Anatomy Semester Exam Review
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
properties of water
cohesion, adhesion, excellent solvent, solid is less dense than liquid, high heat capacity
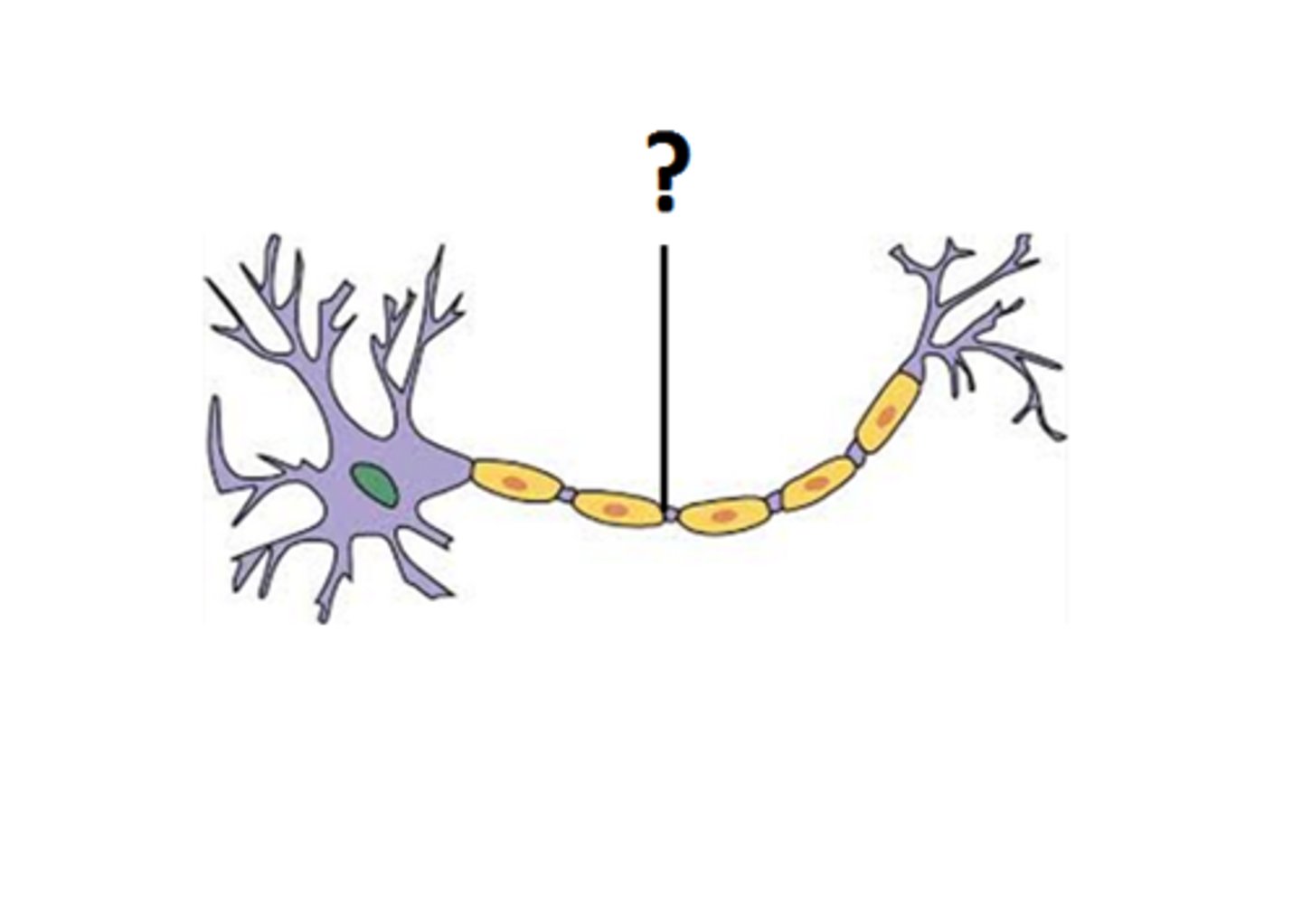
Nodes of Rainvier
gaps in the myelin sheath
ilium, ischium, pubis
fuse to form the coxal bone
coxal bone
hip bone
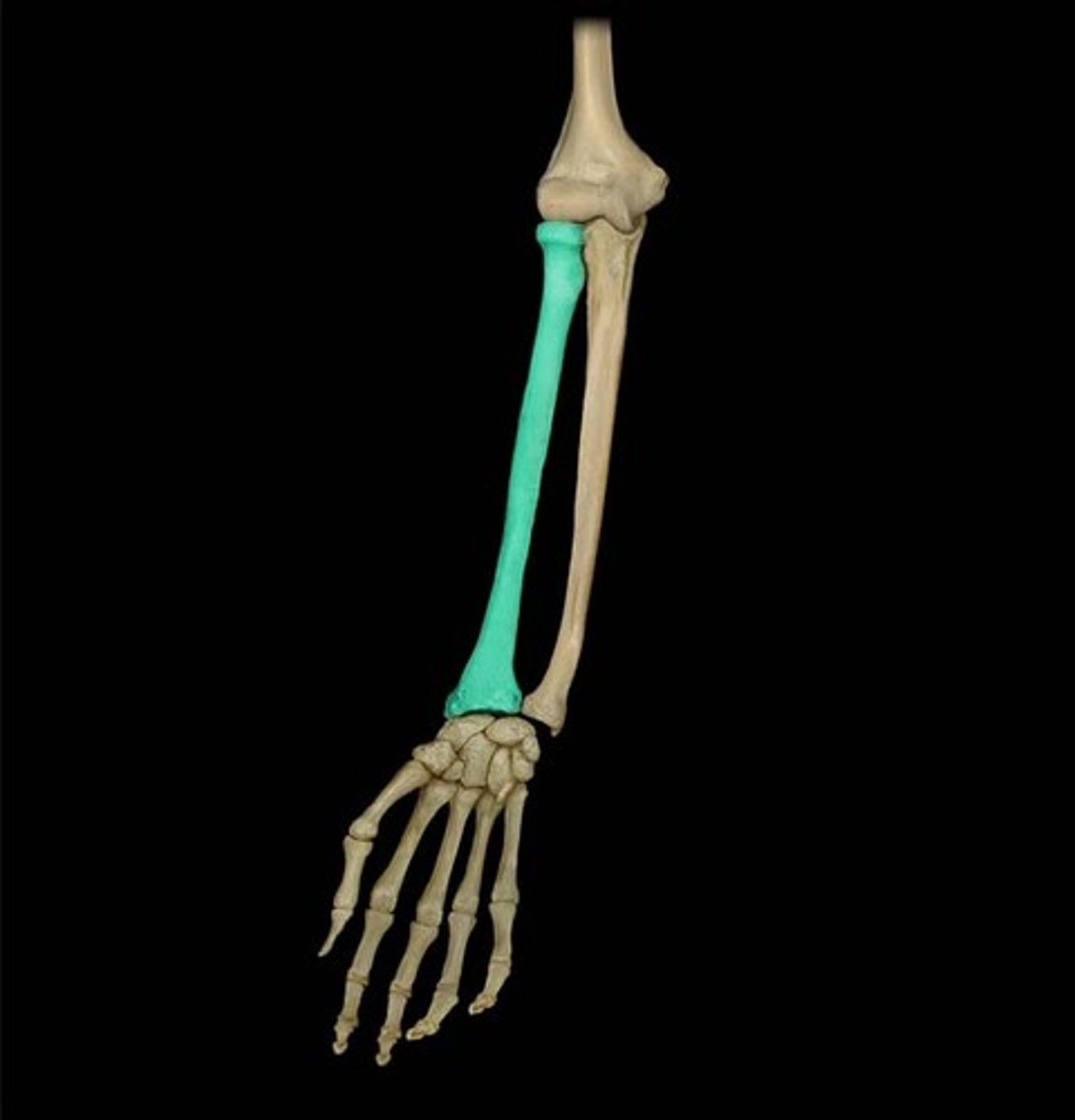
radius
lateral bone of the forearm
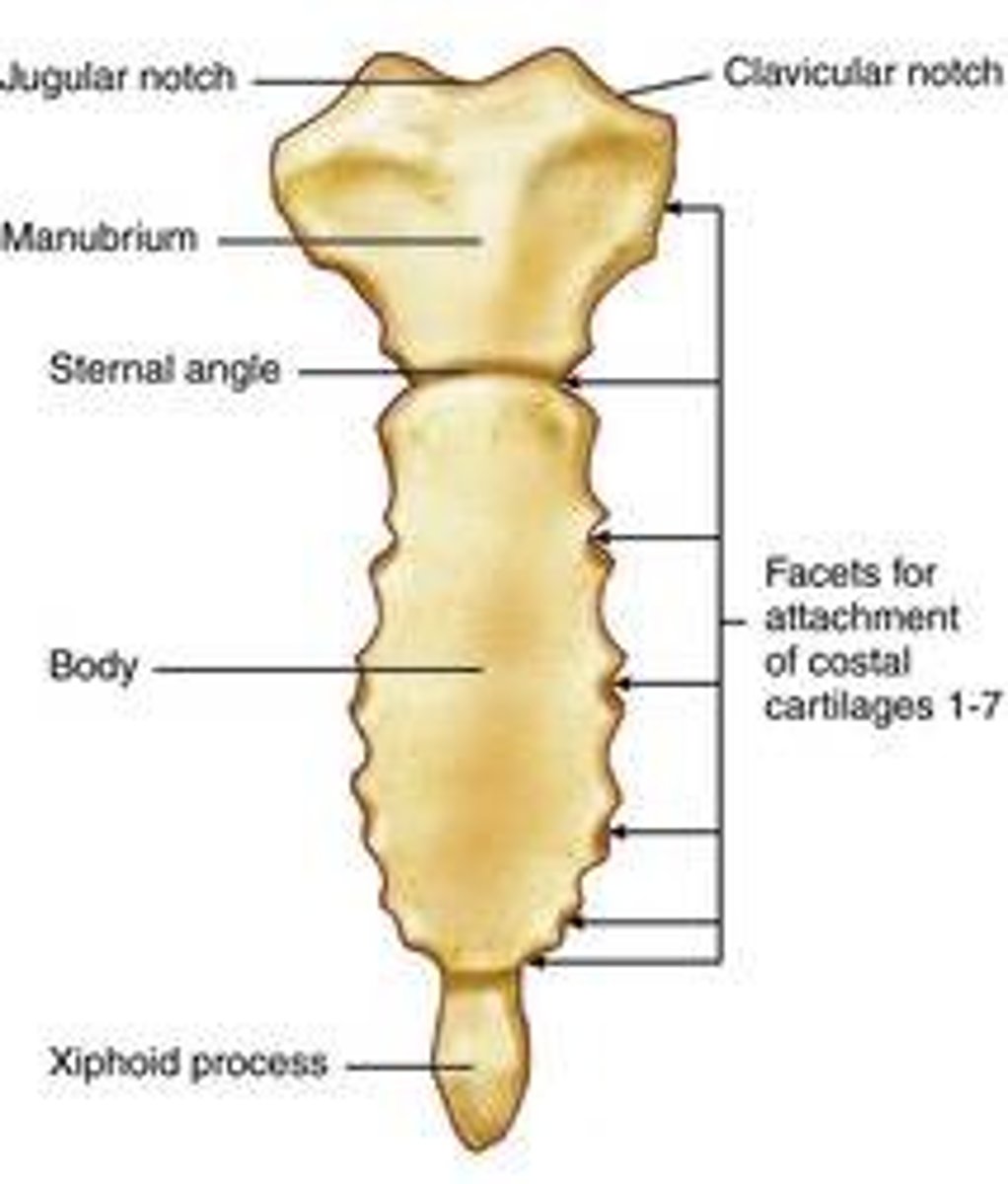
