Chapter 12 lecture: Spinal Cord, nerves, reflexes
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
both brain and spinal cord
Receive sensory input from receptors
Contain reflex centers
Send motor output to effectors
Reflex
Rapid, automatic response triggered by stimuli
spinal reflexes
Controlled in the spinal cord-No brain input
Control some of the most rapid changes to environmental changes
Conduction
Carry information up and down spinal cord
locomotion
repetitive, coordinated actions of several muscle groups
Neurons controlling flexor and extensor muscles
spinal cord structure
Adult length: about 45 cm (18 in)
ends at L1-L2 vertebrae
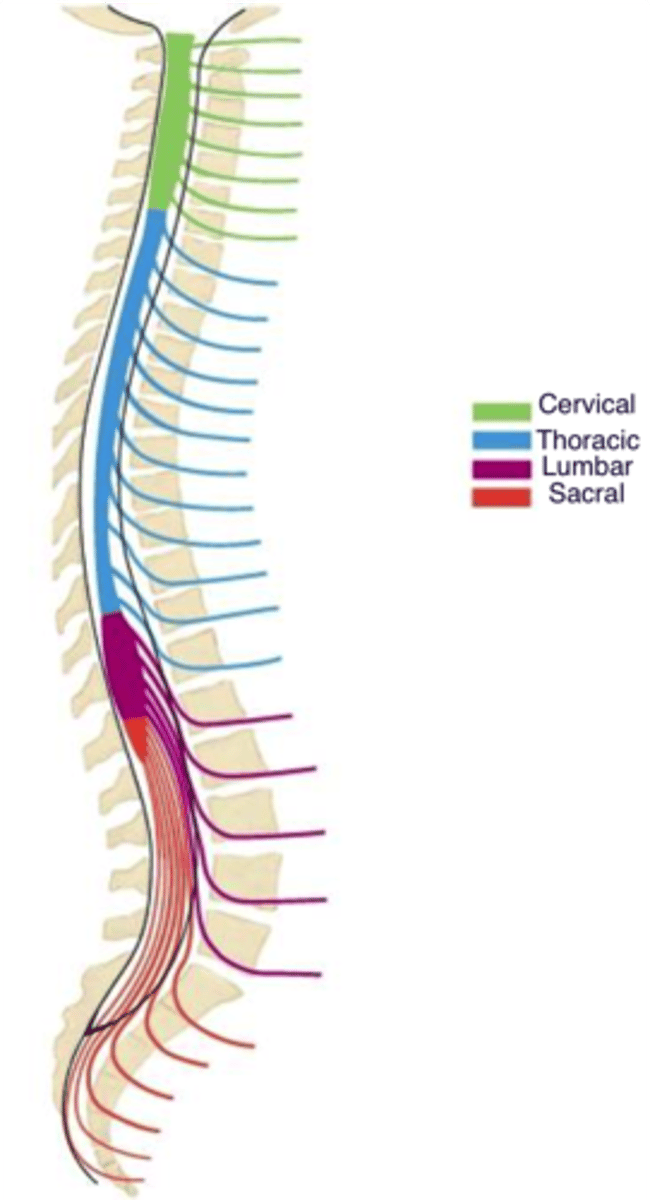
Segments of the spinal cord
31 segments:
8 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
5 sacral
1 coccygeal
conus medullaris
