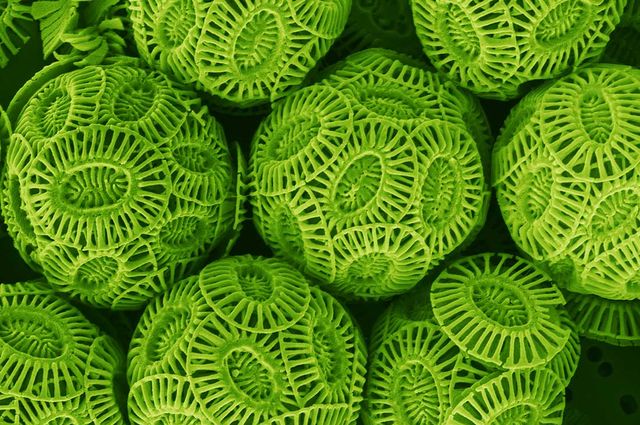

Average size flagellated cells
Numerous genera/species
Numerous genera/species
Microflagellates
5
New cards

Amoeba that form silica exoskeletons
Radiolaria
6
New cards
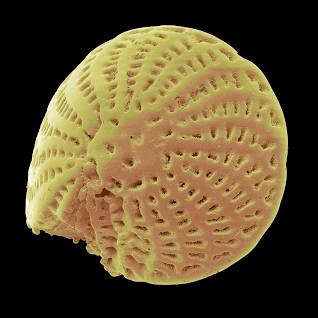
Amoebic protists that inhabit shells composed of calcium carbonate
Foraminifera
7
New cards

Type of Meso- and Macrozooplankton that uses spikes and spears to consume prey
Copepods
8
New cards

Macrozooplankton related to Shrimp
Euphausiid(ae) (Krill)
9
New cards
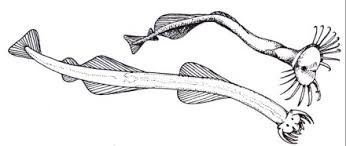
Macrozooplankton that listen to their prey and spear them when nearby
Arrow Worms
10
New cards
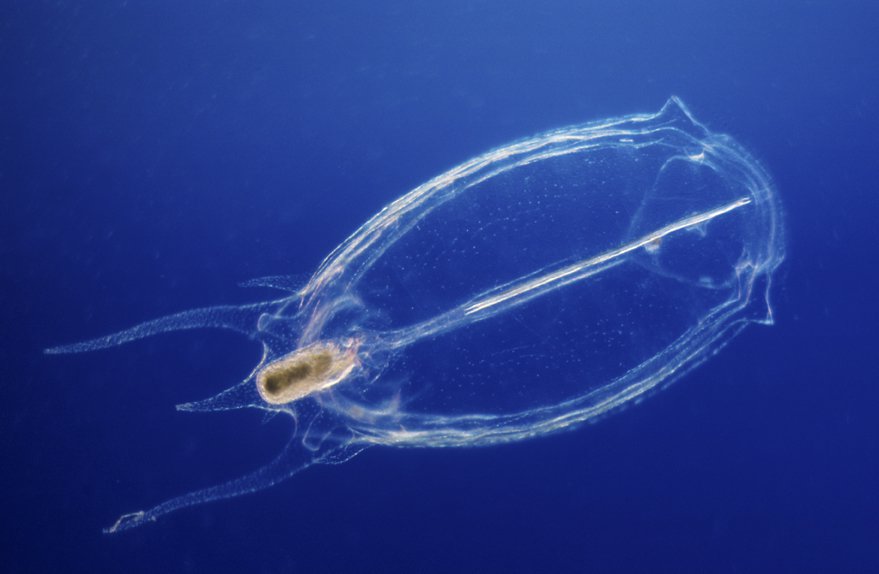