manubrium, body, xiphoid process
3 parts of the sternum
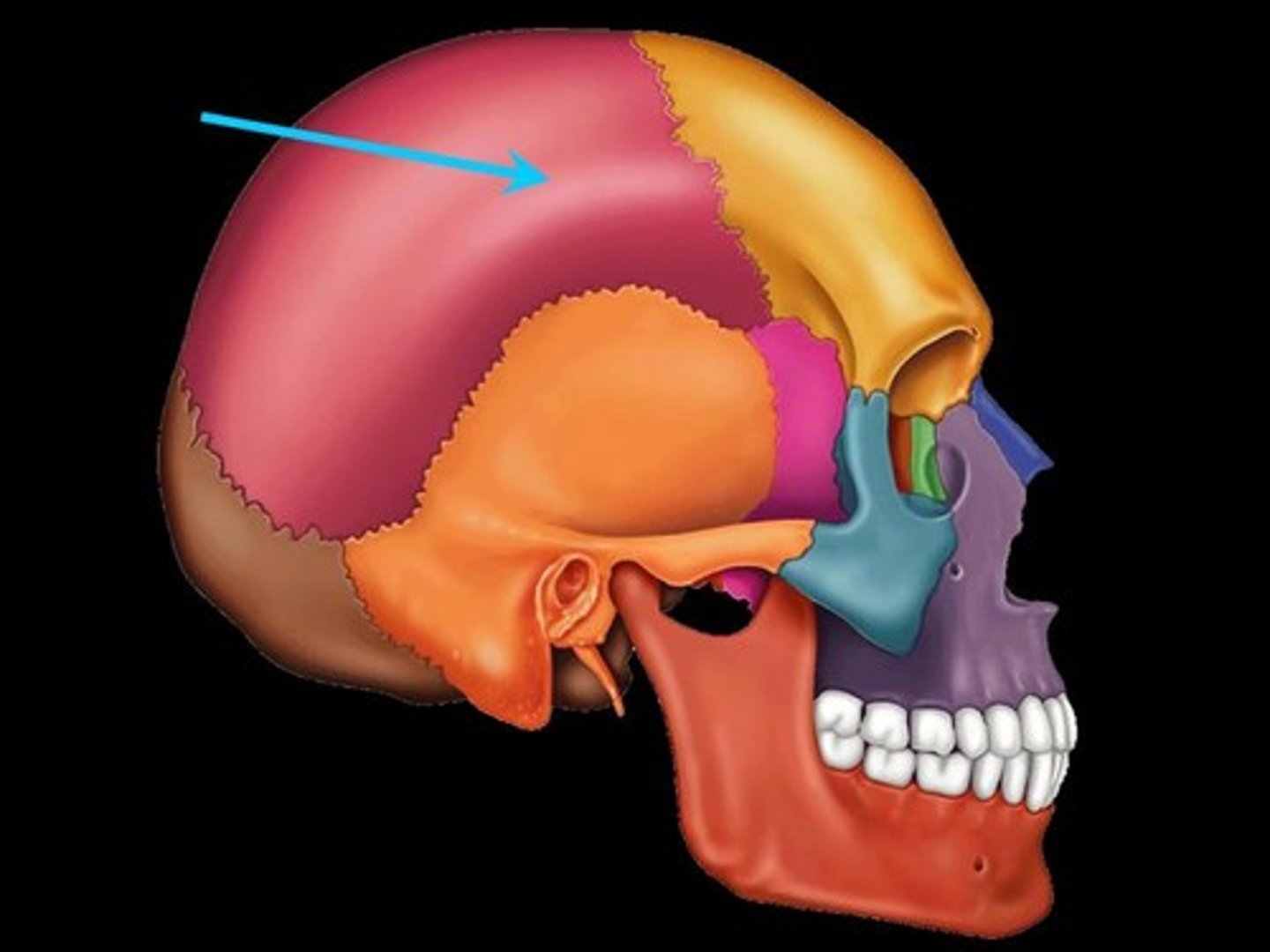
Parietal bone
a bone forming the central side and upper back part of each side of the skull.
adenine
The base that pairs with Thymine in DNA
nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
weak acid
pH 4-6, the weakest being closest to 7.
blood pH
7.35-7.45
Vitamin D
sunshine vitamin, produced in the skin by exposure to UV light.
