Cell division and cellular organisation exam Q's and flashcards
1/190
Earn XP
Description and Tags
q
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
191 Terms
name one process that occurs in G1 and G2 (1)
-growth of cell
-growth of organelles
-protein synthesis
name the type of nuclear division that produced two genetically identical nuclei (1)
mitosis
during interphase the genetic material is copied and checked, state two other processes that occur during interphase (2)
-checking DNA for errors
-protein synthesis
-ATP production
-cell growth
in the cell cycle during the S phase, the genetic information is copied and checked, suggest what might happen if this does not occur (2)
-mutation/faulty DNA produced
-daughter cells do not receive identical genetic information
-daughter cells/proteins will not function
describe the role of mitosis (3)
-makes 2 genetically identical daughter cells
-growth
-repair of tissues
-asexual reproduction
during mitosis the chromosomes line up at the equator, describe what happens to chromosomes after this, until the nuclear envelope disappears (4)
-attached to spindles by centromeres
-centromeres splits
-spindle fibres shorten and pull chromosomes to poles of cell
-centromere leading
-spindle fibres disappear
-DNA starts to uncoil
outline what happens to the chromosomes during the mitotic cell cycle (9)
-prophase the chromosomes condense and become visible, nuclear envelope disappears
-metaphase they align on the equator attached to spindle fibres by their centromeres
-anaphase the centromeres split, spindles shorten and chromatids move to either end of cell separating them
-telophase the chromosomes uncoil, nuclear envelope starts to reform, spindles disappear
-cytoplasm splits into two identical cells in cytokinesis
state two ways cell division in plants differs from cell division in animals (2)
-in plants a cell wall will form
-no centrioles in plants
-only occurs in meristem cells
state three reasons why mitosis is important to organisms (3)
-growth of tissue
-repair of tissue
-asexual reproduction
-maintaining chromosomes number in all cells
during mitosis before the division of the cell, the genetic material must replicate, explain why this is essential (2)
-cells produced from mitosis must have the same DNA
-replication ensures both daughter cells are genetically identical to parent (diploid cells)
explain what is meant by a homologous pair of chromosomes (3)
-one maternal and one paternal
-carry the same genes
-usually similar length
-genes occur at same loci
-centromere in the same position
state what is meant by the term stem cell (2)
-a cell that is unspecialised capable of mitosis and able to differentiate
-able to divide
-can become any type of cell
name one tissue in plants that contains stem cells (1)
meristem
state what is meant by a tissue (2)
-a group of specialised cells
-working together to perform a specific function
what is the function of a squamous epithelium (2)
-cells that can act as a surface
-provide a short diffusion pathway
where are squamous epithelium located in the body (1)
-cheek lining
-alveoli
-blood vessels
what is the function of a ciliated epithelium and where is it located in the human body (2)
-waft mucus away from lungs
-found in the bronchi/trachea
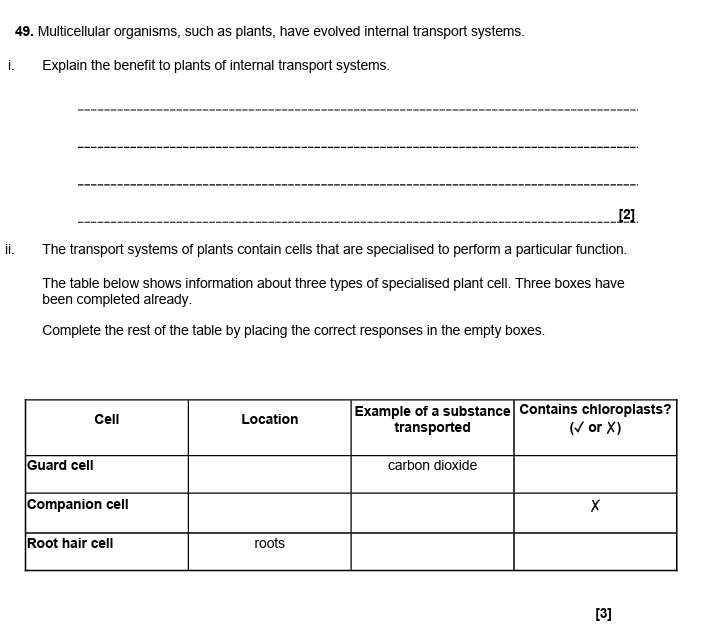
describe how cells are organised into tissues, using the xylem and phloem as examples (4)
-xylem made up of dead cells joined end to end to form a continuous tube (no cell contents)
-walls are lignified
-have pits in walls to allow lateral movement of water
-involved in movement of water (transpiration)
-phloem made up of sieve cells and companion cells
-sieve cells have no nucleus and many plasmodesmata
-involved in translocation (transport of assimilates/sucrose)
describe how cells in a multicellular organism are organised (5)
-cells differentiate and become specialised
-groups of cells form tissues
-groups of tissues form organs
-groups of organs form organ systems
-all of these work together to form a particular function
-e.g the digestive system is made up of many organs such as stomach, gall bladder, intestines, mouth etc.
meiosis is used in many organisms for the production of gametes, explain why meiosis needs to have twice as many stages as mitosis (2)
-to half the chromosome number (make haploid cells)
-to separate the homologous pairs and sister chromatids
-because DNA replicated have two chromatids at start
describe the difference between prophase I and prophase II of meiosis (2)
-prophase I the homologs chromosomes pair up and crossing over occurs
-in prophase II no crossing over occurs
describe the behaviour of the chromosomes in meiosis which results in genetic variation (8)
-prophase I the homologous chromosomes form bivalents/pair up
-crossing over occurs at the chiasmata
-DNA is exchanged between homologous chromosomes
-metaphase I independent assortment as bivalents line up randomly on the equator
-metaphase II independent assortment of chromatids as they line up randomly
-chromosomal mutation
state two processes that occur in a cell during interphase to prepare for a meiotic division (2)
-DNA replication
-protein synthesis
-organelle synthesis
-generation of ATP
explain why DNA in two sister chromatids is identical (2)
-semi conservative DNA replication
-DNA helices breaks H bonding between two DNA strands
-each DNA strand acts as a template
-complimentary base pairing
-sugar phosphate backbone forms
explain why the DNA in two sister chromatids in metaphase may no longer be identical (2)
-crossing over
-in prophase
-recombination of non sister DNA
state one difference between meiosis in plant and animal cells (1)
-centrioles absent
-no telophase I/nuclear membrane formation
-spore formation in plants, gamete formation in animals
explain how meiosis and fertilisation in sexual reproduction leads to variation within a population (8)
-prophase I the homologous chromosomes form bivalents/pair up
-crossing over occurs at the chiasmata
-DNA is exchanged between homologous chromosome - results in new combination of alleles
-metaphase I independent assortment as bivalents line up randomly on the equator
-metaphase II independent assortment of chromatids as they line up randomly
-gametes are genetically different
-random fusion of gametes
-random mating within population
-any sperm can fertilise any egg
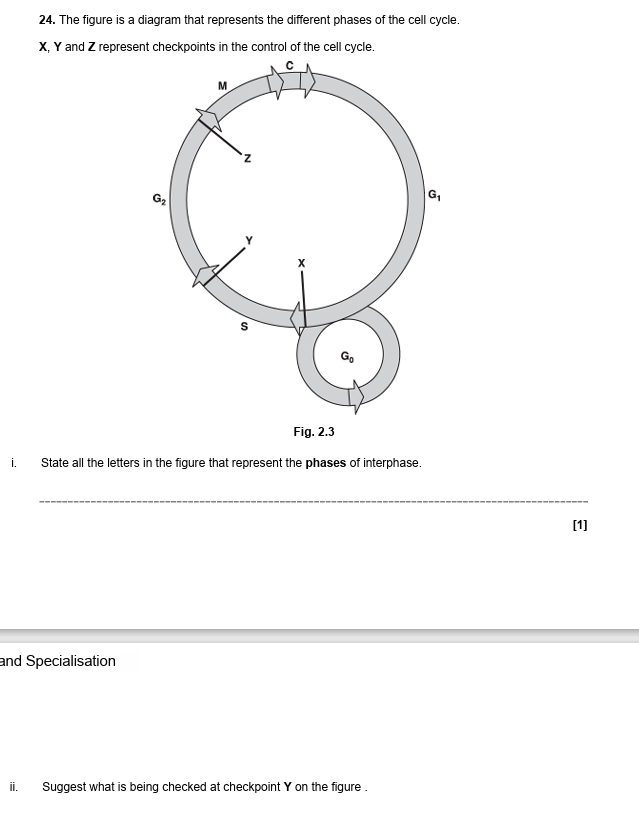
what does the G1 check point check for? (1)
cell growth
what does the S checkpoint check for (1)
-DNA synthesis
-correct DNA replication
what does the G2 checkpoint check for (1)
-checks whether mitosis is completed
-DNA damage
suggest how the organisation of homologous chromosomes during metaphase I increases genetic variation (3)
-bivalents randomly line up on equator
-independent assortment
-can be maternal or paternal
name two potential sources of human stem cells, and for ONE source describe an ethical issue associated with the use (3)
-foetus/embryonic
-bone marrow
-embryo must be destroyed
state 3 processes that occur in interphase (3)
-DNA replication
-DNA checked for errors
-protein synthesis
suggest why it is important that the gametes in the life cycle contain the haploid number of chromosomes (2)
-to make a diploid gamete when fuse
-prevents doubling of chromosome number
before the division of a cell, genetic material must replicate, explain why this is essential (2)
-so that the cells are genetically identical
-both daughter cells receive a full copy
name the process of asexual reproduction in yeast (1)
budding
suggest how cells produced by meiosis may differ from cells produced by mitosis (2)
-4 haploid daughter cells made
-genetically non identical
state the correct term for the communication between cells (1)
cell signalling
name the process of cell division in bacteria (1)
binary fission
describe how the structure of cell walls in xylem would differ from the cell walls of plant cells (2)
-made of lignin
-have pits
-thicker
state the name given to cancer causing chemicals (1)
carcinogens
describe the products of a mitotic cell division (3)
-2 diploid genetically identical daughter cells made
-genetically identical to parent

