Chapter R-15: Genetics of Bacteria and Bacteriophages and Beginning of Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression in Bacteria
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
bacteria are good experimental organisms because...
-haploid
-single chromosome
-small genome
-short generation times
-easy to maintain
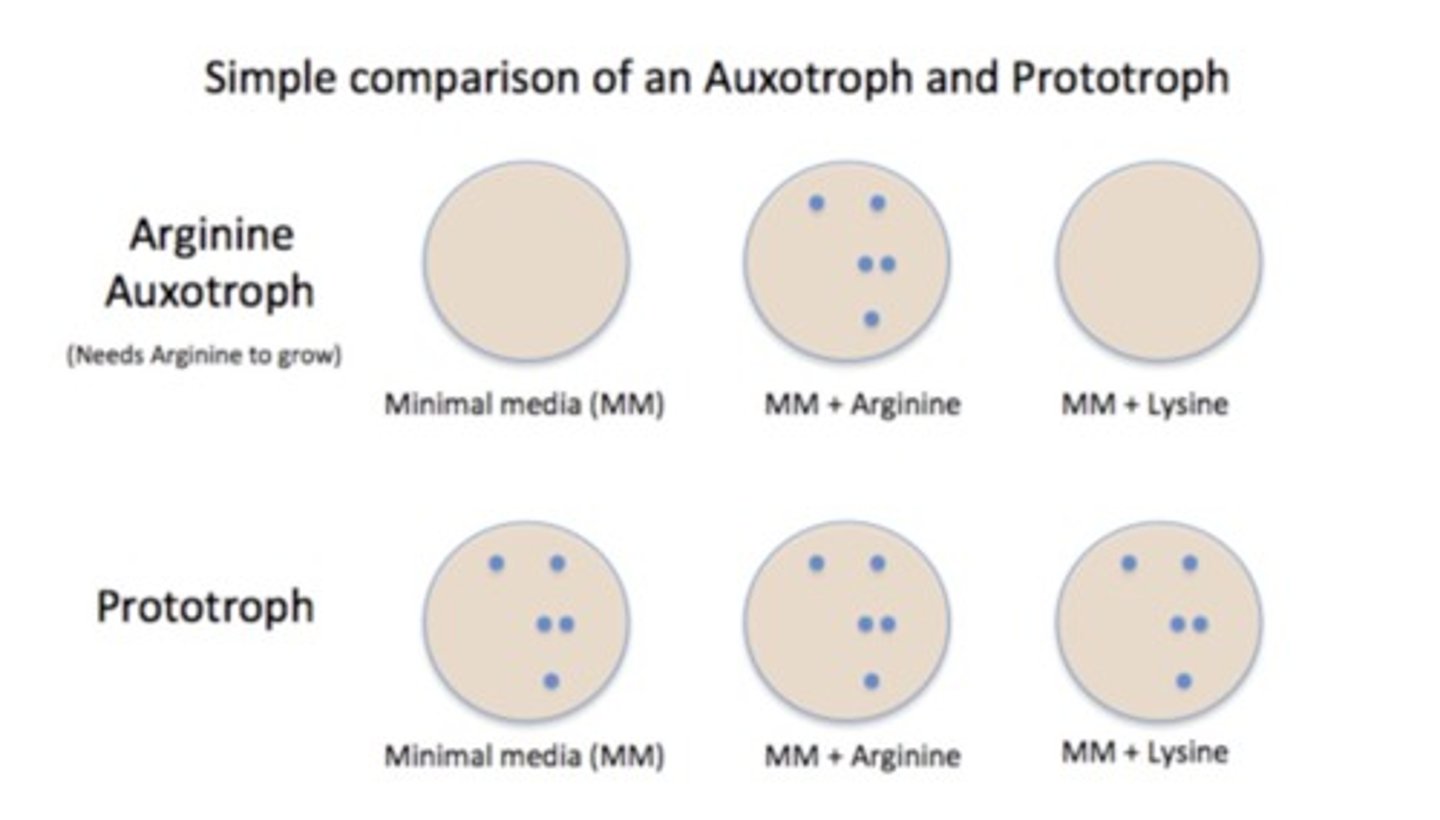
prototroph
-can synthesize all of the building blocks from a carbon source and salts
-a strain can grow on minimal medium (wildtype E.coli is a prototroph)
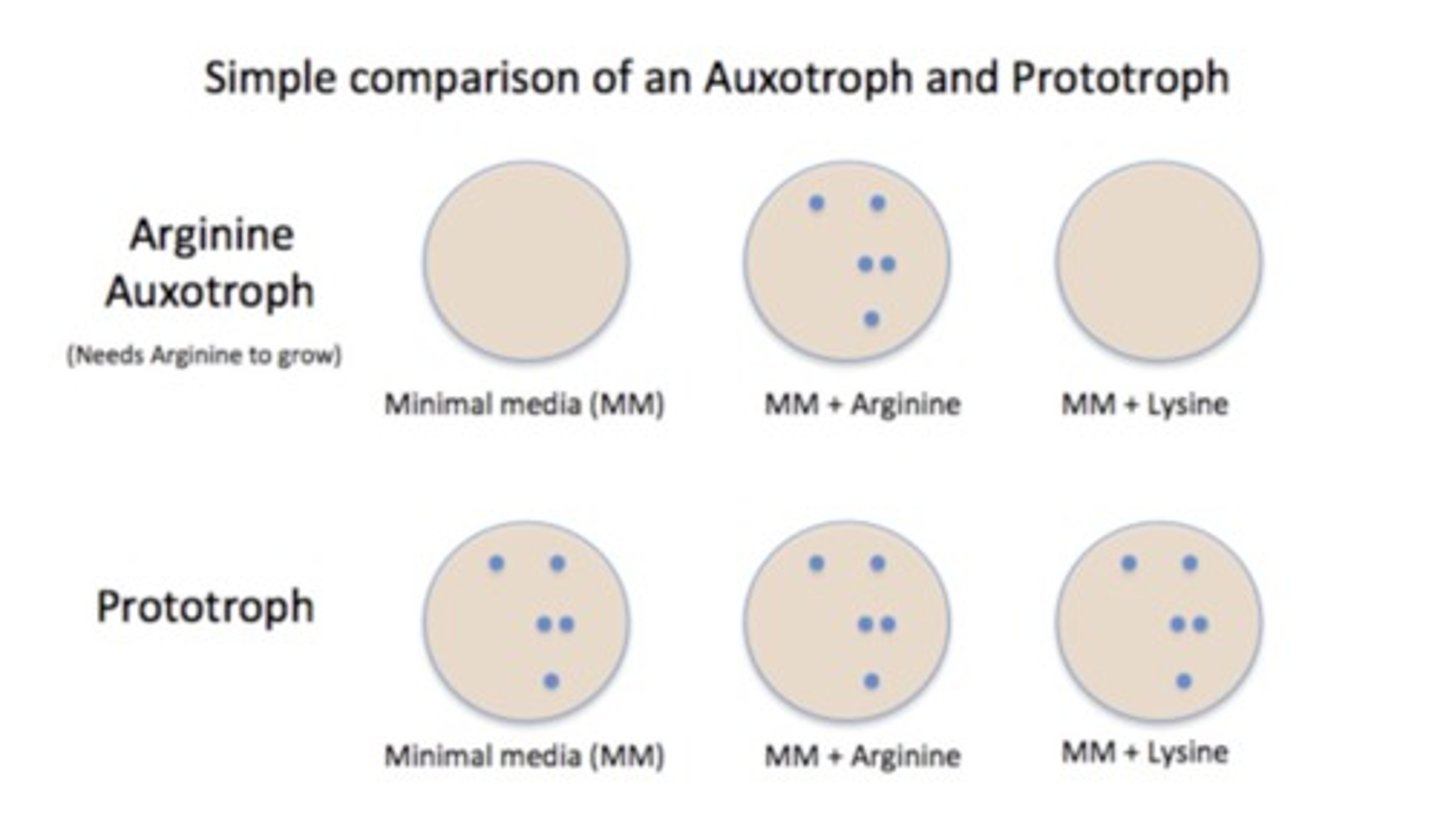
auxotroph
-does not grow on minimal medium
