BIO 1A03 T5M3-4: Applied Lecture - Genetic Variation and Innovations in Biology
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
hematocrit analysis
test to determine what your blood is composed of
1) prick finger and put blood into microcapillary
2) centrifuge ⇒ separation of blood into platelets, WBC and RBC
Should see:
Most is plasma
99.9% RBC (transport O2) + 0.1% platelets (helps w clotting) and WBC (immune)
production of RBC
First 7 stages = in bone marrow (where stem cells are constantly dividing and replicating & some stems cells are committing to become a RBC (committing cells)
Day 2-6: committing cell express hemoglobin
Day 4: nucleus is “kicked” out of the cell (∴ to make more space for hemoglobin)
⤷ kicked so it cannot control cell growth and repair
Day 5-7: cell is released into blood stream
Day 7: officially form the biconcave disc shape and become red (bidning O2, carried on hemoglobin)
* old/ruptured cells are replace new cells every 120 days (with 2 million RBC being produced by bone marrow per sec)
structure of RBC and hemoglobin
Each hemoglobin protein has 4 iron-containing heme-groups (1 per subunit) ⇒ allow each one to bind oxygen
Subunit co-operatively: the Fe3+ heme group captures oxygen → once oxygen binds to one unit, the other units change shape and are easier to bind to oxygen
270 million hemoglobin molecules PER RBC
Center @ biconcave disc = 1 micron, @ edge of donut = 3 microns
Small and high in quantity to maximize O2
ABO gene
blood type is expressed on this gene on chromosome 9
⤷ encodes for glycosyltransferase (enzyme that adds sugar to surface of RBC – modifies the carb content of the antigen)
⤷ diff patterns of sugars for people with type A, B, and O blood etc.
universal recipient and universal donor
AB blood type ⇒ universal recipients (can receive blood from anyone)
O blood type ⇒ universal donor (can donate for anyone) – ideally for O⊖ for rhesus factor
antigens
sugar-based markers on the cell membrane of RBC that are specific to ur blood cell type
⤷ genetically determined
blood types and their corresponding antigens found
Type A: blood type with type A antigens on the surface of RBC
Type B: blood type with type B antigens on the surface of RBC
Type AB: blood type with both type A and type B antigens on the surface of RBC
Type O: blood type with no blood type antigens on surface
⤷ ∴ universal donors
** if O blood is in the system for people with type A, B, AB, immune system will not attack
** if A, B, AB blood is in someone with type O ⇒ body is not used to seeing any of these antigens, will attack it
mismatch bloodtype during blood transfusion
During blood transfusions, the blood of donor must match with the blood of recipient
If mismatch, then the immune system of the recipience will recognize these cells as “foreign” and generate antibodies to teh donors RBC antigen
These antibodies will bind to the donor blood’s RBC and clotting (agglutination) will occur
Why is this a problem?
Makes blood transfusion useless
Can causes extreme blood clotting (agglutination) ⇒ leads to circulatory failure, organ failure and death
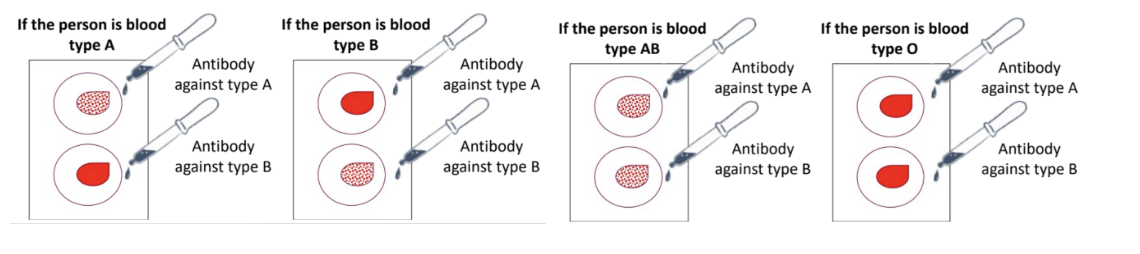
blood type testing
Take a glass slide with wells
Prick finger and add blood sample to the wells
Add antibodies against different antigens into the wells ⇒ see if clotting occurs
If clotting occurs, WILL BE that blood type ʙ that “antibody against type A” will look for type A antigens ⇒ if found == clotting = blood is type A
Dr Stephen Withers
Guy was able to make any blood type become any blood type by removing sugars
Inspired by gut microbes
Bacteria in body is able to acquire energy from multiple source s(esp when humans are not eating)
Eg. bacteria gets energy from sugars that are attached to the glycoprotein, mucin
Bacteria is able to cut and use these sugars because they have the right enzymes
Mucins have very similar structures to the sugars in our blood type ⇒ ∴ want to find enzymes that cuts sugars
Withers was able to isolate enzymes that are produced by the bacteria that live in the guts and these enzymes are added to donated blood to cut the antigens (sugars) from any RBC type ⇒ convert into O-type
Now in preclinical trials (other animal testing) ⇒ then tested in clinical trials (human) on a larger scale to see if its safe for humans and make sure it won’t lead to any complications
modified organ transplant
Currently
If A type blood = only receive organs from A type people
Research found (Withers + working with other people)
Able to strip away antigens from organs ⇒ tested a human’s kidney and see if body would have a reaction (the modified kidney inserted into brain dead person) ⇒ the body didnt attack it
∴ able to have a kidney transplant of a modified kidney