Animal Phylogeny Exam 3
1/373
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
374 Terms
What is the #1 parasitic phylum? Why?
Arthropods because they have such a large number of organisms
What group are Arthropods a part of?
Ecdysozoa (and Panarthropoda)
What kind of cleavage and cell fate do Arthropods have?
Spiral cleavage and mosaic cell fate
How many germ layers do Arthropods have?
Three germ layers
Are Arthropods Protostomes or Deutrostomes?
Protostomes
What type of body cavities do Arthropods have?
True coelom, but coelom reduced (does not serve as a hydroskeleton)
What type of symmetry do Arthropods have?
Bilateral symmetry (have cephalization)
Do Arthropods have segmentation and limbs?
Yes (with segmentation on limbs — extreme of all segmentation)
What kind of support structures do Arthropods have?
Exoskeleton
What is the largest phylum?
Arthropods (5,000,000 species)
Where are arthropods found?
Found in almost all ecosystems
What is/are the jointed appendages and exoskeleton of arthropods made of?
Chitin (+ CaCO3)
What is metamorphoses and what phylum is able to do this
Metamorphosis is (in an insect or amphibian) the process of transformation from an immature form to an adult form in two or more distinct stages
Arthropods exhibit this (and some amphibians)
What are the 5 subphyla’s of Arthropoda?
Trilobites
Chelicerans
Myriapoda
Crustacea
Hexapoda
What is the structure of the exoskeleton for Arthropods?
The exoskeleton has several layers (some with hardened plates).
How is the exoskeleton for Arthropods produced?
Exoskeleton is secreted by the epidermis… the exoskeleton does not grow, so the organisms must most to increase in size
What is the process of molting and developing called in Arthropods?
Ecdysis
What is the premolt of Ecdysis in Arthropods?
When the old cuticle becomes thinner and the materials are withdrawn and stored in the body
What happens after the premolt of Ecdysis in Arthropods?
The new cuticle is secreted/grows and the animal swells with water/air to burst old cuticle
What is the postmolt of Ecdysis in Arthropods?
The new cuticle stretched and hardens
What is tagmata?
The grouping of many segments (e.g. head, thorax, abdomen in insects)
Which subphyla of Arthropods are aquatic? Which are Terrestrial?
Aquatic
Trilobite (extinct)
Crustacean
Terrestrial
Chelicerata
Myriapoda
Hexapoda
Which subphyla’s of Arthropods have Chelicera?
Trilobites and Chelicerata
Which subphyla’s of Arthropods have Mandibles?
Myriapoda, Crustacea, and Hexapoda
How do spiders eat and digest food?
Spiders inject enzymes into their prey and suck out digested juices
How do crustaceans eat and digest food?
Crustaceans are suspension feeders with some being predators
What kind of feeders are Hexapoda?
Most Hexapoda are herbivores
What kind of circulation do Arthropods have?
Arthropods have open circulation with a heart and arteries
What is unique about the blood Arthropods have?
Arthropods have Hemolymph as their blood
How do Arthropods respire (individually as crustacean and insects)?
Crustaceans have gills near their legs (filled with hemolymph) - small crustaceans have no respiratory structures
Insects have spiracles (holes) which lead to tracheal tubes (that develop from ectoderm)
How do Arthropods excrete wastes (individually as crustacean and insects)?
Crustaceans dilute their ammonia waste and excrete it via their gills
Insects use malpighian tubules to conserve water (excrete dry waste and uric acid)
What kind of nervous/sensory features do Arthropods have?
Arthropods have a brain and ventral nerve cords
Arthropods also have sensory structures like ocelli and compound eyes, setae (touch) and chemical receptors in their cuticle, auditory membranes, and antennae which help detect moisture, temperature, chemicals, touch, and vibration.
What kind of muscles do Arthropods have?
Arthropods have a lever system (like vertebrates) which is attached to exoskeleton
What is serial homology (present in Arthropods)?
Repeated structures in the body, modified for various uses
When did flight evolve in insects?
~350 mya (first to evolve flight)
What is the difference between uniramous and biramous appendages?
The appendages of arthropods may be either biramous or uniramous. A uniramous limb comprises a single series of segments attached end-to-end. A biramous limb, however, branches into two, and each branch consists of a series of segments attached end-to-end.