-requires nutritional supplements in the media because it can't synthesize it
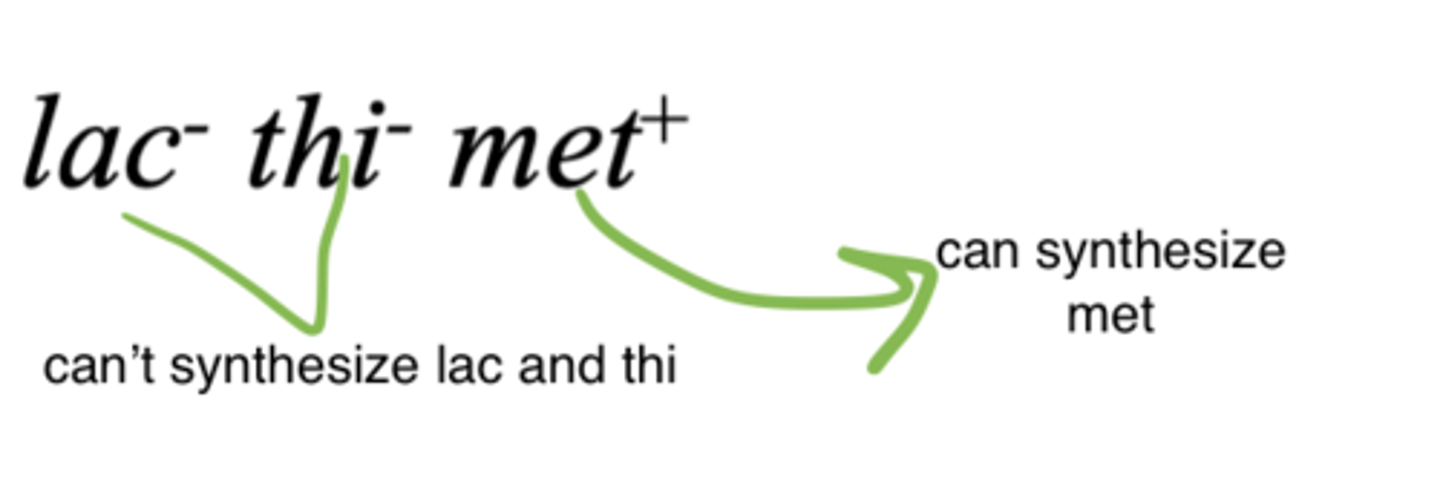
genotype designations
a bacterial strain that can't synthesize something will have a minus and a if it can synthesize something it will have a plus
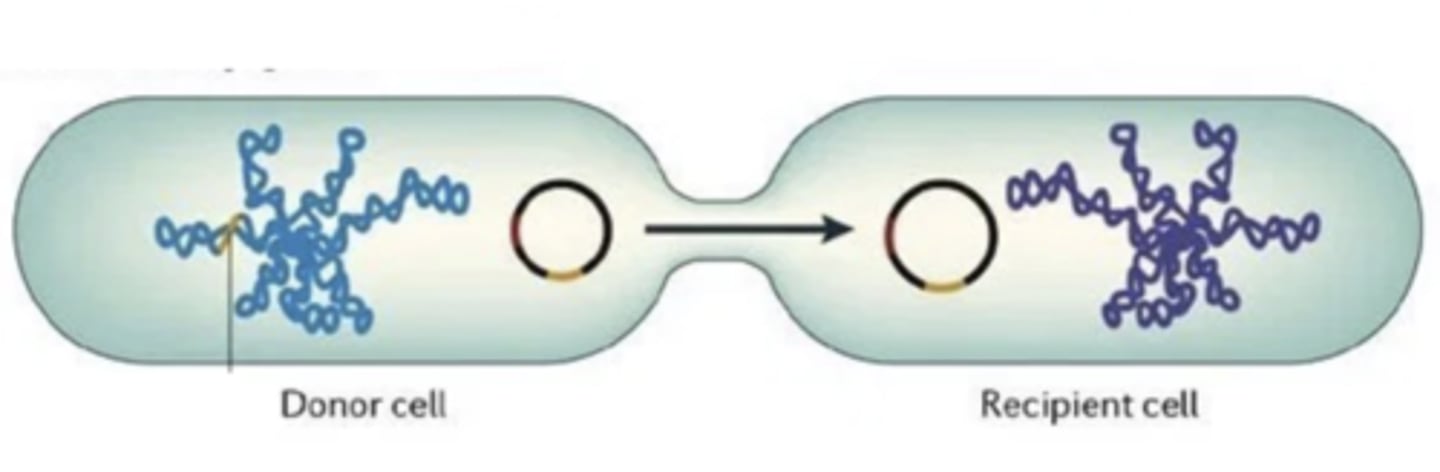
conjugation
a process in which there is a unidirectional transfer of genetic information through direct cellular contact between a donor bacterial cell and a recipient bacterial cell
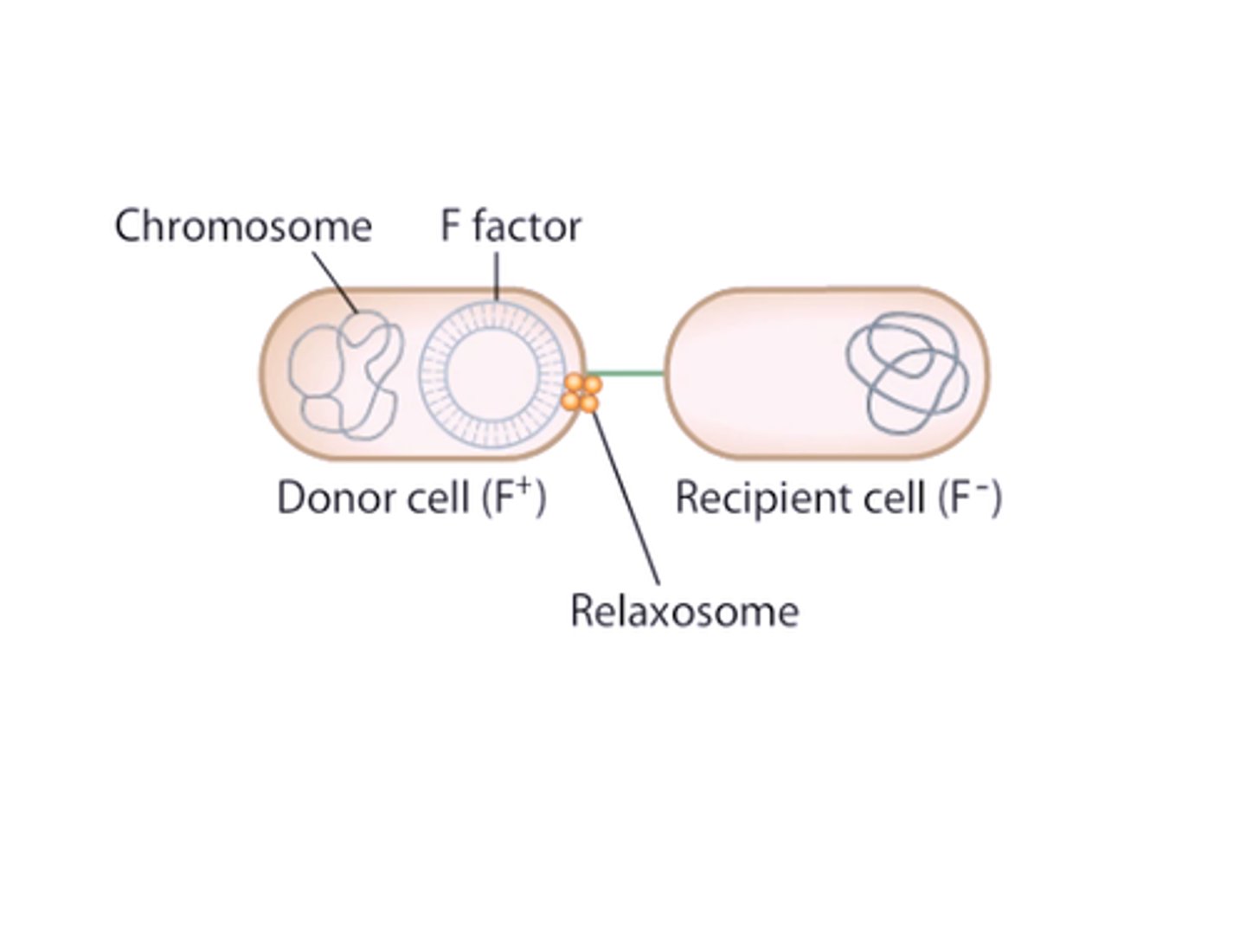
Conjugation Details
-conjugation is from donor to recipient