glycogen
polysaccharide, storage form of glucose in animals
triglyceride
lipid compound composed of a glycerol molecule bonded with three fatty acid chains
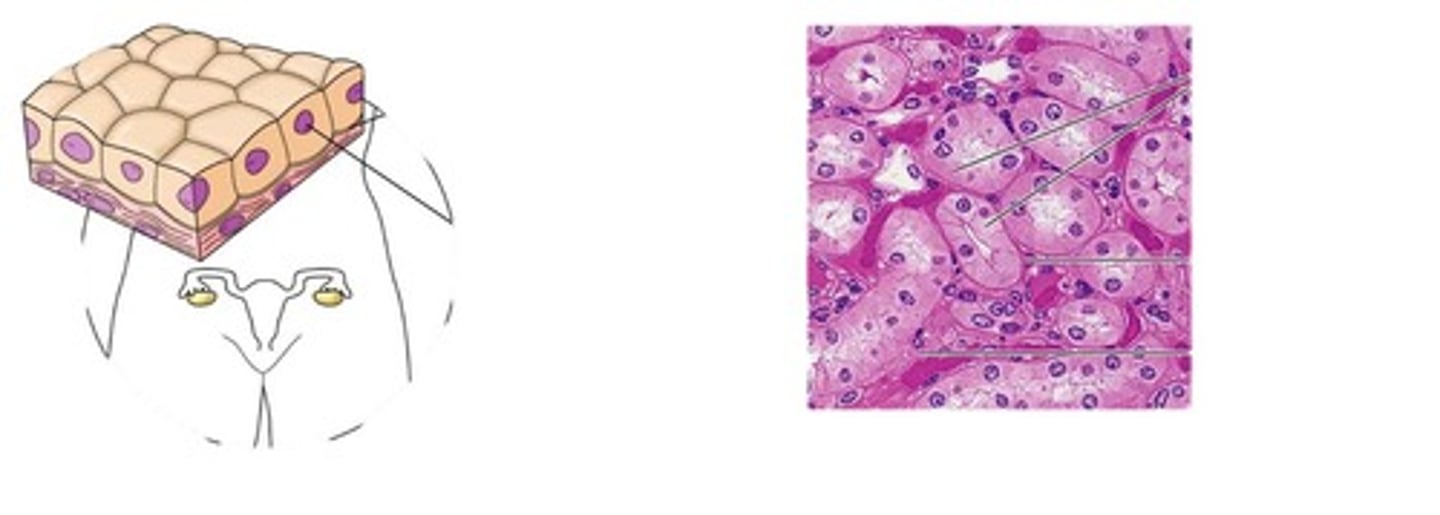
simple cuboidal epithelium
single layer of cube shaped cells
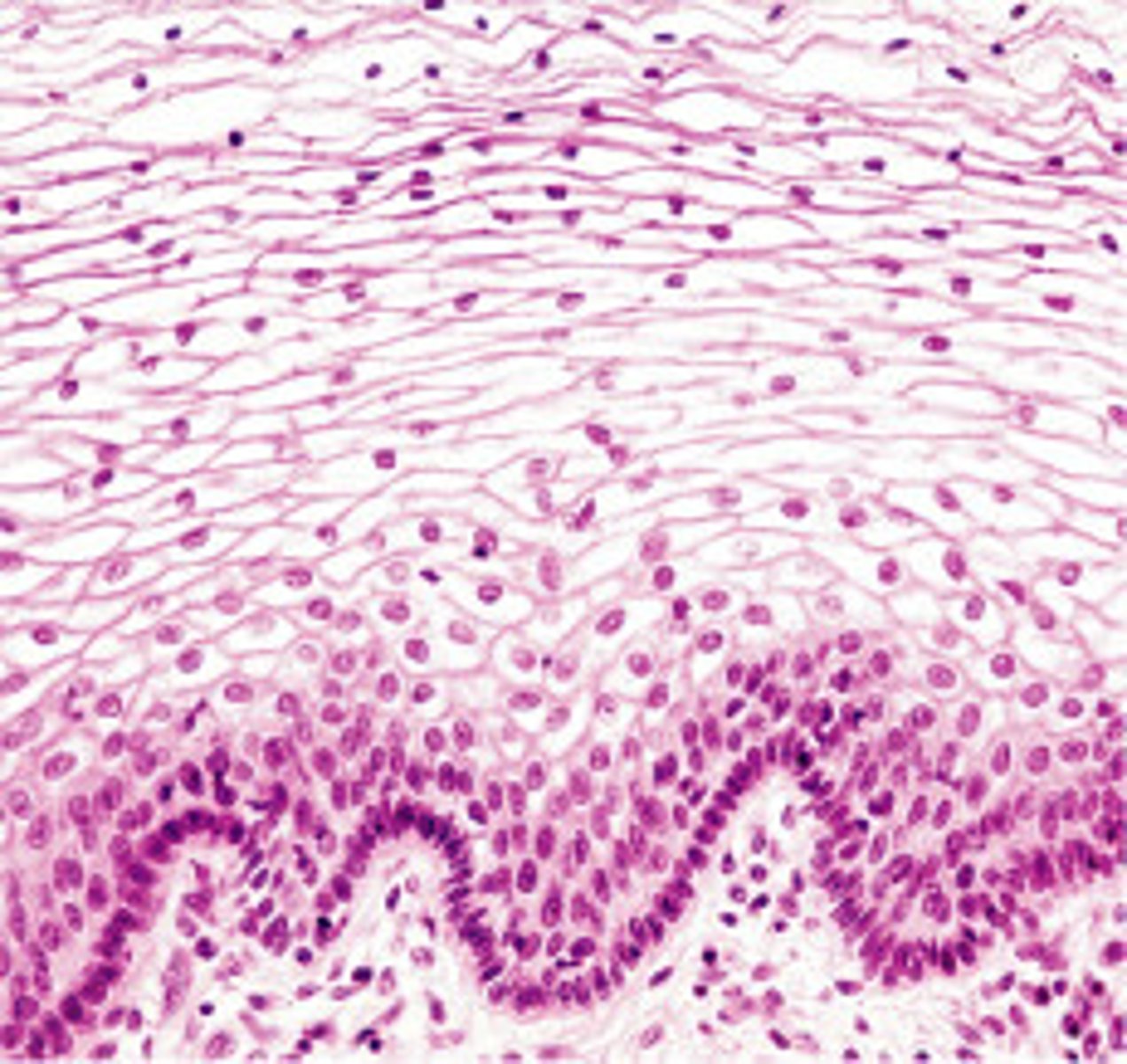
stratified squamous epithelium
multiple layers of flat cells
axial skeleton