1.
i = some cells contain incorrect number of chromosomes
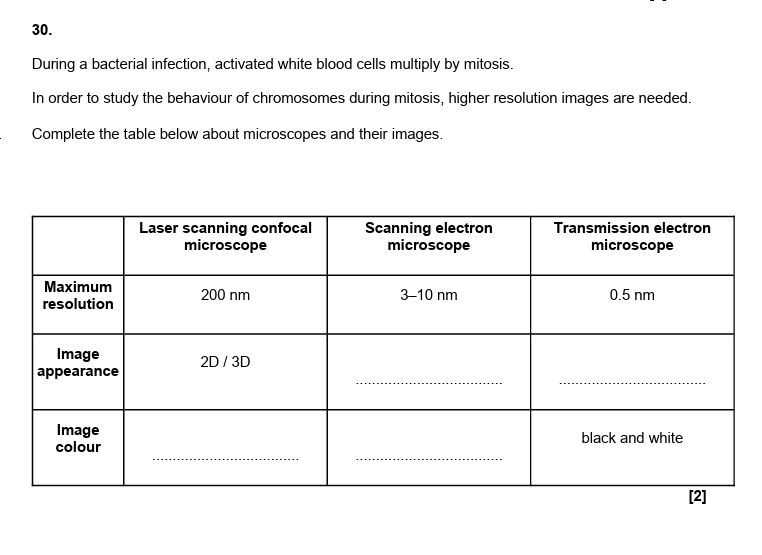
ii = G1 checkpoint
cells with damaged DNA should be stopped from entering S phase
G1 checkpoint is the point where DNA damage is checked
2.
G1, S and G2
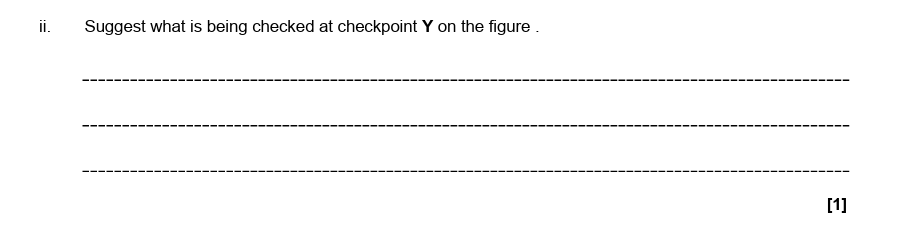
3.
checking that DNA has been replicated correctly
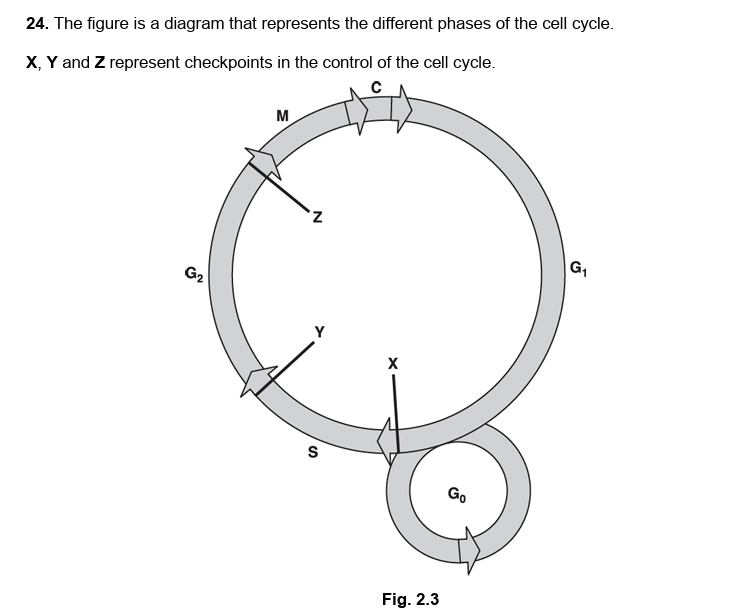
4.
G1 first growth phase
G2/ second growth or end of S/ synthesis
G1 first growth phase