-donor must have F-factor which is a plasmid that is self-replicating circular DNA that is seperate from the chromosome. it has an origin and contains genes to make f-pilli which allow the donor to attach to the recipient
transconjugants
recipients that have incorporated a piece of donor DNA into their chromosomes
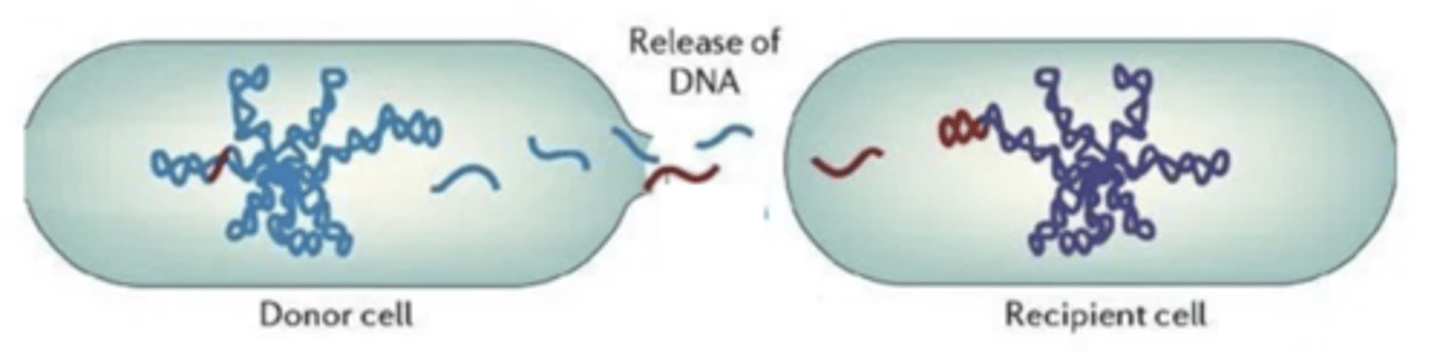
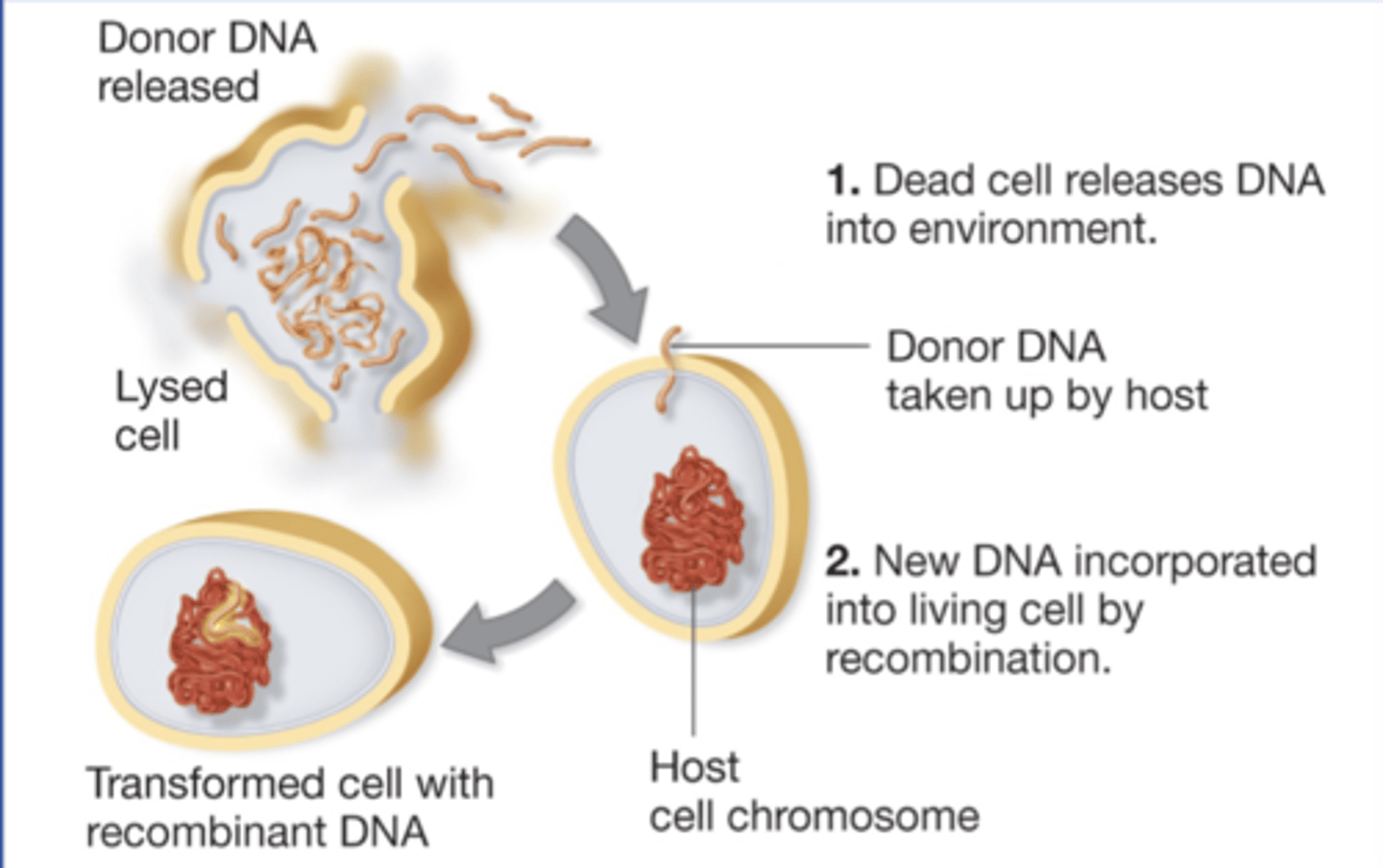
transformation
-the unidirectional transfer of extra-
cellular DNA into cells, resulting in a phenotypic change
in the recipient
-incorporates naked DNA from the environment
competent
cell that is able to take up DNA from the environment