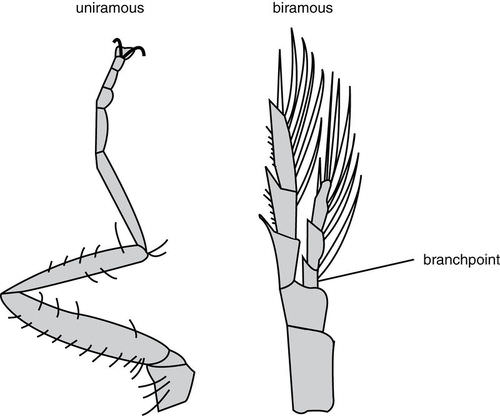
How are marine annelids (polychaetes) and marine arthropods similar?
They have similar locomotion and respiratory structures (like parapodia)
How do Arthropods reproduce?
Most Arthropods reproduce via sexual reproduction
Aquatic reproduce via external or internal fertilization
Terrestrial reproduction is internal fertilization only via penis or spermatophore
What kind of defense features do Arthropods have?
Exoskeleton, venom, poison, camouflage, mimicry, community defense (ants, bees), acid spray, odors, adhesives, etc.
What subphylum of Arthropoda was abundant during Cambrian and Ordovician periods?
Subphylum Trilobita
When did Subphylum Trilobita go extinct?
During Permian Extinction
What subphylum of Arthropoda has a trilobed body?
Subphylum Trilobita
What kind of feeding habits do Subphylum Trilobita have?
Variety of feeding habits (can be predators, scavengers, filter/suspension feeders)
What kind of eyes do Subphylum Trilobita have?
Compound (crystal) eyes
Which Arthropod subphylum is the oldest?
Subphylum Chelicerata
What are the two tagma of Subphylum Chelicerata?
Cephalothrax and Abdomen
Do Subphylum Chelicerata have mandibles and antennea?
No
What are the 6 pairs of cephalothoracic appendages in Subphylum Chelicerata?
1 pair of chelicerae (pincer or fang)
1 pair of pedipalps (antenna-like or claw)
4 pairs of walking legs (uniramous)
What are the three classes of Subphylum Chelicerata?
Horseshoe crabs, sea spiders, and arachnids (spiders, scorpions, harvestmen, ticks and mites)
How many species of Horseshoe crabs are there?
Only 4 species
What kind of respiratory structures do horseshoe crabs have?
Book gills
Which class is used for their blood for testing medical equipment/injections for bacterial infections? What impact is this causing?
Horseshoe crabs - thus research is causing a decrease in populations and reproductions
Which class has ovigers? What does it mean?
Sea spiders - ovigers are a sea spider’s egg-carrying organs (males carry the eggs)
What distinct tagma do sea spiders have?
Sea spiders have large cephalothorax with proboscis and a small abdomen
What respiratory/excretory structures do sea spiders have?
Sea spiders have no respiratory or excretory structures because their organs spill into their legs giving them high surface area
What kind of relationship do sea spiders have with Cnidarian polyps?
Sea spider larvae is ectoparasitic on Cnidarian polyps
How many species are in class Arachnida?
80,000+ species
What species are considered in class Arachnida?
Spiders, scorpions, pseudoscorpions, ticks, mites, harvestmen, etc.
What kind of feeders are spiders? How do they feed?
All are predaceous and they feed using their Chelicerae (fangs with venom)
Which order can use web spinning to attract prey and travel?
Spiders
What kind of respiratory structures do spiders have?
Book lungs
How do spiders reproduce?
Spiders have elaborate courtship rituals, once the male attracts a female the males use their pedipalps to transfer sperm to female (both contribute to parental care?)
What kind of feeders are scorpions? How do they feed?
All scorpions are predaceous and use their pedipalps (claws) to capture prey and chelicerae to rip apart the prey
What are the different tagma of scorpions?
Scorpions have short cephalothorax (with appendages) and an abdomen divided into pre-abdomen and post-abdomen (with stinger)
Do males or females care for young of scorpions?
Scorpions have maternal care for young
What is a capitulum and which order(s) exhibit this?
The head of a tick/mite - the chelicera/palp make up the capitulum
What are the tagma of ticks and mites?
Ticks and mites have a cephalothorax and abdomen completely fused
How many species does the Subphylum Myriapoda have?
13,000 species
What are the 2 tagmata of Subphylum Myriapoda?
