Ecdysozoans
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Nematoda Phylum
exist everywhere. parasites of plants and animals or free living. have external cuticle that is shed during growth and secreted by hypodermis. syncytial cells with nucleus below surface are gathered together into hypodermal cord
only have longitudinal muscles so can whip by shortening and relaxing them
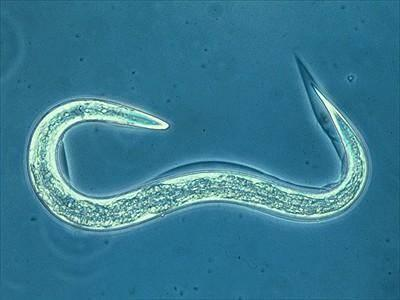
Nematoda Digestion
has mouth and muscular pharynx to suck in food. intestinal wall is only 1 cell thick. waste exits by anus via muscular contractions (squeezes and blasts out)
Nematoda Hypodermal Cord
4 chords. 2 lateral that have excretory ducts, 1 dorsal and 1 ventral that have dorsalventral nerve cords
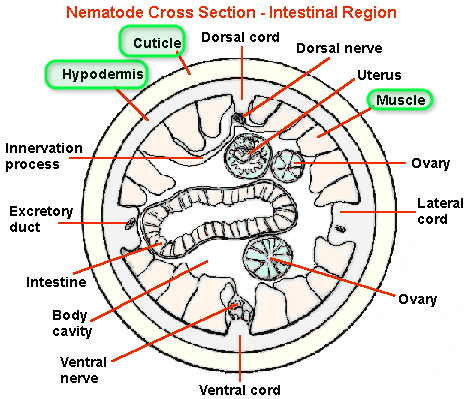
Nematoda Nerve Cord
contractile portion is under hypodermis with muscle cell body and nucleus below it, will extend arm (non-contractile) to meet the nerve cord. essentially the muscles send extensions to contact the nerve cord, instead of vice versa
Nematode Parasites
Ascaris - thru soil & feet
Hookworms - suck blood in intestine
Trichina - live in muscle cells, cause trichonosis
Filarial Worms - cause elephantiasis in humans and heartworm in dogs
Nematomorpha Phylum