transformants
recipients whose genotype + phenotypes are changed by
transformation
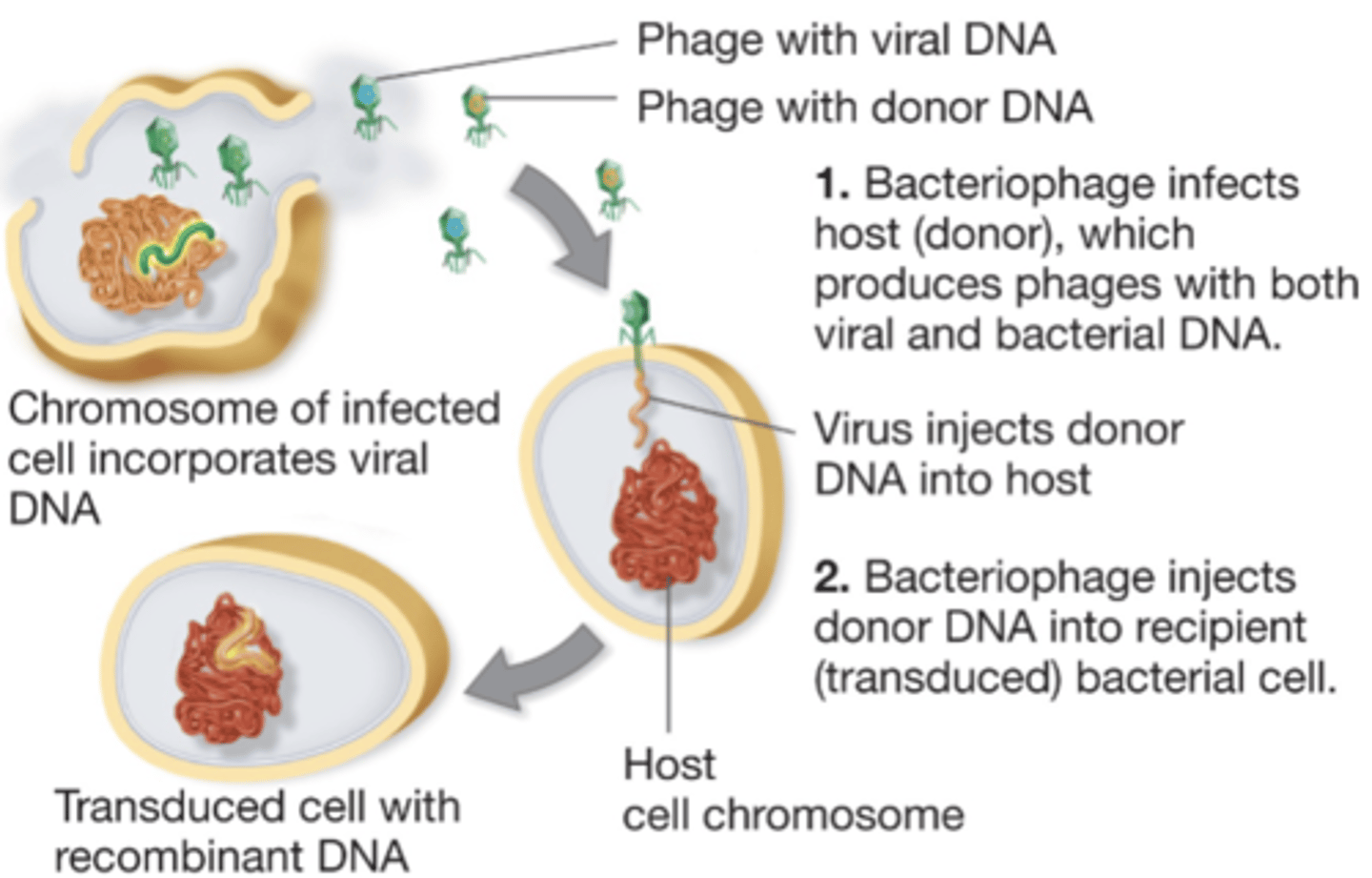
transduction
a process by which bacteriophages (bacterial viruses; phages, for short) transfer genes from one bacterium (the donor) to another (the recipient)
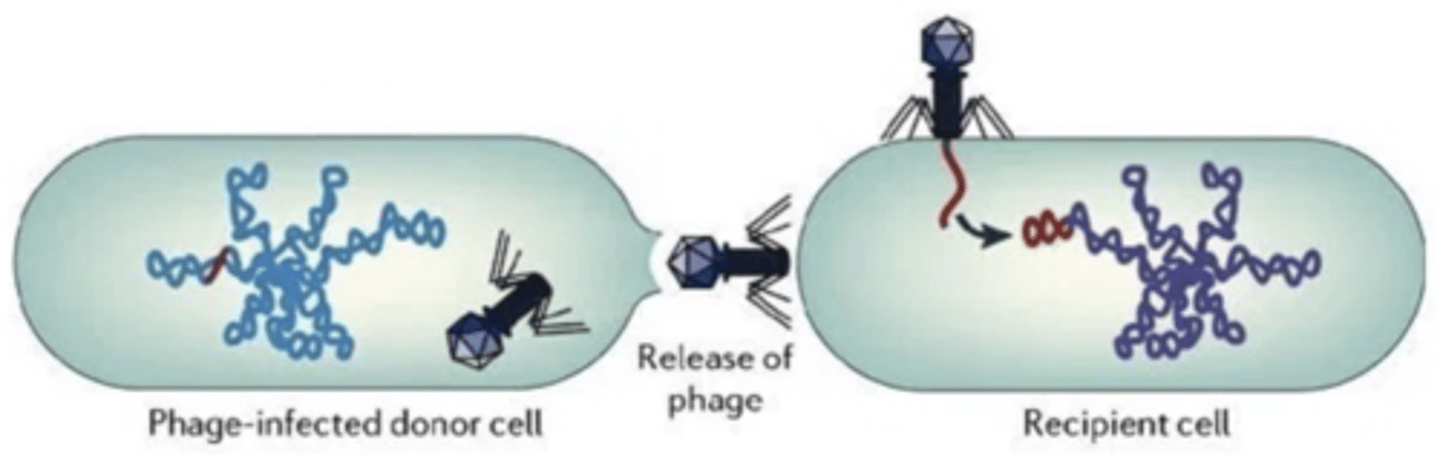
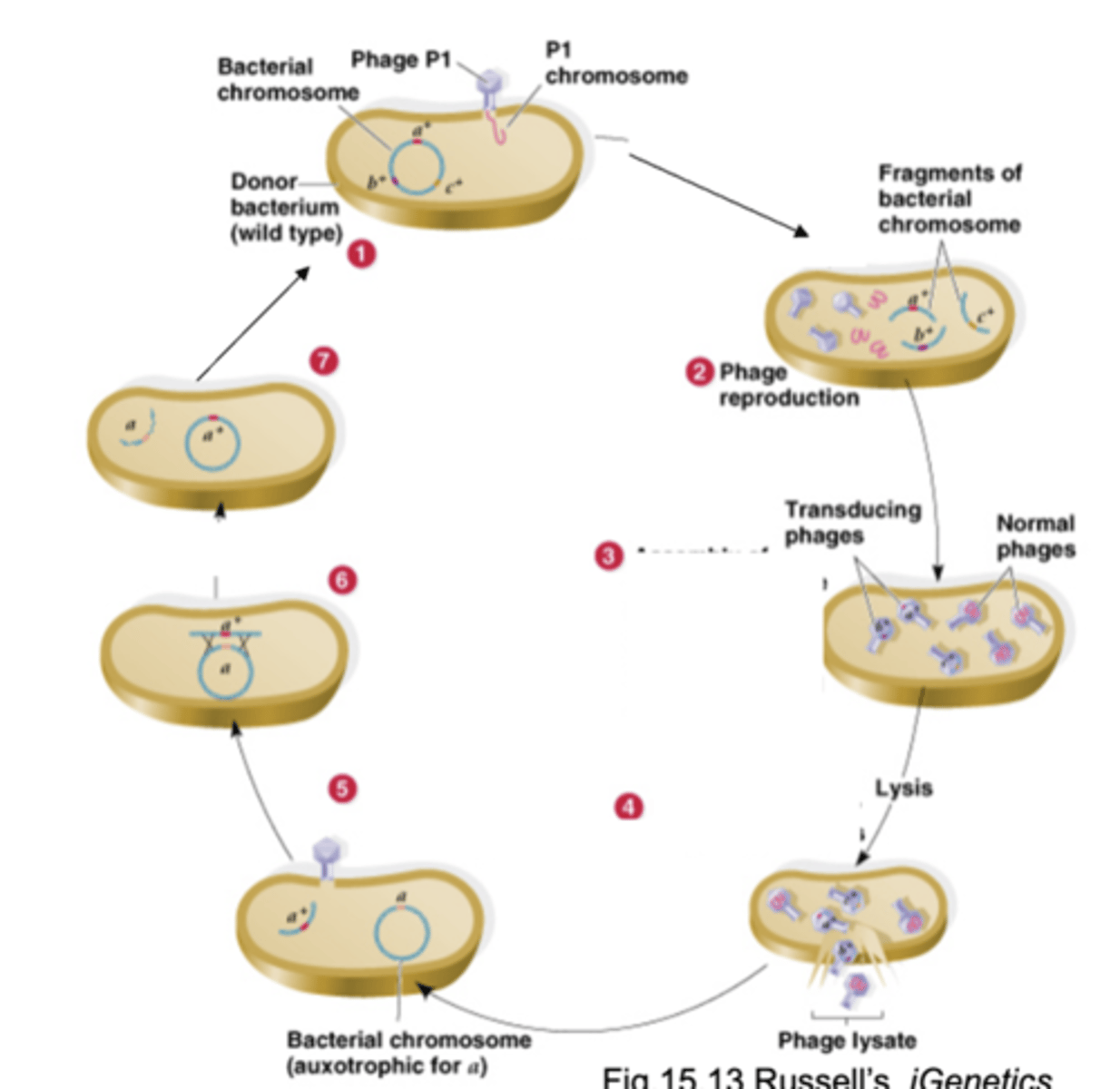
generalized transduction
-the process by which a phage can transfer any gene from a donor to a recipient bacterium
-phage puts pieces of the host cell's DNA into phage particles
-the phages only have donor genes and infect bacteria but do not kill them, recipient's phenotype may be changes