Cone shaped end of spinal cord at L1-L2
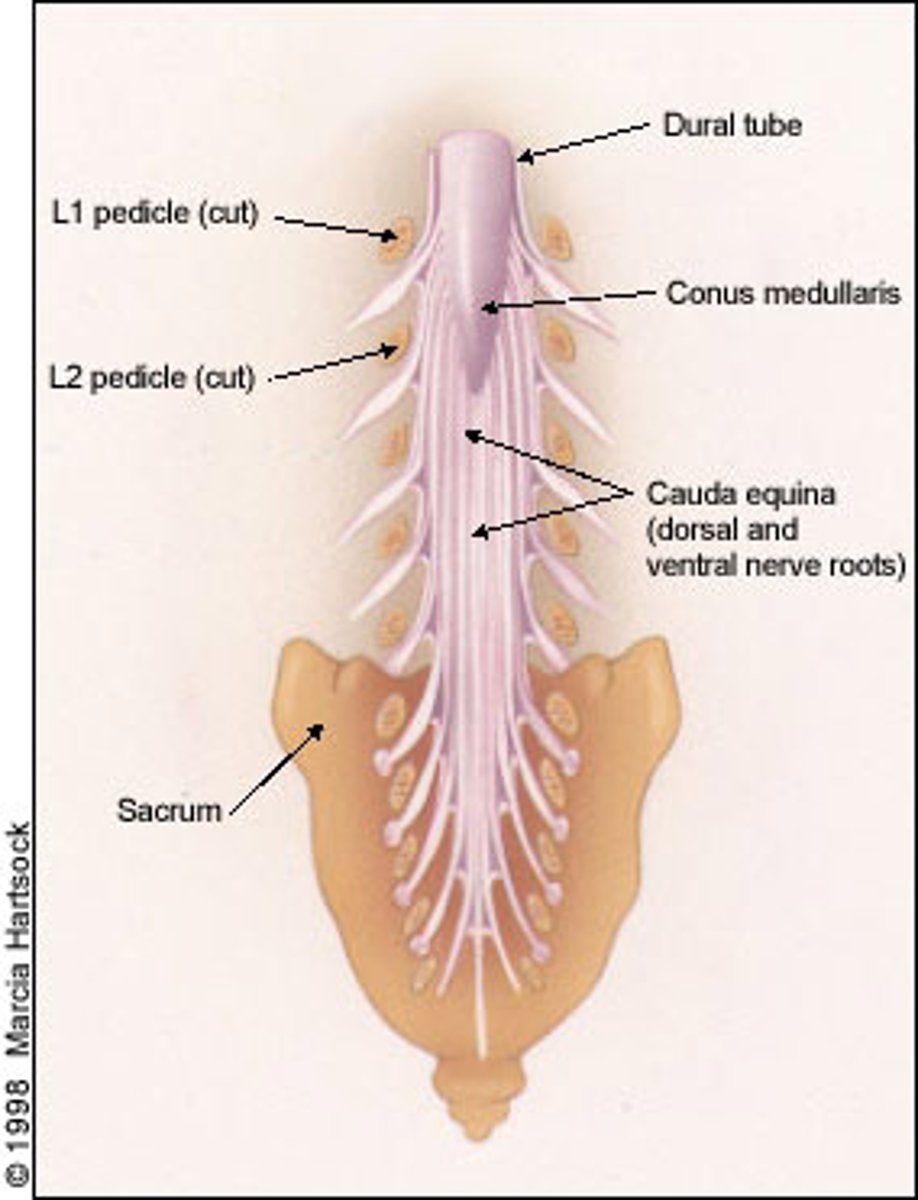
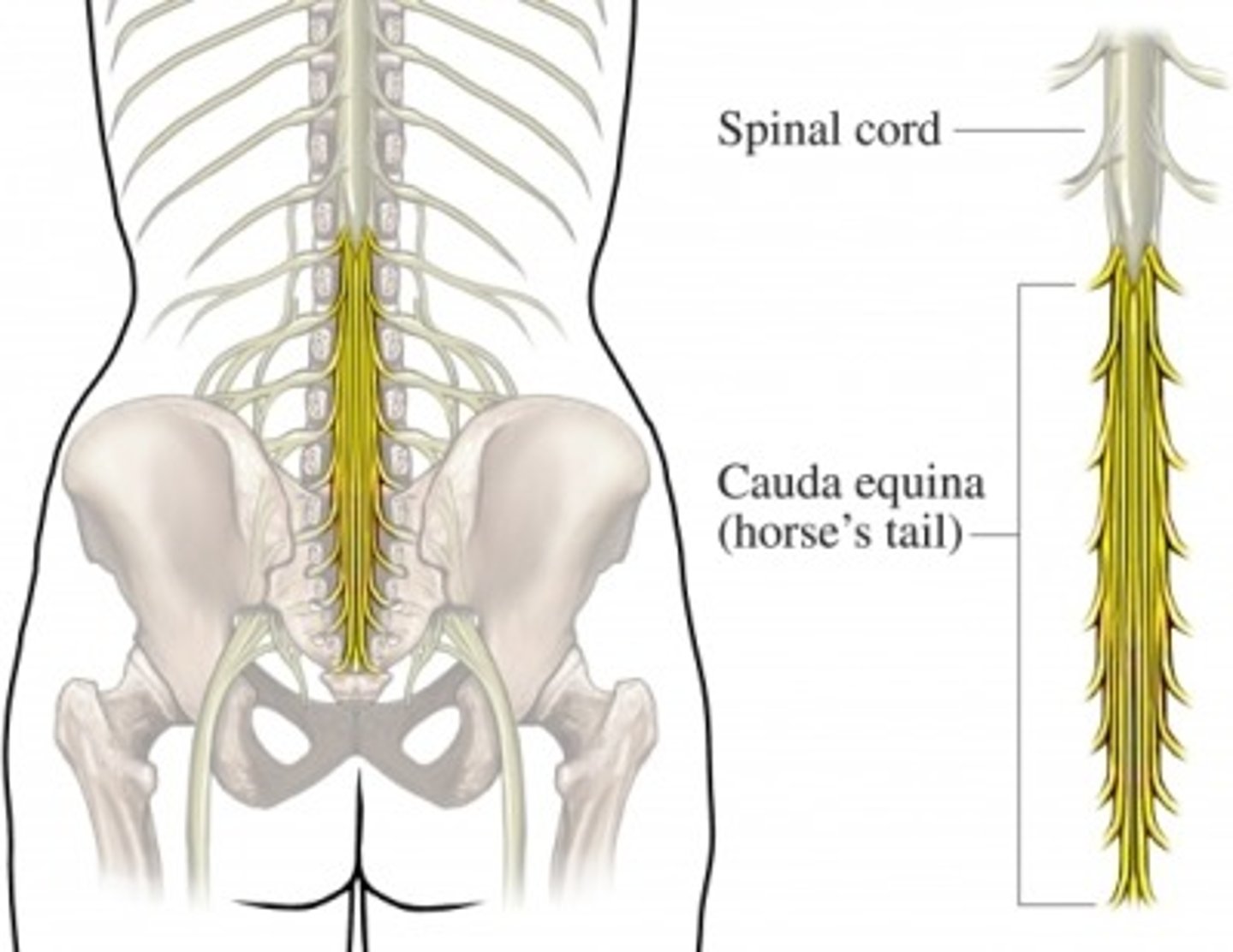
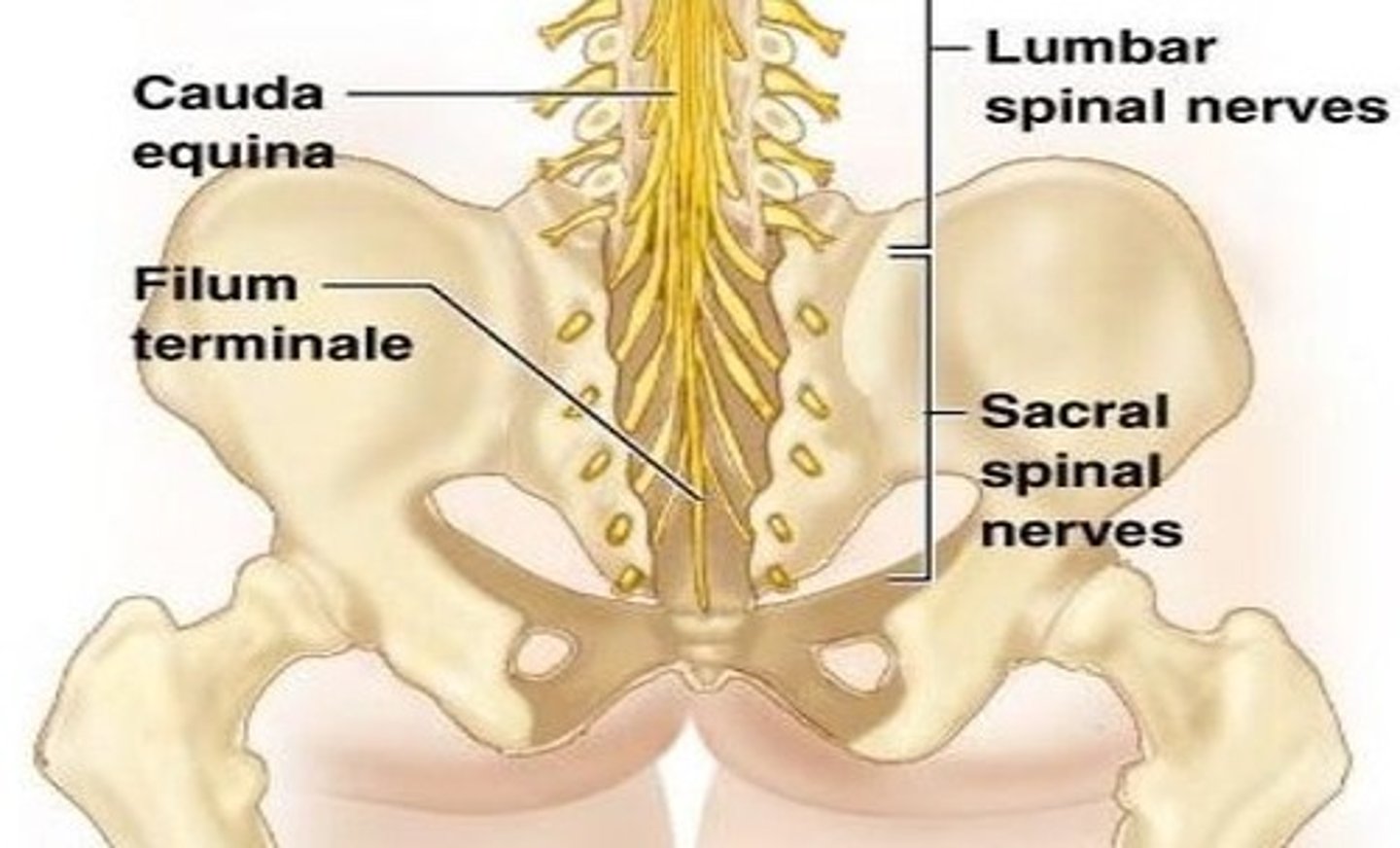
cauda equina
Nerve roots from spinal cord to lower intervertebral foramen to exit
L2 to S5 and filum terminale
filum terminale
anchors the spinal cord to the coccyx and sacrum
Pia mater
terminal thread
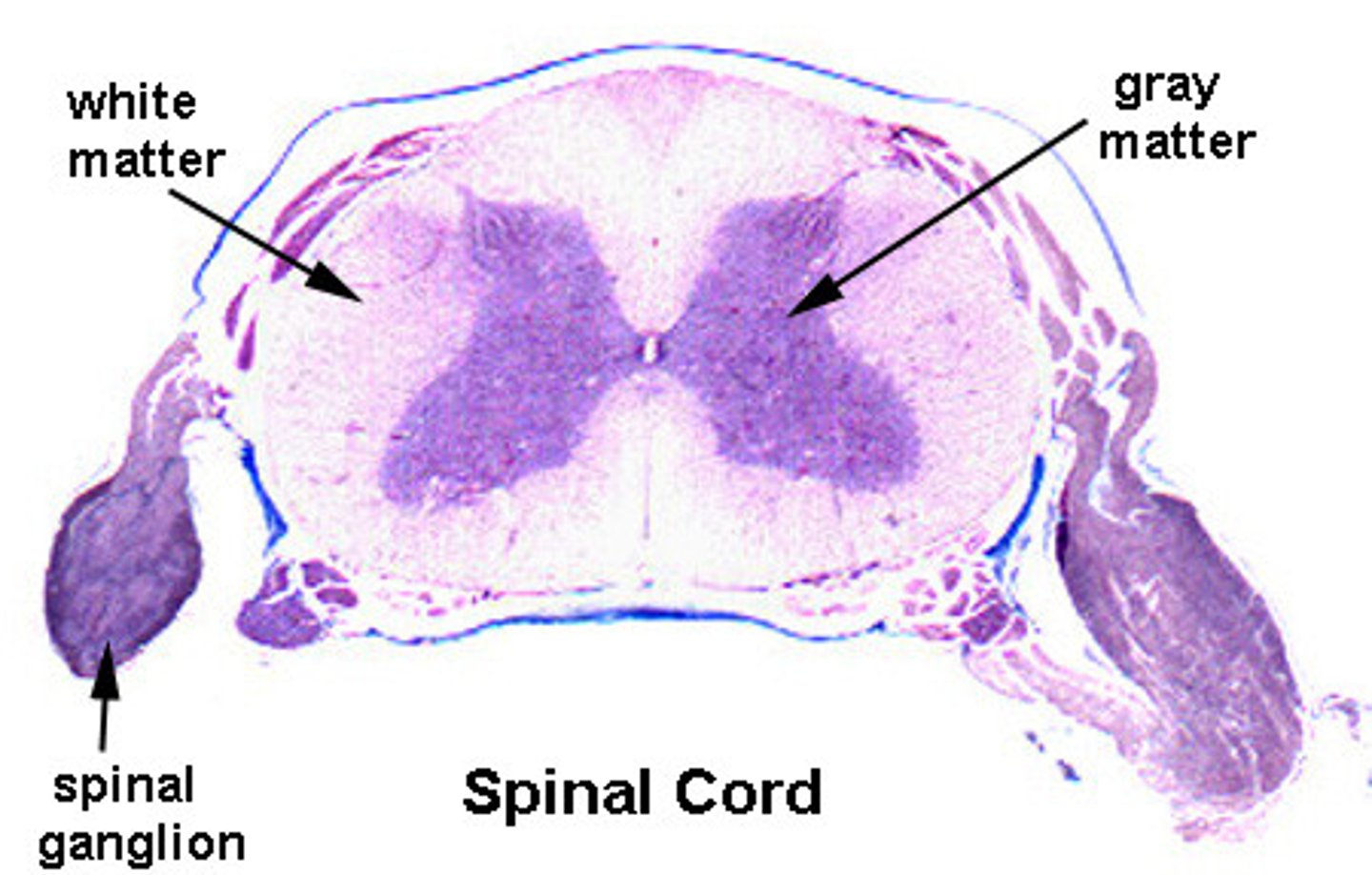
white matter of spinal cord
Primarily myelinated axons, but also has unmyelinated axons
Contains major sensory and motor tracts to and from the brain
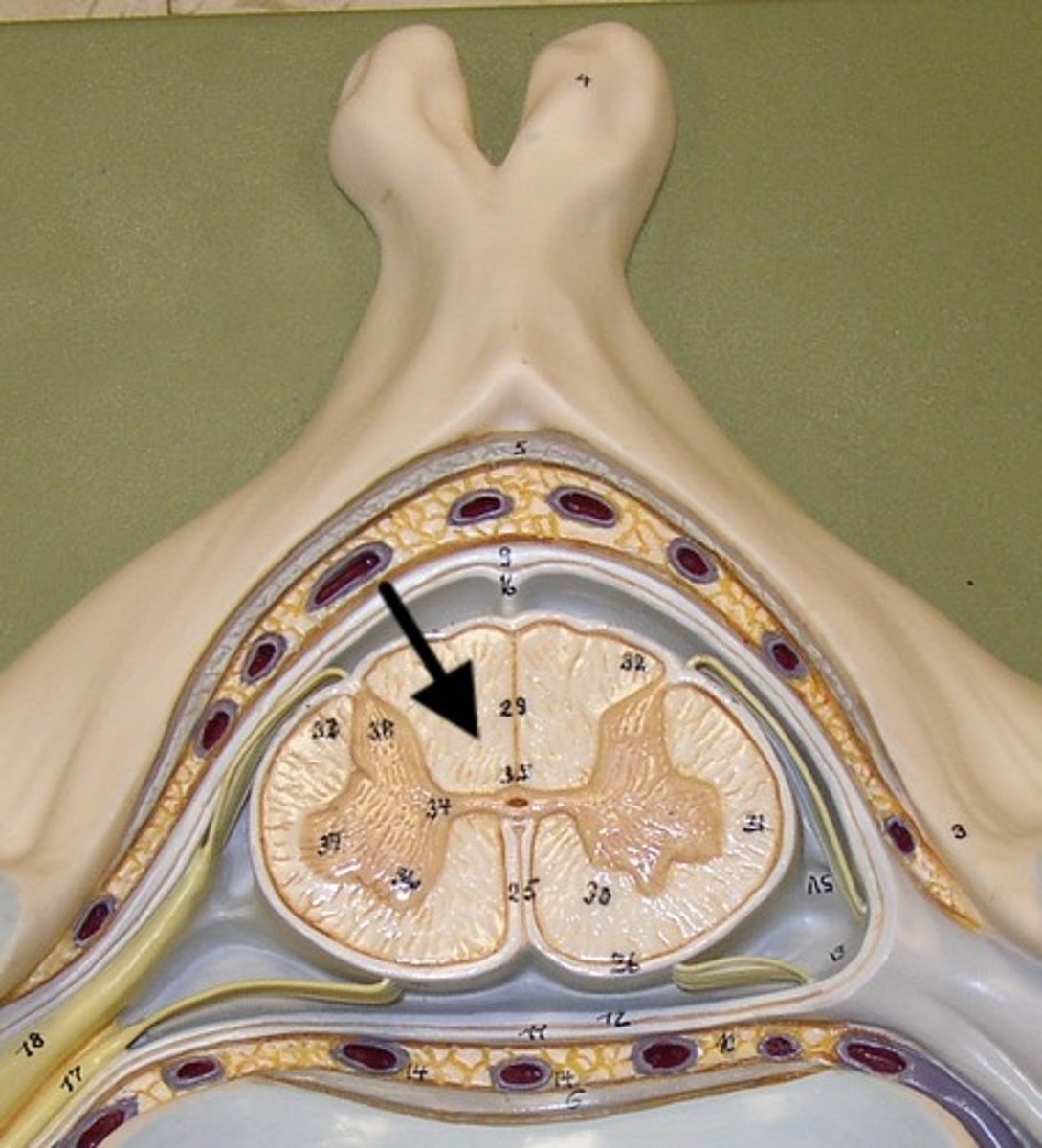
gray matter of spinal cord
Mostly neuron cell bodies, neuroglia, unmyelinated axons
Has central canal in the middle - contains cerebrospinal fluid
Site for integration of postsynaptic potentials
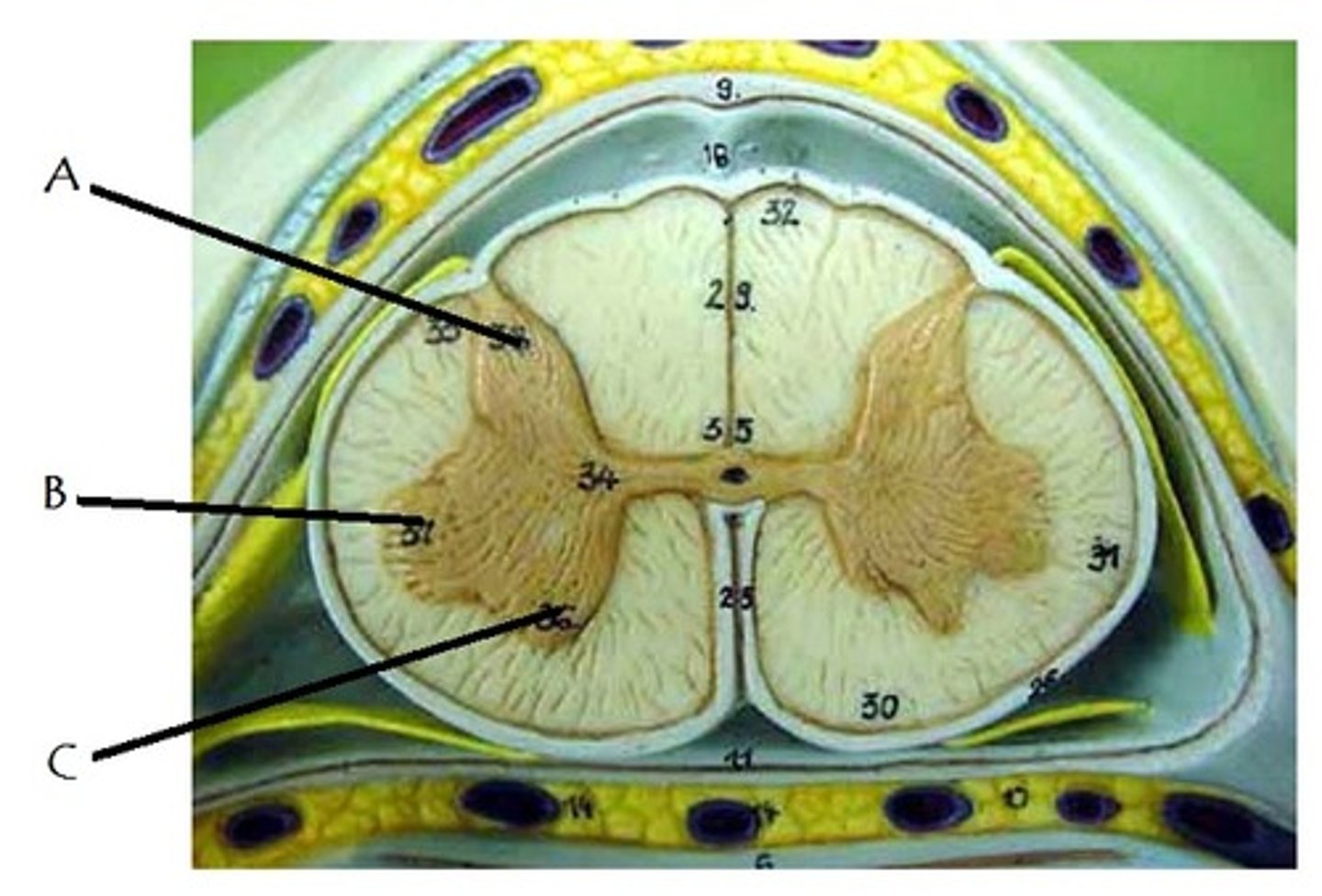
