SB4: Natural Selection + GM
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What did Charles Darwin and Alfred Wallace contribute to biology?
They developed the theory of evolution by natural selection.
How does evolution usually happen according to Darwin and Wallace?
Evolution branches out into several species, not just one evolving directly into another.
What are the steps of evolution by natural selection?
1. Genetic variation
Individuals in a population’s characteristics vary
2. Competition
Environmental change
→ Competition
→ Selection pressure
3. Natural selection
Individuals w/ advantageous traits better adapted → higher chance of survival (survival of the fittest)
4. Inheritance
Survivors reproduce + pass on advantageous traits to offspring
5. Evolution
Next gen has more individuals with the trait
Repeats if environment keeps changing → Gene pool changes
Over many gens: may → new species (have become different to individuals unaffected by environmental change)
(Good Crows Never Invite Eagles)
What causes genetic variation in a population?
Differences in DNA among individuals.
How old is Ardi’s fossil?
4.4 million years old
What are Ardi's physical characteristics?
1.2 m tall
50 kg
Leg bones - may have been able to walk upright
Long arms
Long big toes on sides of feet - climb trees
How old is Lucy’s fossil?
3.2 mil. yr old
What are Lucy's physical features?
1.07 m tall
Probably walked upright
Curved toes, same arrangement as modern humans
What are Homo habilis’ physical features?
Short
Long arms
Walked upright
What did Richard Leakey discover?
Homo erectus
What were the features of Homo erectus?
1.79 m tall
Strong build
What does fossil evidence overall suggest?
That human features evolved over millions of years in stages.
How do scientists use stone tools as evidence for human evolution?