5.
i = 1.3 × 10^11
ii = red blood cells do not contain DNA
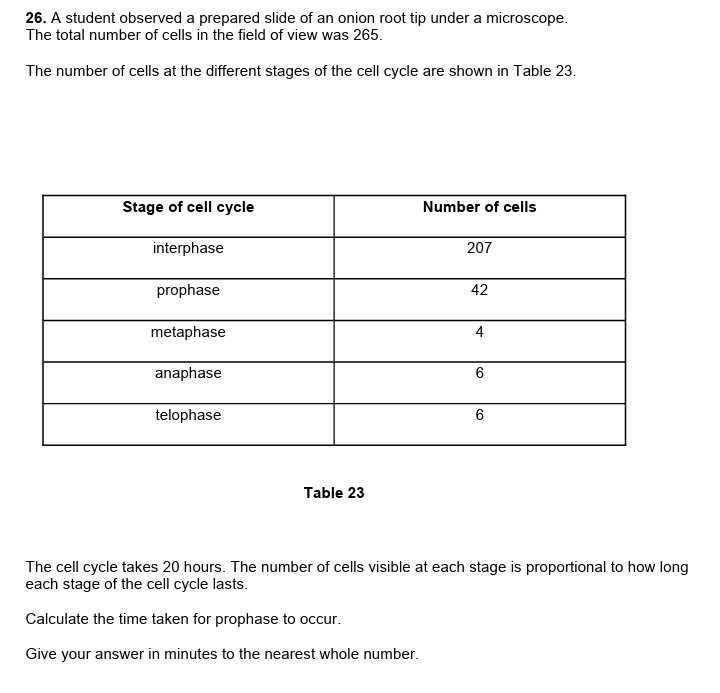
6.
Calculate

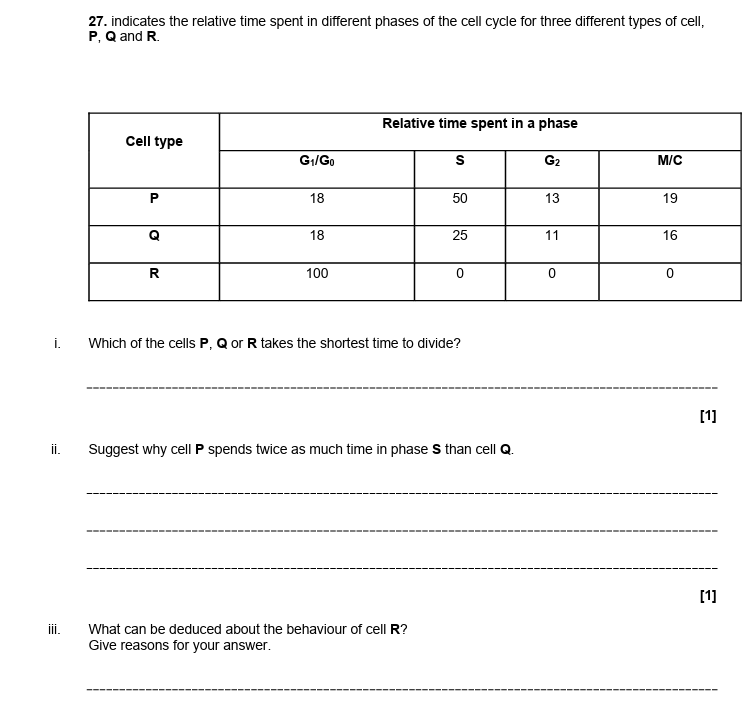
7.
i = Q
ii = P needs to synthesise/ contains more DNA/ more genetic material/ more chromosomes
iii = it spends all of its time in G1/ does not leave G0
so is not dividing/ replicating/ undergoing mitosis
specialised/ differentiated
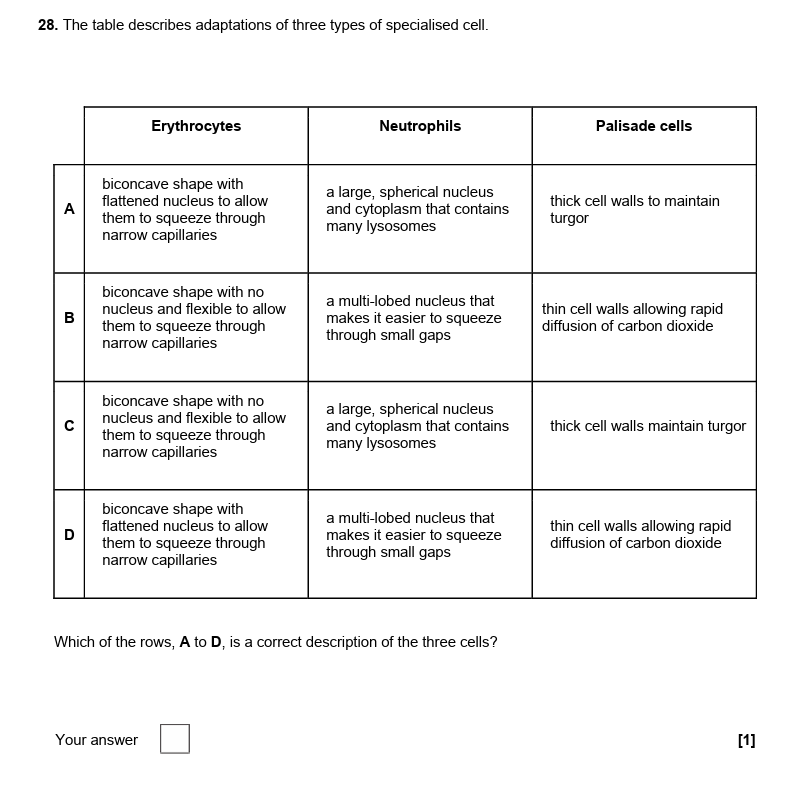
8.
B
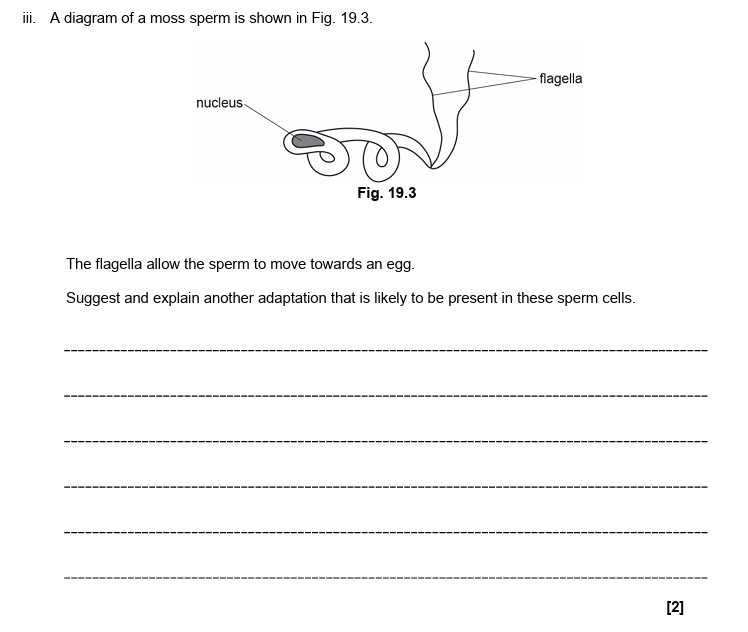
9.
many mitochondria
to supply energy/ ATP for movement
10.
write