Portion of the skeletal system that consists of the skull, rib cage, and vertebral column
axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
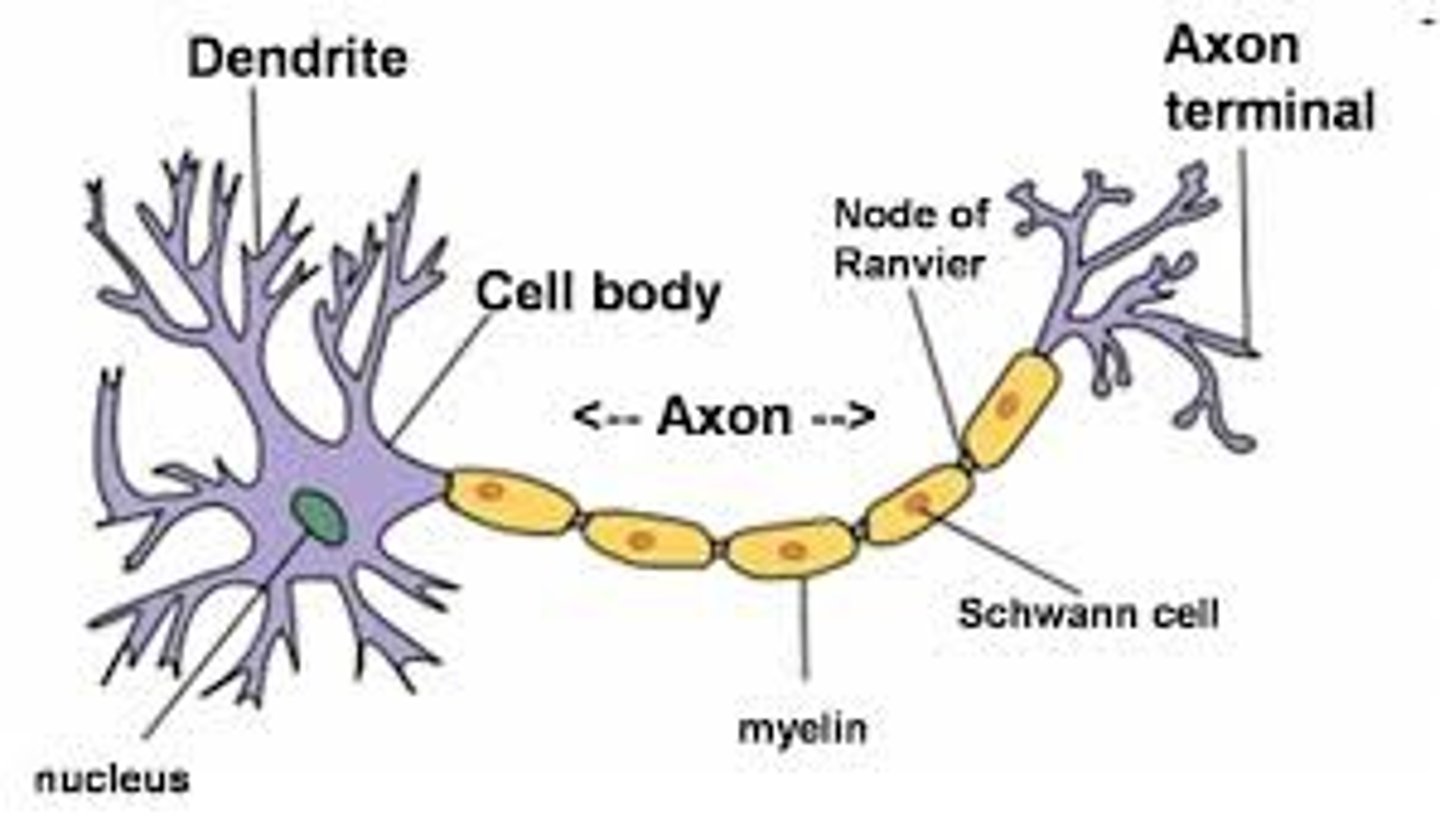
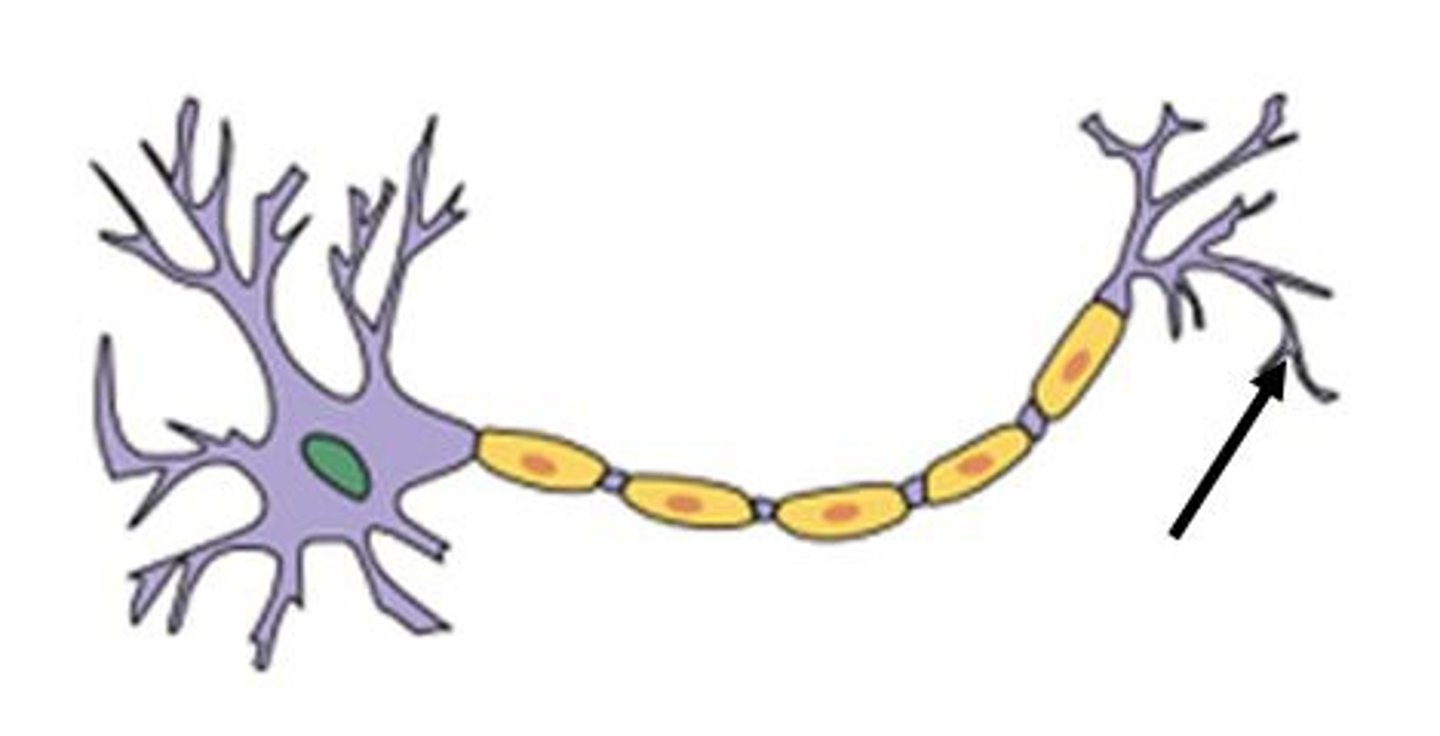
axon terminal
The endpoint of a neuron where neurotransmitters are stored
functional subdivisions of the nervous system
Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems
muscular disytrophy
