Polymers
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 3 Prep
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Polymer
A large molecule composed of many repeated subunits
Condensation And Addition
General methods of polymer production
Monomers And Covalent Bonds
Polymers are synthesized from ______, linked by ______________
Length And Branching And Co-polymers
Polymers can vary in ______, connectivity (_______), and even mixtures of different monomers (_________)
Alkenes And Addition Polymerization
______ can be monomers for ___________________
Division Between Monomers
What do the parentheses represent?
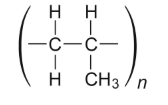
Two
How many single electrons are there due to the division of monomers?
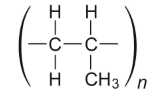
The Degree Of Polymerization (DP)
Defined as the number of repeating units in a polymer chain.
Molecular Weight of the Repeating Unit
In polymers synthesized through addition polyermization, the molecular weight of the monomer is equal to the:
Whole Number
The DP of a polymer is typically rounded to the nearest:
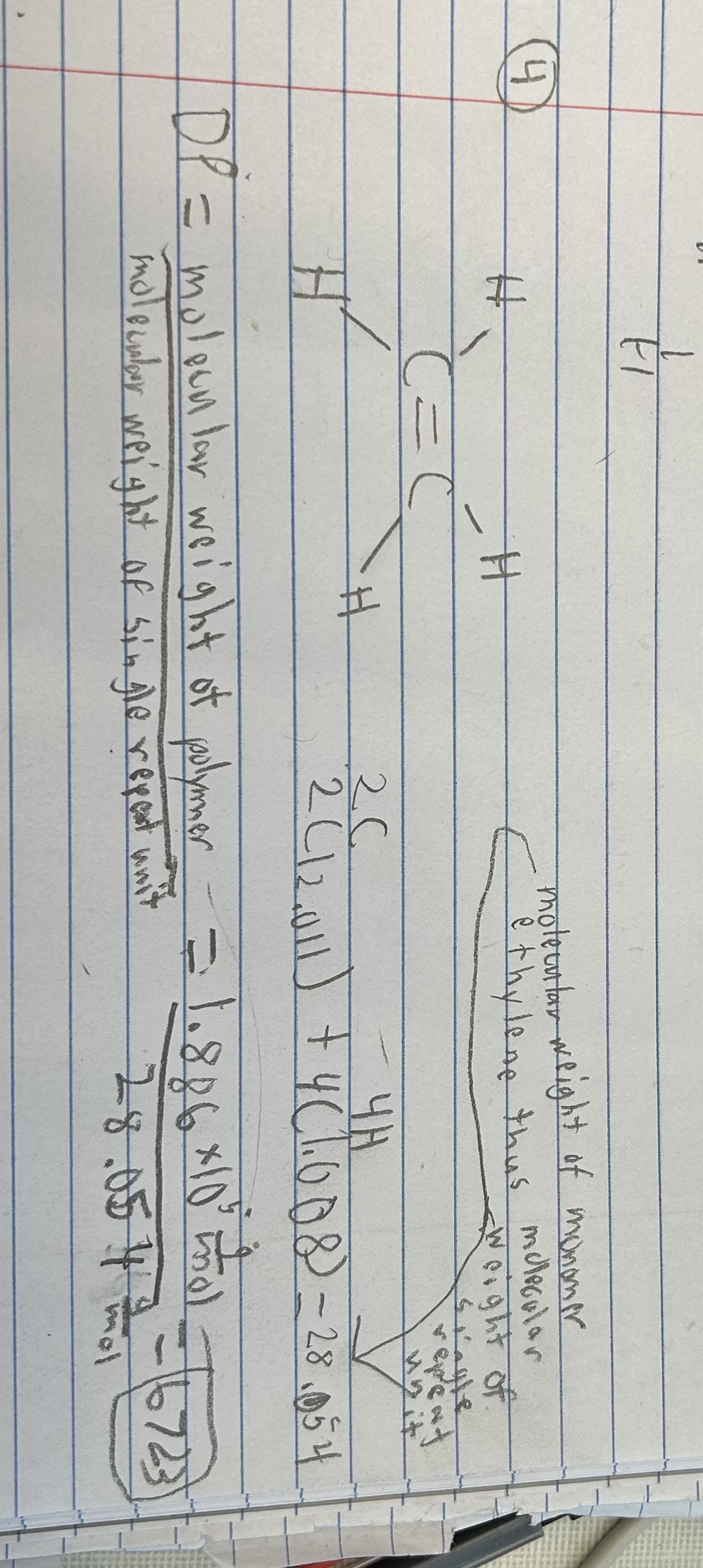
6723
Calculate the answer to nearest whole number.

Condensation Polymerization
Produces a covalent bond between monomers plus a small molecule (often H2O)
Alkenes
While condensation polymerization can perform with many kinds of monomers, Addition Polymerization only works for:
Crosslinking
Chemistry that introduces covalent bonds between polymer chains
Higher Density
Molecules with linear chains pack more tightly, thus having a __________________ than molecules with kins or branches.
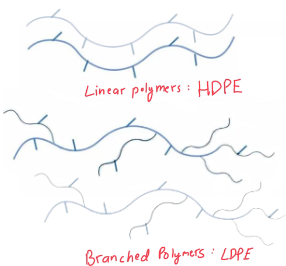
Stronger Induced Dipolar (ID-ID) Forces in a Condensed State
In terms of molecular size, larger/ long molecules have more surface area than short, thus producing:
Activation And Propagation
What are the two stages of addition polymerization?
Activation
the initial step where the monomer is made reactive enough to undergo polymerization, typically through the creation of a free radical or another reactive species
Propagation
the subsequent step where this reactive species repeatedly adds to other monomer units, extending the polymer chain
All
____ Atoms from alkene are incorporated into the addition polymer
carbon–carbon double bonds
Monomers for addition polymers are usually unsaturated compounds containing _______________.