Tools show increasing complexity over time e.g. sharper for cutting, more sophisticated shape reflecting increased skull volume
How are stone tools dated?
Age assumed from rock layer age (deeper = older)
What is the pentadactyl limb?
A limb with five digits found in many animals
What is the five-kingdom classification system?
Closely related organisms are grouped into Animals, Plants, Fungi, Protists, and Prokaryotes based on traits.
What are the traits of fungi?
Mostly multicellular (except yeast)
Live in/on dead matter on which they feed
Chitin cell walls
Nuclei
What are the traits of protists?
Mostly unicellular
Nuclei
Some have cell walls (not chitin)
What are the traits of prokaryotes?
Unicellular
Flexible cell walls
What are the three domains and their traits?
Archaea
Bacteria: No unused DNA
Eukarya: Unused DNA
(Prokaryotes in Bacteria/Archaea)
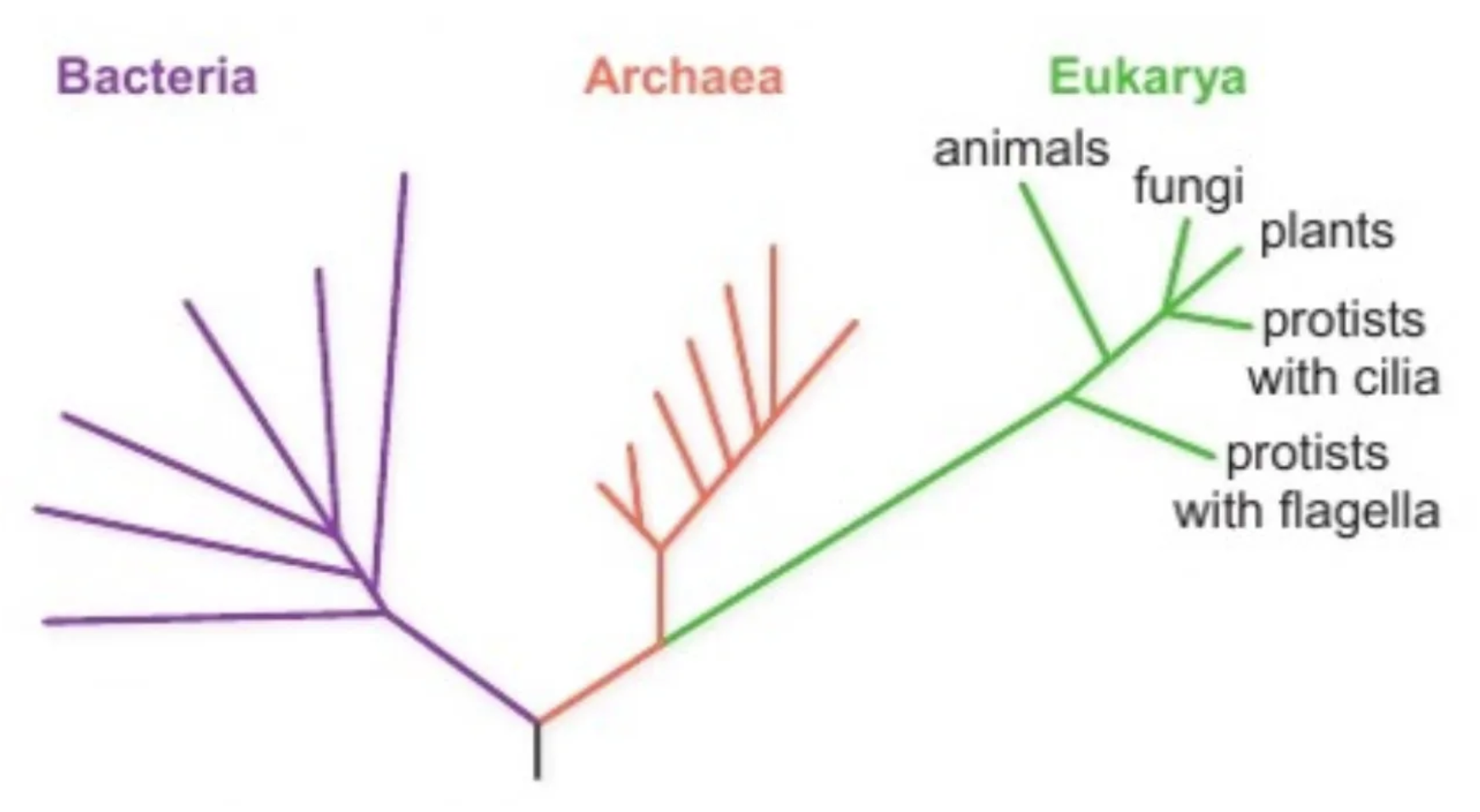
How did Archaea lead to the creation of the 3 Domain system?
Archaea discovered w/ no nucleus → Put in prokaryotes
Genetic analysis: All organisms except prokaryotes have unused DNA sections
→ Archaea had unused DNA
What are the steps of selective breeding?
1. Select organisms with desired traits 2. Breed them 3. Select best offspring 4. Breed 5. Repeat Steps 3-4
What is tissue culture?
Growing cells/tissues in nutrient media
What are the advantages of tissue culture?
1. Grows rare/endangered species
2. Grows plants hard to grow from seed
3. Makes GM clones
What are scientific uses of tissue culture?
Easy to study cell communication
Study viruses (cannot replicate outside cells)
Infected cells’ response to new medicine w/o harm to living organisms
Cancer cultures: How cancers develop + spread
Growing organs from your own stem cells to reduce transplant rejection
(Every Stage Idol Can Glow)
How is genetic engineering of insulin-producing bacteria done?