11.
larger number of organelles
more DNA/ larger nucleus
no visible chromosomes
nuclear membrane present
12.
D

13.
D
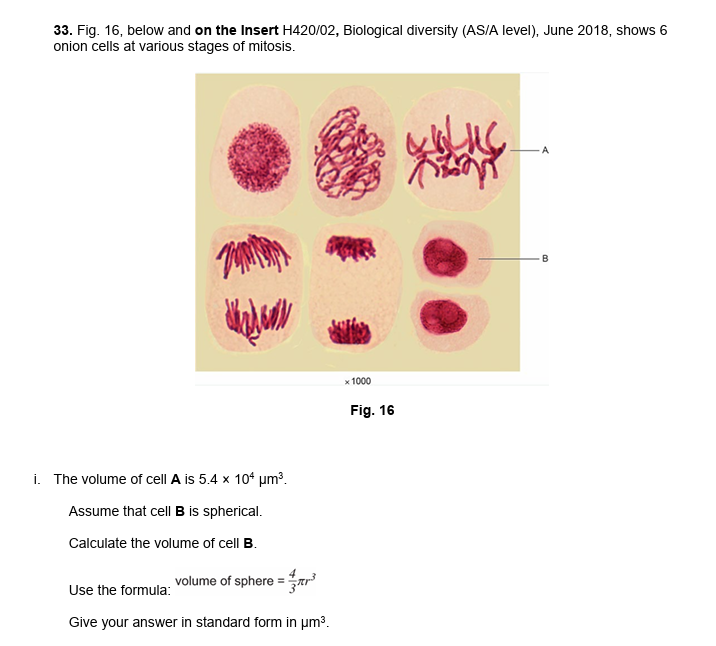
14.
calculate

15.
light microscope because magnification is only 1000 within LM range
colour visible
other subcellular structures/ organelles not visible
wide field of view

16.
cloning
proliferation of white blood cells
producing gametes from haploid cells
production of new stem cells
17.
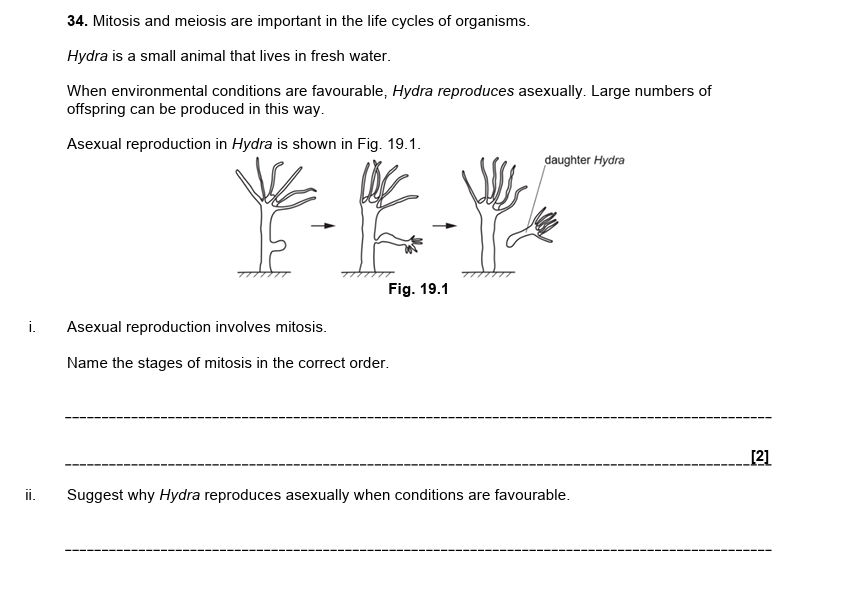
i = prophase then metaphase then anaphase then telophase
ii = genetically identical offspring
offspring produced rapidly/ in large numbers
all offspring will find conditions favourable/ have same adaptations
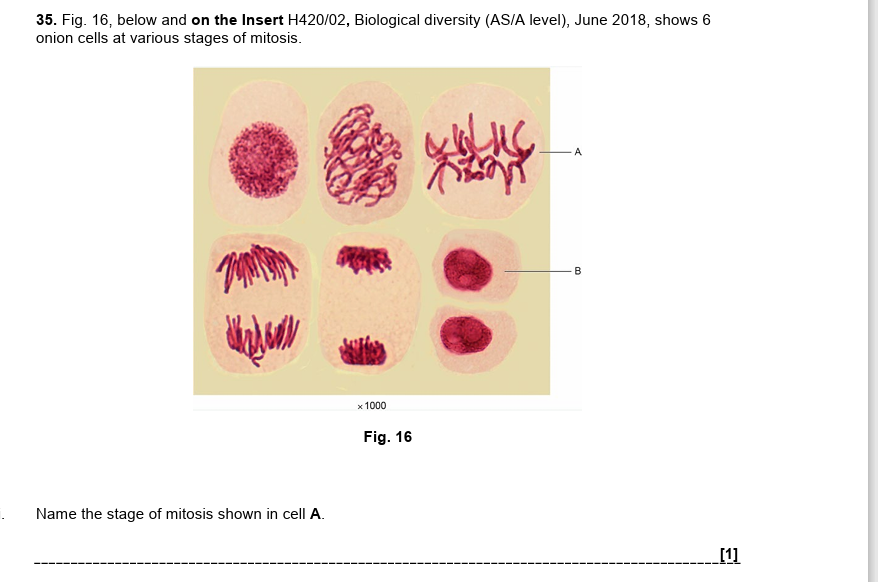
metaphase
18.
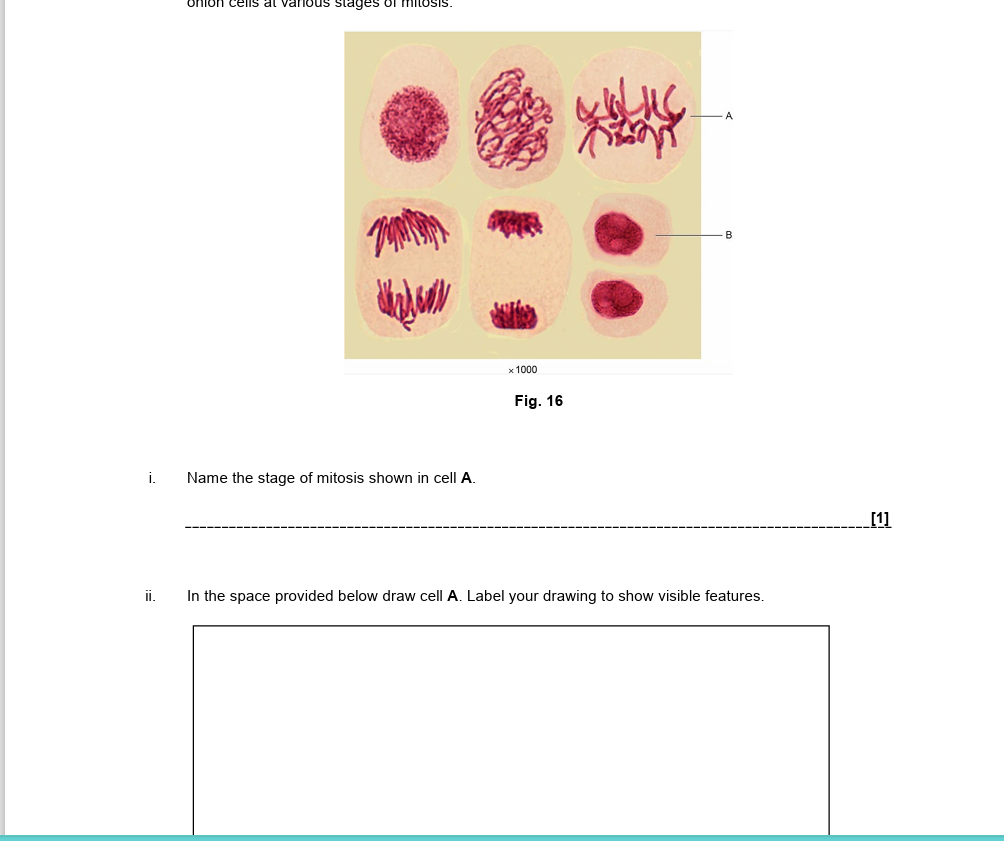
19.
draw
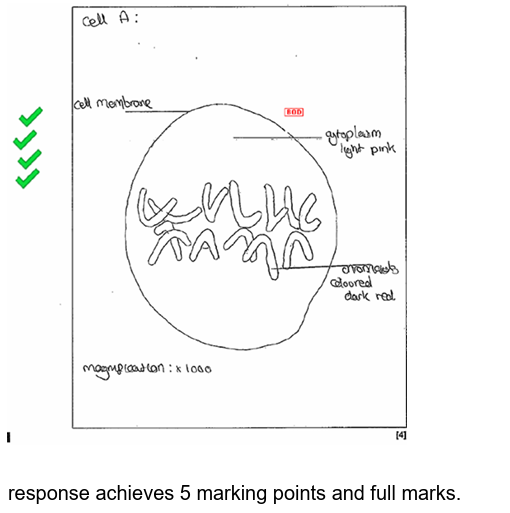
20.
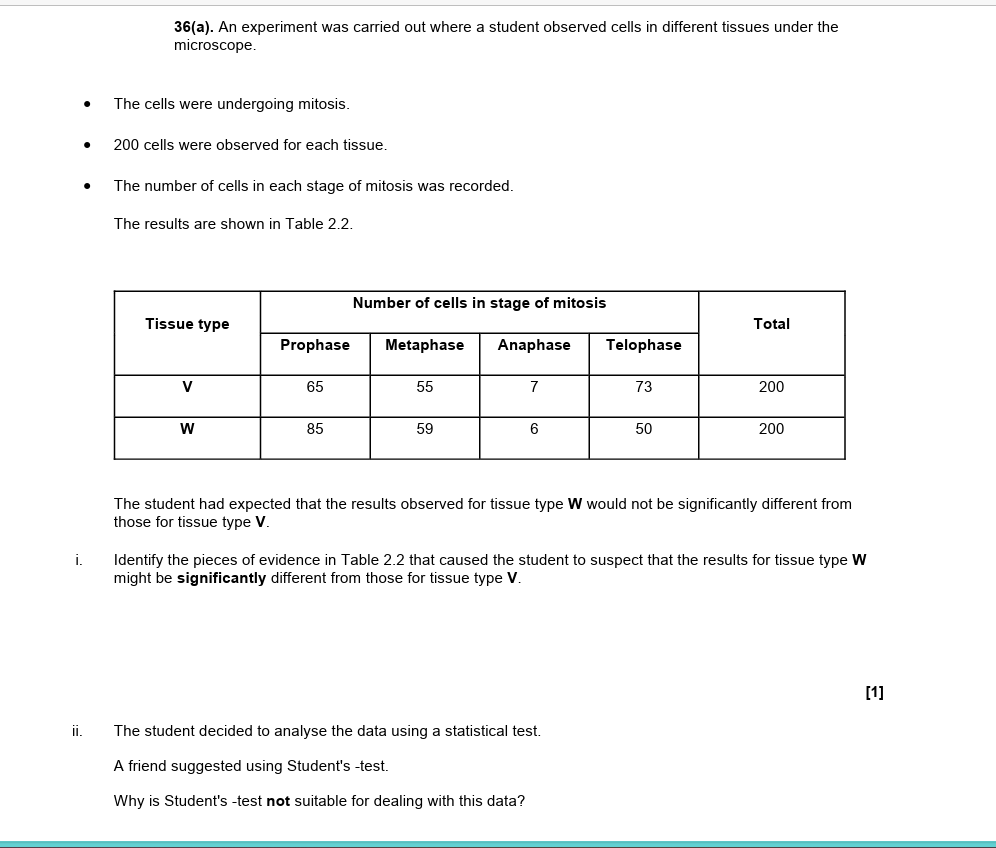
i = W it has many more cells in prophase and far fewer cells in telophase
ii = t - test compares two or more means
cannot calculate mean from this data
the idea that there are two or more categories