posterior gray horn
A
Location of sensory nuclei
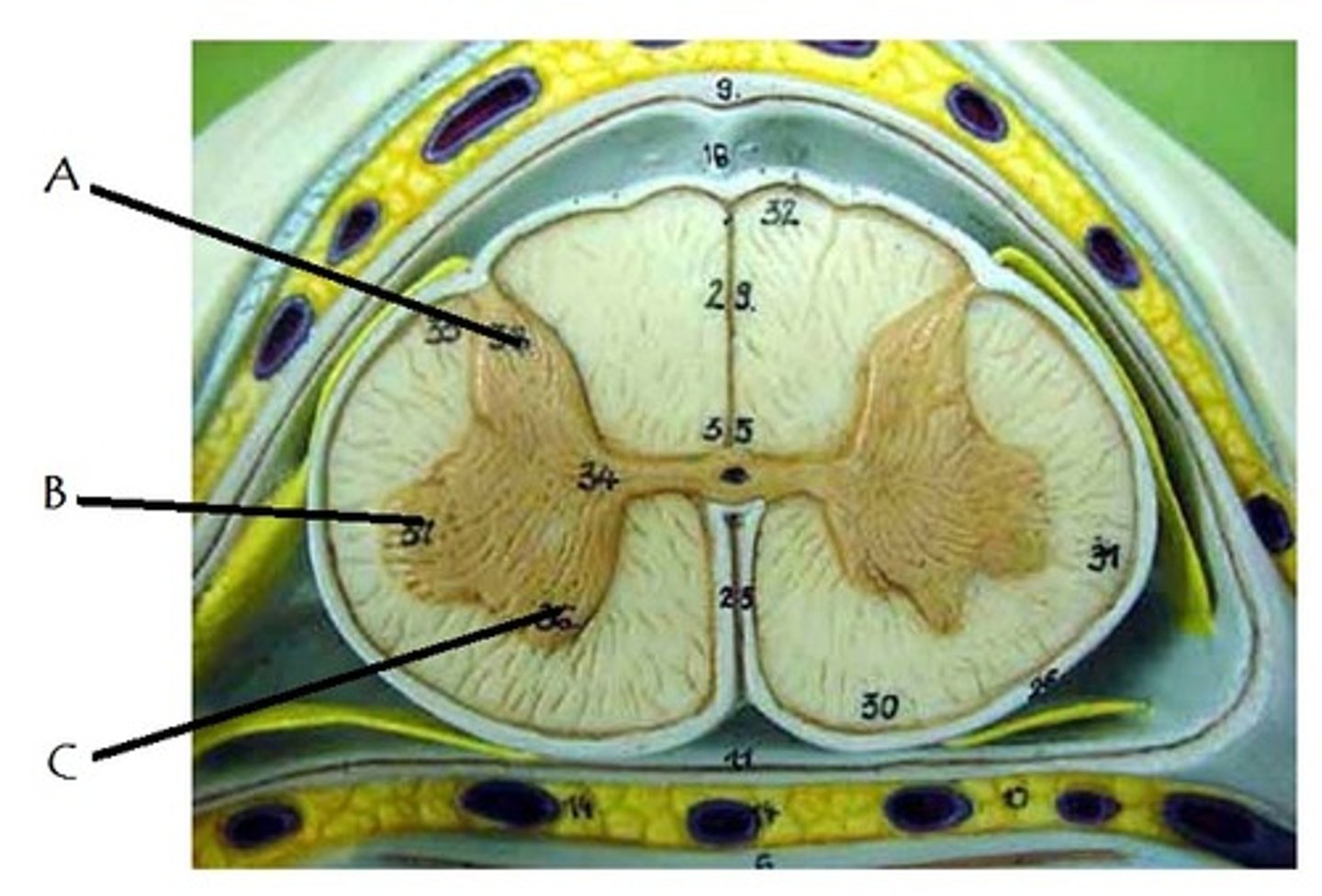
lateral gray horn
B
Contains Motor nuclei (visceral)
only in thoracic and lumbar vertebrae
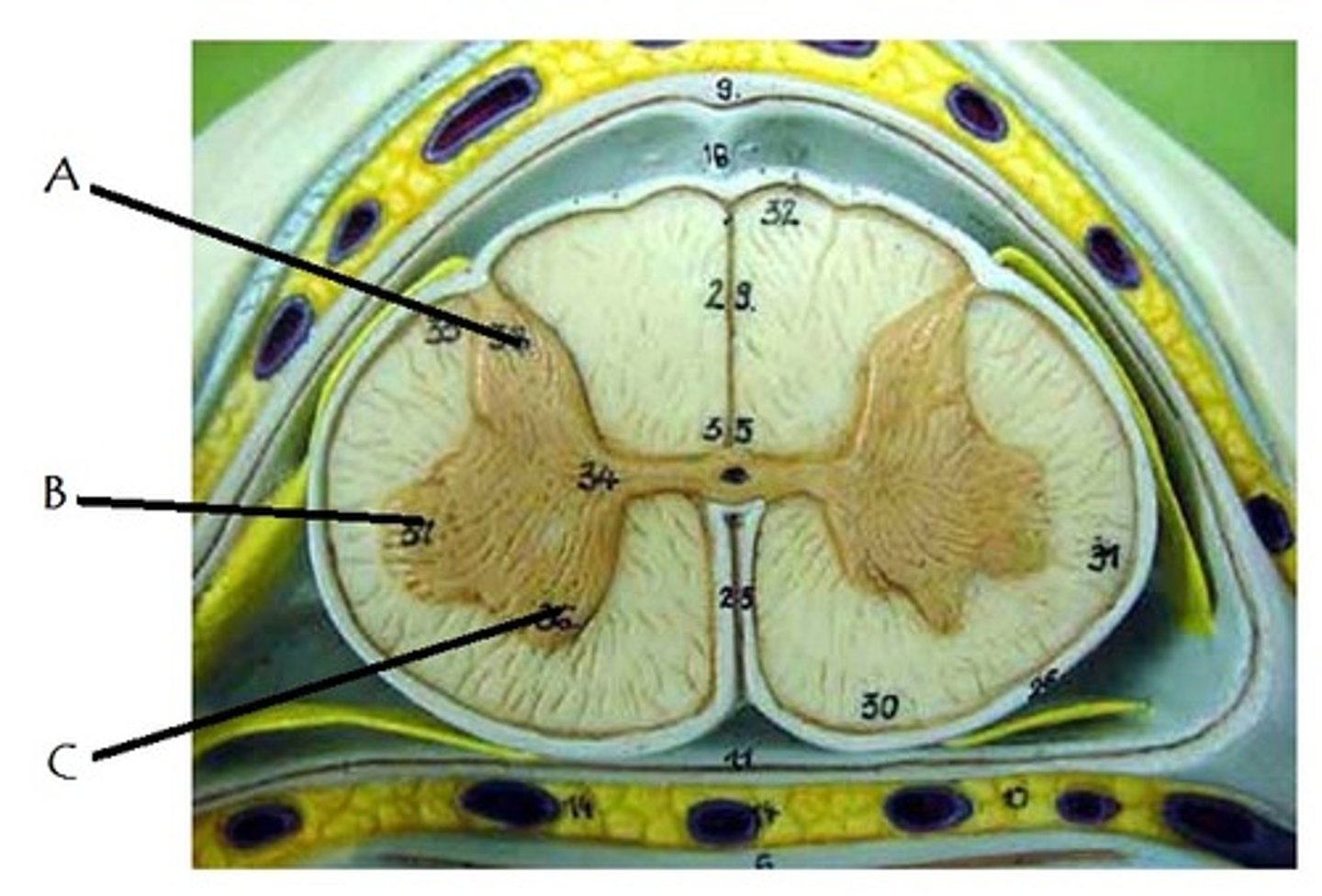
anterior gray horn
C
Contains Motor nuclei (Somatic)
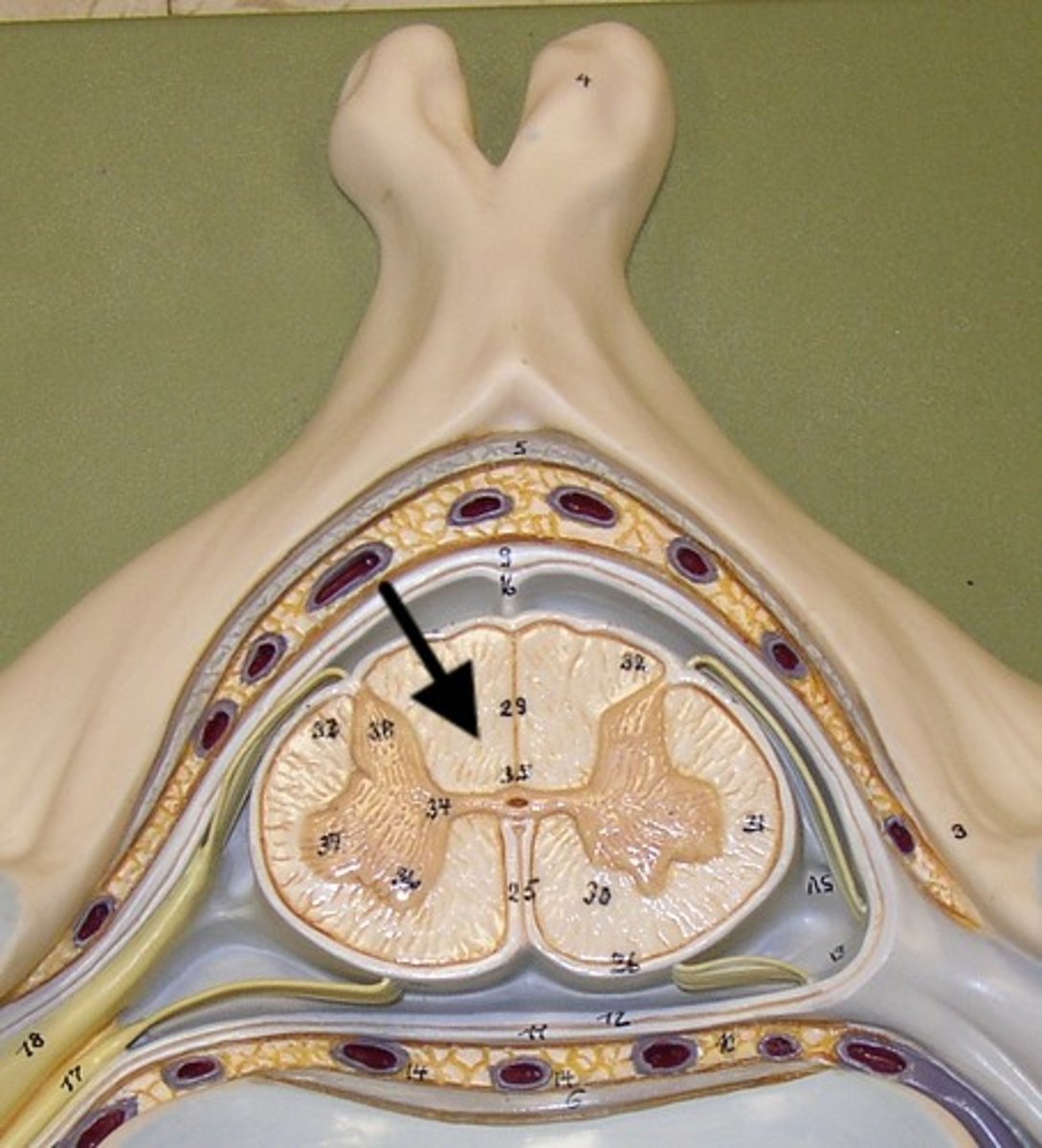
posterior white column
Sends information up to the brain
sensory info
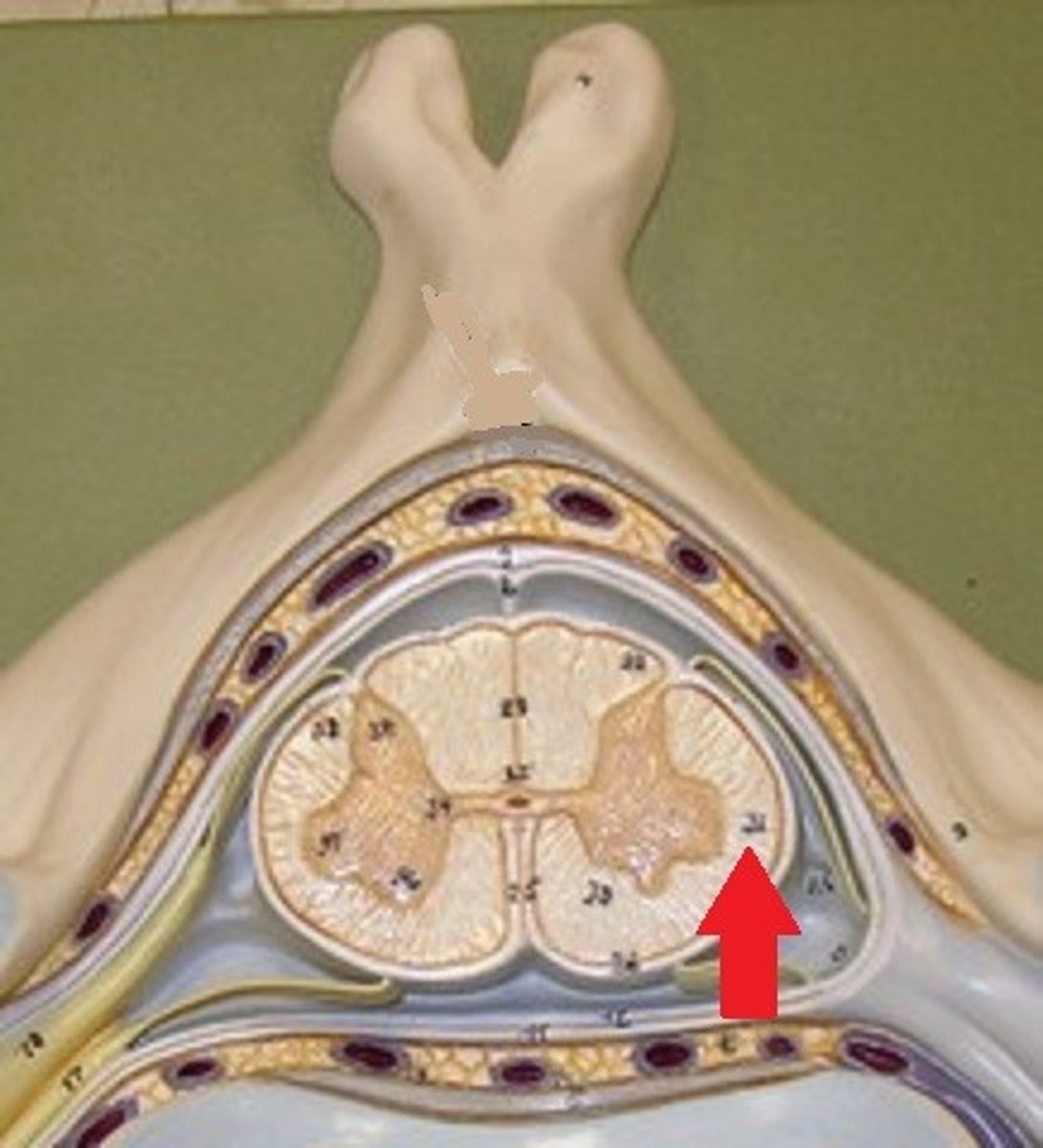
lateral white column
Information descends from the brain
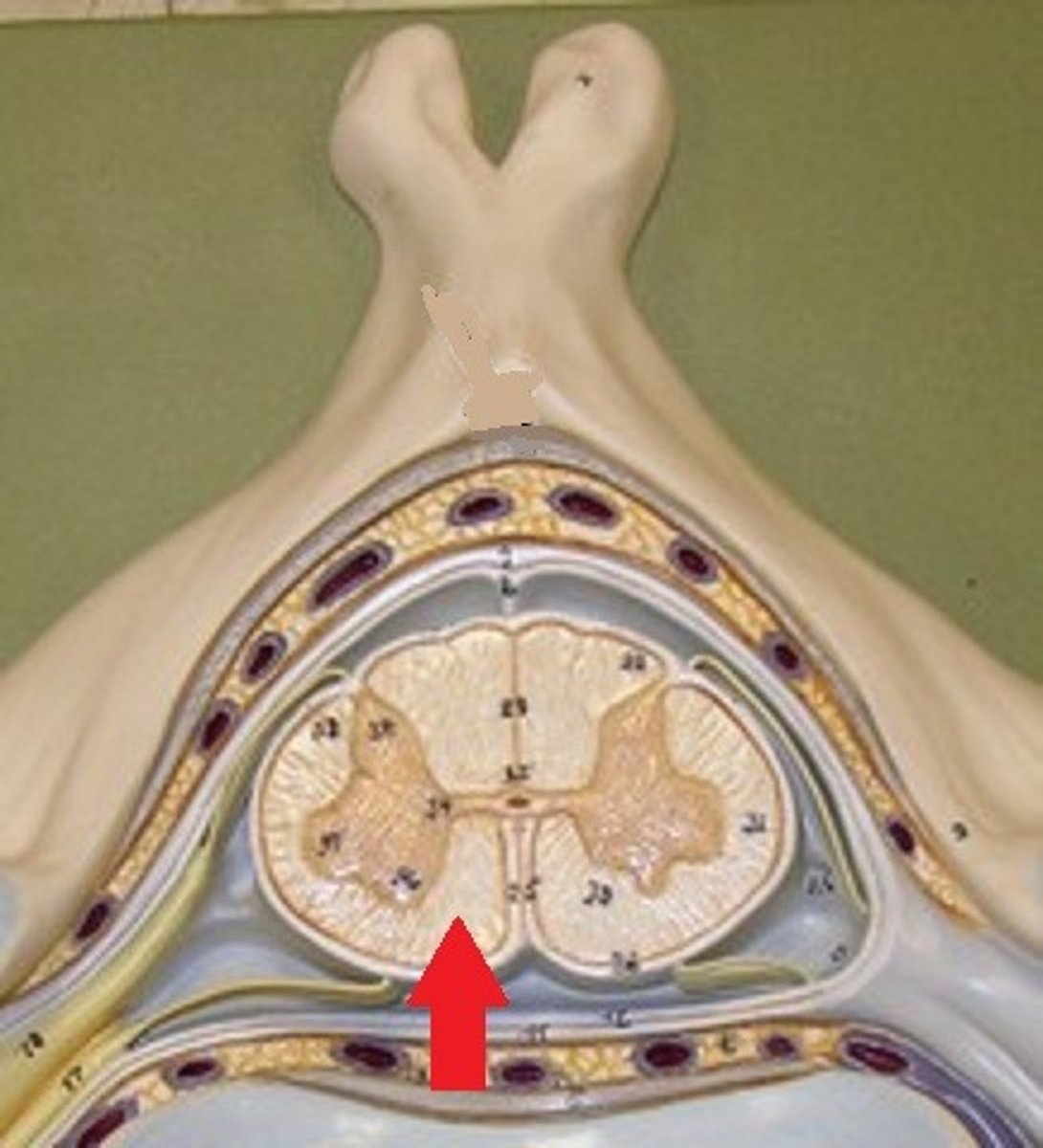
anterior white column
Information descends from the brain (Brings info back to the spinal cord)
motor commands
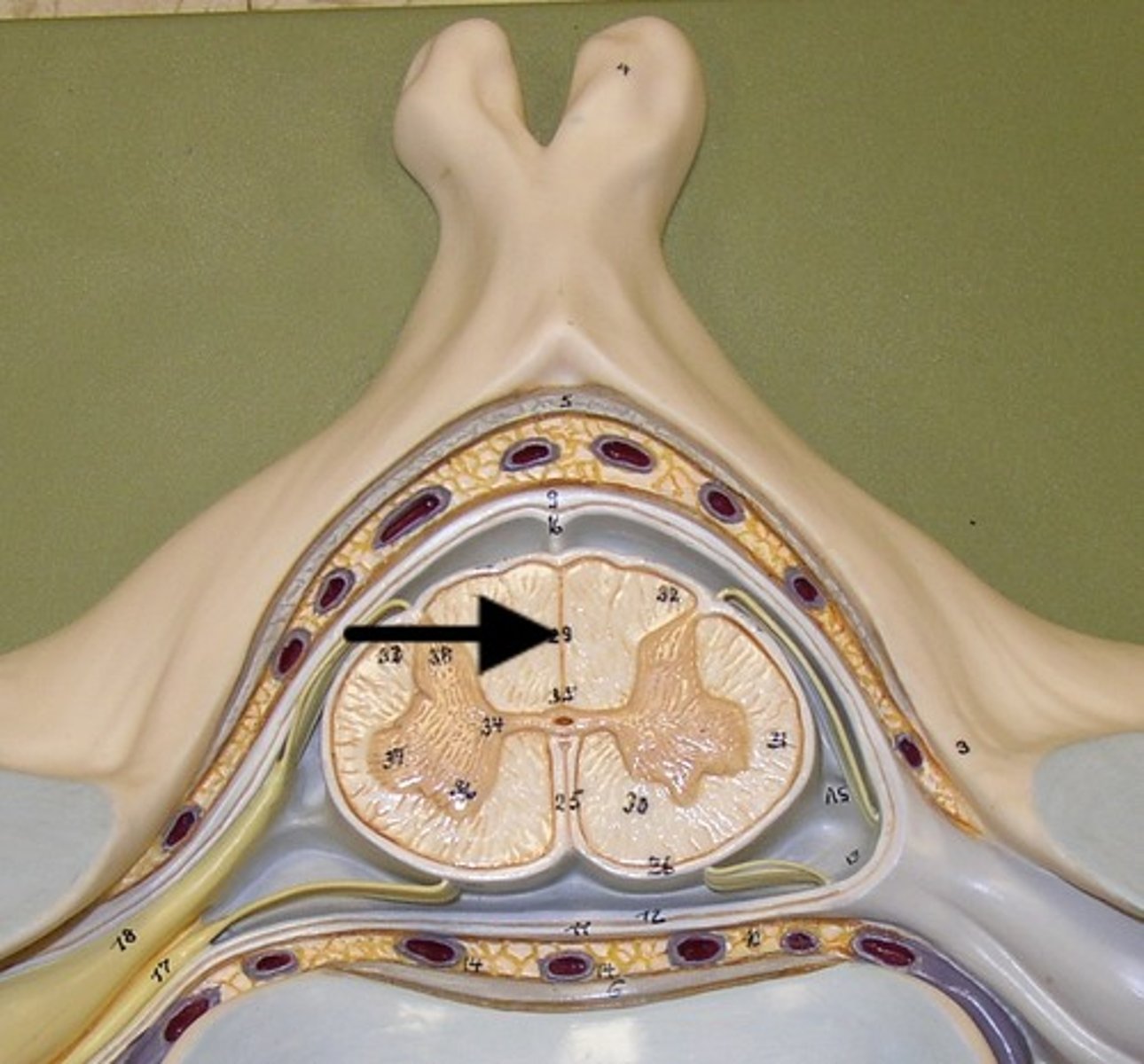
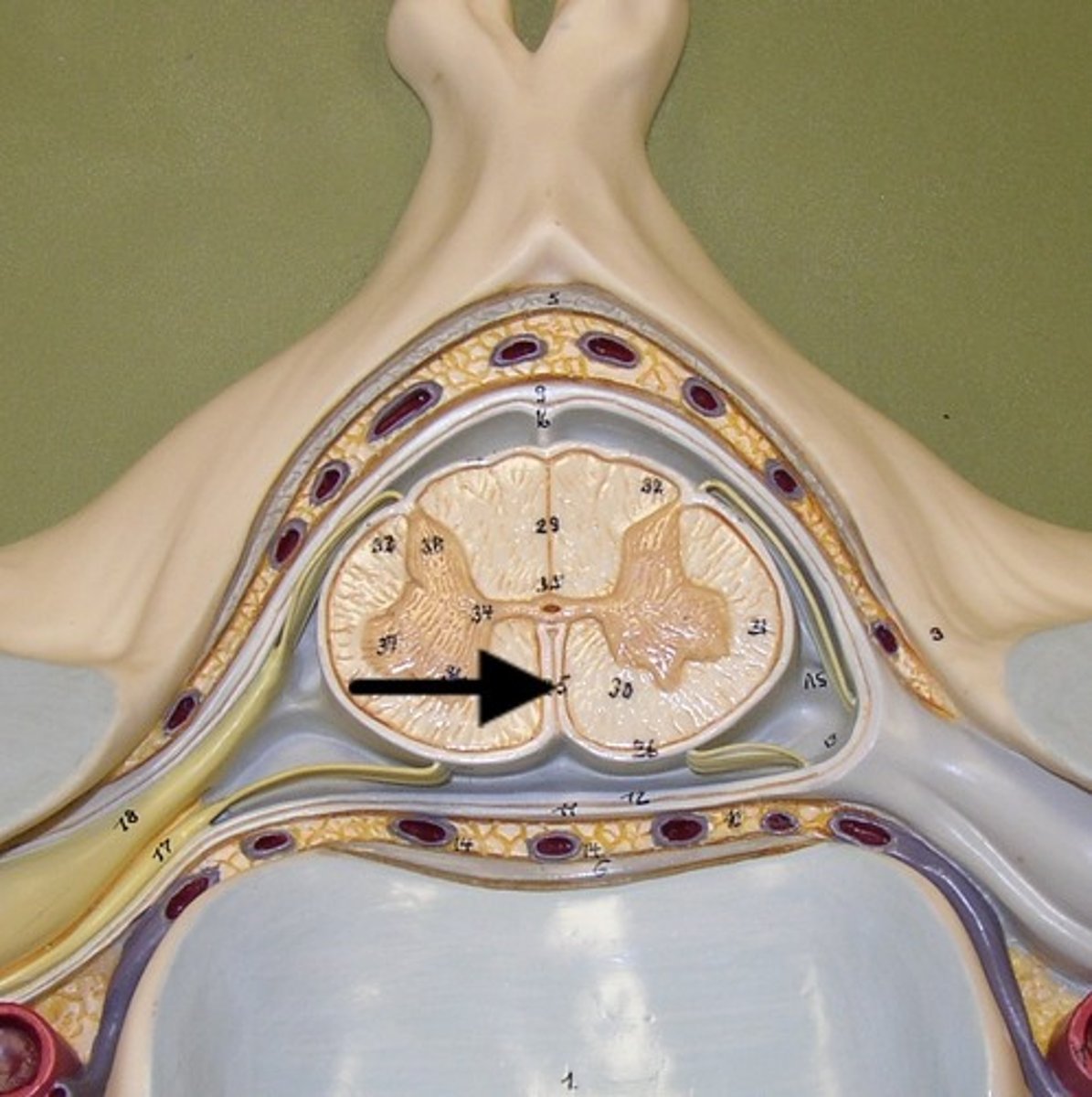
central canal of spinal cord
contains cerebrospinal fluid
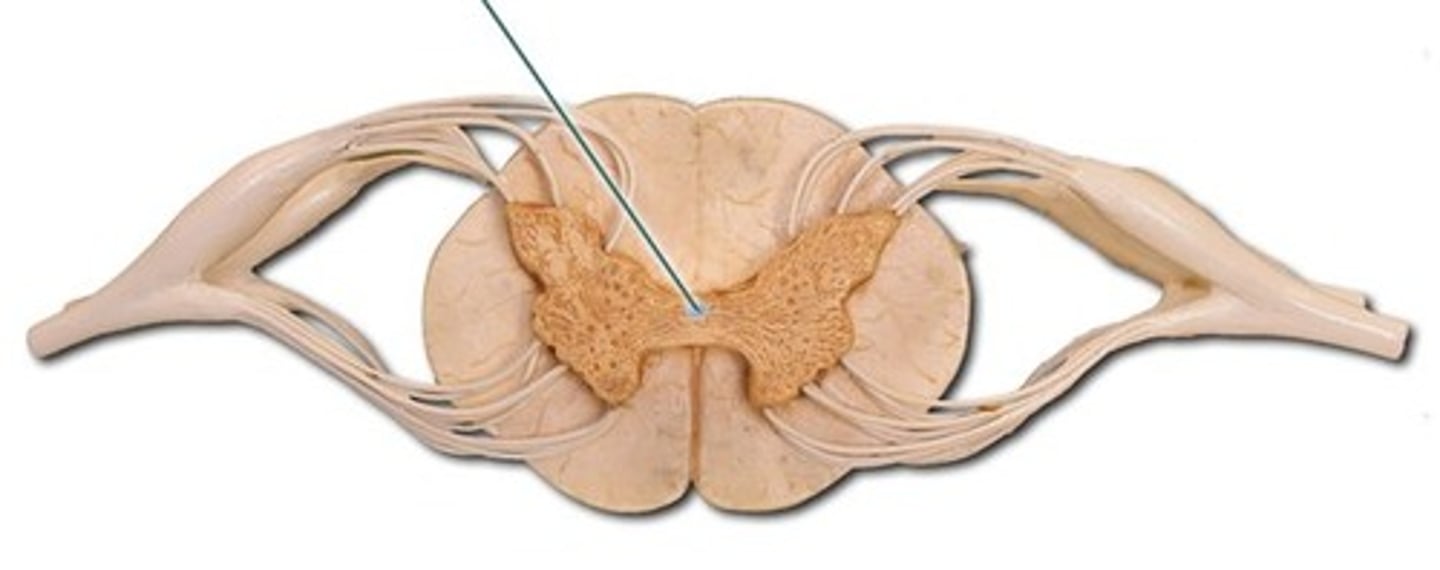