Megalozooplankton that collect prey through stinging or sticky cells
Ctenophores and salps
11
New cards
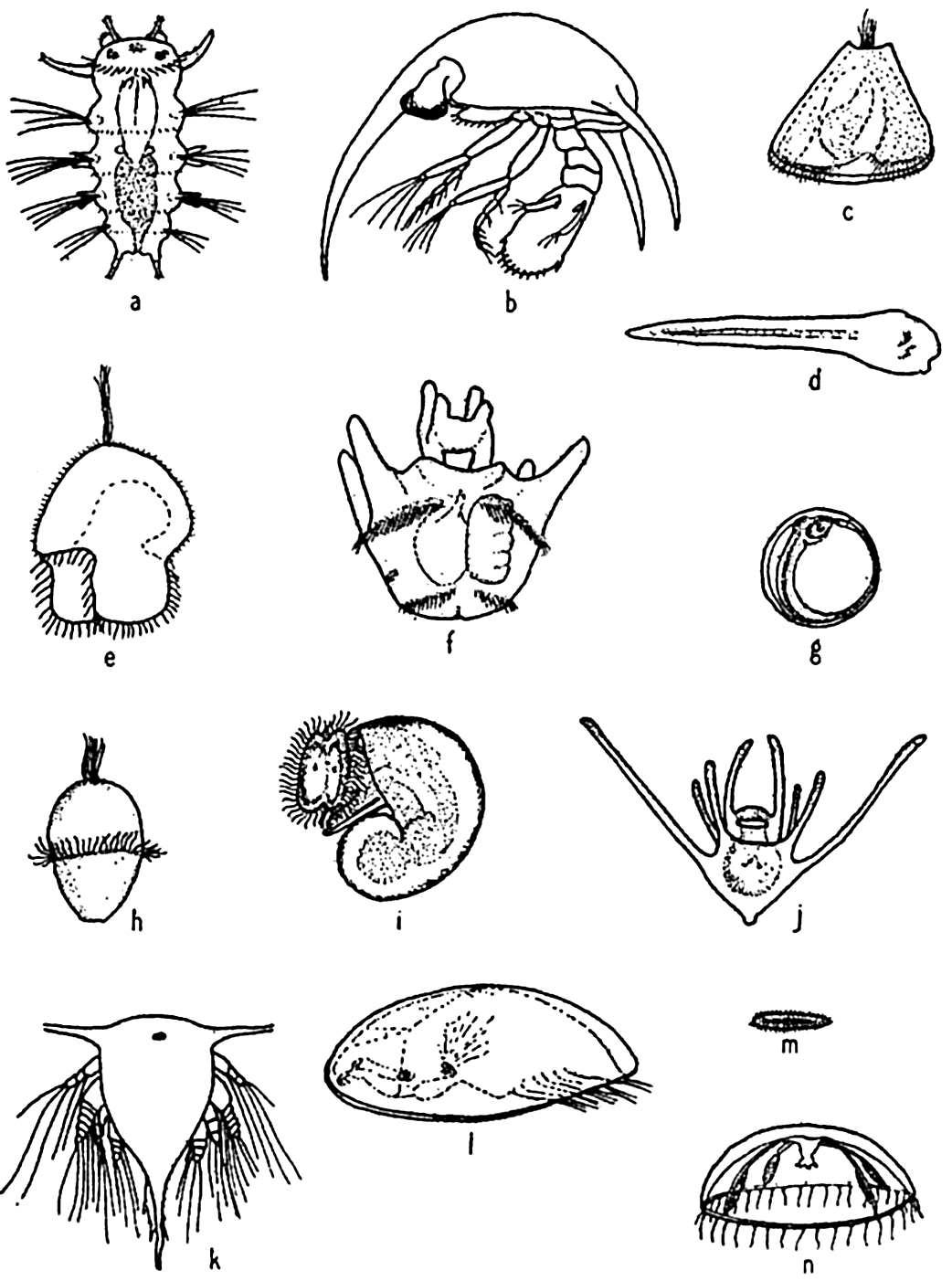
Crab larvae, polychaete larvae, barnacle cyprid, & ichtyoplankton are all types of…
Meroplankton
12
New cards

Deep-sea polychaete worm found only in the extreme heat of hydrothermal vents feeding on chemosynthetic bacteria
Pompeii worms
13
New cards