21.
i = R, Q, S, P
ii = chromosomes/ centromeres aligning on equator/ mitotic plate/ metaphase plate of cell
chromatids either side of equator
spindle fibres attaching to chromosome/ centromere
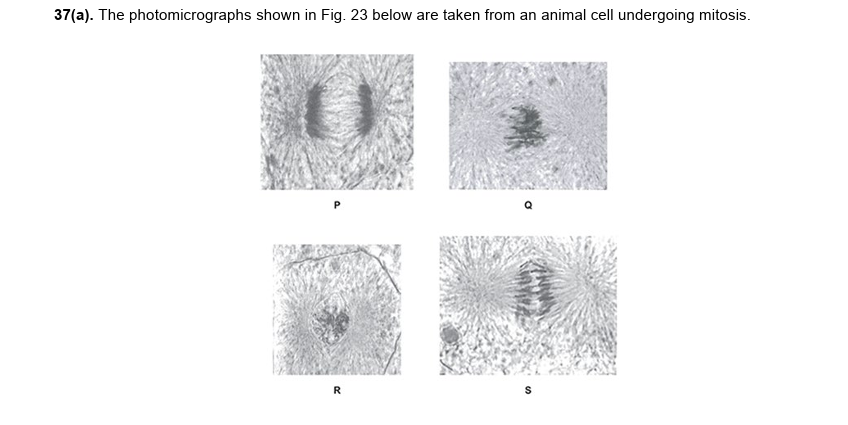