Additional genes added to plasmid (the vector) → recombinant DNA
Restriction enzymes cut DNA section containing gene for making insulin from human DNA → sticky ends (unpaired bases at each end)
Same restriction enzyme used to cut plasmids open → same ‘sticky ends’
DNA sections w/ insulin gene mixed w/ cut plasmids
Enzyme ligase joins complementary ‘sticky ends’
Plasmids inserted back into bacteria
Bacteria grown in huge tanks + produce insulin
Insulin extracted to treat type 1 diabetes
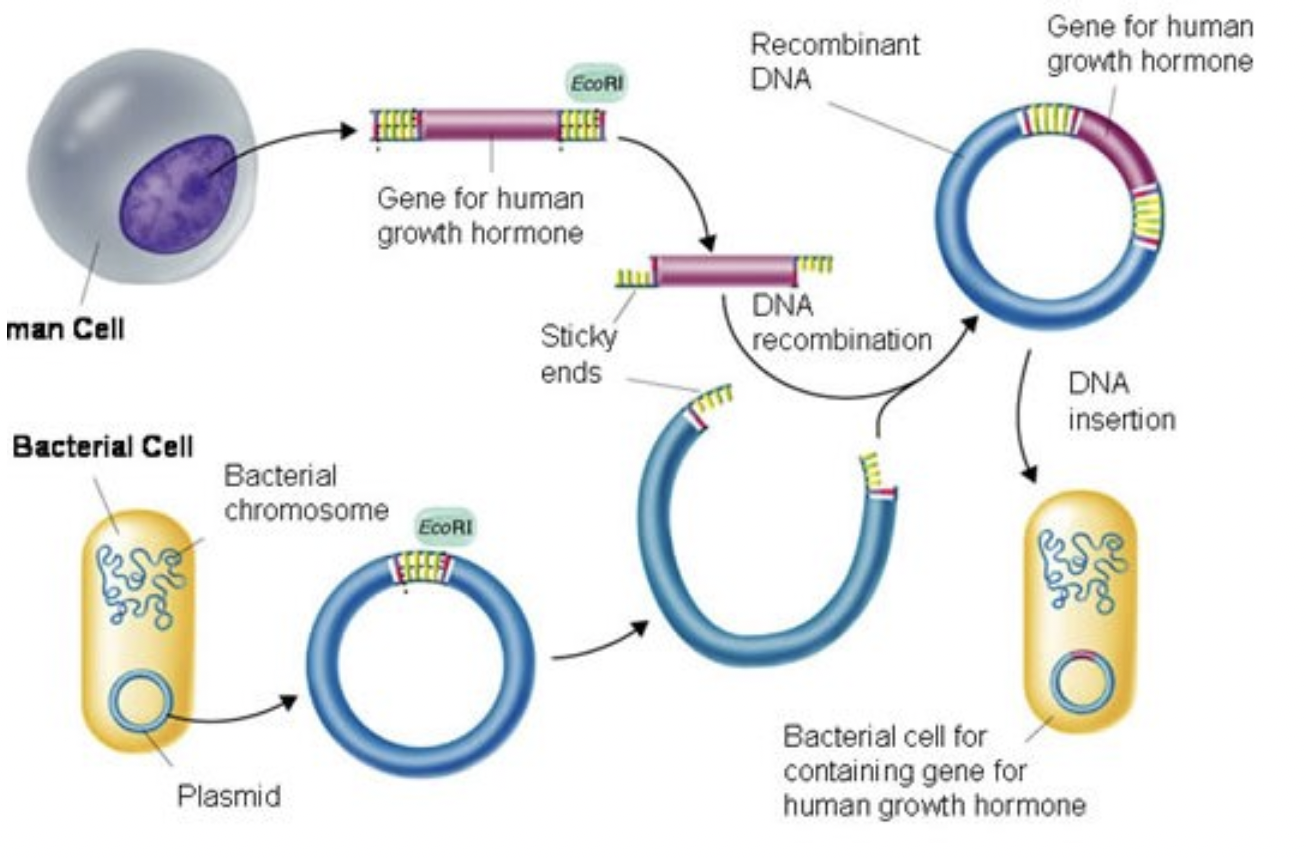
vector
carrier that transfers genes into organisms
What is Bt toxin?
Poison from Bacillus thuringiensis (bacterium) - spraying Bt crystals kills insects
How is Bt used in GM crops?
Genes controlling Bt toxin production introduced into plant → All cells produce toxin
What are the benefits of Bt crops?
• Less insecticide needed → Will not harm humans/other animals
• Higher yield → More profit for farmers
• Toxins released when cells broken → Only affects insects that chew plant tissues + not insect predators (e.g. ladybirds, spiders)
• Different strains of bacteria produce different forms of the toxin → New GM plants
(Lewis Hamilton Touch Down)
What are the pros of fertiliser use?
Plants absorb mineral ions from mineral salts
→ Make new cells/substances
→ growth
→ more yield
What are mineral salts?