inherited disease that causes muscles to degenerate and atrophy
smooth muscle
Visceral, Involuntary and non-striated muscle found inside many internal organs of the body
cardiac muscle
Involuntary, striated muscle tissue found only in the heart.
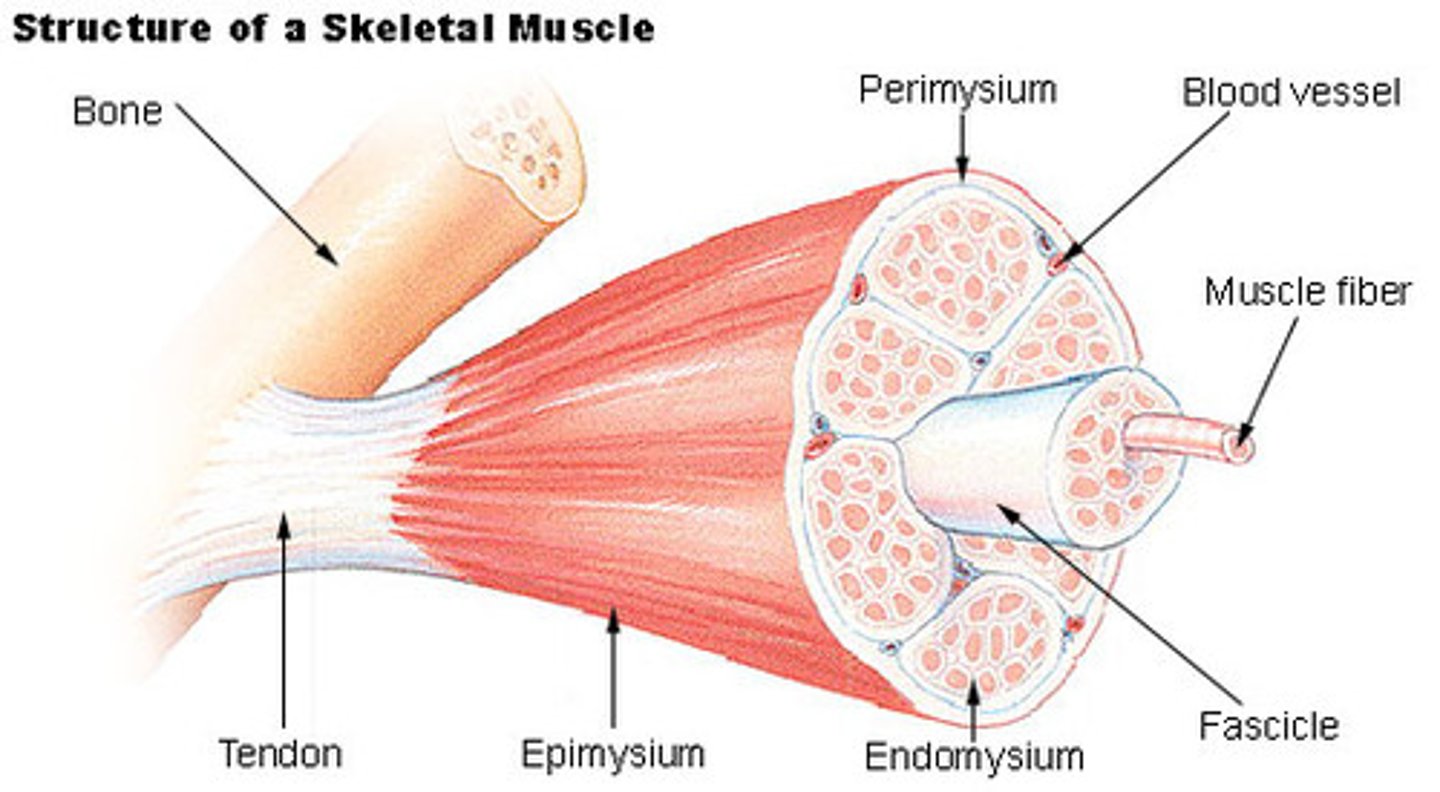
perimysium
Connective tissue surrounding a fascicle
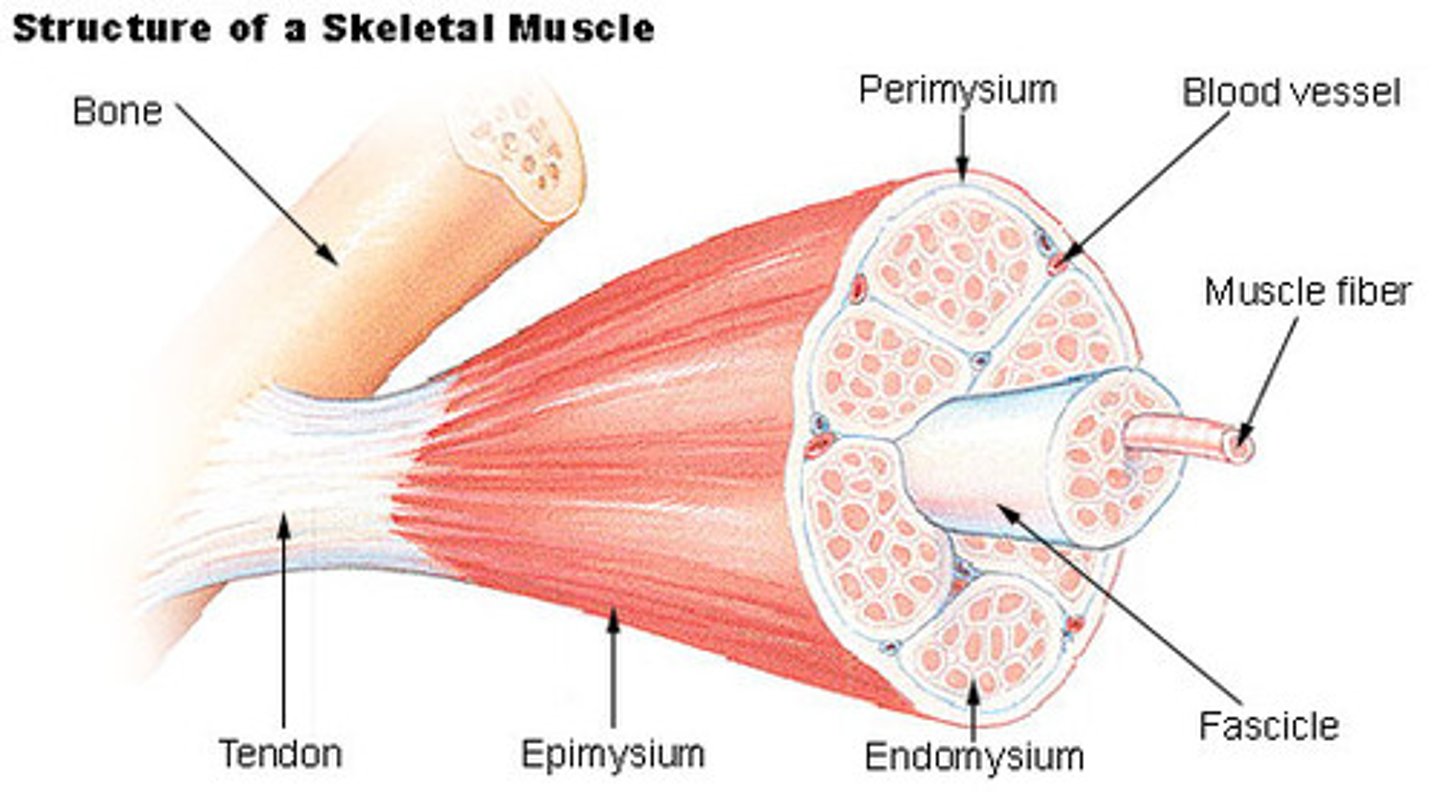
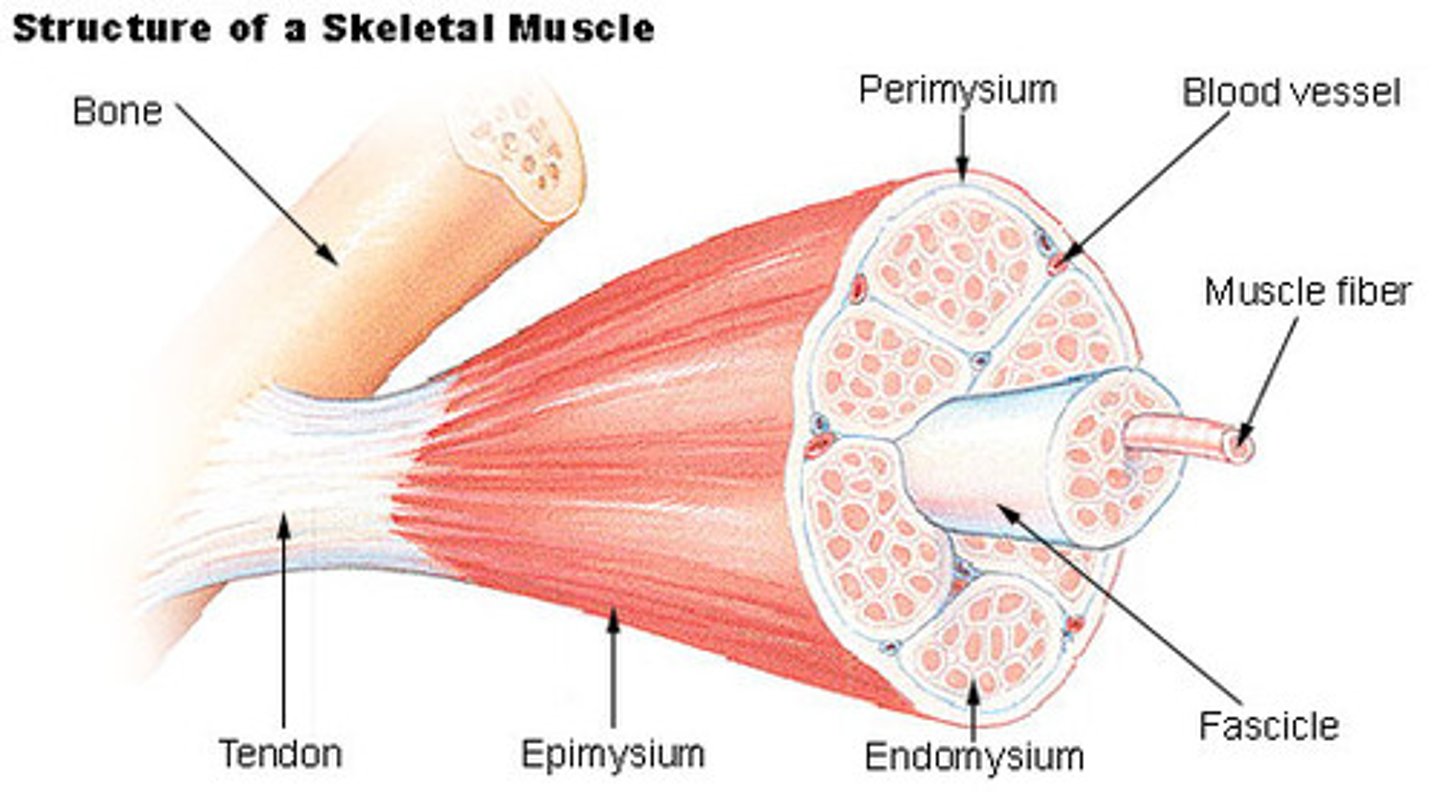