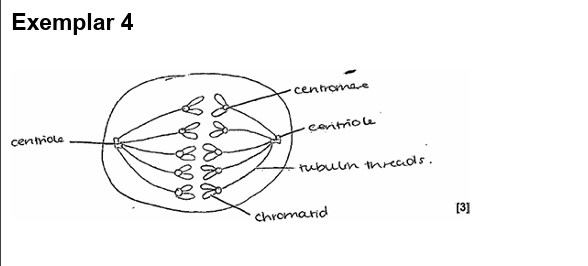
22.
drawings

23.
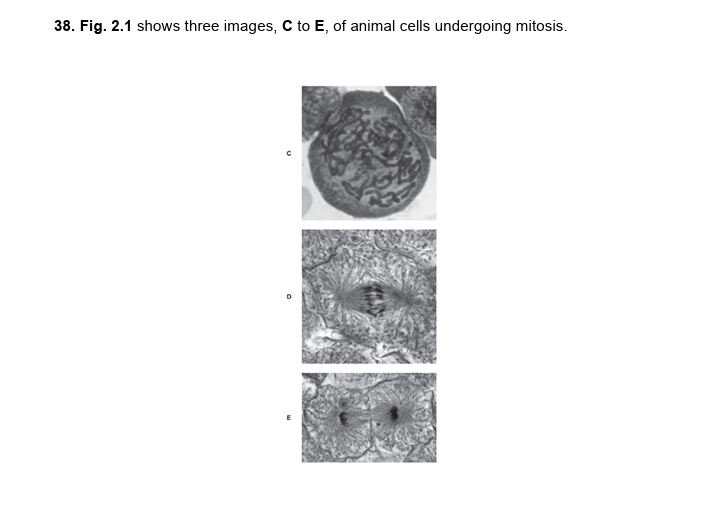
cell C:
prophase
chromosomes condense
chromosomes have become visible
nuclear envelope and nucleolus have disappeared
cell D:
early anaphase
spindle fibres are shortening
chromatids are separating and are being pulled to opposite sides of the cell
cell E:
late telophase
chromatids have been pulled to opposite sides of the cell
a new cell membrane is visible down the centre of the cell
cytokinesis/ the cell is beginning to divide

24.
mitosis for growth of zygote/ embryo
which needs genetically identical cells
not meiosis as gametes/ haploid cells not produced

25.
B
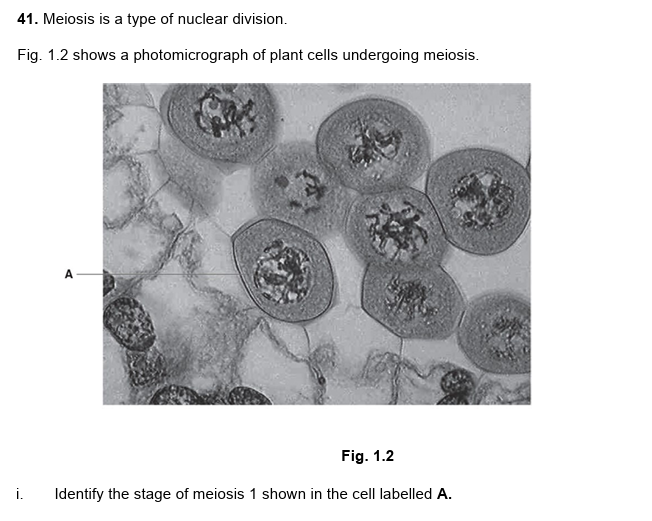
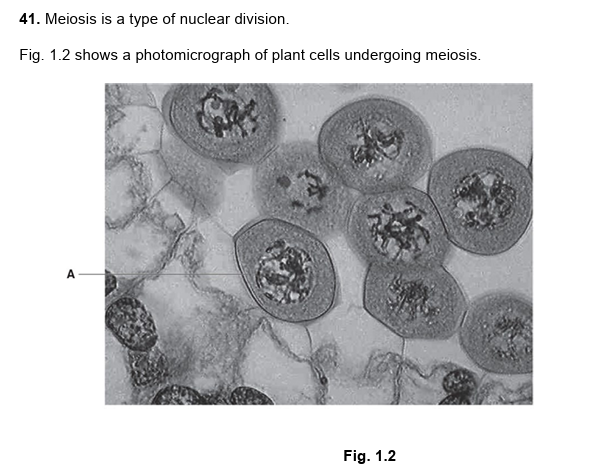
26.
prophase

27.
chromosomes/ chromatids visible/ condensed
chromosomes not organised/ yet aligned/ chromosomes not at the end of the equator
nuclear envelope around chromosomes/ nuclear membrane is present/ chromosomes separated from cytoplasm
no visible nucleolus
28.
independent assortment
homologous chromosomes line up on the equator/ on the metaphase plate
maternal or paternal chromosomes
each chromosome of the homologous pair is genetically different/ contains different alleles
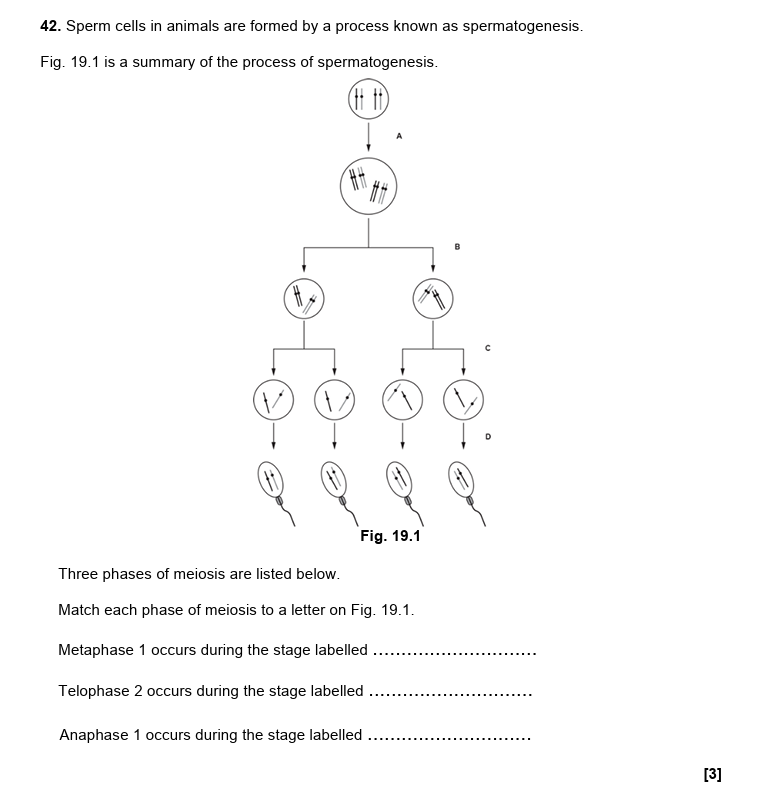
29.
B, C, B

30.
genetic variation is the variety of alleles
offspring have alleles from more than one parent
random fertilisation
meiosis produces genetically unique gametes
crossing over in prophase 1
alleles swapped between non-sister chromatids
base sequence of chromosomes altered
independent assortment in metaphase 1
independent assortment may occur in metaphase 2 if crossing over has occurred
the sperm from one hydra can fertilise an egg from any other Hydra individual
the two hydra can have different alleles
sperm carried in water might travel large distances to unrelated hydra

31.
some offspring might survive unfavourable conditions
some offspring have useful alleles
unfavourable conditions mean all offspring might die if asexual
32.
write