bacterialphage
bacterial virus
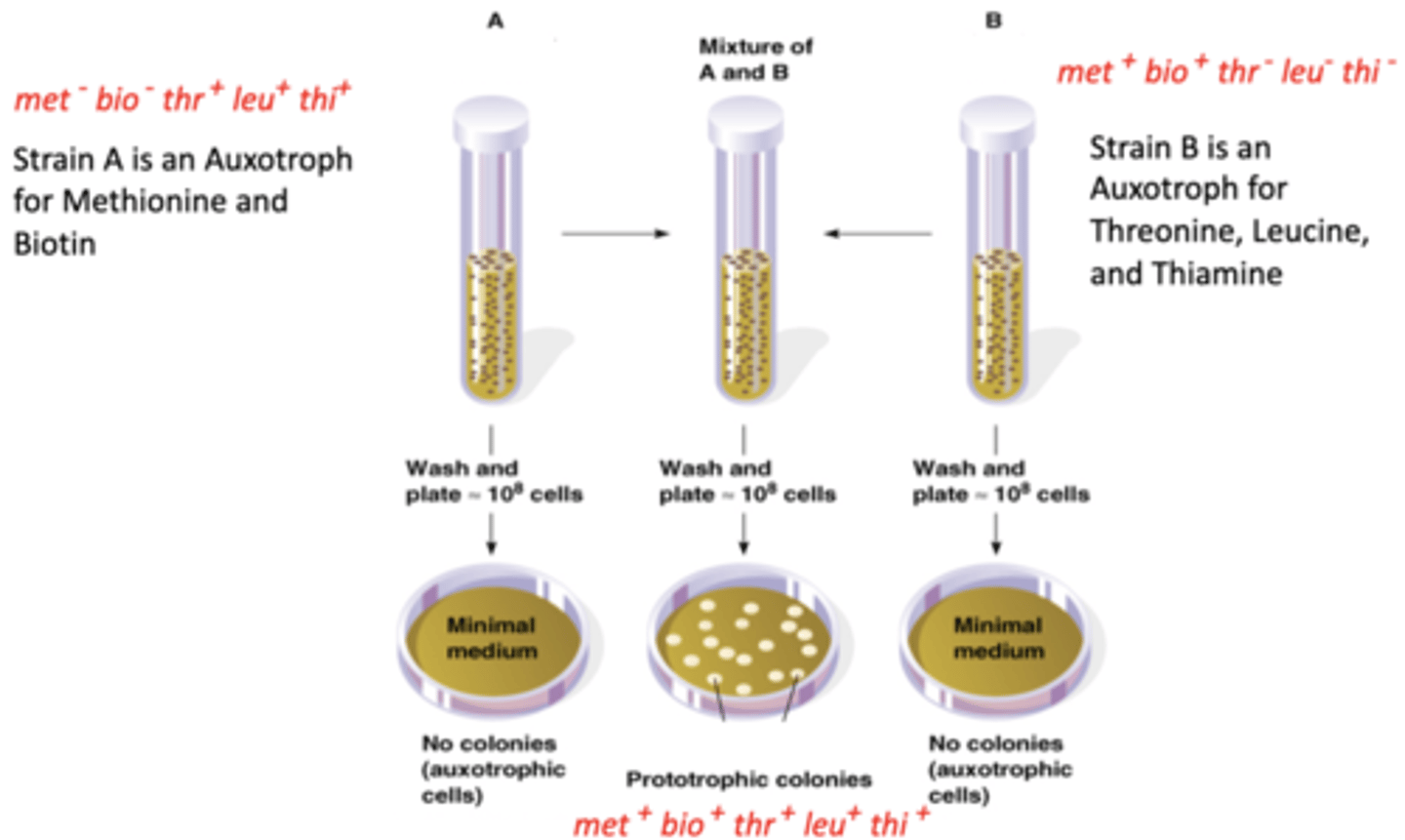
Lederberg and Tatum Experiment
demonstrated recombination and conjugation in E.coli by using a mixture of two auxotrophs, one for Met and Bio and auxotroph thr, leu, and this. they combined to make a prototroph
strain
mutant form of an organism that differs in some way from wild-type
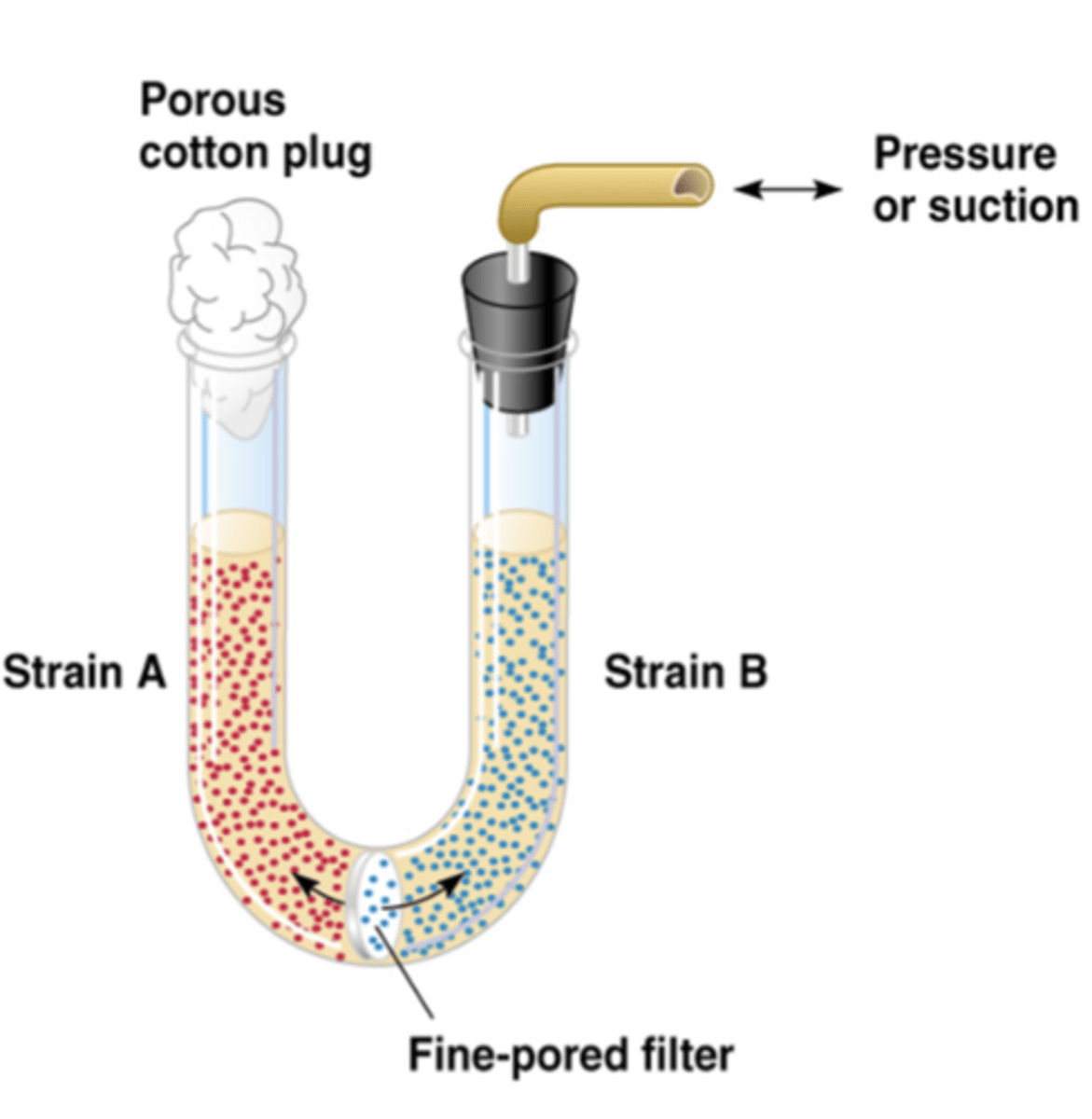
Davis' U-tube Experiment
-2 different strains on opposite sides separated with pores too small for the bacteria to pass through and no prototrophic recombinants were formed