horsehair worms. adults live in water and juveniles are parasites of arthopods, will make grasshoppers and crickets jump into pools because of attraction to shiny surfaces so adults can emerge. Have cuticle & only longitudinal muscles.
hypodermal cords like nematodes
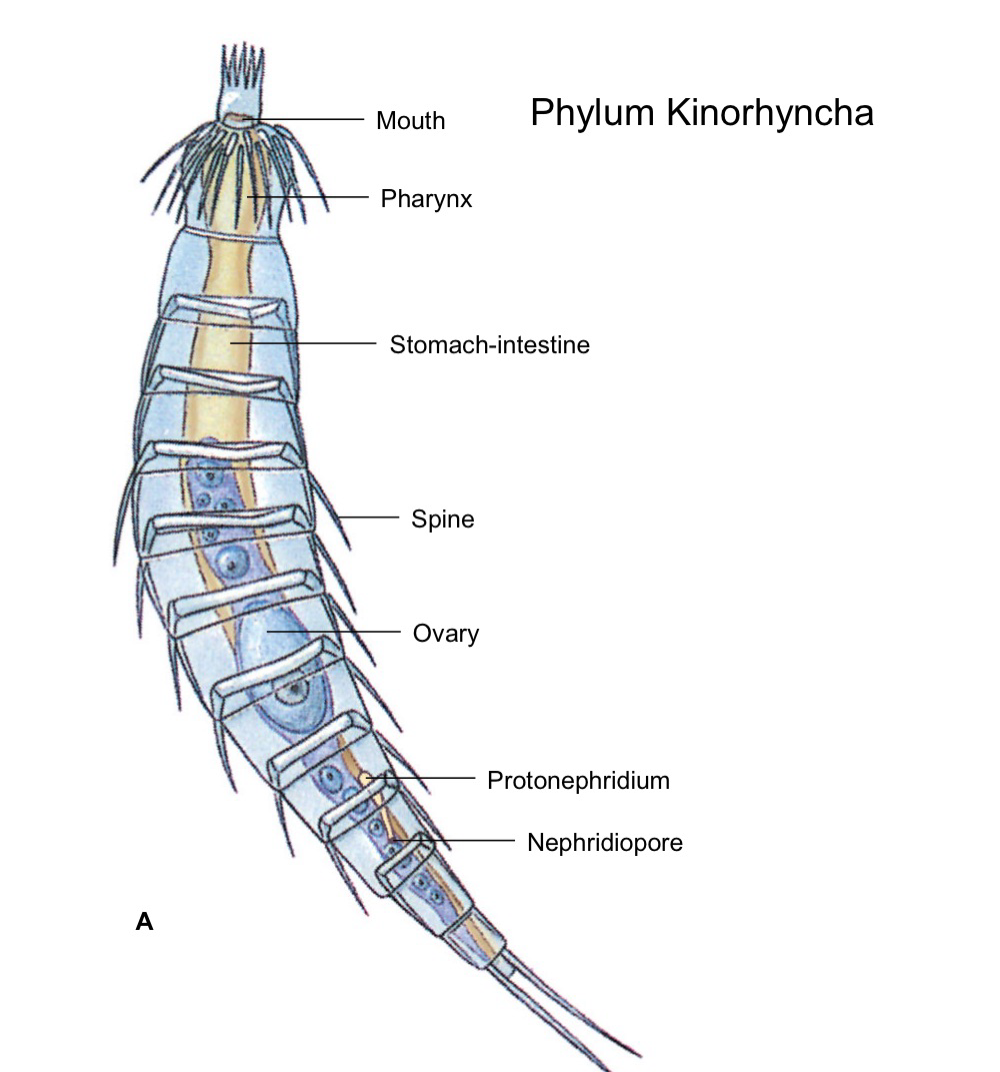
Kinorhyncha Phylum
marine, live in mud and eat detritus. covered in spiny plates. head has circlets of spine + neck + trunk (11 segments). Will pop out of spiny head to pull themselves. Hypodermal cords present, and only 1 pair of protonephridia. Many muscles present (longitudinal, circular, diagonal)
complete gut + proboscis
nervous system has brain + ventral cords
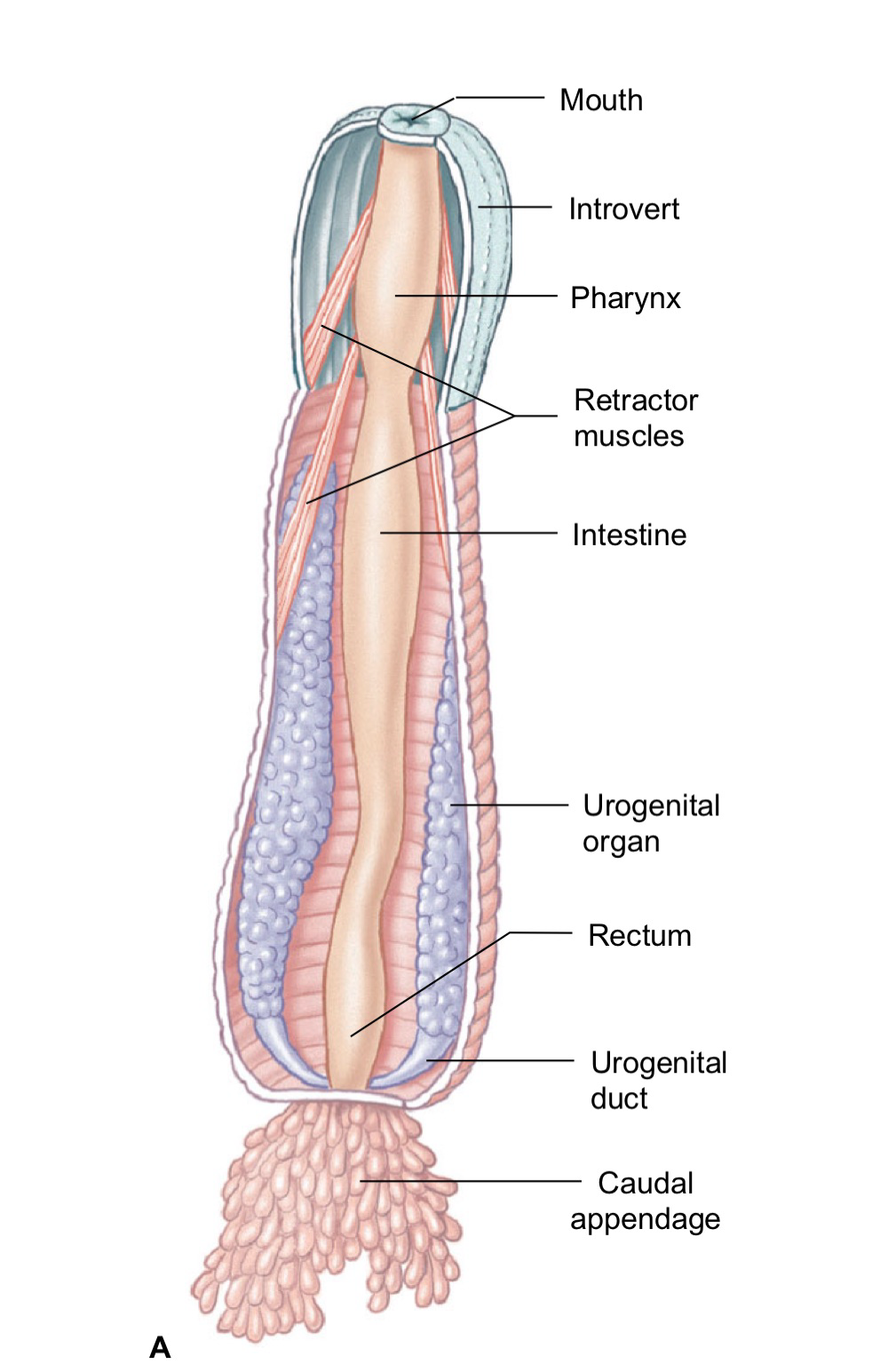
Priapulida Phylum