33.
produced in meristems
by differentiation from stem cells
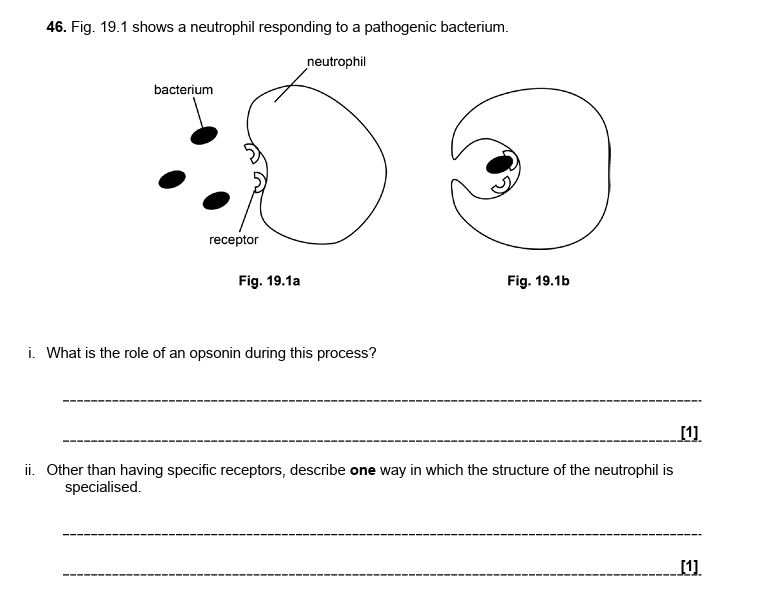
34.
i = opsonin binds to antigen on pathogen and assists binding to phagocyte'
ii = well-developed cytoskeleton
many lysosomes
many mitochondria
lobed nucleus

35.
a) synthesise a lot of haemoglobin
remove/ digest organelles associated with protein synthesis
b) can be grown into different tissues to test how effective new medicinal drugs are
can be grown into different tissues to test for side effects/ toxicity of new drugs
can be grown and studied (developmental research)
cell function can be studied to find out what can make it fail to work properly in certain diseases e.g. cancer

36.
muscle tissue is a group of cells which contract together
a muscle is an organ that consists of muscle tissue and other tissues working together
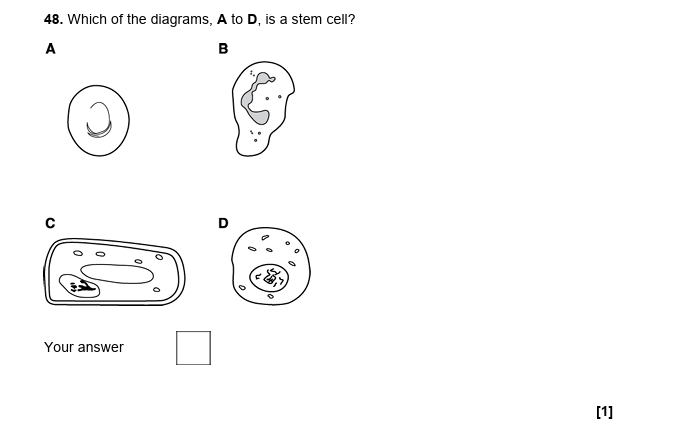
37.
D
38.
i = surface area to volume ratio too small
diffusion from outer surface is not sufficient
transport system ensures molecules/ nutrients/ sugars/ water reach all tissues
allows high metabolic rate

39.
organ is a collection of tissues
perform a function/ role
leaves have epidermis/ spongy mesophyll/ palisade mesophyll/ vascular/ phloem/ xylem tissues
to carry out photosynthesis/ gaseous exchange

40.
have already differentiated/ specialized so cannot divide
are in G0 phase of cell cycle/ resting phase
shape is too irregular/ asymmetrical so cannot divide
cytoskeleton cannot function/ spindle fibres cannot form
if mitosis occurred it would alter number/ size of the gaps
it would alter an aspect of ultrafiltration

41.
adult stem cells are multipotent
differentiate to become any cell type within kidney/ nephron tissue
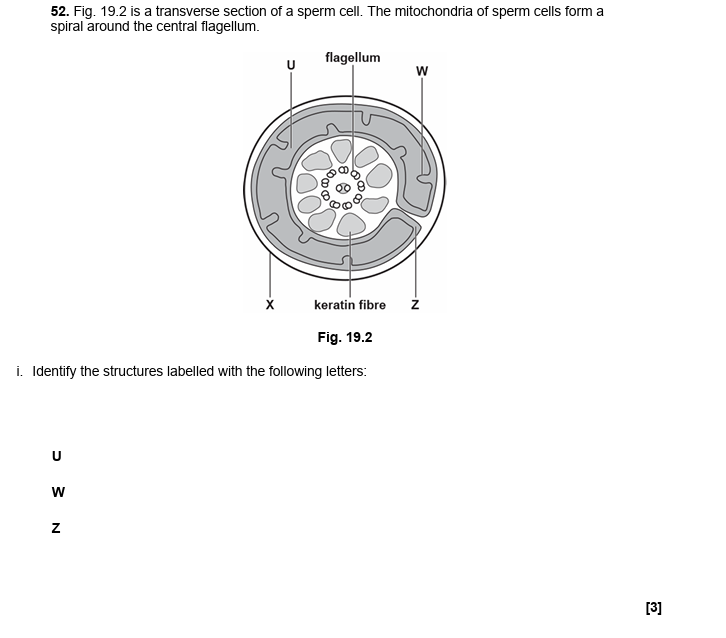
42.
U = matrix
W = cristae/ inner mitochondria membrane
Z = inter-membrane space
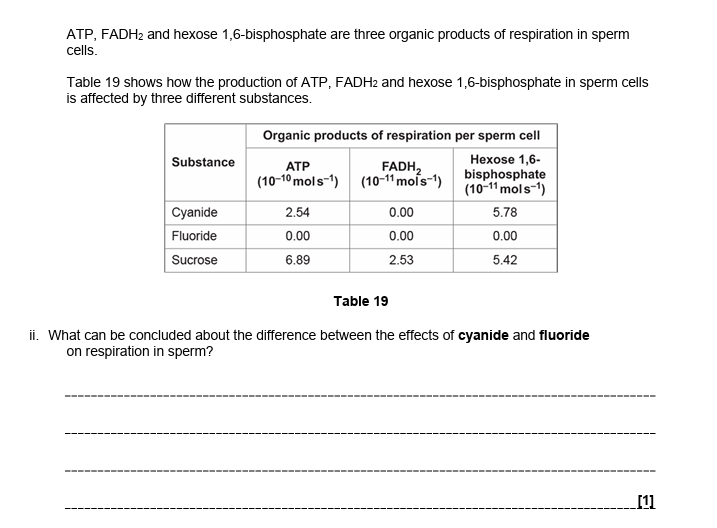
43.
cyanide prevents aerobic respiration
fluoride prevents anaerobic respiration which also prevents aerobic respiration