posterior median sulcus
anterior median fissure
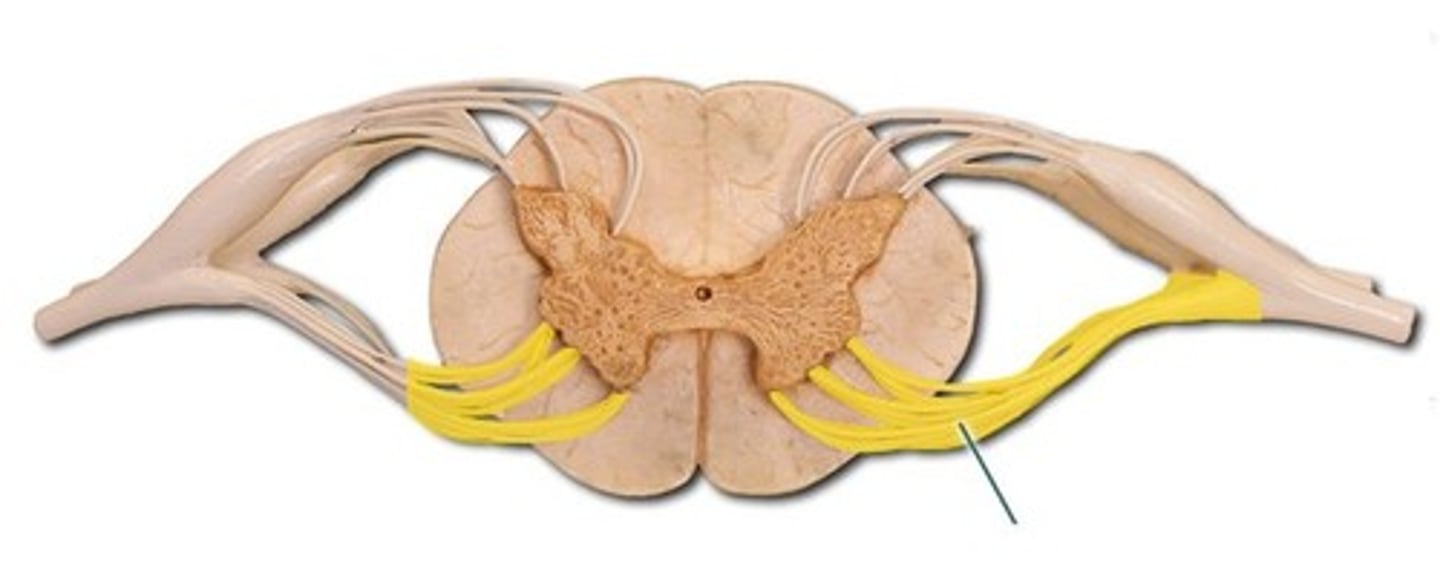
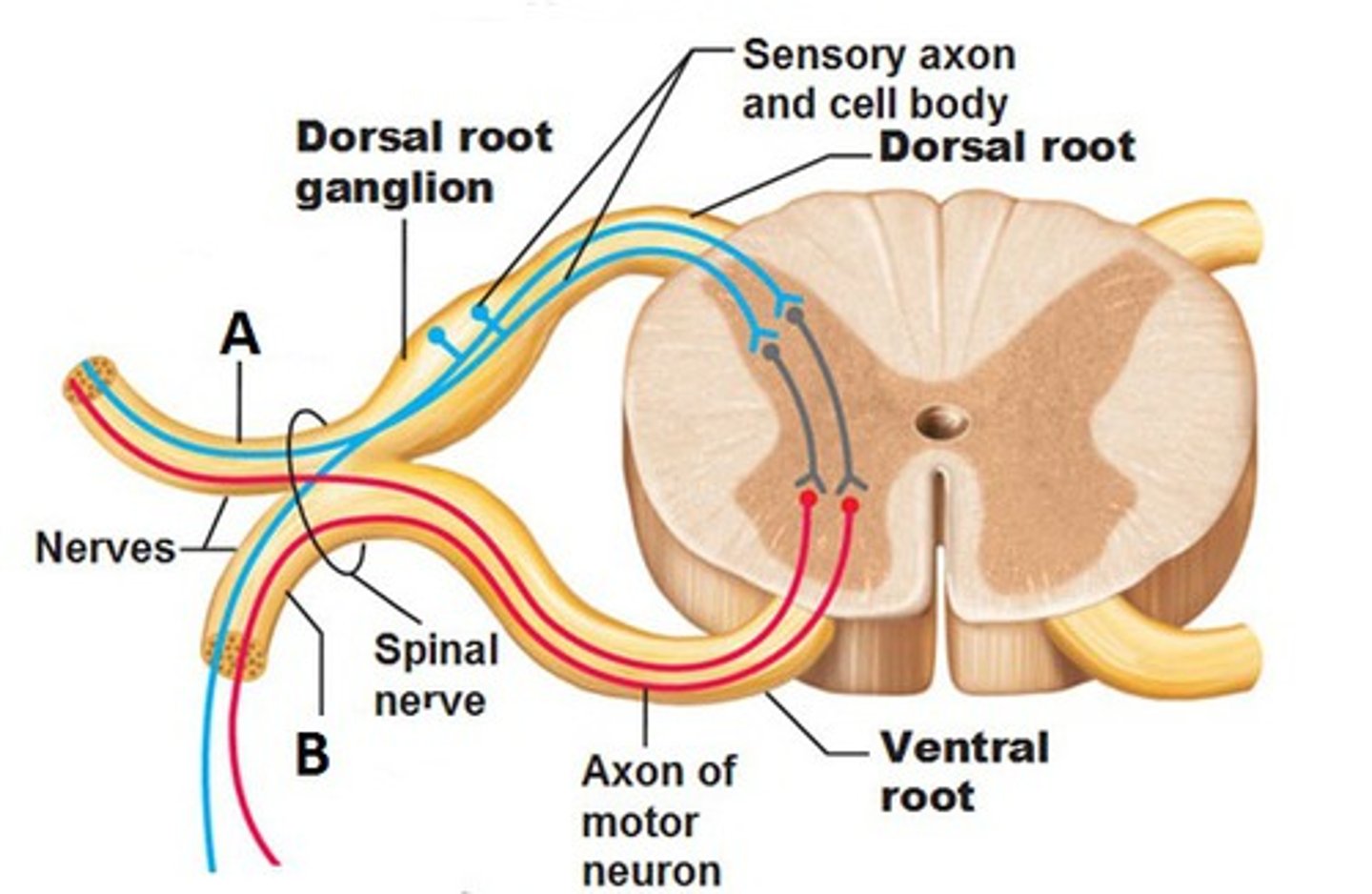
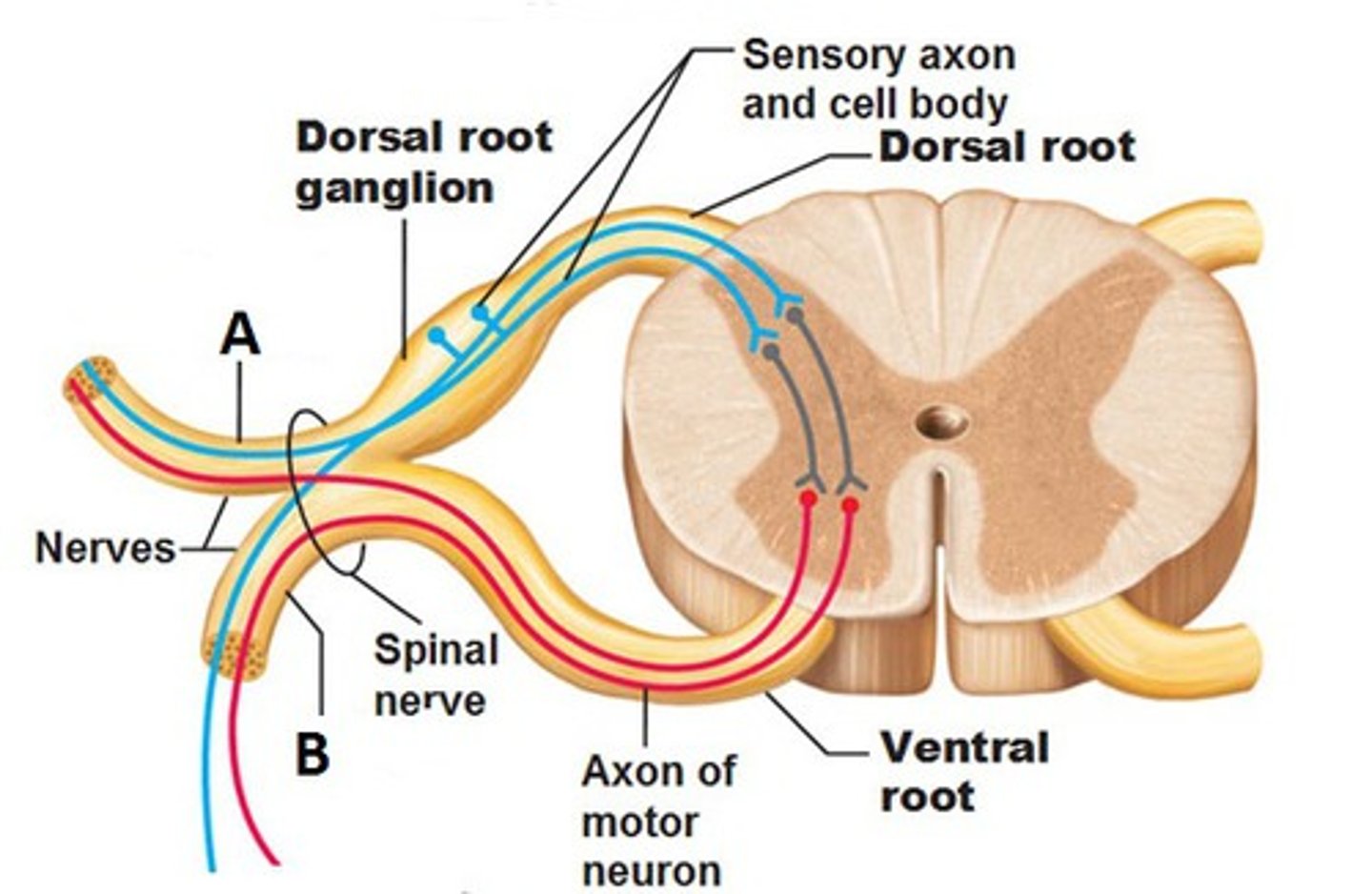
Posterior Root
Carries sensory neurons
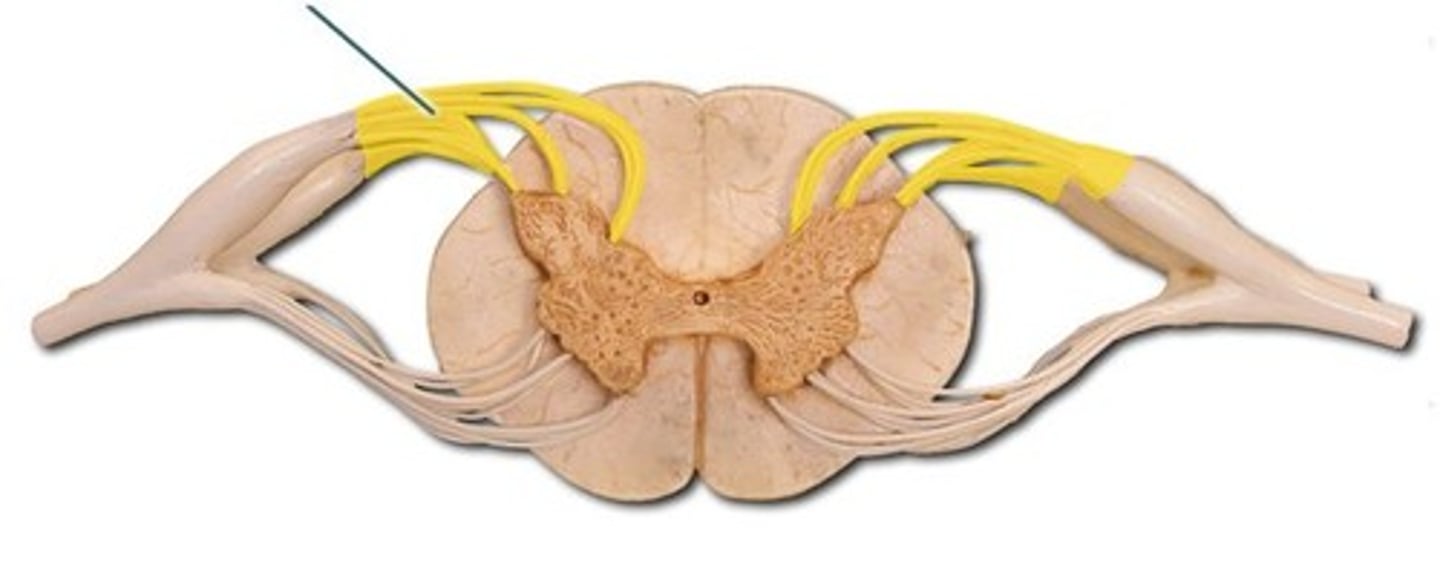
posterior root ganglion
Contains sensory nerve cell bodies
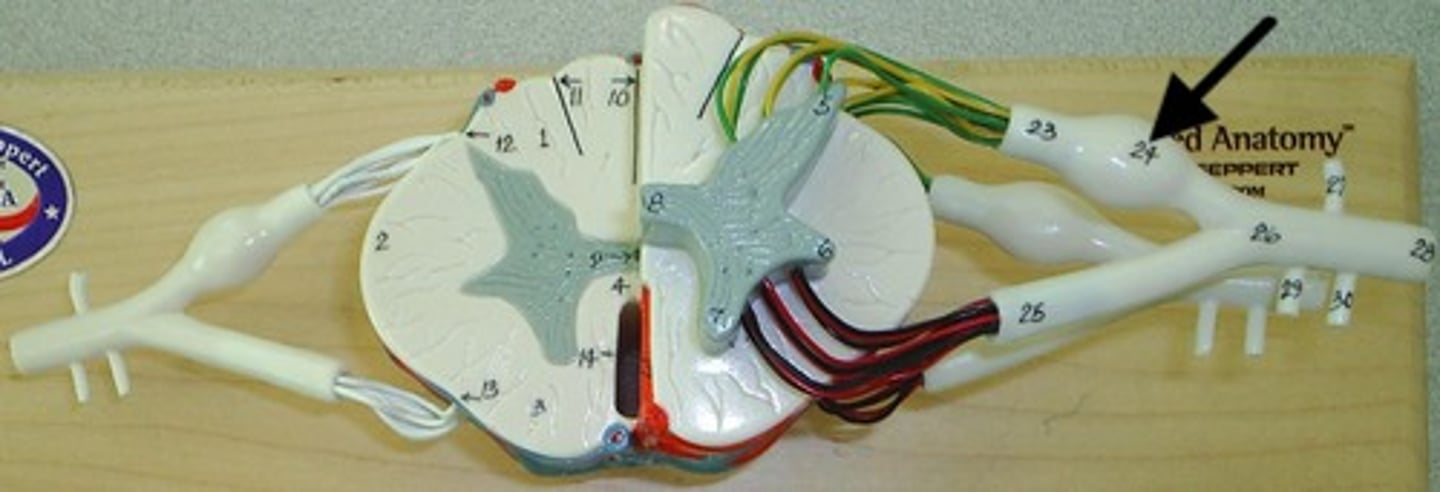
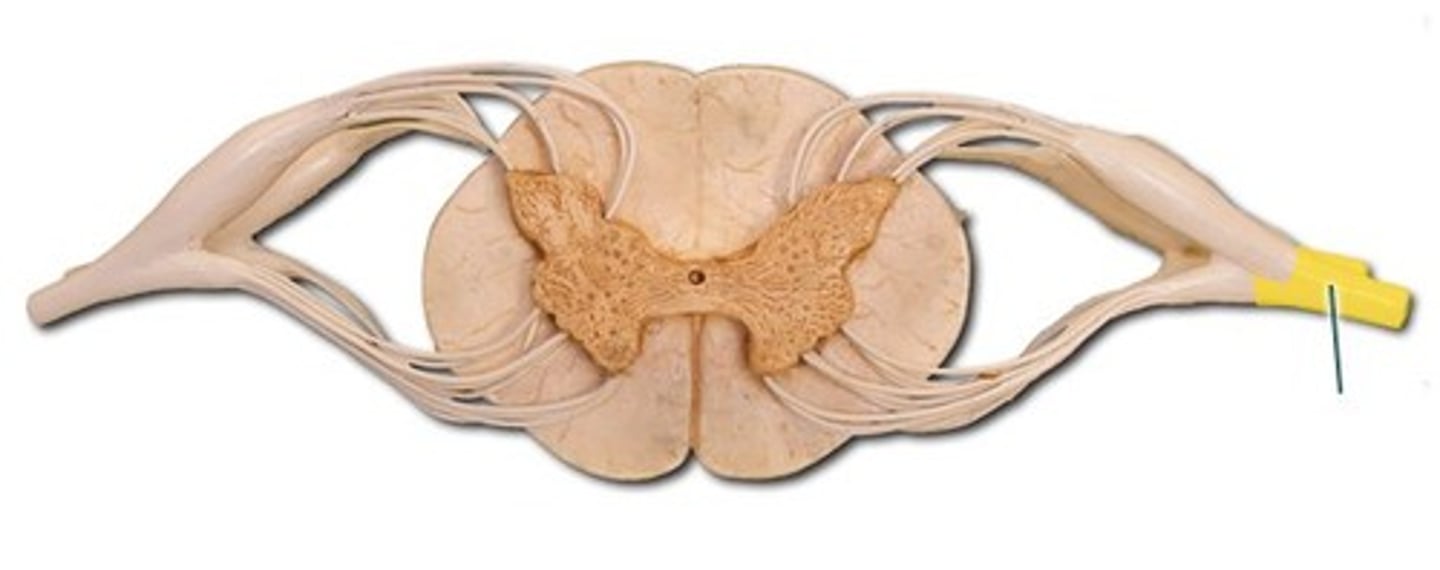
Anterior root
carries motor information
Spinal Nerve
Collection of axons
posterior ramus
Letter A in image
relates to muscles, joints, and skin of the back
Sensory info comes in and motor response going out
Anterior ramus
Letter B in image
Impacts Anterior and lateral trunk, as well as limbs
Sensory info coming in and motor going out
rami communicantes
Spinal nerves of autonomic nervous system
See chapter 12 supplemental video for image