penis worms, live in marine burrows and eat polychaetes by sticking out head and grabbing them with their introvert. Trunk & caudal appendages are thin for respiration and posterior end. larger (can be up to 39 cm).
nervous system with nerve ring + nerve cord
reproduction is dioecious. larvae burrow in mud and eat detritus. males not found in some species
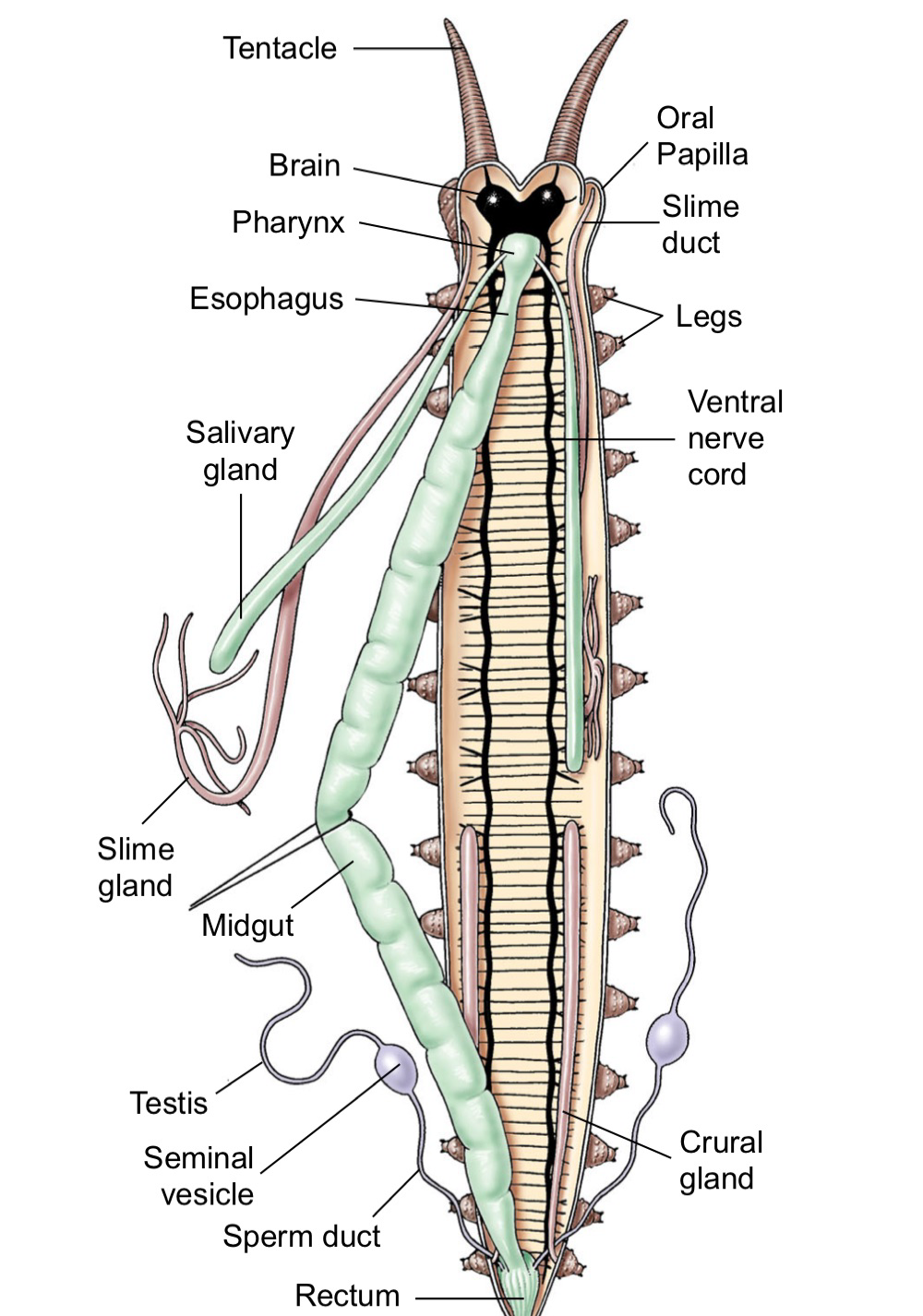
Onochophora Phylum
velvet worms bc of tubercules. Predator on insects, snails, worms in tropical or temperate environments. Has pair of antennae with eye at the base of each. claw like mandibles/jaws & dorsal tooth rip into prey after oral papillae makes and shoots slime to stick them, then enzymes liquify them.