epimysium
surrounds entire muscle
actin
thin filaments
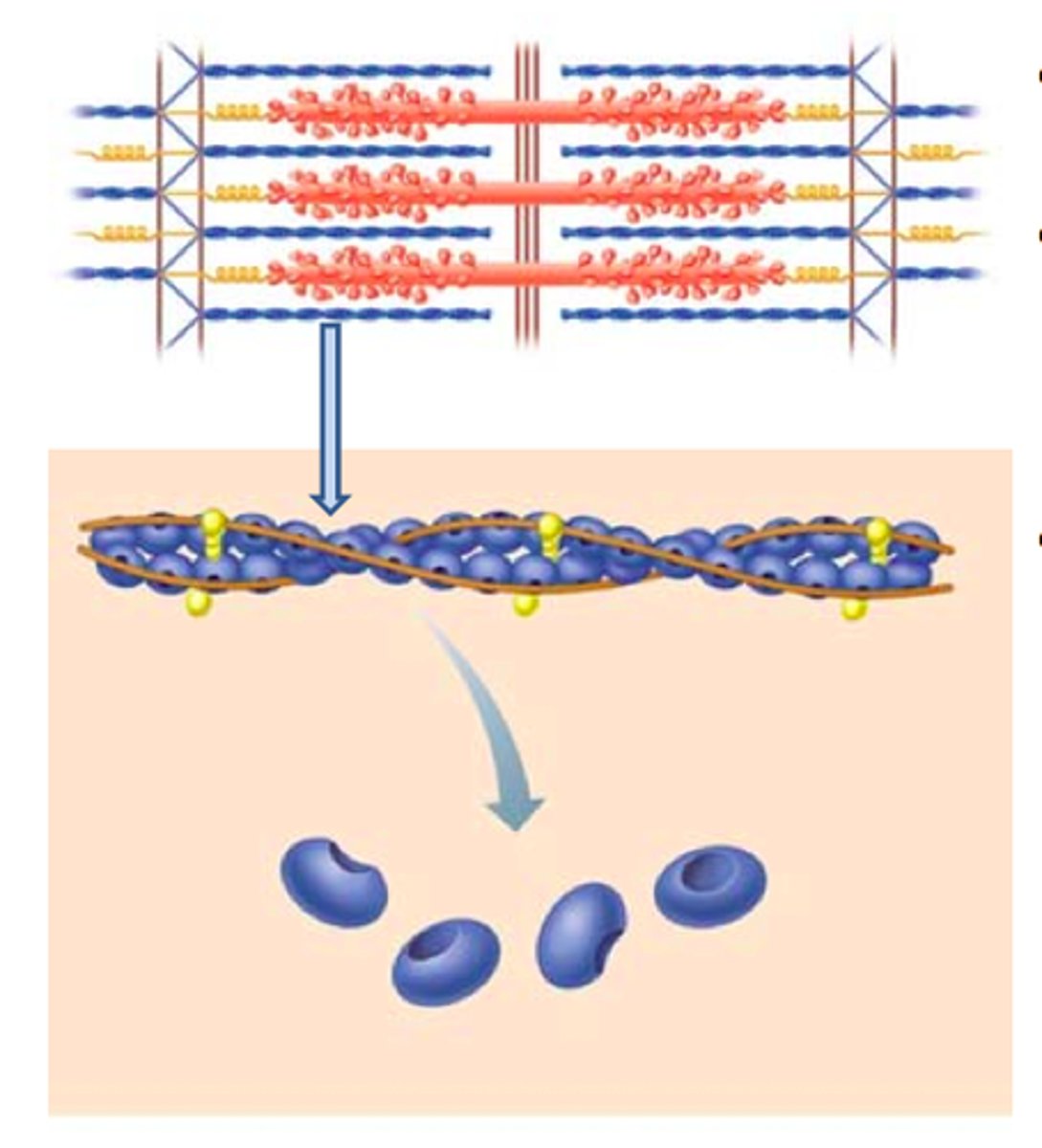
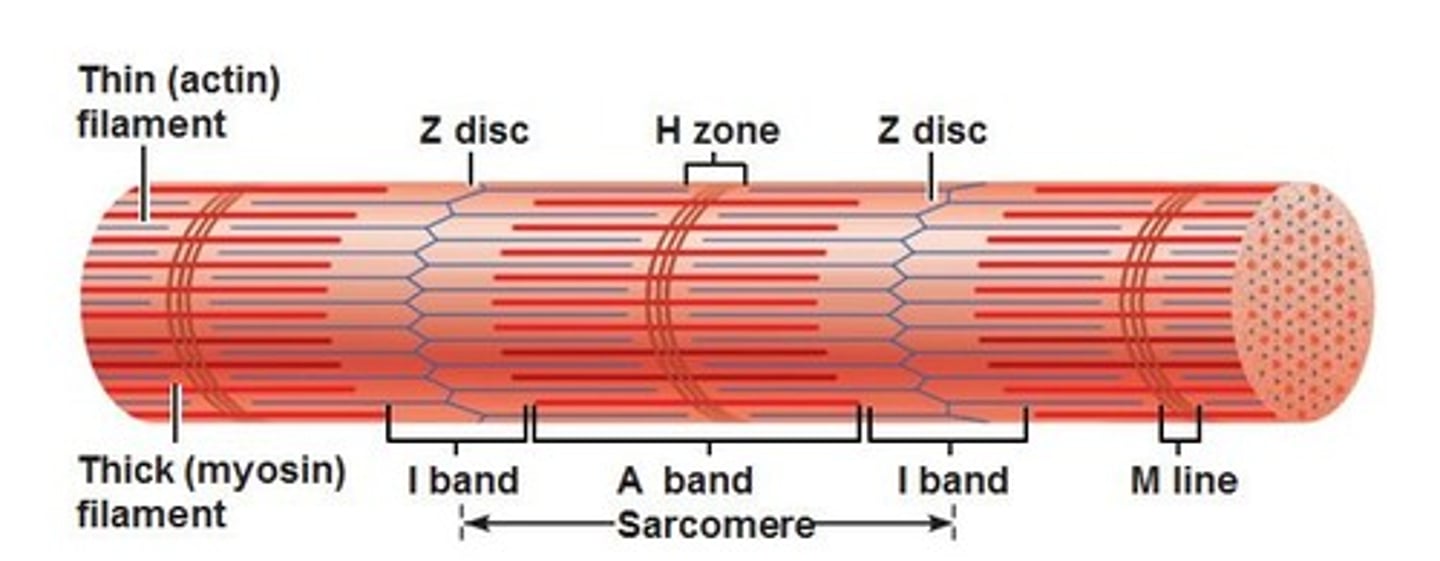
I band
thin filaments only
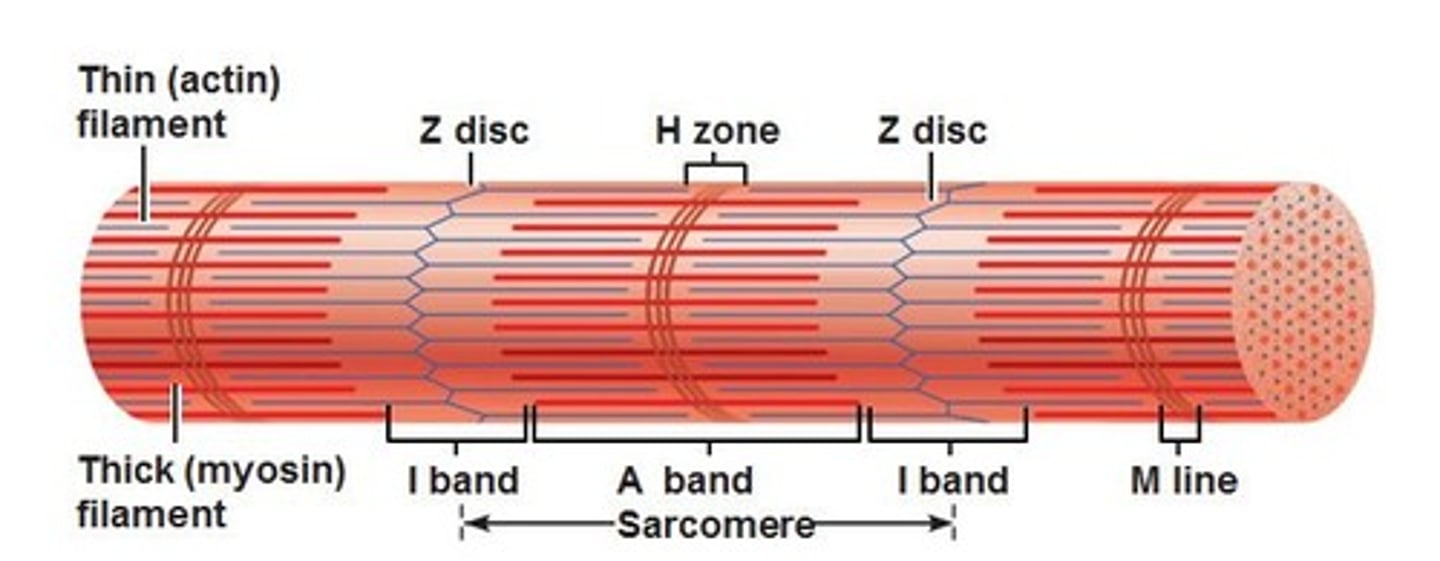
A band
dark area; extends length of the thick filaments
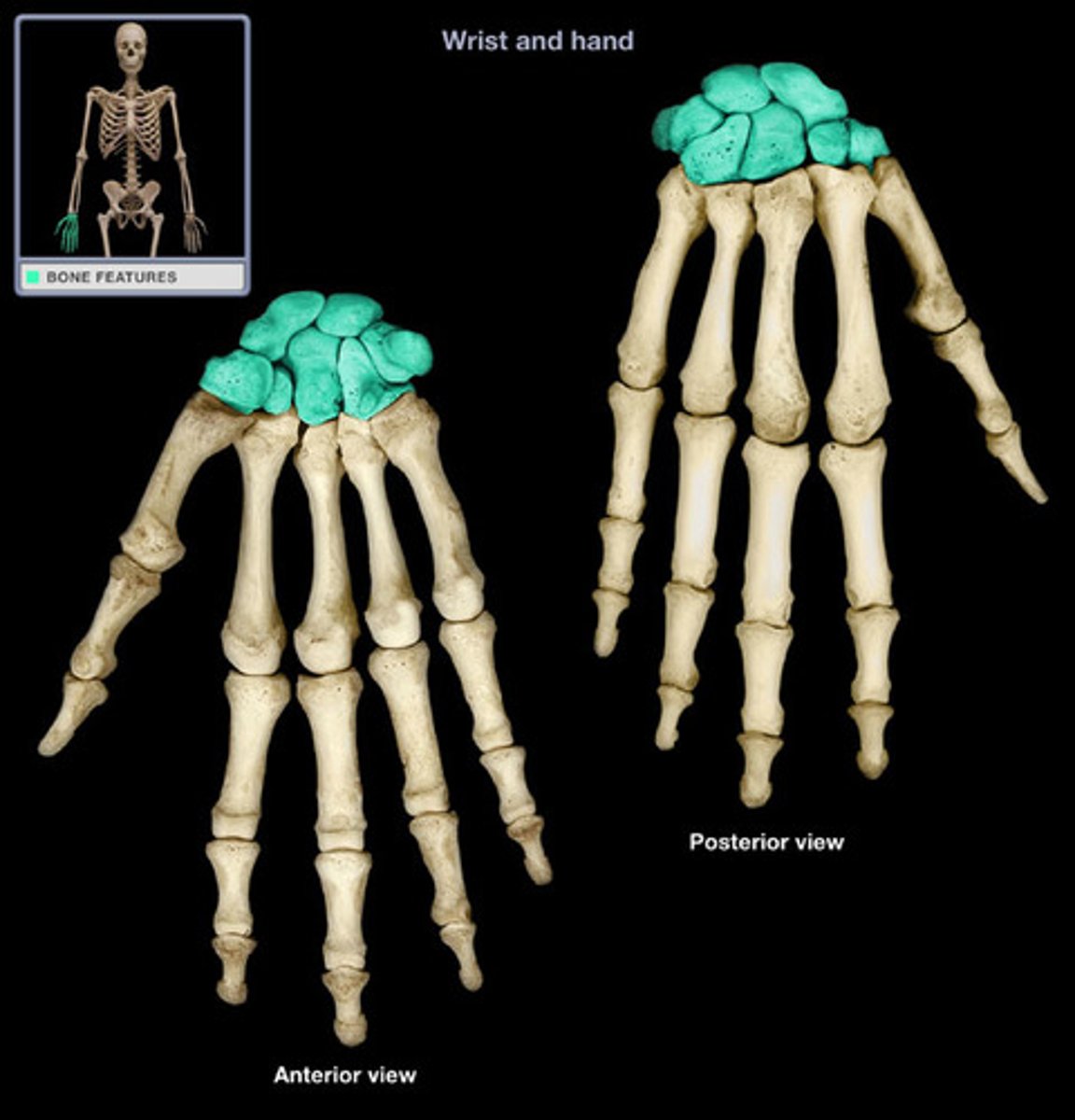
carpals
wrist bones
skeletal muscle tissue
Voluntary muscle pulls on bones and causes body movements.