-showed that physical contact was needed for conjugation
donor
must be F+
recipient
must be F-
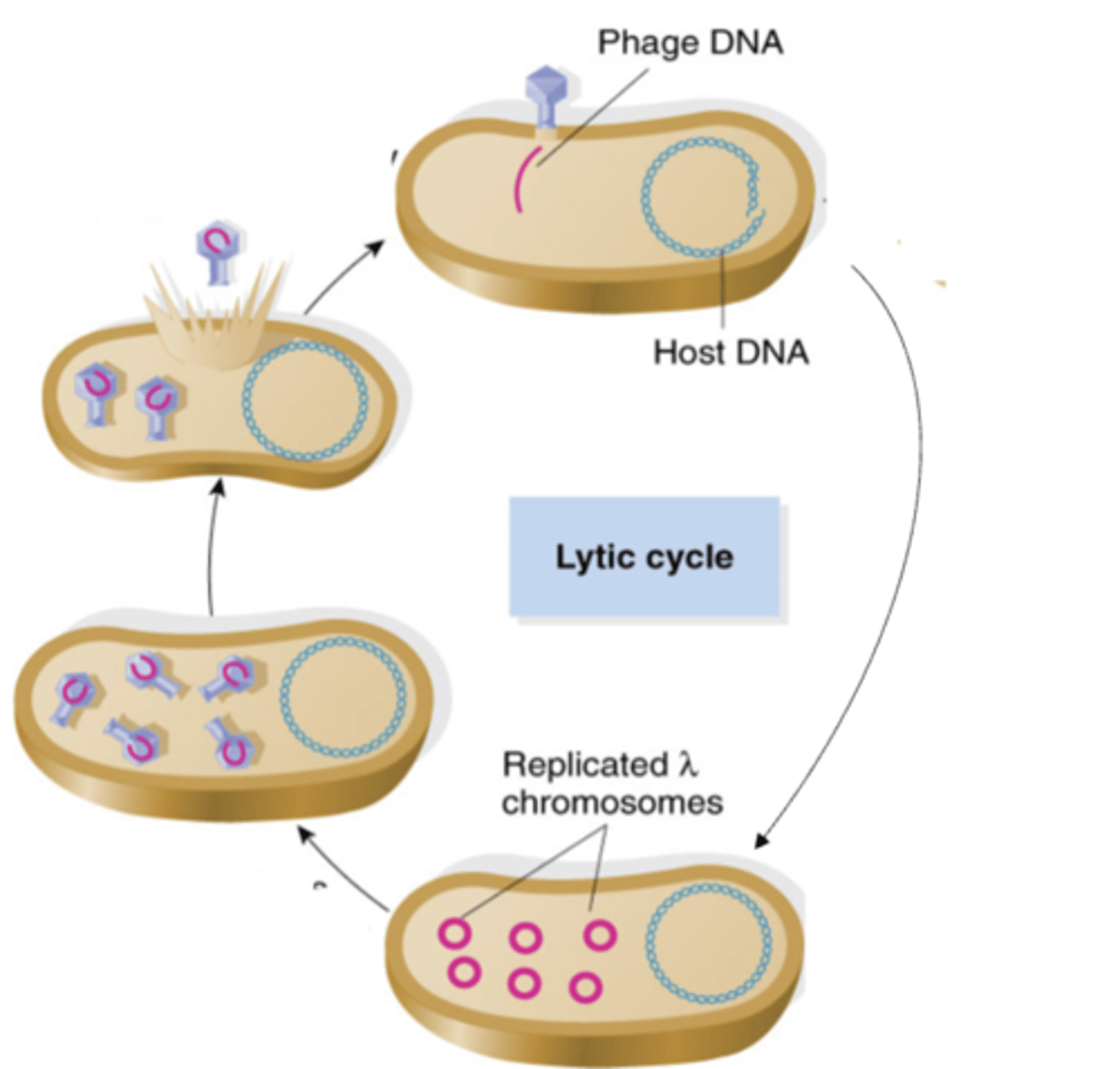
lytic cycle of bacteriophages
gene expression in bacteria
-it is the process by which information contained in a gene is converted into a function gene product that performs some function of the gene
-not all genes are regulated all the time and regulation of gene expression is critical
constitutive
-gene that is expressed all the time and product of gene is always needed
-they are always on
-ribosomal proteins, ribosomal RNA, proteins that make up core RNA polymerase