Natural compounds in soil and rocks that plants use to grow.
What are the cons of fertiliser use?
Used up by previous crop → More fertiliser needs to be added with each new crop
Not all absorbed → Pollution of water sources → Death/Health issues for animals/humans
What is biological control?
Using natural predators or parasites to reduce pest populations.
What are pests and why are they a problem?
Pests reduce crop yield by feeding on plants
What do chemical insecticides do?
Kill different insects (often by contact)
What are the steps of tissue culture?
Plant sterilised in bleach
Small piece/cells cut, grown in sterile nutrient medium
Callus/plant treated w/ hormones → plantlets grow shoots + roots
(Plantlets separated + grown on sterile nutrient medium) ONLY FOR CELLS - multiple plantlets grown from a callus
When large enough: Planted in soil/compost
What are the benefits of selective breeding in agriculture?
• disease resistance
• yield
• coping w/ environment
• fast growth
• flavour
• make new products
(Don’t You Care For Frozen Mangoes)
What are the risks of selective breeding?
→ Alleles’ disappearance/becoming rare (might be useful in future)
High similarity → All affected if environmental change
GM bacteria pros
• Cheaper than extracting substances from dead pigs or cows
• Suitable for vegans/people who don’t eat pork
• Faster than artificial selection
What is a con of using GM bacteria vs. insulin extraction dead pigs/cows?
Different to insulin in mammals → Not all diabetics can use
What are the cons of Bt toxin?
• Seeds expensive
• Might reproduce w/ wild plants + pass on resistance w/ unknown effects - rare
• Health concerns
• Aphids do not chew/eat toxin (insecticides still needed)
• Insects develop resistance
(Some Mothers Have An Impact)
How old is Homo habilis?
2.4-1.4 mil. yr old
Who is Homo habilis closely related to?
Homo sapiens
How old is Homo erectus?
1.6 mil. yr old
What does Homo erectus show evidence for?
Human evolution in Africa
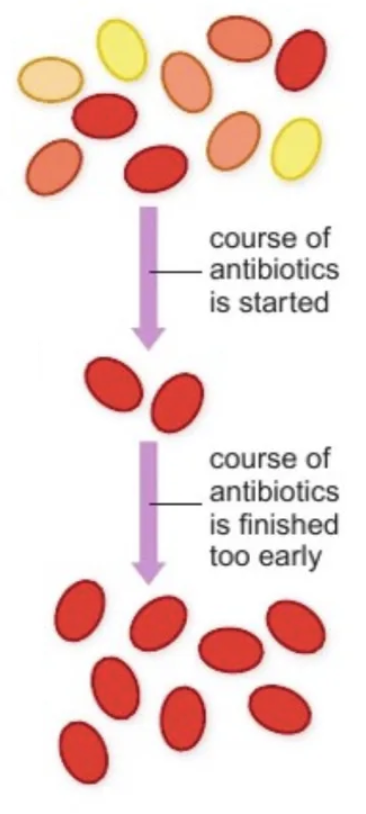
What happens when you stop taking an antibiotic to treat an infection too early?
Variation
Antibiotic → Competition
Less resistant = first to die, then medium
Most resistance survive + reproduce
Resistance passed on to offspring
Population of antibiotic-resistant bacteria
What does the pentadactyl limb suggest?
A common ancestor between humans/animals
Bones were designed for independent purposes
What does more DNA in common suggest?
More recent evolution from common ancestor → More closely related
Why are monocultures prone to pests?
Encourage population growth until insects become them
Microbial culture uses
Studying effects of
plant extracts
antibiotics/antiseptics
List the hierarchical classification system
Domain - Dear
Kingdom - King
Phylum - Philip
Class - Came
Order - Over
Family - For
Genus - Good
Species - Spaghetti
What were the 2 kingdoms?
Animals and plants
What did Linnaeus invent?
2-kingdom system + taxonomical hierarchy
How does taxonomical hierarchy work?
Characteristics of organisms get more similar as group gets smaller
2-kingdom cons
Protists + prokaryotes ignored
Organisms shared traits due to adaptations, not inheritance → Unrelated grouped together
Fungi in Plantae