arrector pili
tiny muscle fibers attached to the hair follicles that cause the hair to stand erect

greenstick fracture
bending and incomplete break of a bone; most often seen in children
metaphase
second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
muscle fiber
muscle cell
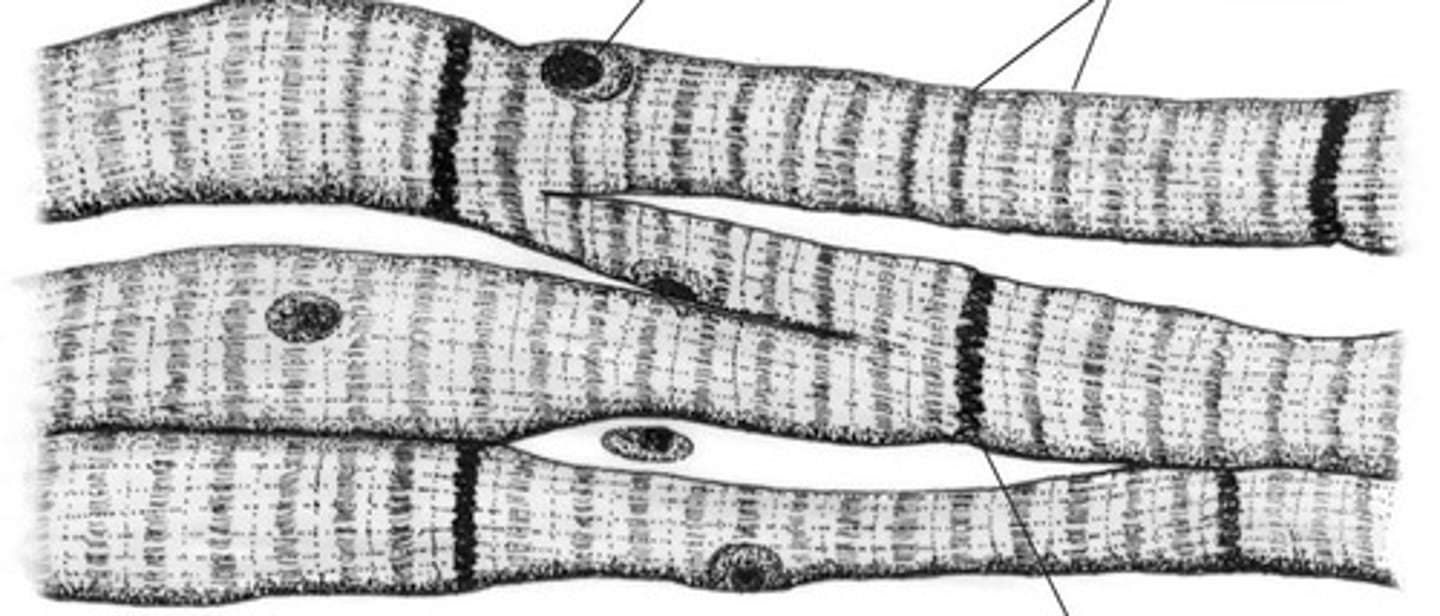
cardiac muscle tissue
specialized muscle tissue found only in the heart
epithelial tissue
Tissue that covers outside of the body and lines organs and cavities. Has a basement membrane, apical surface and fits closely to form continuous sheets.