Bore into the bones of whale to feed on lipids and other nutrients. Related to hydrothermal vent worms
Osedex
14
New cards
New sea floor is created at
Spreading centers (mid-ocean ridges)
15
New cards
Plate tectonics are driven by
Gravity (ie. density differences)
16
New cards
Boundary between two tectonic plates moving away from each other
Divergent
17
New cards
Boundary between two tectonic plate colliding into each other
Convergent
18
New cards
Boundary between two tectonic plates sliding against each other
Transformative
19
New cards
Sea floor is destroyed at these ocean trenches
Subduction zones
20
New cards
Primary force of ocean currents
Pressure gradient
21
New cards
Three secondary forces of ocean currents
Coriolis; Wind; Gravity
22
New cards
Variation in pressure over a distance of space
Pressure gradient
23
New cards
Flows parallel to isobars, modified by the Coriolis Effect
Geostrophic Flows
24
New cards
As friction pulls on the surface of the sea, ocean water twists until the deep water is flowing in separate directions than the surface water
Ekman Spiral
25
New cards
Areas of high water pressure slightly bulge above the surface of the sea
Ocean mounds
26
New cards
Replacement of surface water with deep water at continental shelves
Upwelling
27
New cards
Great Ocean Conveyor supplies the deep-sea with oxygen and carbon dioxide
Thermohalean circulation
28
New cards
Upwelling is significant because it
Brings cold, nutrient rich water from the deep ocean to critical coastal locations
29
New cards
The primary driver of ocean salinity
Rivers
30
New cards
Quantity of dissolved solids in seawater
Salinity
31
New cards
Density increases as temperature __ and as salinity __
Decreases; increases
32
New cards
Strong, vertical layering of seawater that prevents mixing
Stratification
33
New cards
Temperature __ as ocean depth increases
Decreases
34
New cards
Salinity __ as ocean depth increases
Increases
35
New cards
Nutrient content __ as ocean depth increases
Increases
36
New cards
Dissolved oxygen __ as ocean depth increases
Decreases until the Oxygen Minimum zone, then increases
37
New cards
Three primary marine nutrients
Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Iron
38
New cards
Photosynthetic equation
6CO2 + 6H2O + light → C6H12O6 + 6O2
39
New cards
Respiration equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
40
New cards
Redfield ration (total amount of organic molecules in an ecosystem)
106 C : 16 N : 1 P
41
New cards
Nitrite
NO2-
42
New cards
Nitrate
NO3-
43
New cards
Ammonium
NH4+
44
New cards
Rate of creation of food
Productivity
45
New cards
Total rate of productivity produced by (a) phytoplankton
Gross primary productivity (GPP)
46
New cards
Total rate of productivity produced by (a) phytoplankton after respiration
Net primary productivity (NPP)
47
New cards
Total rate of productivity exhibited by the whole food web after respiration
Net ecosystem productivity (NEP)
48
New cards
Diploids that divide through mitosis
Divide until too small, then undergo sexual reproduction (meiosis)
Divide until too small, then undergo sexual reproduction (meiosis)
Diatom life cycle
49
New cards
Haploids that produce long-lasting resting cysts
When cysts are exposed to better conditions, they develop functioning organelles
When cysts are exposed to better conditions, they develop functioning organelles
Dinoflagellate life cycle
50
New cards
Ocean productivity can be seasonally self-limiting when this aspect of productivity fluctuates with the seasons
Net ecosystem productivity (NEP)
51
New cards
Phytoplankton abundance can be measured in which two ways?
Rate of productivity; amount of chlorophyll
52
New cards
The principle stating that a competitive dominant species can exclude other, less efficient species from valuable resources
Competitive Exclusion Principle
53
New cards
Nitrogen gas
N2
54
New cards
Cyanobacteria convert this nitrogen-based molecule to another nitrogen-based molecule
N2 to NH3 (Nitrification)
55
New cards
Ammonia
NH3
56
New cards
When cyanobacteria are consumed, the predator converts this nitrogen-based molecule to another through excretion
NH3 to NH4+ (Ammonification)
57
New cards
When anaerobic bacteria respire, they convert this nitrogen-based molecule to another for oxygenation
NO2+/NO3+ to N2 (Denitrification)
58
New cards
The efficiency of nutrient uptake is correlated with
Cell size
59
New cards
Smaller phytoplankton are __ efficient at nutrient acquisition
More
60
New cards
The population growth rate
Change in amount of organisms / change in time
61
New cards
The per capita growth rate