Subphylum Myriapoda have a head and a trunk
What specific structures do Subphylum Myriapoda have?
Subphylum Myriapoda have a pair of antennae, eyes (group of ocelli), and uniramous legs
What classes fall into Subphylum Myriapoda?
Centipedes and Millipedes
What kind of feeders are centipedes?
Centipedes are carnivores and predators
How many legs are on each segment for centipedes? What about Millipedes?
Centipedes - each segment with 1 pair of legs
Millipedes - most segments with two pairs of legs
What is the body shape of a centipede?
Centipedes are dorsoventrally flattened
What kind of defense do centipedes have?
First pair of legs in a centipede is modified into venom claws
What kind of feeders are millipedes?
Millipedes are detrivores (eat plant matter)
What is the body shape of millipedes?
Millipedes have cylindrical bodies
What kind of defense do millipedes have?
Chemical defense
How many species are in subphylum Crustacea?
~70,000+ species
Which Arthropod subphylum has 2 pairs of antennae?
Subphylum Crustacea
Are Subphylum Crustacea appendages uniramous or biramous?
Appendages are mostly biramous for Subphylum Crustacea
What are the 5 classes in Subphylum Crustacea?
Malacostraca (lobsters, crab, shrimp, krill, pillbugs), Branchiopoda (daphnia, brine shrimp), copepods, ostracods, cirripeds (barnacles)
What type of appendages do Subphylum Crustacea have?
Subphylum Crustacea have 2 pair of antennae, mouth appendages, thoracic appendages (maxillipeds and walking legs), and abdominal appendages (swimmerets)
1 pair of appendages per segment**
What is a uropod and what Subphylum is it found in?
A uropod is the last pair of abdominal appendages which is used for backwards movements and protection of eggs or young
Found in Subphylum Crustacea
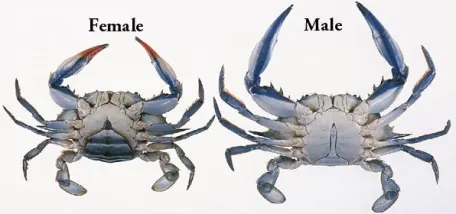
What is the anatomical difference between a male and a female crab?
Which class is the largest and most diverse group of Subphylum Crustacea?
Class Malacostraca (40,000+ species)
What species are included in Class Malacostraca?
Amphipods, isopods, decapods (lobster, crab, shrimp), and krill
Which class of Subphylum Crustacea are an important component of freshwater zooplankton?
Class BraNchiopoda (“shield shrimp, brine shrimp (“sea monkeys”, and cladocerans (daphnia))
How can one differentiate between Brachipods and BraNchiopods?
Brachiopods have a digestive system with no anus → therefore no “end/n”
BraNchiopods have a digestive system with an anus → therefore have an “end/n”
Which class of Subphylum Crustacea are in every water habitat (including in pitcher plants and puddles) and are biodiversity indicators?
Class Copepods (zooplankton, ex: nauplius)
Which class of Subphylum Crustacea are the most common arthropods in fossil record?
Class Ostracoda
Which class of Subphylum Crustacea have an enclosed bivalve carapace?
Class Ostracoda
Which class of Subphylum Crustacea have a carapace which surrounds the body and secretes plates?
Class Cirripedia (barnacles)
Which class of Subphylum Crustacea have a reduced head, absent abdomen, and long thoracic legs (cirri) with hair-like setae?
Class Cirripedia (barnacles)
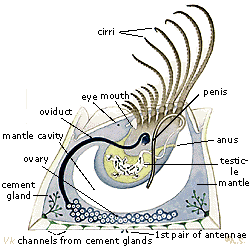
Which subphylum of Arthropoda is the most numerous and diverse group?
Subphylum Hexapoda
What are the 3 tagmata of Subphylum Hexapoda?
Head, thorax, and abdomen
How many legs and wings do Subphylum Hexapoda have?
Subphylum Hexapoda have 3 pairs of uniramous legs and 2 pairs of wings
What are the two classes of Subphylum Hexapoda?
Class springtails and class insecta
Which class of Subphylum Hexapoda is the most numerous animal in the soil (after nematodes)?
Class Springtails
What is Furcula and what class exhibits this?
Furcula is the posterior appendage that can snap to push animal into air
Exhibited in Class Springtails