Sympathetic nerve
Brings in sensory information from visceral organs
Carries out motor information to visceral organs
See chapter 12 supplemental video for image
spinal meninges
3 specialized membranes surrounding spinal cord and brain
Stability, shock absorption, carry blood supply (oxygen and nutrients)
3 spinal meninges (Superficial to deep)
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
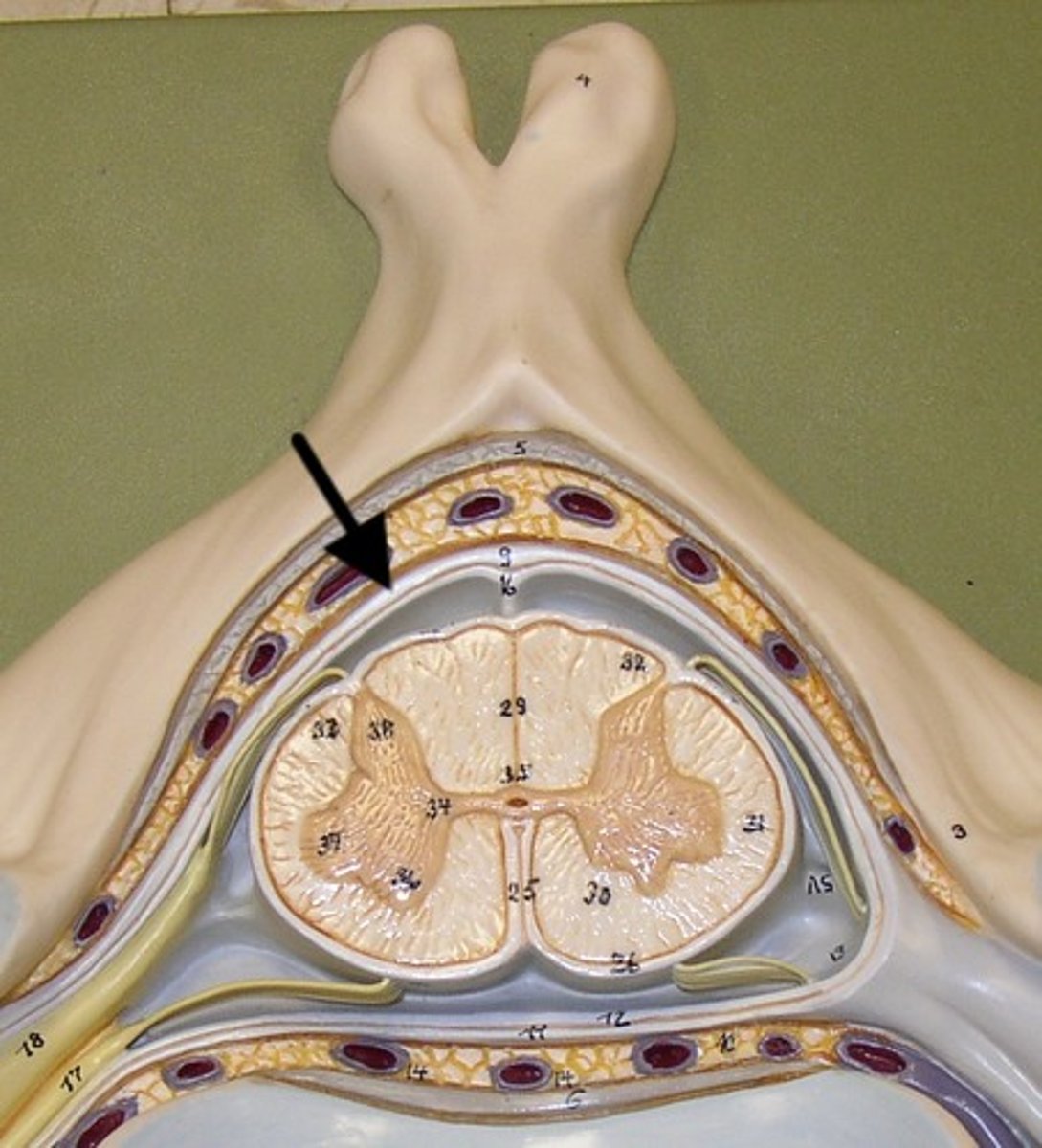
Dura mater
tough outer layer of the meninges
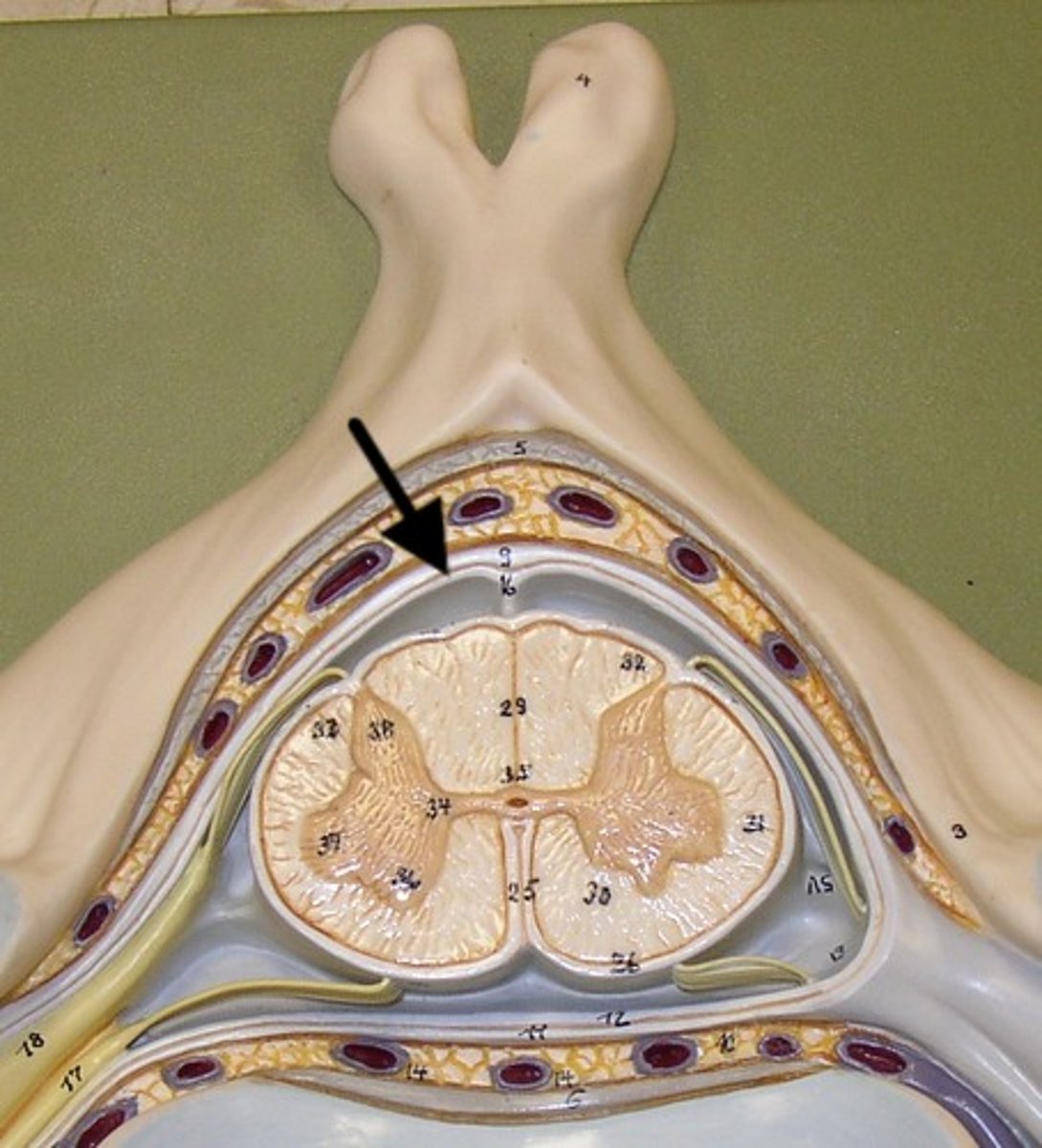
arachnoid mater
Made of simple squamous epithelium
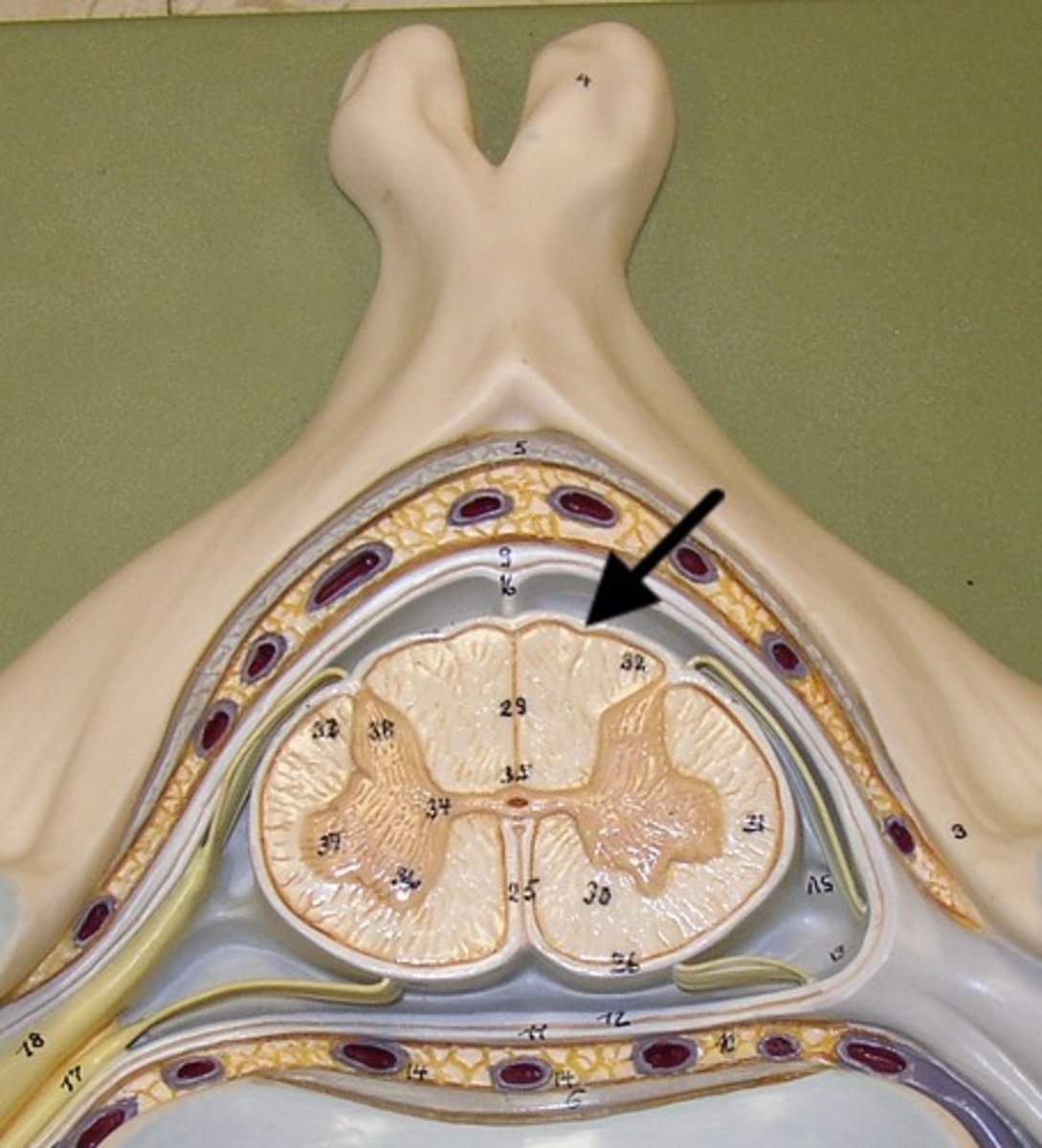
Pia mater
thin, delicate inner membrane of the meninges
subarachnoid space
between arachnoid mater and pia mater
filled with cerebrospinal fluid
shock absorber; diffusion of gases, nutrients, etc.