Population growth rate / population size
62
New cards
The smaller the cell, the tendency for a __ growth rate
Faster
63
New cards
Small phytoplankton cells are common in the
Open ocean
64
New cards
Large phytoplankton cells are common in
Coastal waters
65
New cards
Dead organic matter
Detritus
66
New cards
Single-celled protists
Dinoflagellates, ciliates
Consume majority of phytoplankton productivity
Dinoflagellates, ciliates
Consume majority of phytoplankton productivity
Microzooplankton
67
New cards
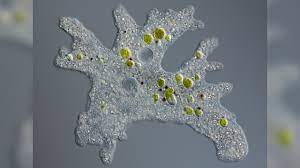
Large single-celled zooplankton
Form calcium carbonate/silica shells
Form calcium carbonate/silica shells
Amoeba
68
New cards
Possess antennae, thoraxes, and tails to predation
Grazing copepods, pteropods
Grazing copepods, pteropods
Mesozooplankton
69
New cards
Possess senses and predatory appendages
Possess complex organs/organelles and body functions
Arrow worms, krill (euphausiids), mysids
Possess complex organs/organelles and body functions
Arrow worms, krill (euphausiids), mysids
Macrozooplankton
70
New cards
Often possess sticky or stinging cells
Large, may form mats/chains
Large, may form mats/chains
Megalozooplankton
71
New cards
Plankton that stay plankton their entire lives
Holoplankton
72
New cards
Plankton that spend a portion of their life as a plankton
Meroplankton
73
New cards
Zooplankton migration and fecal matter influence
Nutrients in the deep-sea
74
New cards
Reynold’s number (Re)
(Length x velocity) / viscosity
75
New cards
Laminar water’s Re
Re < 10
76
New cards
Transitional water’s Re
10 < Re < 10^4
77
New cards
Turbulent water’s Re
Re > 10^4
78
New cards
Grazing copepods can only feed in __ waters
Laminar
79
New cards
Grazing copepods have a natural threshold for a maximum feeding rate, but during times of starvation, copepods will
Ignore the threshold
80
New cards
The main adaptation strategy for large phytoplankton is
To avoid predation from microzooplankton
81
New cards
Zooplankton fecal pellets sink ______ than phytoplankton, increasing __ in the deep-sea
Faster; nutrients
82
New cards
Zooplankton spatial variation and specialization is largely dependent on
Species type
83
New cards
Surface layer of the ocean
200-300 ft in depth
High biodiversity and herbivore count
200-300 ft in depth
High biodiversity and herbivore count
Epipelagic zone
84
New cards
300-1000m below the surface
Lack of wave action
Most of O2 Minimum Zone
Large, gelatinous species
Lack of wave action
Most of O2 Minimum Zone
Large, gelatinous species
Mesopelagic zone
85
New cards
Zooplankton spend huge amounts of energy on daily vertical migration to
Avoid surface predators during the day and feed on phytoplankton at night
86
New cards
This rate is the length of residence time nutrients have in a body of water (too short and no nutrients will be taken; too long at phytoplankton will deplete available nutrients)
Flush Rate
87
New cards
PSP (paralytic shellfish poisoning) is caused by
Alexandrium catanella
88
New cards
Productivity in puget sound is limited by ______ in the summer and __ in the winter
Nutrients; light
89
New cards
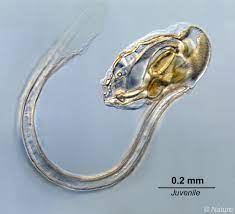
Free-swimming filter-feeders who catch prey through mucus houses
Appendicularia
90
New cards
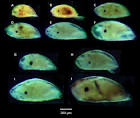
Meroplanktonic larvae
Barnacle cyprids
91
New cards
Agnatha (jawless)
Eel-shaped site-producing fish
Invertebrate
Eel-shaped site-producing fish
Invertebrate
Hagfish
92
New cards
Barnacles’ primary method of competing for space is
Undercutting
93
New cards
Mussels’ primary method of competition of space is
Overgrowth
94
New cards
In the intertidal zone, species are segregated by elevation because of these two forms of stress
Physical & biological
95
New cards
Biodiversity tends to decrease when the population of the __ isn’t kept in check
Competitive dominant species
96
New cards
Hydrothermal vents occur when
Pockets of magma are close enough to the ocean floor so that seawater can infiltrate the crust and shoot back up at high temperatures
97
New cards
White hydrothermal vents precipitate and remove many molecules from the ocean water, they primarily convert __ to __
Sulfate; hydrogen sulfide
98
New cards
Equation for chemosynthesis
6H2S + 6H2O + 6CO2 + 6O2 → 6H2SO4 + C6H12O6
99
New cards
The respiration process exhibited by many hydrothermal vent bacteria that transfers hydrogen sulfide and energy into food and sulfuric acid
ChemosynthesisC
100
New cards
Competition in Hydrothermal Vent communities is determined by __ & __ increasing with proximity to smokers
Physical stress; food abundanceA