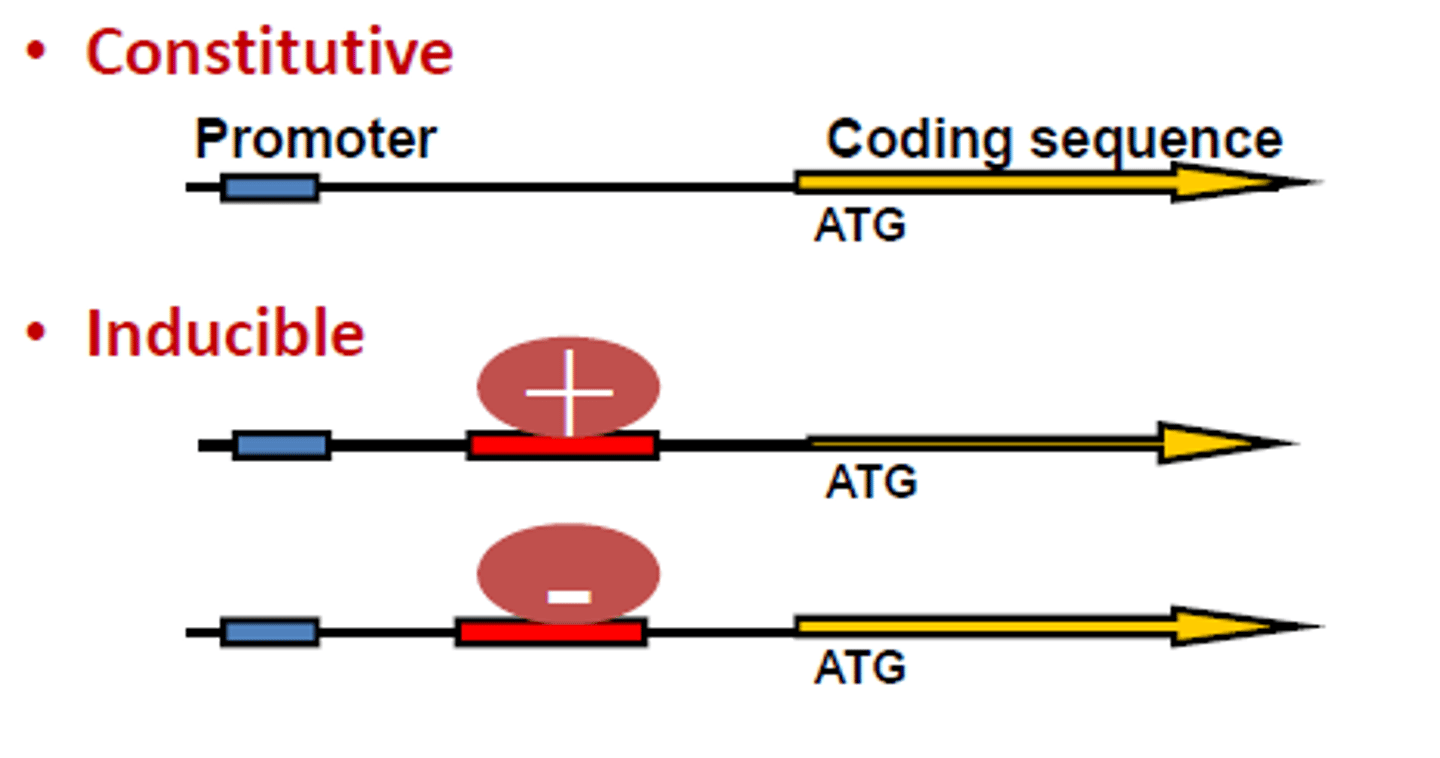
regulated
-sometimes its expressed, sometimes it's not and product of gene is not always needed
-expression can be turned on and off in response to the cell's needs
positive regulation
-regulatory protein triggers transcription
-activator protein

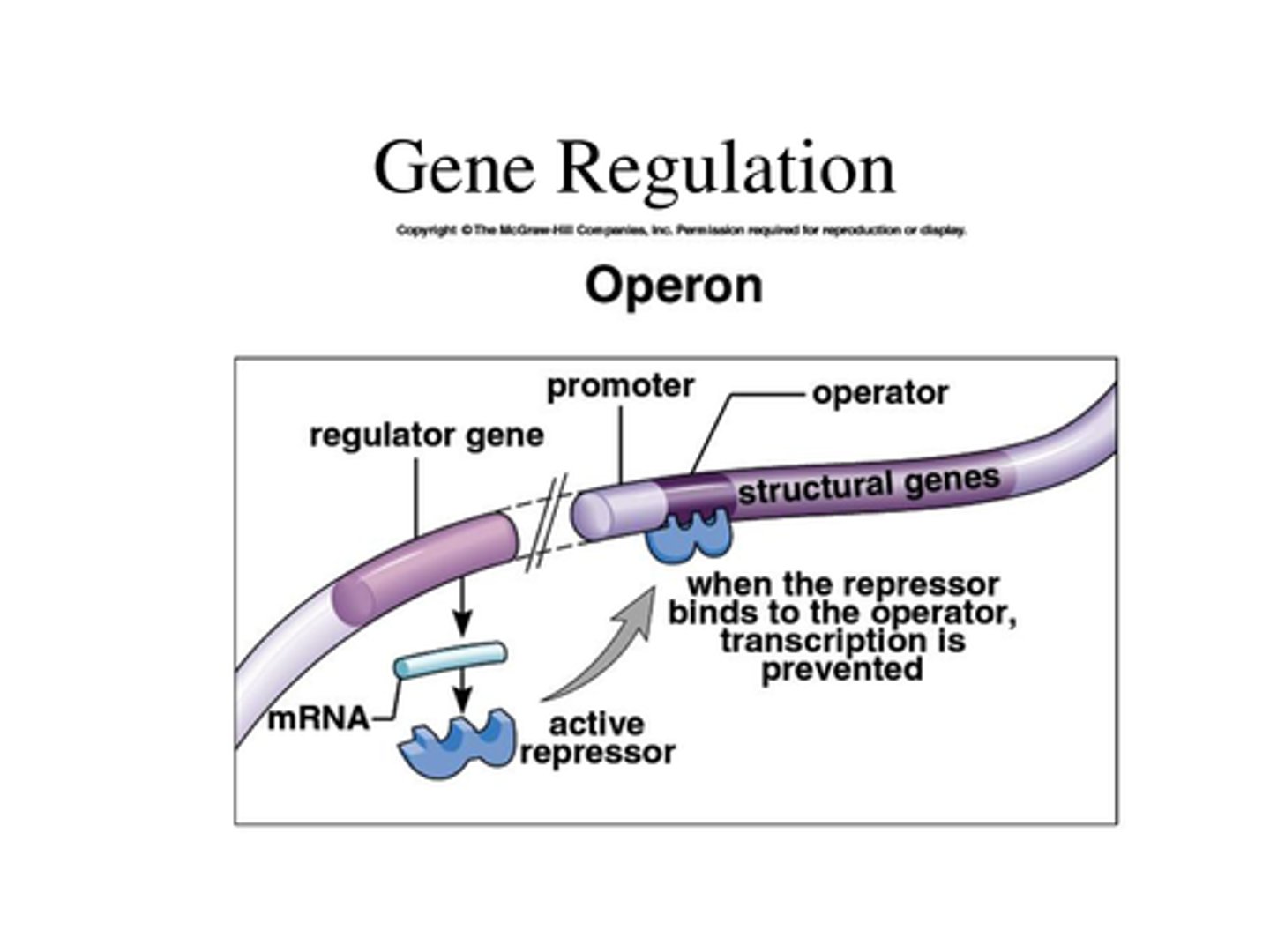
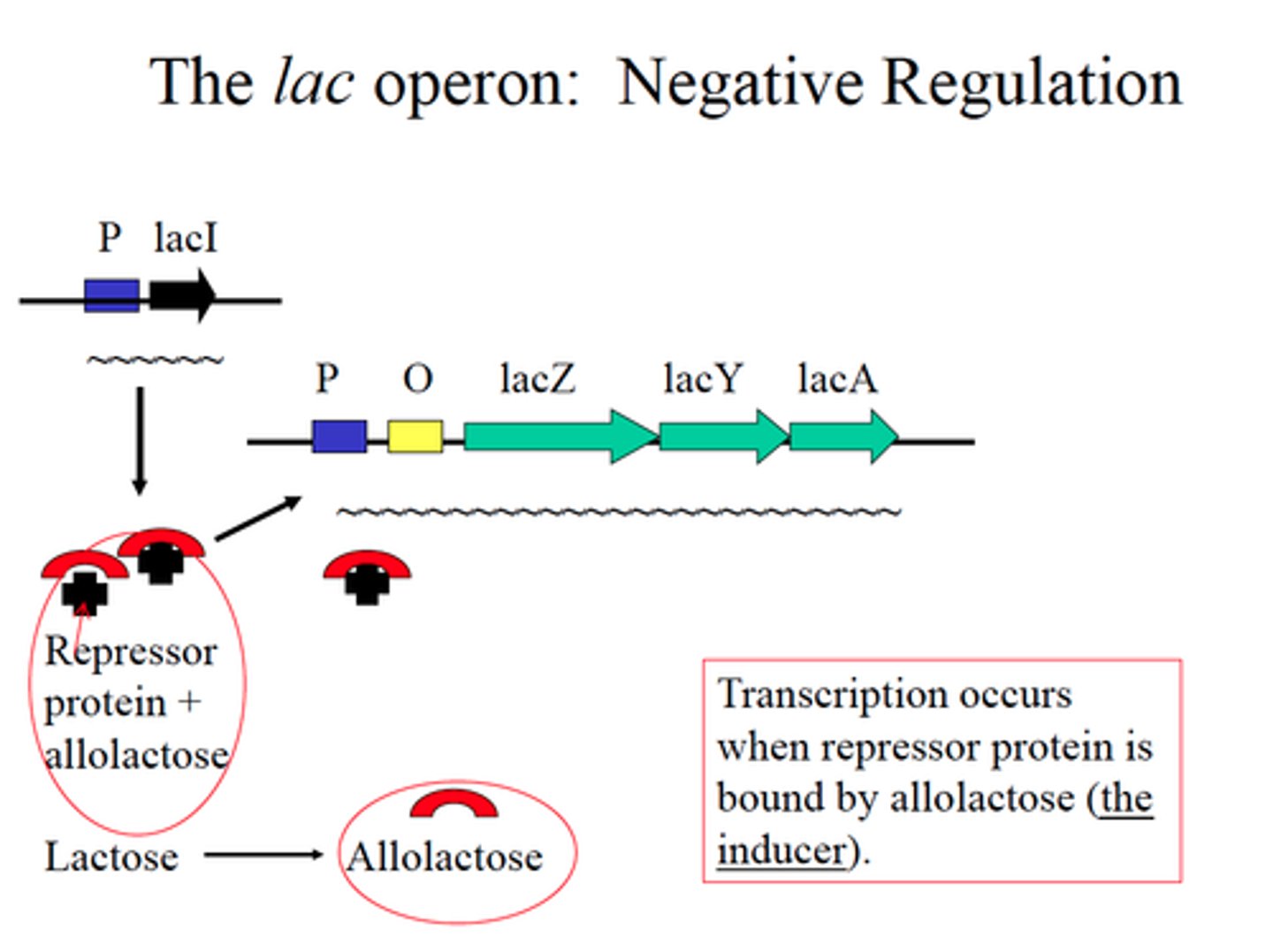
negative regulation
-regulatory protein shuts down transcription
-repressor protein
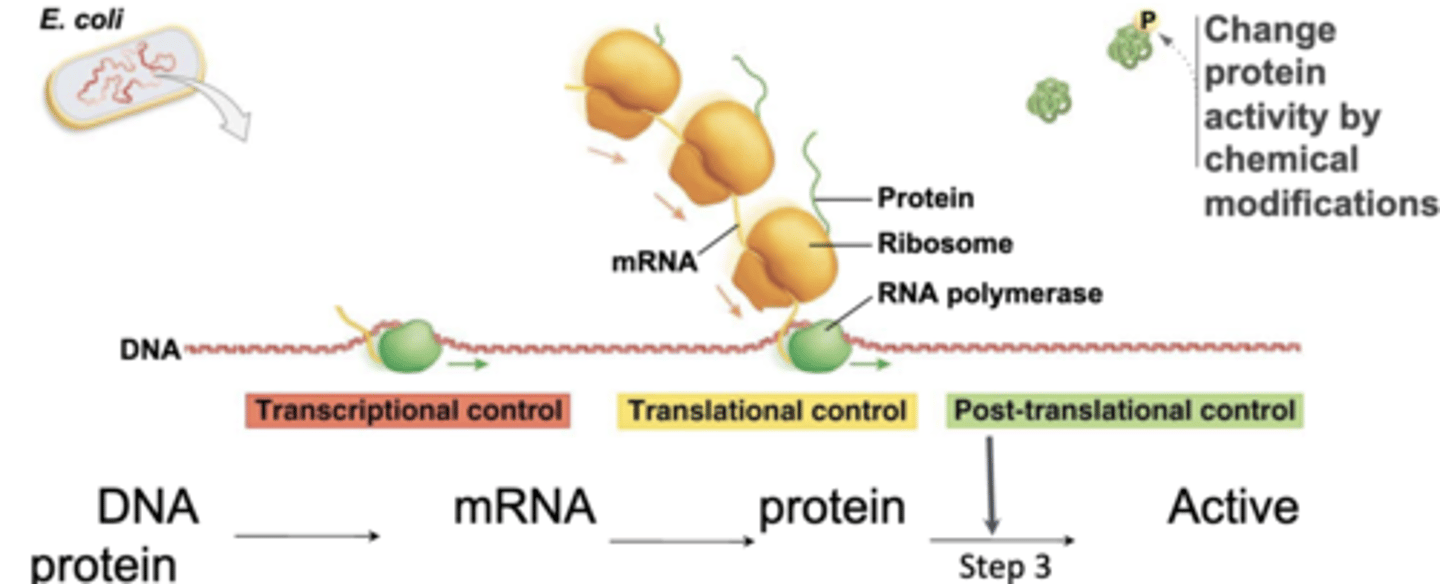
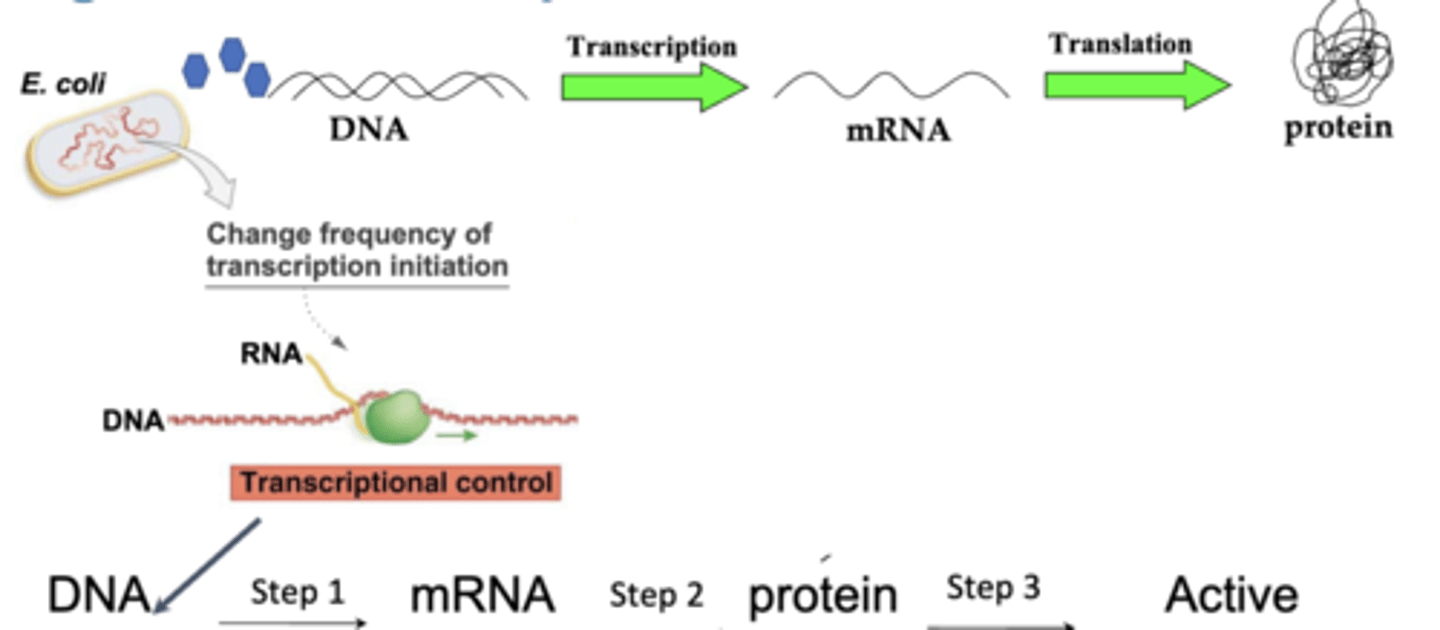
transcriptional control
-regulatory mechanisms that operate on the DNA and affect the rate at which transcription initiates