blood vessels for spinal cord
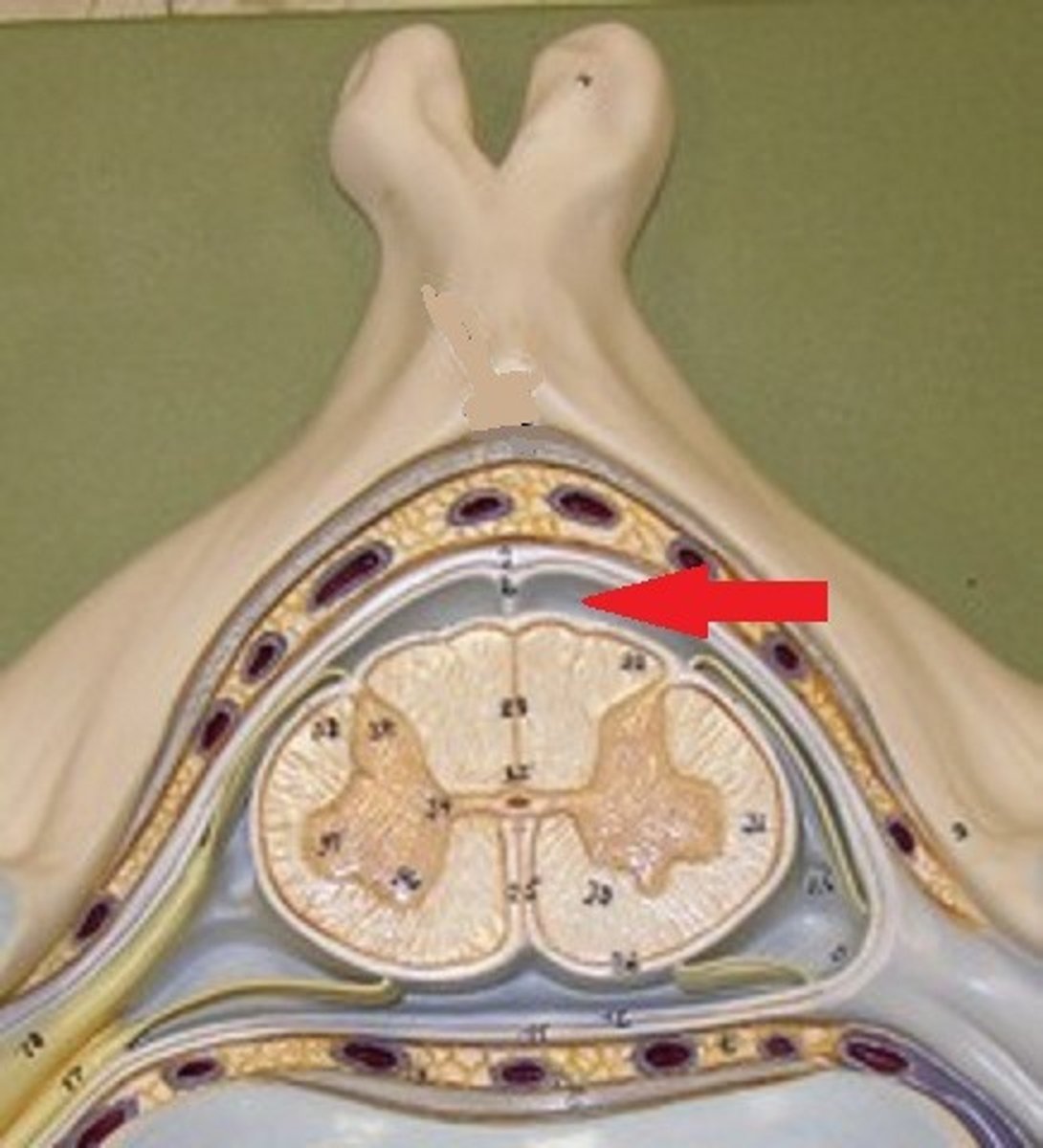
epidural space
space between dura mater and vertebrae

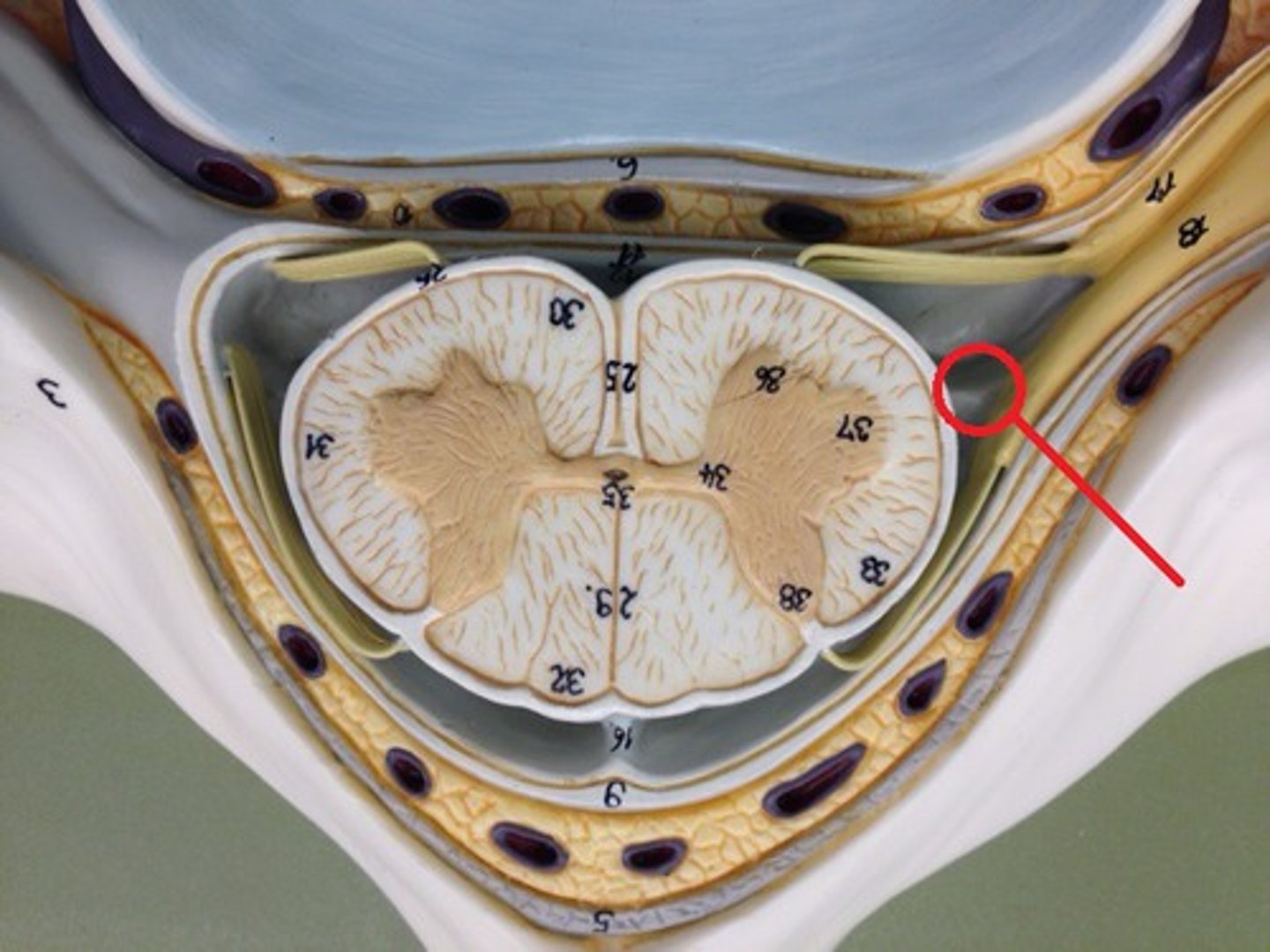
denticulate ligaments
pia mater, through the arachnoid mater, to dura mater
Prevents lateral movement
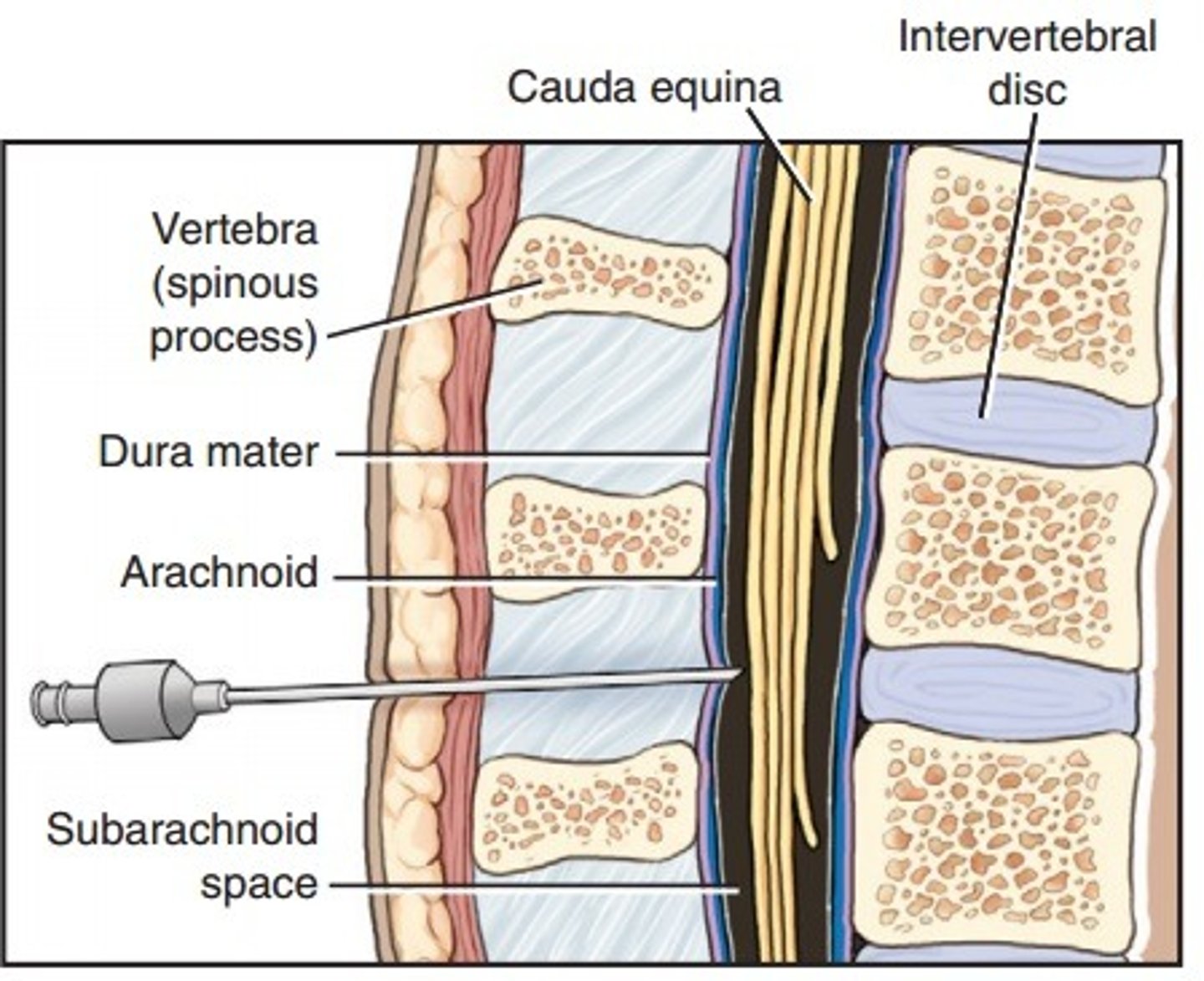
Lumbar puncture
Withdrawal of cerebrospinal fluid
needle inserted into subarachnoid space between two lumbar vertebrae.
Also known as spinal tap
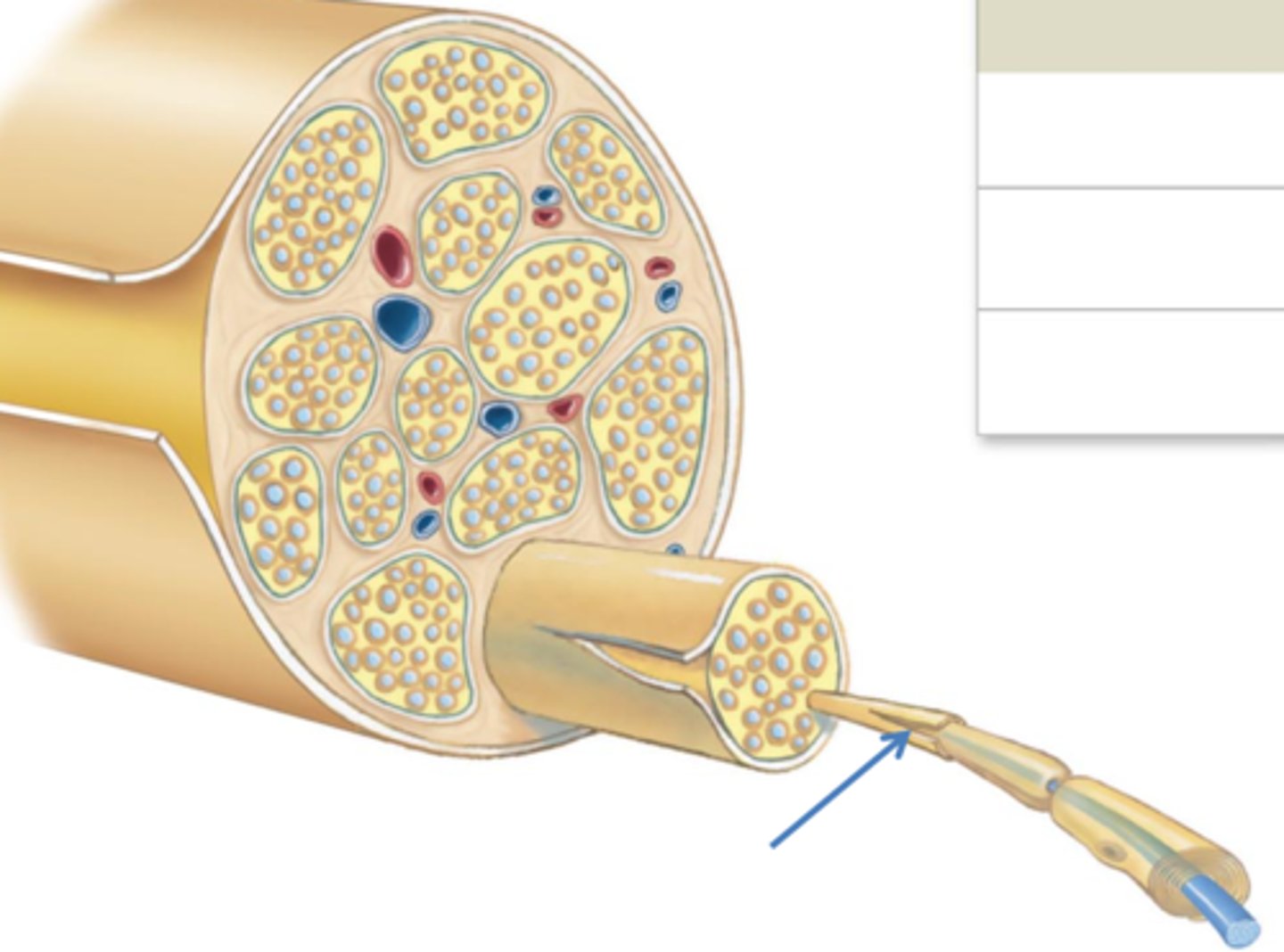
3 connective tissue layers of a spinal nerve
epineurium,
perineurium, endoneurium
Epineurium
surrounds the entire nerve
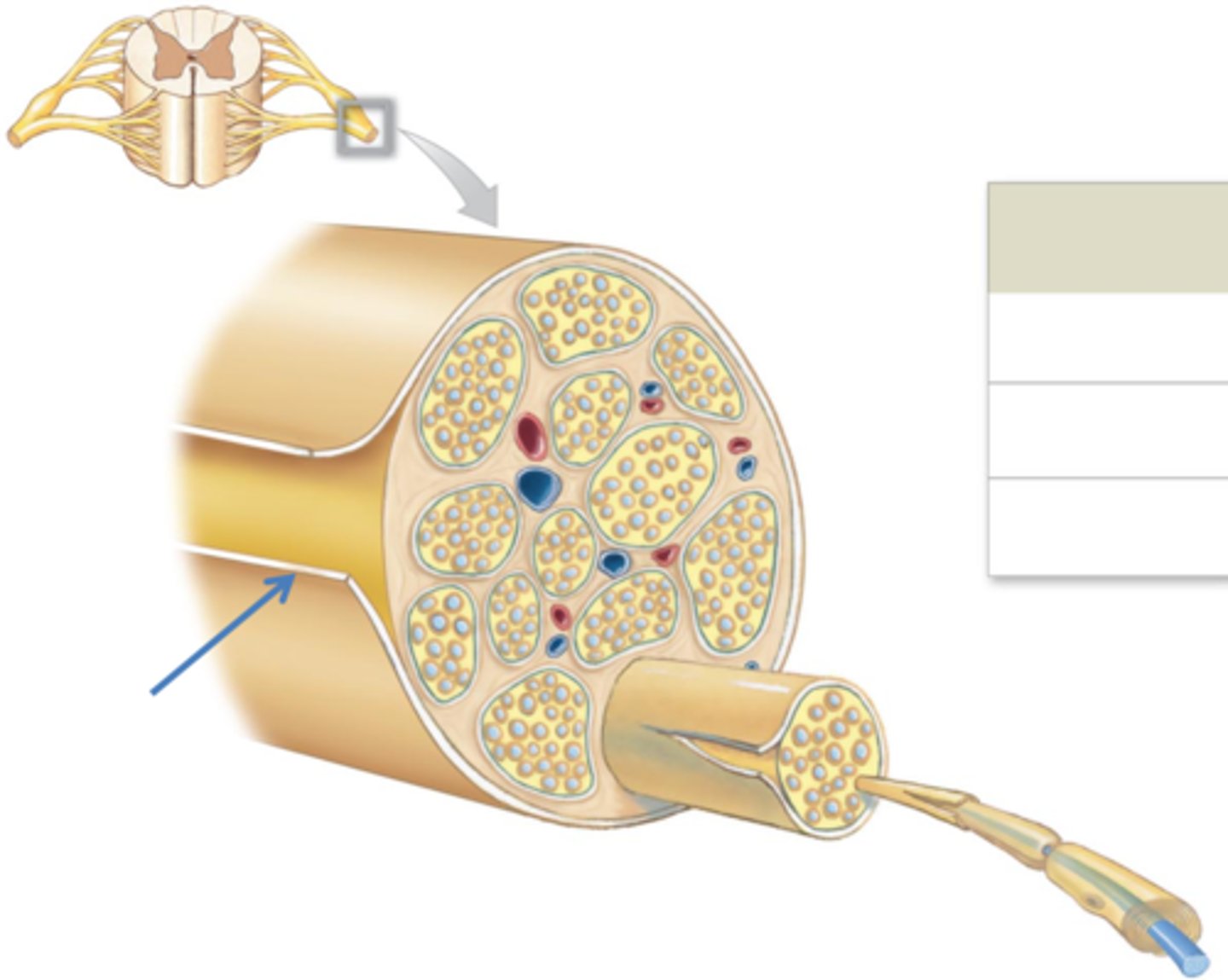
Perineurium
surrounds group of axons (fascicles)
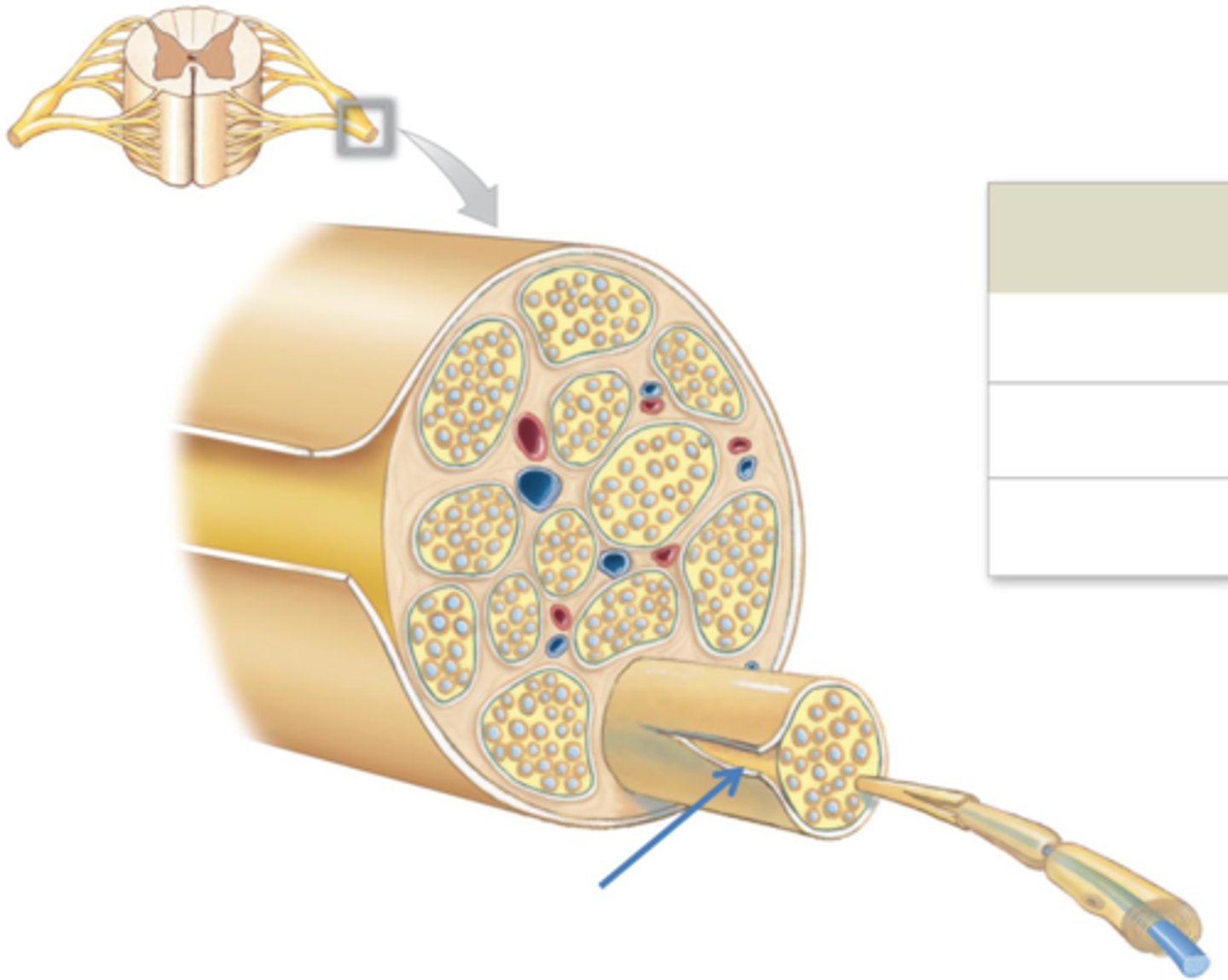
Endoneurium
Surrounds individual axons
