FINAL PRACTICE
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms

Optic canal - Optic nerve

Superior orbital fissure - Oculomotor, trochlear, abducens

Foramen rotundum - Maxillary

Carotid Canal - Internal carotid artery

Foramen Spinosum - Mandibular

Internal auditory meatus - Facial nerve, vestibulocochlear nerve

Jugular foramen - Vagus nerve, accessory nerve, sigmoid sinus

Foramen magnum - Medulla

Hypoglossal canal - Hyperglossal nerve

Foramen ovale - Mandibular



turkish saddle, greater wing, lesser wing & pterygoid plates





corona radiata

Pituitary gland
Protected by sphenoid


Superior colliculous visual inerior hearing

Choroid plexus makes csf
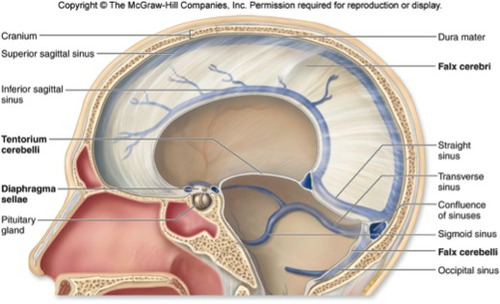
Falx cerebri
Falx cerebelli
Tentorium cerebelli
Diaphragm sellae (near pituitary gland)
Tracts of the spinal cord
Dorsal columns - proproception (gracile & cuneate fasciculus) decussate in medulla
Corticospinal - Voluntary movements decussate in medullary pyramids
Spinothalamatic - Pain and temp decussates at ventral white commisure



Olfactory nerve (CN I) = smell = brown
optic nerve (CN II) = grey = vision
oculomotor nerve (CN III) = green = eye movements & pupil
trochlear nerve (CN IV) = pink = lateral eye movements
trigeminal nerve (CN V) = blue = Facial scences
abducens nerve (CN VI) = orange = abducts eyes
facial nerve (CN VII) = purple = facial and neck muscles anterior 2/3 tongue
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) = yellow = hearing and balance
glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) = gdark blue = speech & saliva
vagus nerve (CN X) = green = swallowing, digestion, cardiac
accessory nerve (CN XI) = not shown = head and shoulders
hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) = blue = tongue muscles
Lobes & fissures of cerebellum
Lobes: anterior (unconsious), posterior (consious), flocculonodular (eye movements)
Fissures: primary & posteriolateral


Cerebellar peduncles Superior (efferents), middle (afferents), inferior (both)
cerebrel peduncle = columns of midbrain
Hippocampus VS amygdala
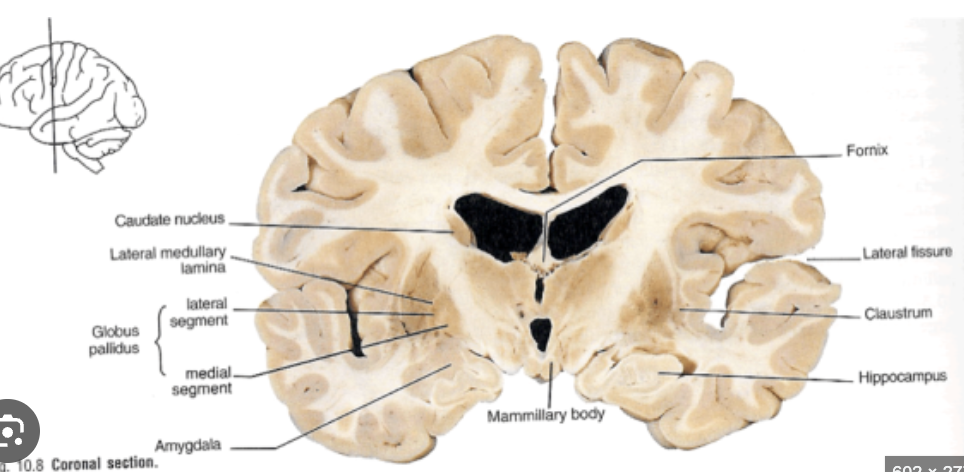

Thalamus & Caudate & Putamen & Internal capsule & red nucleus & crus cerebri & corticospinal fibres

Caudate & putamen & external globus palidus & internal gobus palidus & mamilary bodies

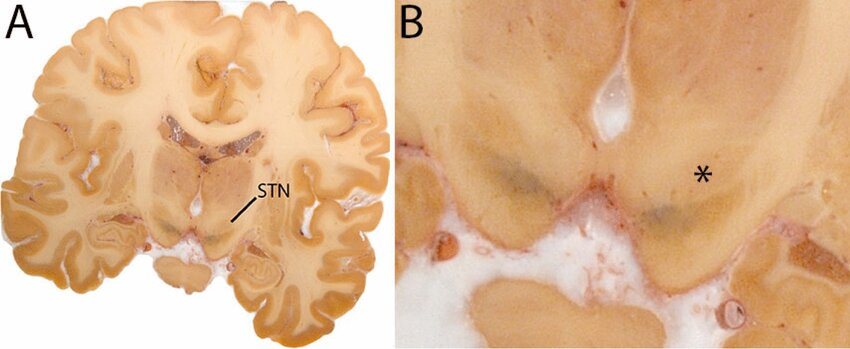
Subthalamatic nucleus
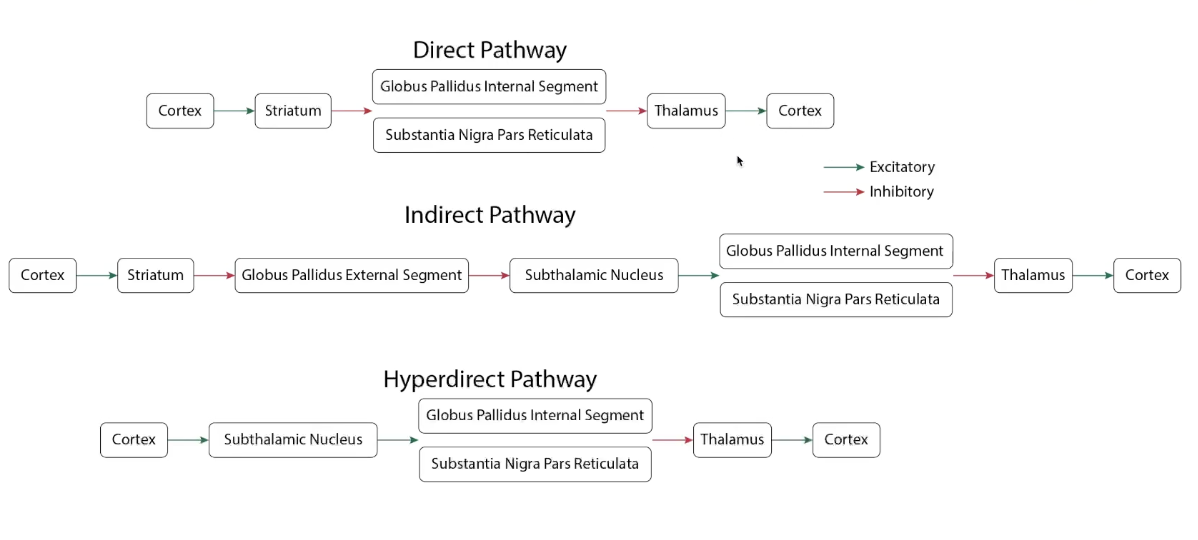
Indirect & Direct Pathways
Indirect pathway inhibits the subthalmaus and supresses signalling through the thalamus and movement
Direct pathway disinhibits thalamus making it easier to fire

Circle of willis