pair of stubby legs with claws per segment and crawl via puristasis (lifting leg and moving forward until wave reaches segment)
muscular body wall + segments + metanephridia in every segment like annelids
Onochophora circulatory system
open system with dorsal heart that opens at both ends to move blood around body
Onochophora nervous system
brain + nerve cords with ganglia at the beach of each leg (2 ganglion per segment)
Onochophora Reproduction
dioecious. male deposits spermatophore somewhere on female body, then their white blood cells dissolve skin underneath it so sperm can enter and find the ovaries. embryos may grow in uterus
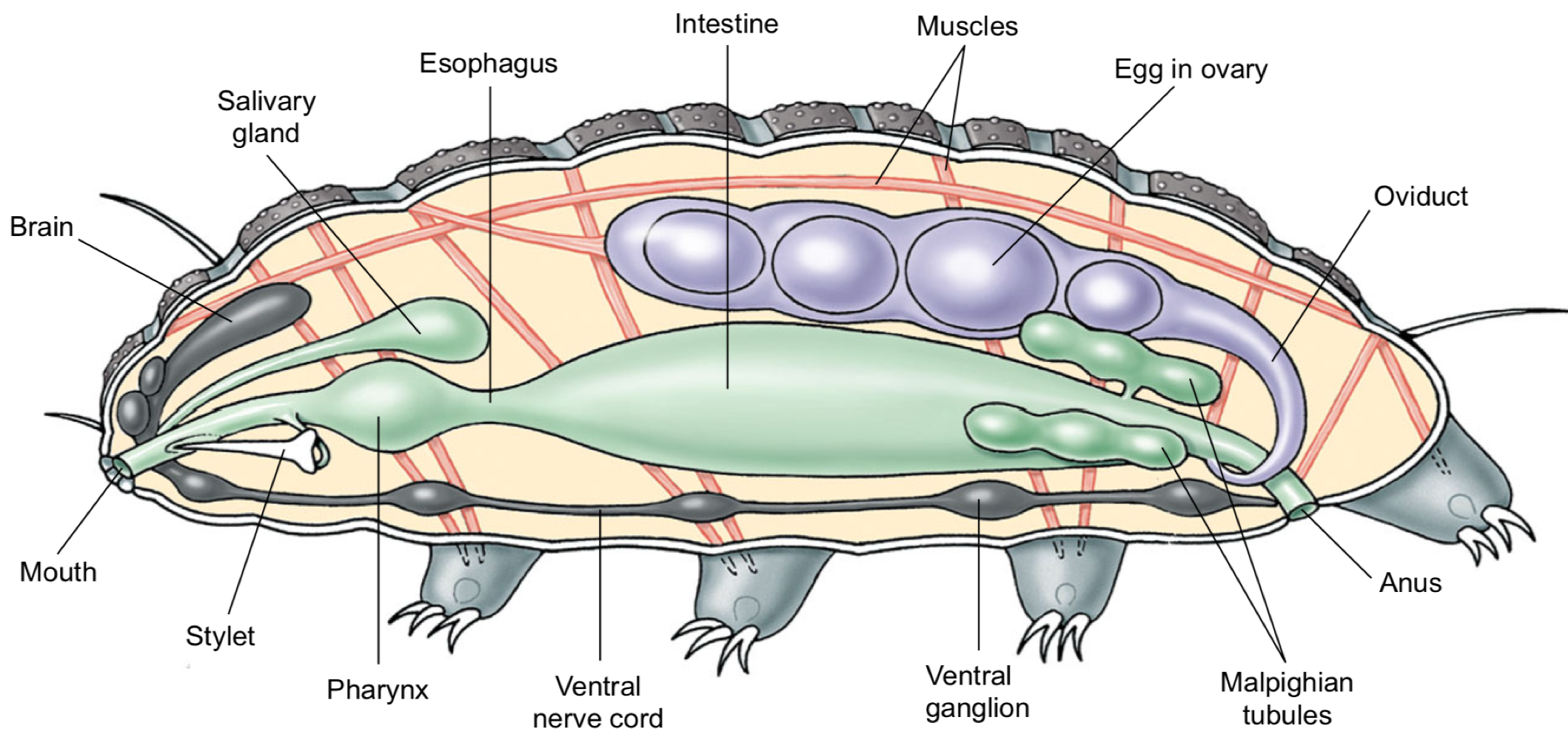
Tardigrade Phylum
water bears. live in water film on moss & lichens. molt a cuticle to over body, and lay eggs as they molt so when cuticle is shed eggs come off inside of it. Dioecious, some males not found.
mouth opens to muscular pharynx that can suck juice, and has stylets like knives. carnivorous on rotifers or nematodes, or just eat plant juices.
body cavity is mostly coelom, and they locomote via muscles and hydrostatic skeleton
no respiratory or circulatory system, exchange gas via body wall