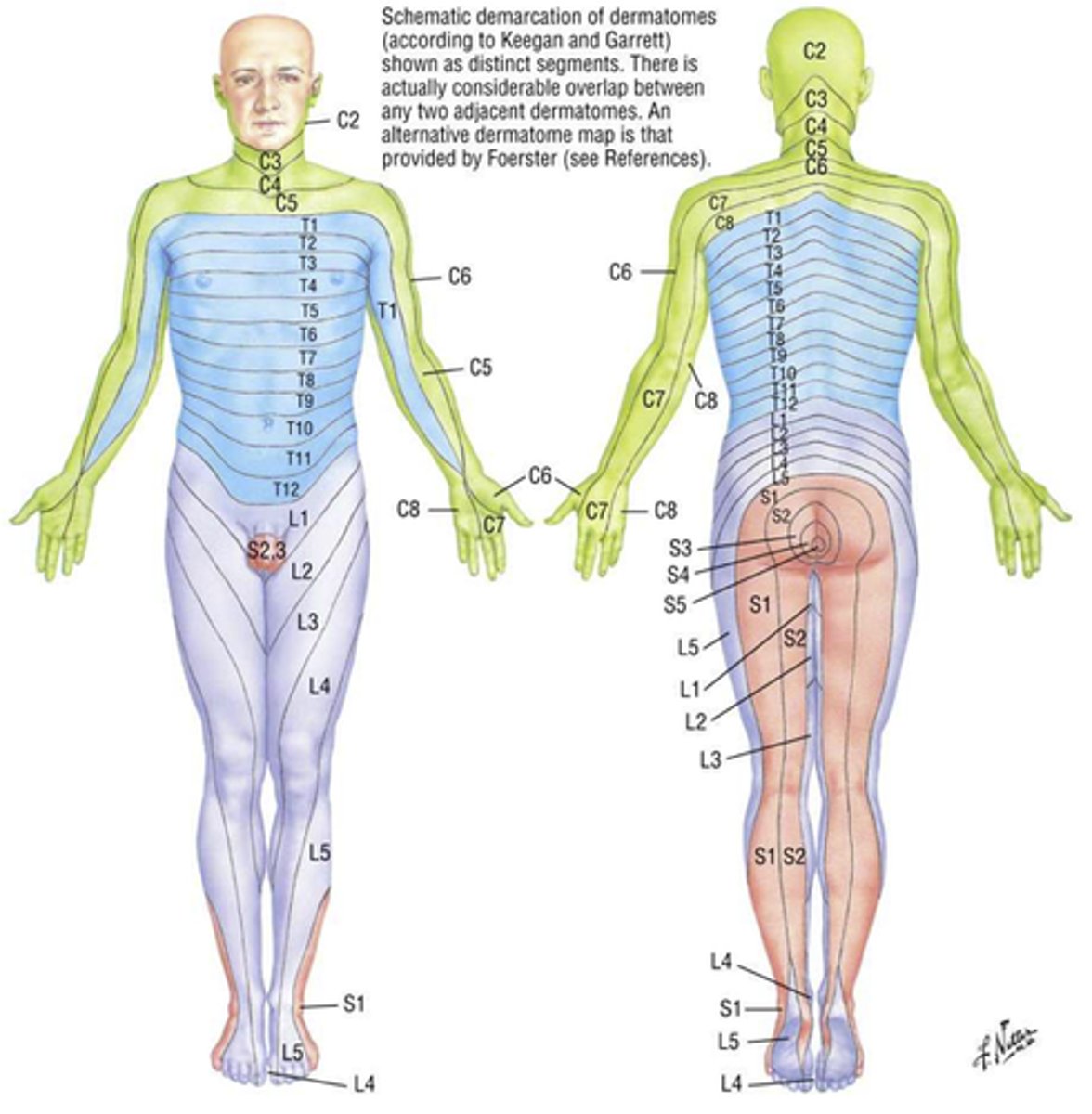
dermatome
Area of skin innervated by spinal nerves
sensory
Not face (CN V) or scalp
Some boundaries overlap
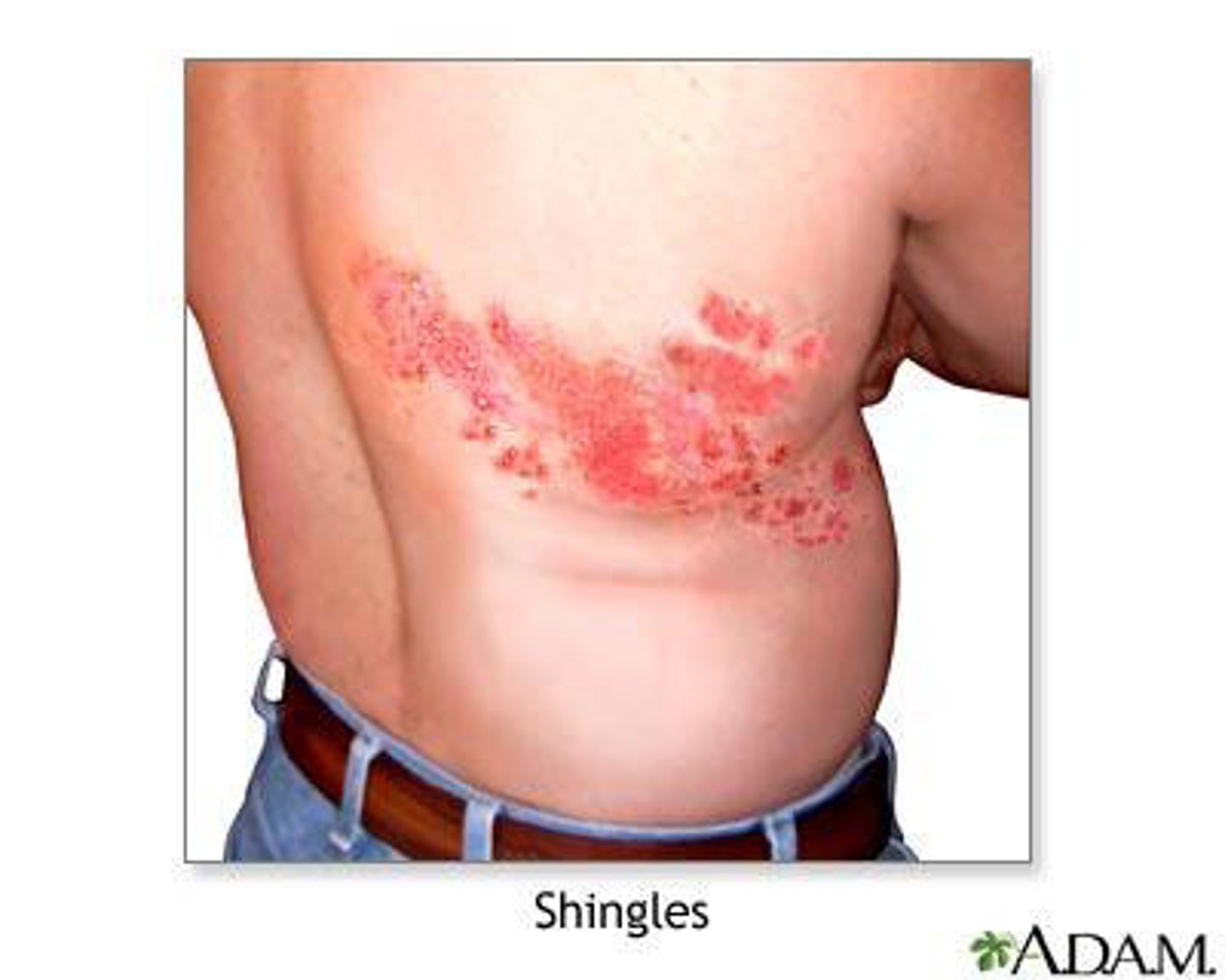
Shingles
varicella zoster virus
Causes chicken pox
Can later attack neurons in posterior roots and sensory ganglia
nerve plexus
anterior rami of adjacent spinal nerves
4 major nerve plexuses:
Cervical plexus - neck + diaphragm
Brachial Plexus - pectoral girdle, upper limb
Lumbar Plexus - pelvic girdle, lower limb
Sacral Plexus - pelvic girdle, lower limb
Cervical Plexus
Anterior Rami of C1-C5
Branches innervate skin/muscles of the neck
Contains the phrenic nerve
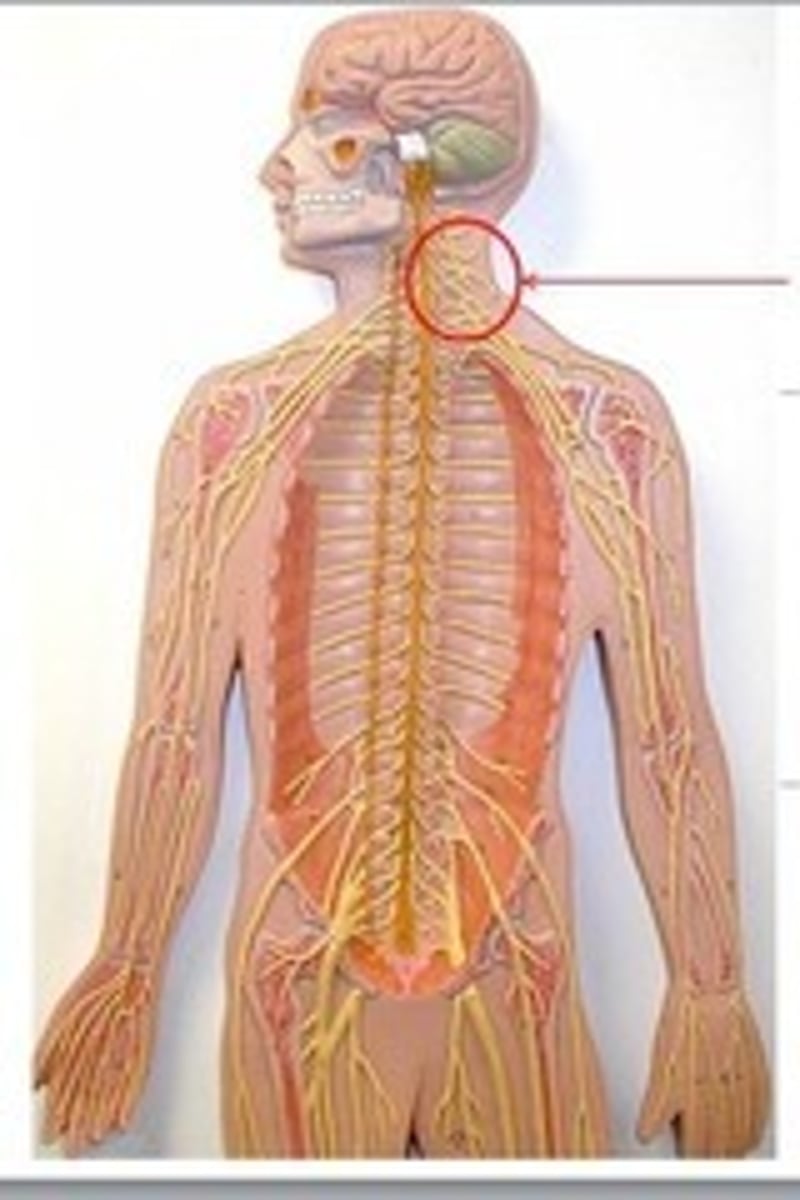
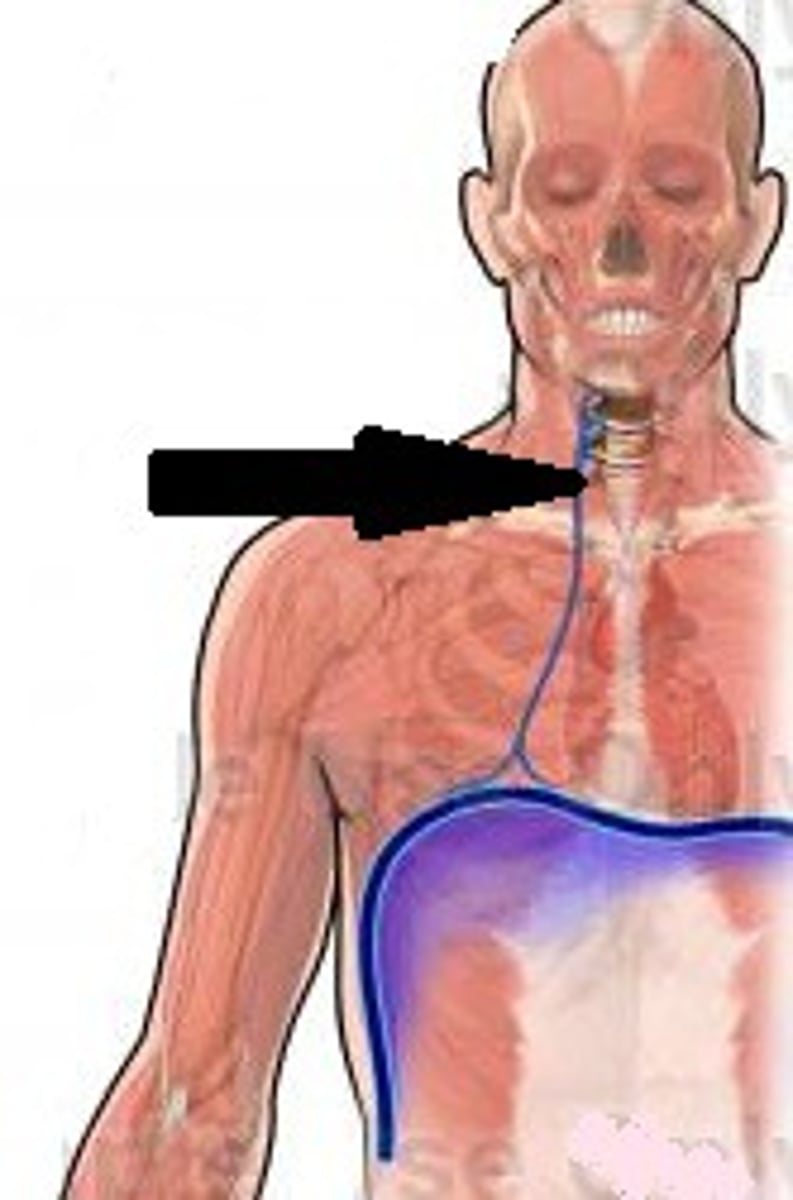
phrenic nerve
C3-C5 to the diaphragm, allows breathing.