44.
A
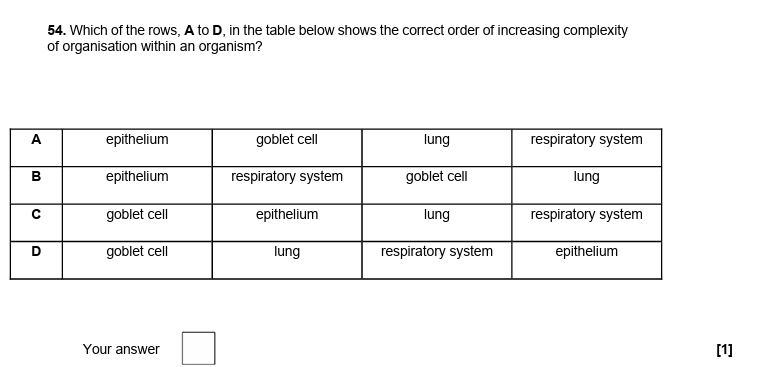
45.
C

46.
i = embryonic stem cells are undifferentiated/ not specialised
are a renewing source of cells
can differentiate into any cell type of the developing foetus
ii = not totipotent stem cells:
as cannot form whole organism
cannot form any cell/ tissue type
cannot give rise to extra-embryonic stem cells
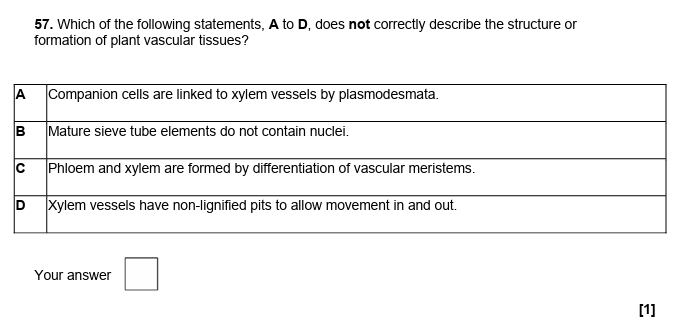
A

48.
i = to provide lots of energy/ ATP
ii = golgi apparatus
to modify/ process/ package protein
vesicles/ secretion of mucus/ exocytosis

49.
error 1: erythrocytes/ neutrophils formed in the spleen
correction: formed in bone marrow
error 2: ciliated epithelial cells in blood vessels
correction: found in trachea/ bronchi/ bronchioles/ airways/ lungs
error 3: cell wall thickest on side furthest from stomata
correction: cell wall thinner on side furthest from stomata

50.
calculate

51.
erythrocyte/ red blood cell:
biconcave/ flattened disc
no nucleus
contain haemoglobin
flexible shape
7.5 μm diameter
2.0 μm thick
contain carbonic anhydrase
transport oxygen
transport carbon dioxide
move/ squeeze through blood vessels/ capillaries
space for oxygen/ haemoglobin is maximised
large surface area to volume ratio
short diffusion distance to centre of cell
neutrophil/ white blood cell:
many lysosomes
hydrolytic/ digestive enzymes
can change shape/ phagocytosis
10-14 μm diameter
immune response
non-specific/ inflammation
destroy/ engulf pathogens
move to site of infection/ wound
squamous/ epithelial cells:
flattened shape
very thin/ form layer/ one cell thick
fit together tightly for rapid diffusion/ short diffusion distance of oxygen/ carbon dioxide/ gases at alveoli/
ciliated epithelial cells:
have cilia/ hair like structures which move/ beat in rhythmic manner to move mucus
and trap pathogens/ dust/ debris from lungs/ airways
to move egg from ovary to uterus/ site of fertilisation
to move ventricular fluid multilobed nucleus
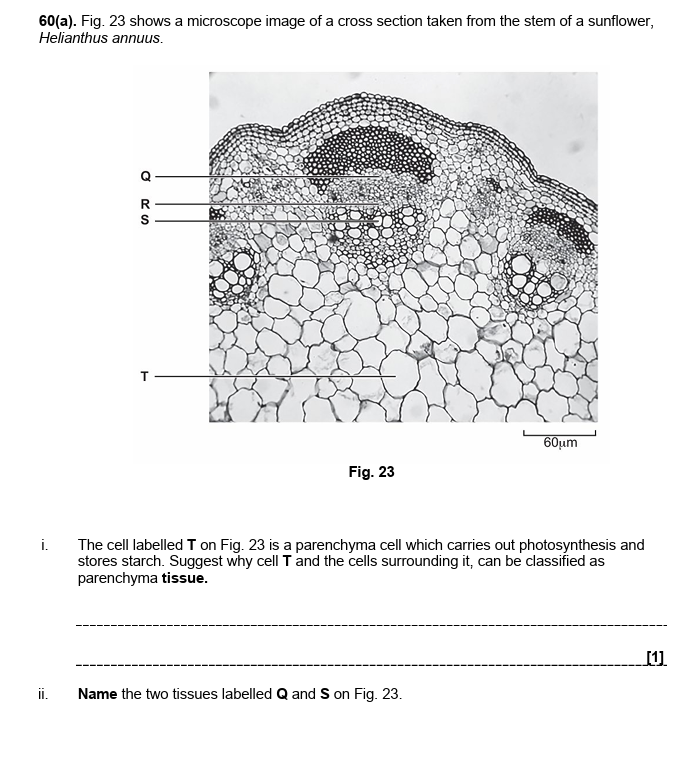
52.
i = similar cells working together to perform a function
ii = Q = phloem
S = xylem

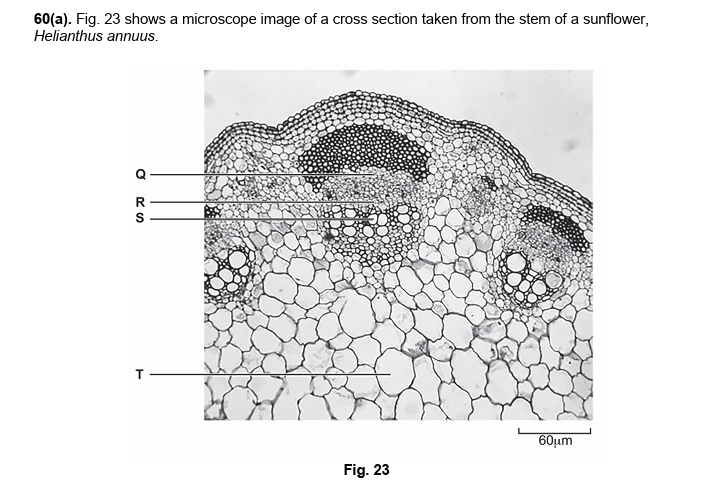
53.
meristem

54.
embryonic/ embryo - embryo destroyed/ killed/ discarded
fetus - debate about when life begins or embryo cannot give consent
umbilical cord
adult bone marrow tissue

55.
i = advantages: can carry more oxygen/ haemoglobin
can squeeze through capillaries easily
disadvantages: limited life span/ cannot divide/ cannot reproduce/ cannot undergo mitosis
no protein synthesis/ repair
no mitochondria for respiration
ii = virus:
virus is unable to replicate/ reproduce on its own outside a host cell
does not contain RER/ ribosomes for protein synthesis
plasmodium:
plasmodium is using the host cell to hide from the immune system
plasmodium uses the host cell as a source of food/ growth/ reproduction

56.
oxygen is bound to haemoglobin while being transported
lack mitochondria
therefore no aerobic respiration
moved by mass flow so doesnt need energy/ ATP to move
less energy/ ATP for metabolic processes

57.
a) lamella
b) many lamellae provide large surface area
presence of secondary lamellae on main lamellae provide large surface area
short distance between blood and water
blood maintains diffusion gradient
faster diffusion of oxygen/ carbon dioxide

58.
tissue has few types of cell and performs few functions
bone has few types of cell
bone performs few functions
organs consist of several tissues
gills contain two or more tissues e.g. bone, blood, epithelial, connective tissue