Genetic Processes: Sex-Linked Inheritance and Mutations
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SBI3U (Secours)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Sex-Linked Inheritance and Transmission
transmission of genetic characteristics when they are carried on the X chromosomes
3 terms for describing the appearance of a sex-linked gene (the phenotypes)
1) Affected: characteristic manifests itself/is visible
2) Carrier: not affected, but have the gene
3) Unaffected: does not have the gene
In general, sex-linked diseases are:
recessive
which sex is more likely to be carriers, and which are more likely to be affected?
Carriers: females, because they have two X chromosomes
Affected: males, because they only have one X chromosome, so if the allele is present, they will have the disease
Pedigree
a diagram that illustrates the genetic relationship in a group of related individuals
another word for pedigree
genealogical tree
On a pedigree, _____ shapes are used for males, and _____ shapes are used for females
squares, circles
On a pedigree, if an individual is completely shaded in, they are ________. If they are ½ shaded, they are ______. If they are not shaded, they are _________.
affected, carriers, unaffected
On a pedigree, _____ are indicated with roman numbers, and _____ (including birth order) are indicated with arabic numbers.
generations, individuals
In human pedigrees, genotypes can only be _______ from the _____, they cannot always be determined with complete certainty.
inferred, phenotypes
the four main inheritance types
autosomal recessive
autosomal dominant
sex-linked recessive
sex-linked dominant
Autosomal Recessive features
traits will often skip a generation
parents can pass it on to offspring as carriers
male and female equally affected
both parents can be carriers
Autosomal Dominant features
no skipping of generations (everyone with the dominant allele is affected)
there will not be carriers
almost all individuals will be heterozygous
male and female equally affected
Sex-Linked Recessive features + examples
fathers can only pass on traits to daughters, not sons (carried on x chromosome)
sons can only recieve the trait from their mother
males are more likely to be affected
ex: hemophilia, colour-blindness, muscular dystrophy
Sex-Linked Dominant features + examples
similar to sex-linked recessive, except females will be affected if they recieve even 1 dominant allele
affected fathers will pass it down to daughters but not sons (again, carried on x chromosome)
ex: Fragile-X syndrome, vitamin-D resistant rickets
Mutation
A change in DNA that has a positive, negative, or neutral effect
What can cause genetic mutations?
Induced Mutations: environmental factors
Spontaneous Mutations: random errors during DNA replication, repair, or recombination
If cancer was caused by carcinogens (ex: smoking, sunlight), can it be passed down? Why?
No, they cannot. This is because only certain cells are affected, usually not the sex cells.
When will a mutation be passed down?
If the mutation occured in a germ/sex cell
5 types of mutations
Deletion
Duplication
Inversion
Insertion
Translocation