-most efficient but longest for cell to respond
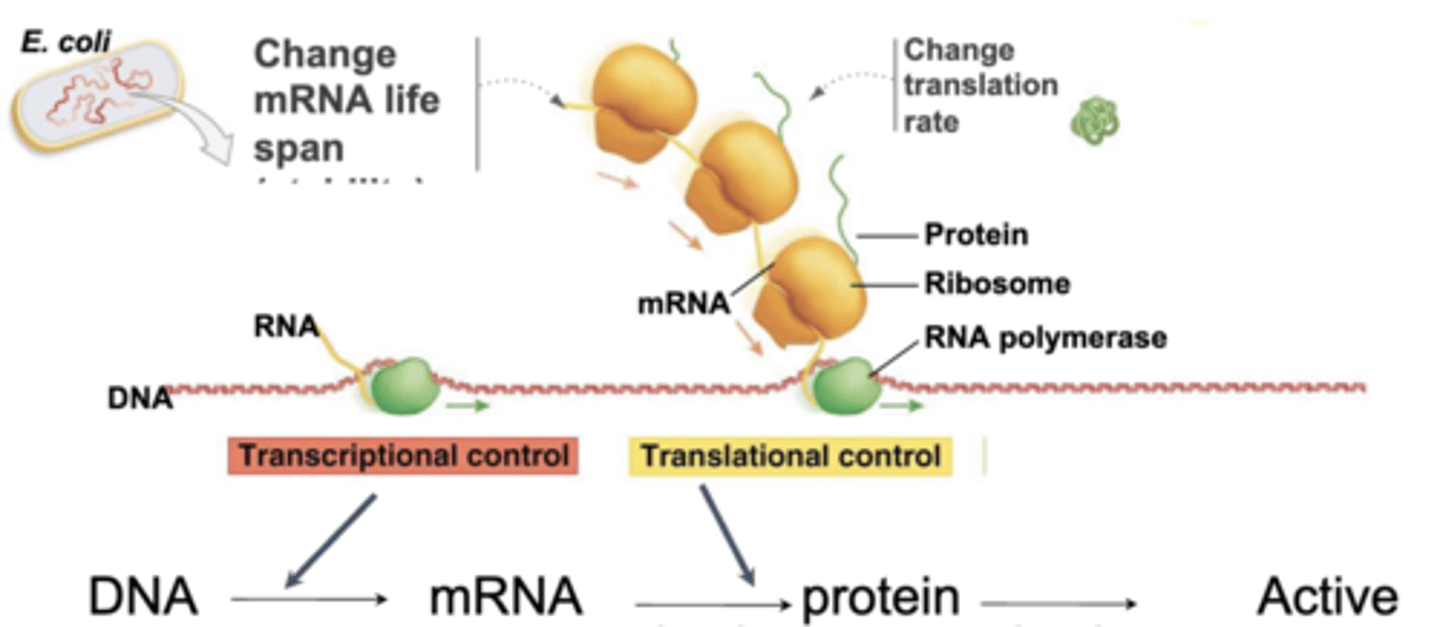
post-transcriptional (translational)
-regulatory mechanism that operates on preexisting mRNA and affects mRNA lifespan, which impacts translation
-more rapid than transcriptional control
post-translational control
-regulatory mechanisms that operate on the protein after synthesis and affect protein activity
-mechanisms that activate and inactivate a protein
-provides the most rapid response and only one step is needed to activate/inactivate an existing protein, but least efficient