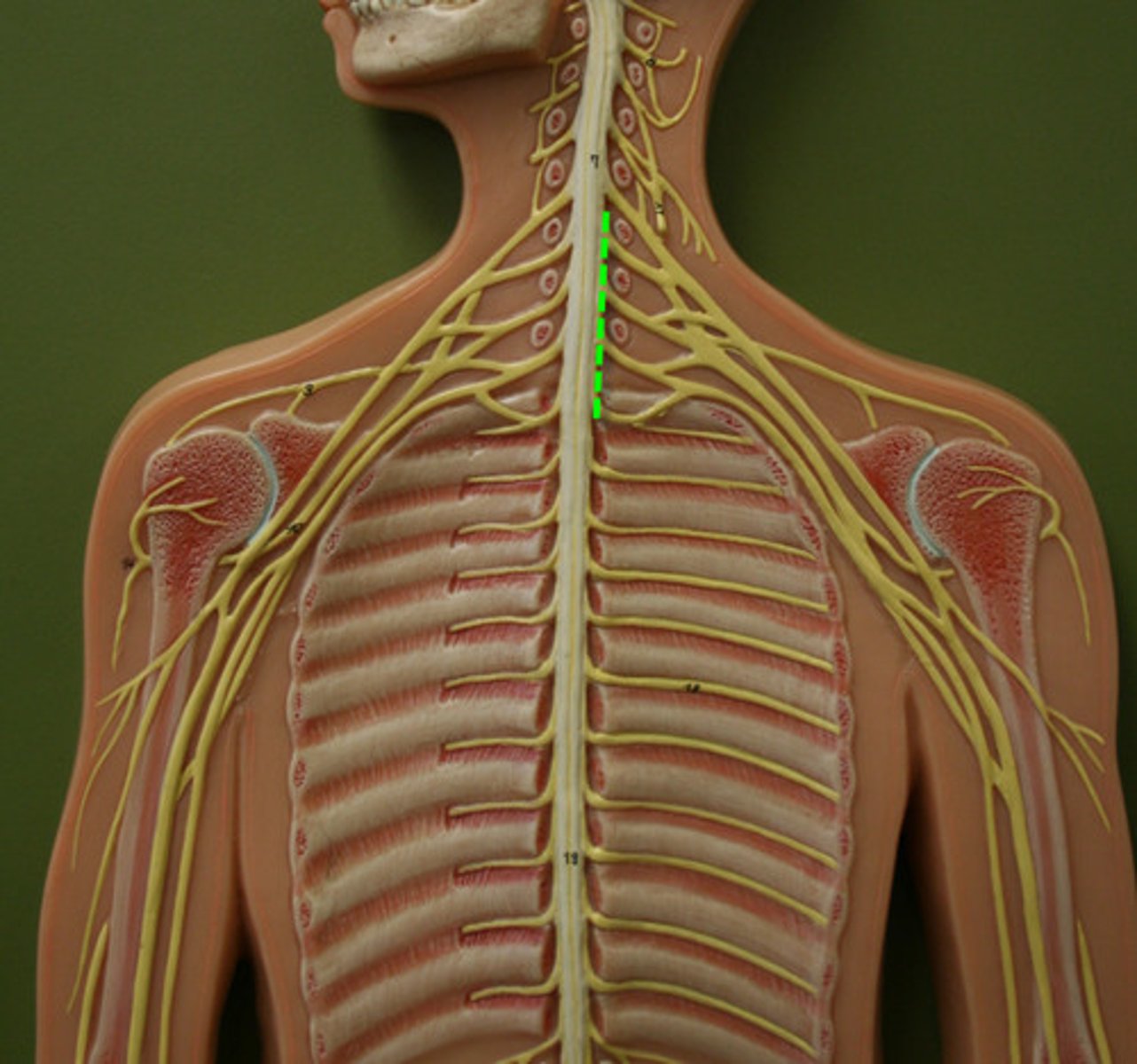
brachial plexus
Anterior Rami of C5-T1
Innervates skin and muscles of Pectoral girdle, upper back, and upper limbs
lumbar plexus
Anterior rami of T12-L4
Innervates skin and muscles of pelvic girdle and lower limbs
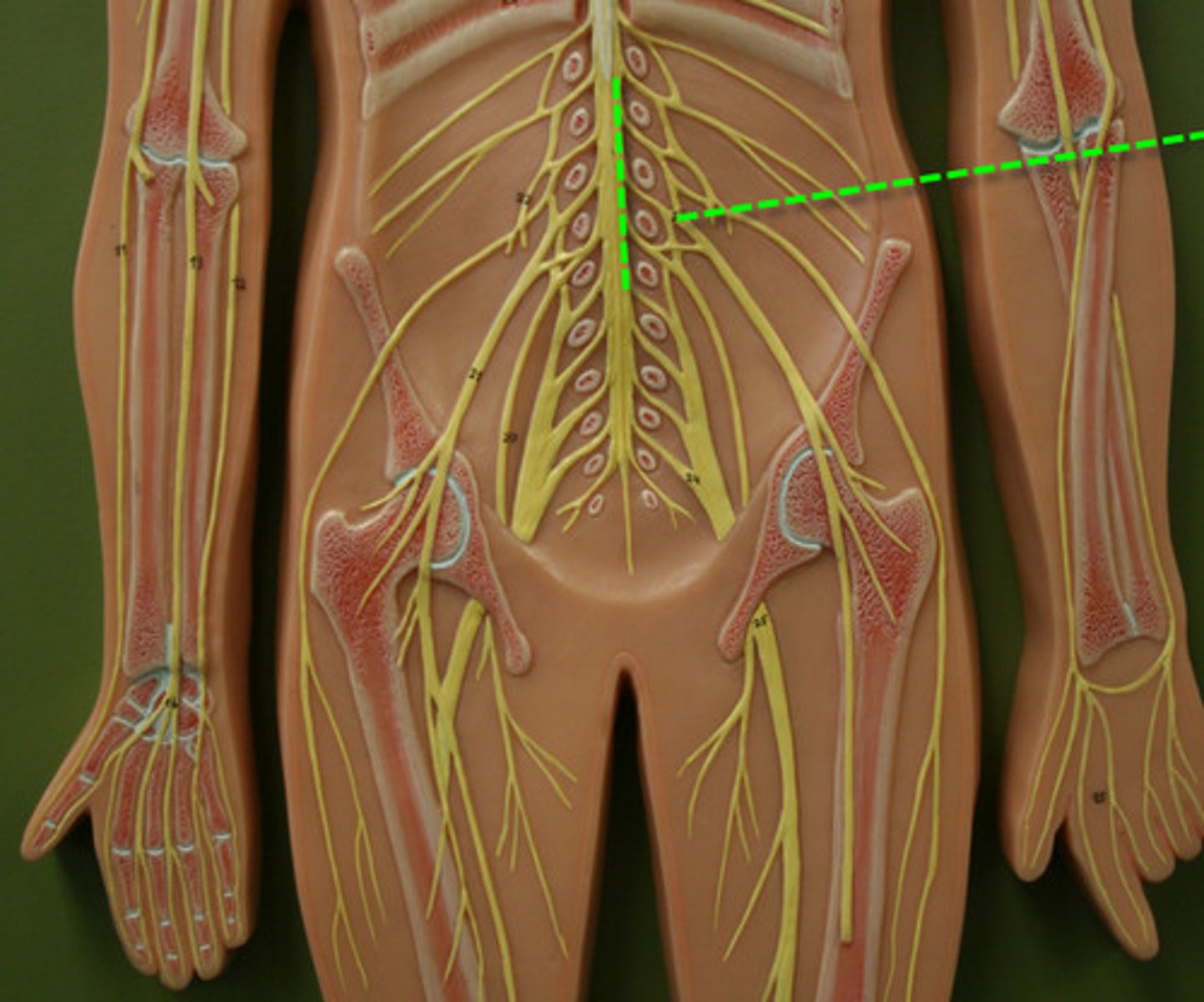
sacral plexus
Anterior rami of L4-S4
Innervates skin and muscles of pelvic girdle and lower limbs
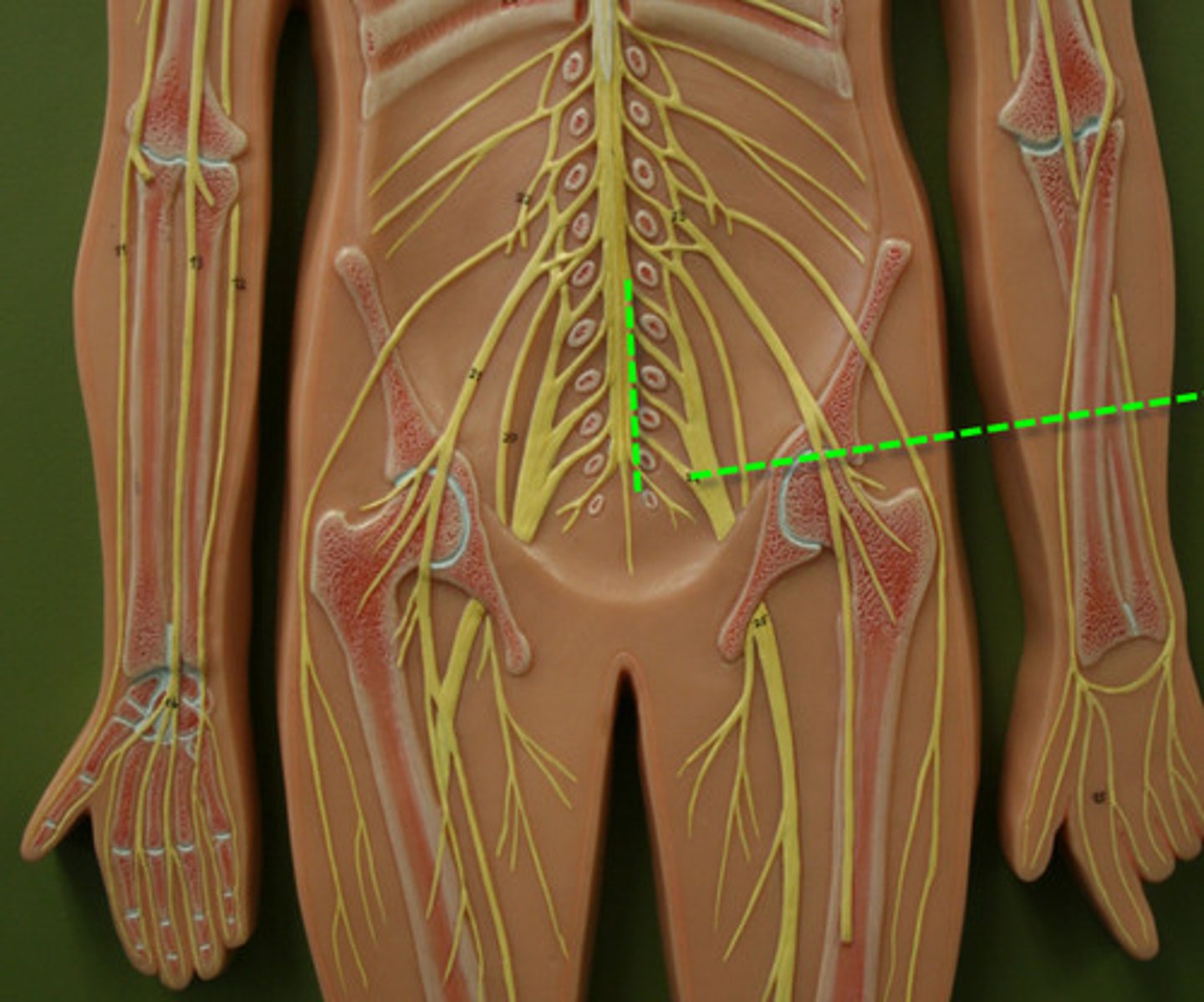
Subunits of nerves (medial to lateral)
Anterior rami unites into Trunks. Trunks branch out into divisions, which come together again to form cords
Lastly, the cords divide into individual nerves
sciatic nerve
lots of leg movement is associated with this nerve
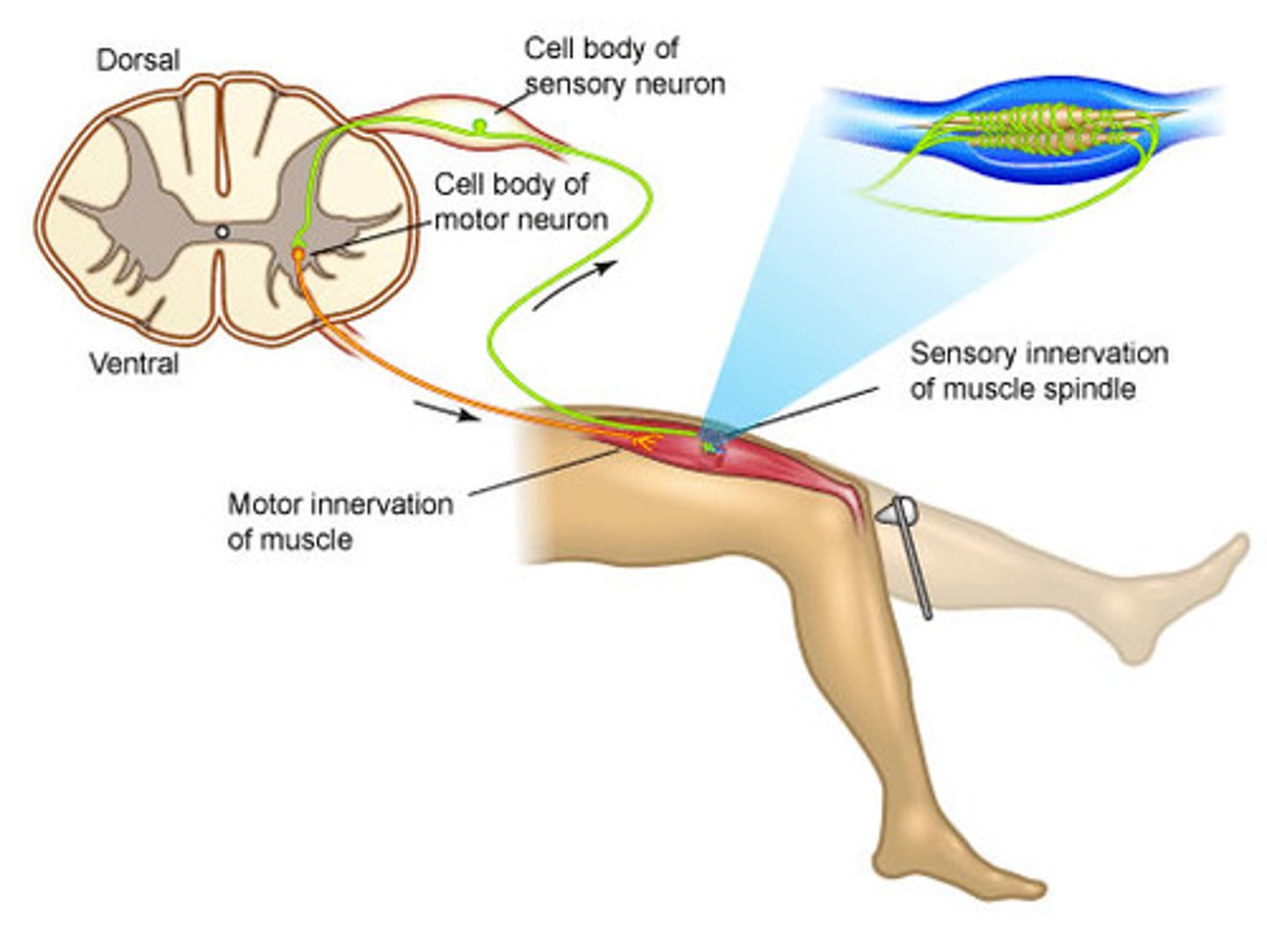
Step 1 of a simple reflex arc
Activation of a receptor by stimulus
Ex: Lean on tack, stimulates pain receptors
Step 2 of a simple reflex arc
Activation of a sensory neuron
Graded potential turns into an action potential in a sensory neuron
Step 3 of a simple reflex arc
Information processing in the CNS
Sensory neuron
→ excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP) at interneuron
Step 4 of a simple reflex arc
Activation of motor neuron
Interneuron stimulates motor neurons
Collaterals from interneuron may send pain sensations to other areas in CNS
Step 5 of a simple reflex arc
Response of a peripheral effector
Ex: Skeletal muscle contraction to pull away from the tack
Classification of reflexes
development, nature of response, complexity of circuit, processing site
development of reflexes (2 types)
innate and acquired
innate reflexes
basic neural reflexes formed before birth (sucking, baby grabbing your finger if you put it in their hand)
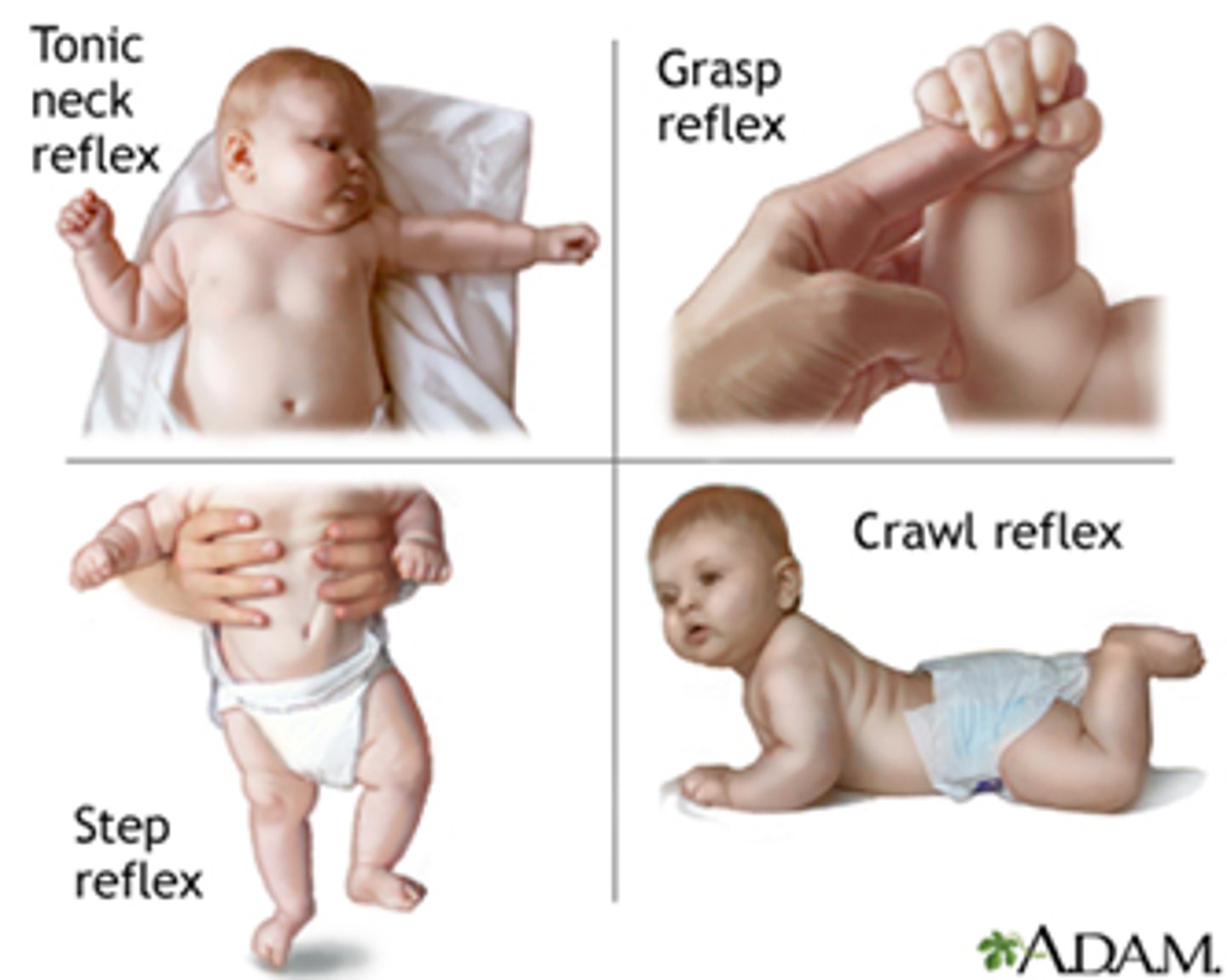
acquired reflexes
rapid, automatic, learned motor patterns
(slamming foot on break while driving)
nature of response (2 types)
somatic reflexes and visceral reflexes
somatic reflexes
involuntary control of skeletal muscles (withdrawal reflex)
Visceral reflexes (autonomic reflexes)
Controls involuntary effectors: smooth muscles, cardiac muscle, glands, adipose tissue
Complexity of circuit (2 types)
monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflexes
monosynaptic reflex
Single synapse—simplest reflex arc
polysynaptic reflex
1+ interneuron, multiple synapses
processing site reflexes (2 types)
Spinal and cranial reflexes
spinal reflexes
processing occurs in the spinal cord, 1+ spinal cord reflexes
Cranial reflexes
Processing occurs in the brain
ascending tracts
sensory information in posterior columns of white matter
descending tracts
motor commands in anterior columns of white matter
reflexes
rapid automatic responses to specific stimuli
preserve homeostasis through rapid adjustments in organ/organ system function
little variability in response
Gray commissures
where axons cross, anterior and posterior sides