Identify the mutation:
deletion


Identify the mutation:
duplication

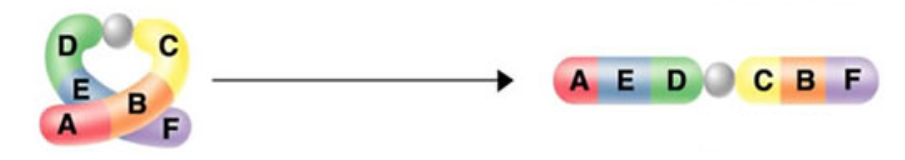
Identify the mutation:
inversion
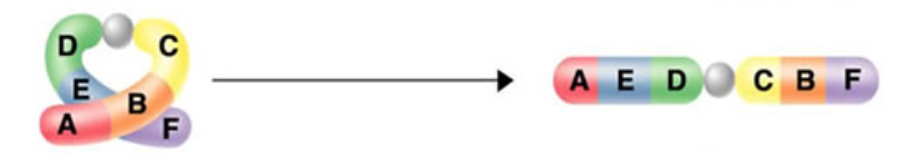
Identify the mutation:
insertion
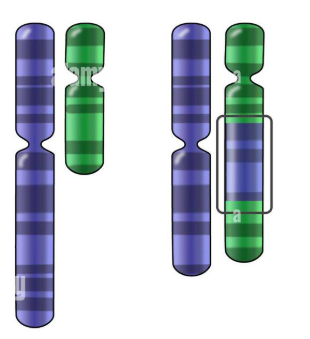
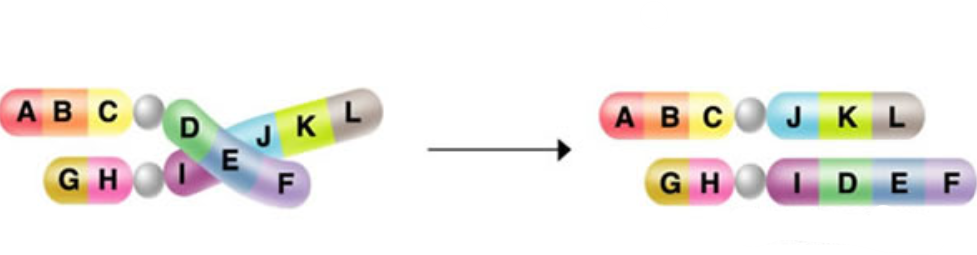
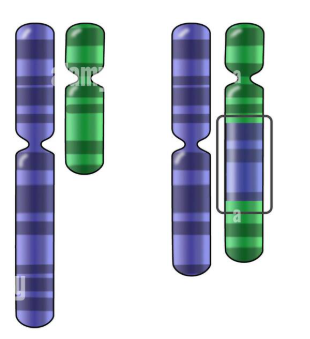
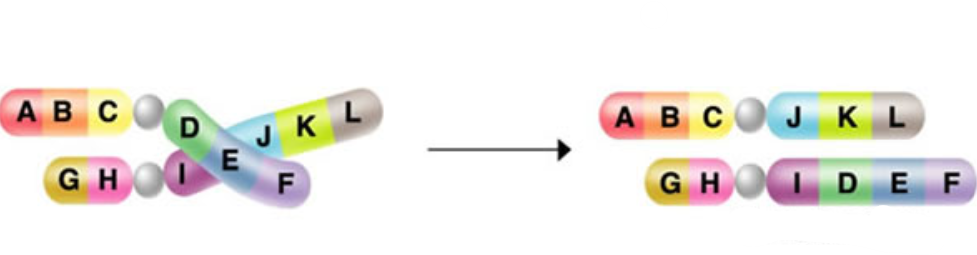
Identify the mutation:
translocation
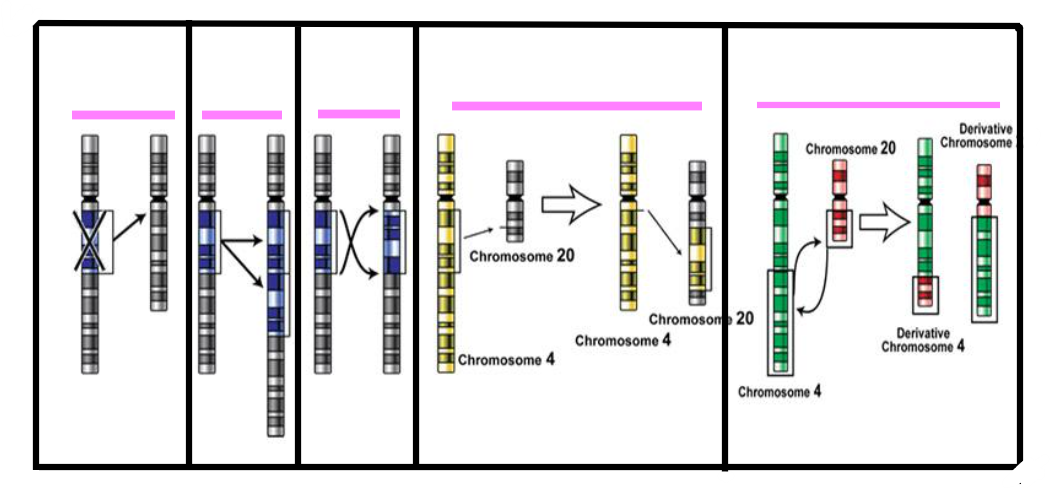
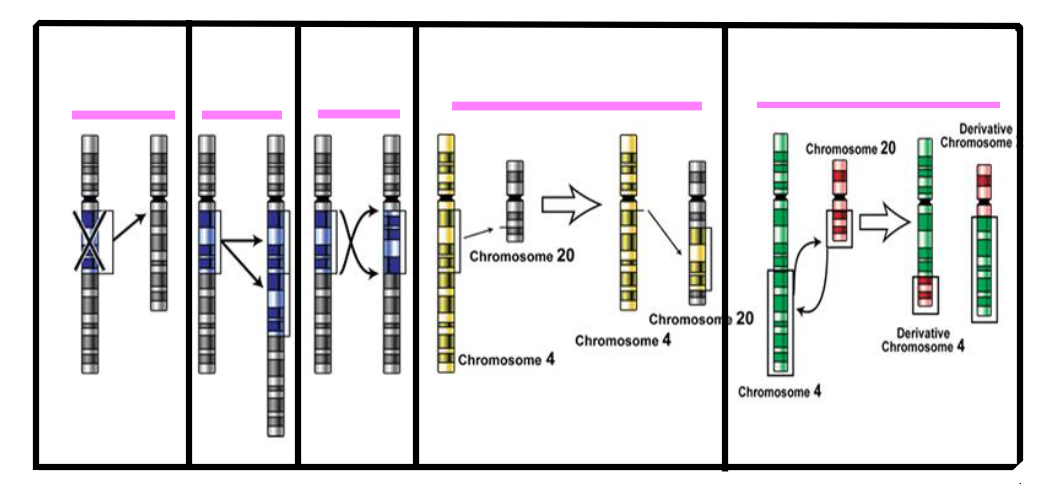
Identify all mutations:
deletion, duplication, inversion, insertion, translocation
Silent mutation
A mutation where the code changes, but the resulting amino acid does not (neutral effect)
Depending on the magnitude/size of the mutation, it is considered either:
Large scale mutation or point mutation
Large Scale Mutation
An entire portion of the chromosome is altered (rare)
Point Mutation
A small scale change in the sequence of the nitrogenous bases
⇨ Frame-Shift: a kind of insertion or deletion, where one of more nucleotides are added/deleged