connective tissue
Animal tissue that functions mainly to bind and support other tissues, having a sparse population of cells scattered through an extracellular matrix.
adipose tissue
fat
hypodermis
loose connective tissue layer of skin below the dermis
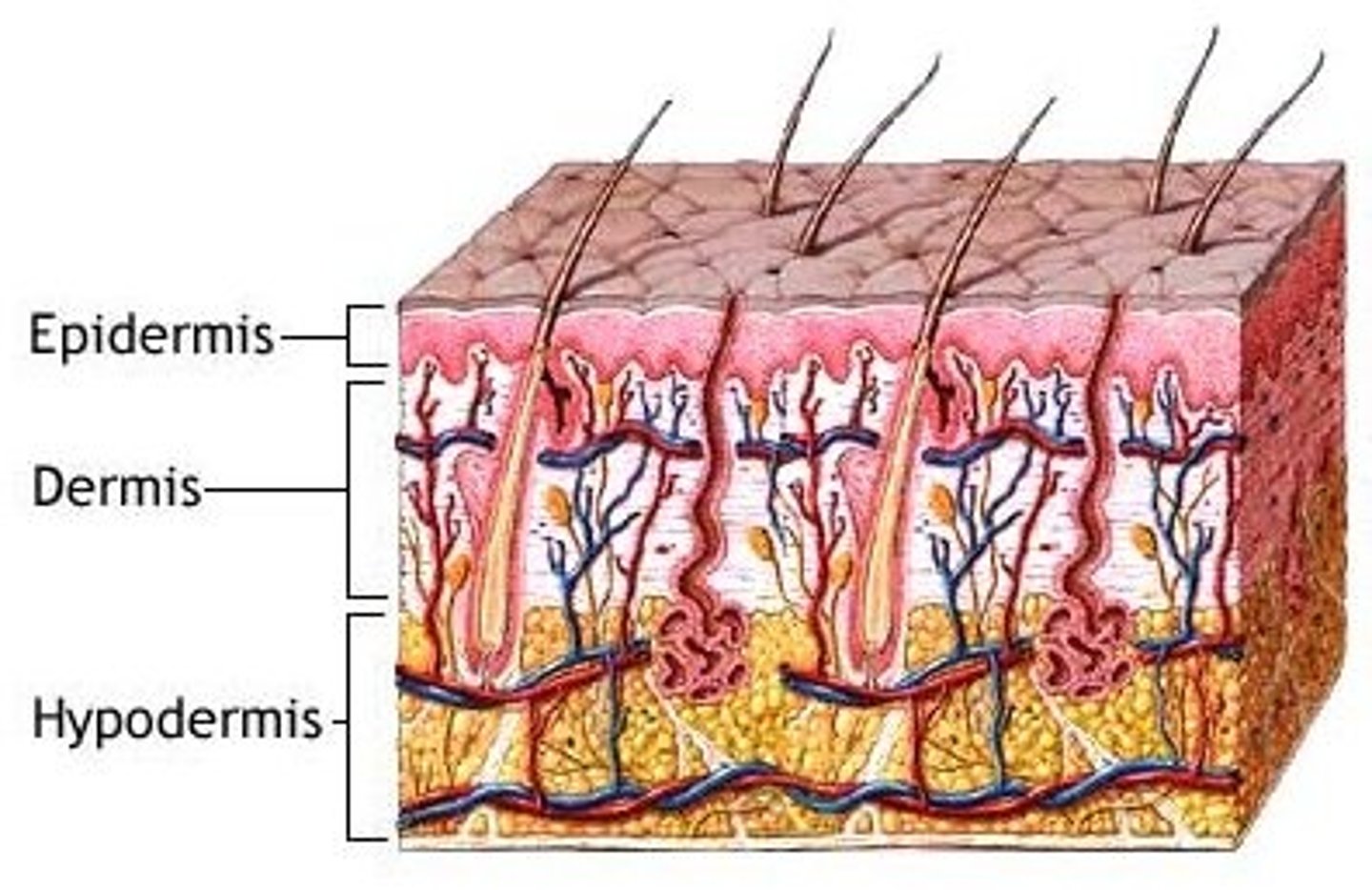
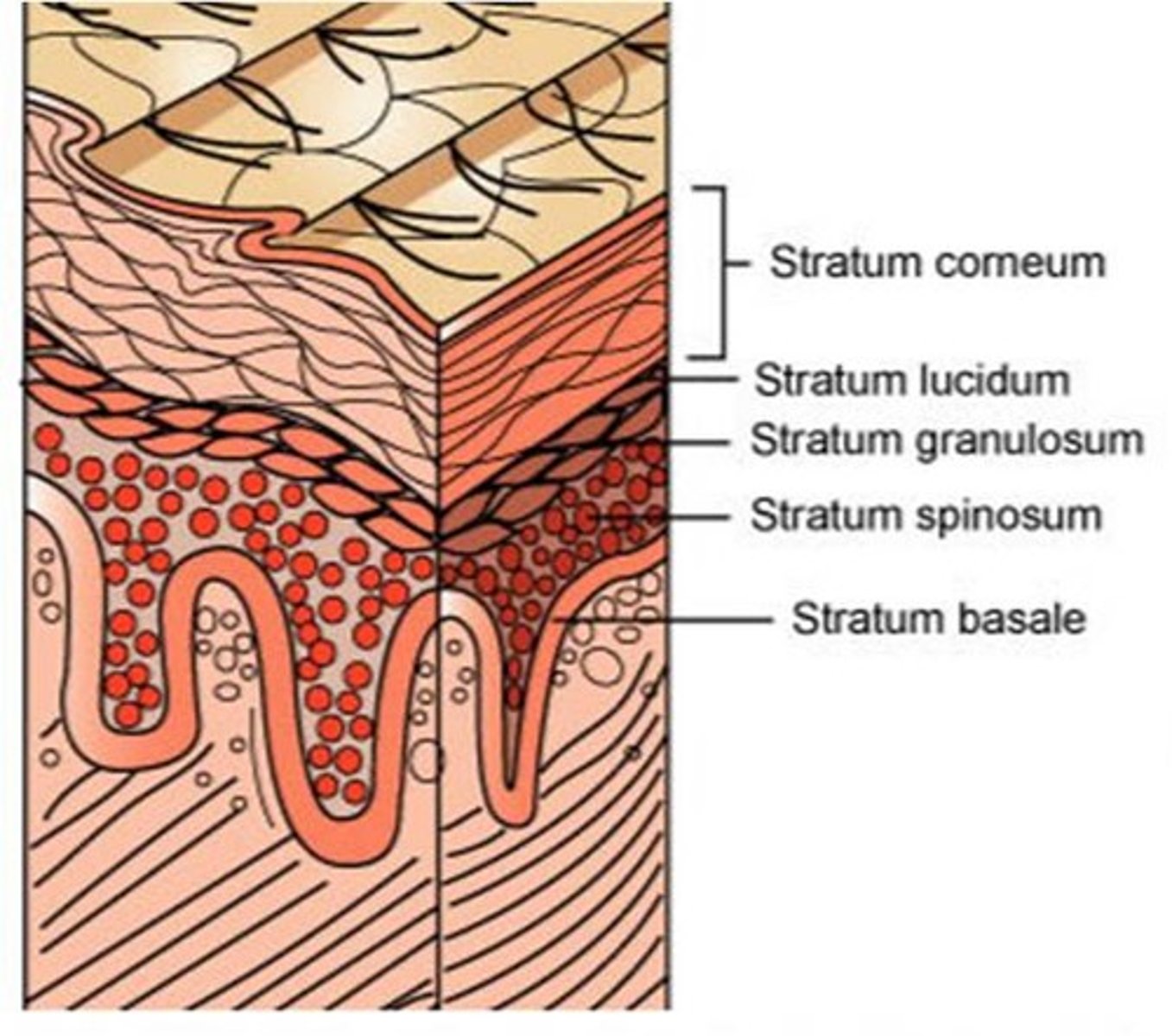
stratum basale
deepest layer of epidermis responsible for the whorled ridges of fingerprints
eccrine gland
sweat gland
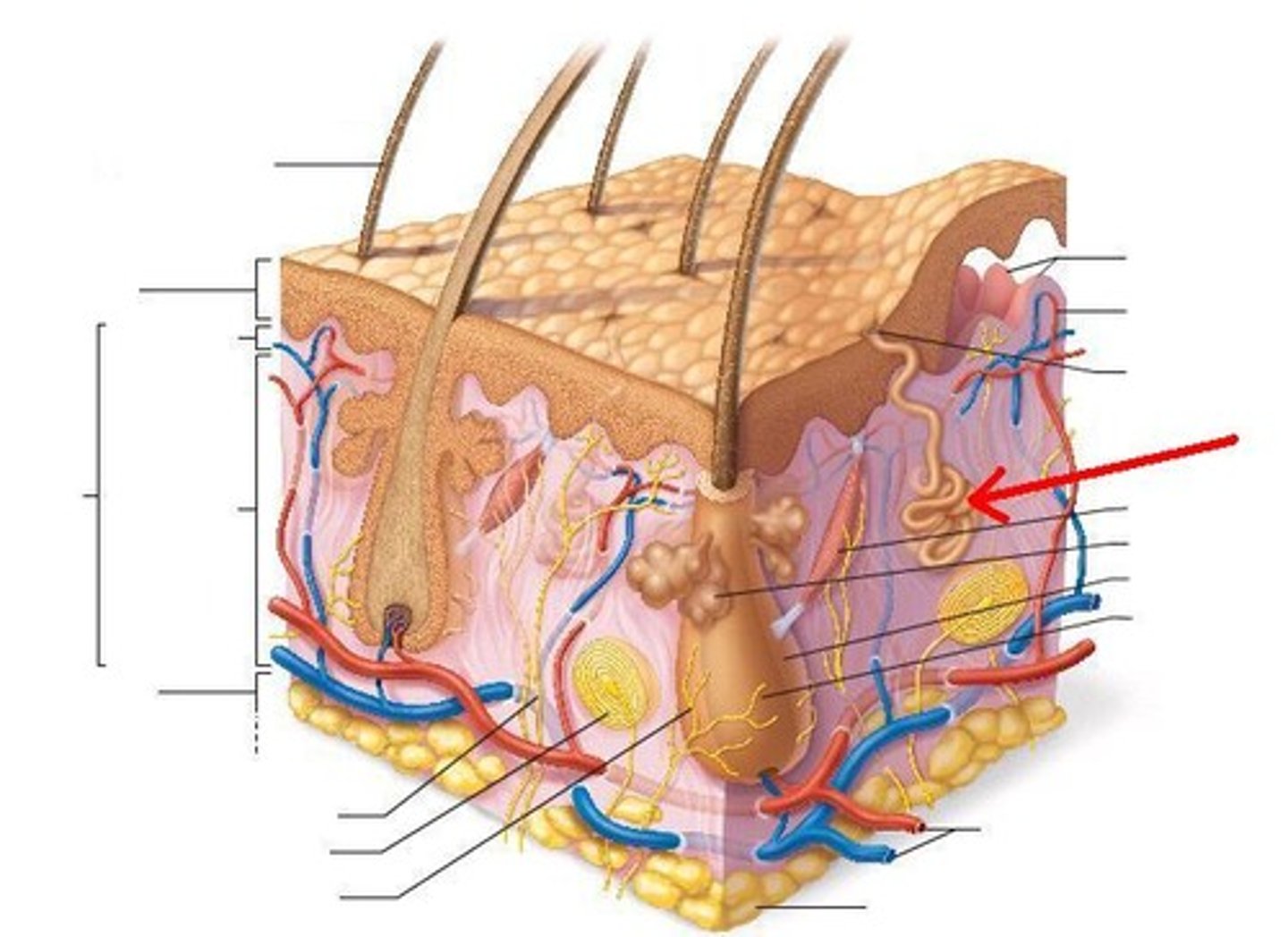
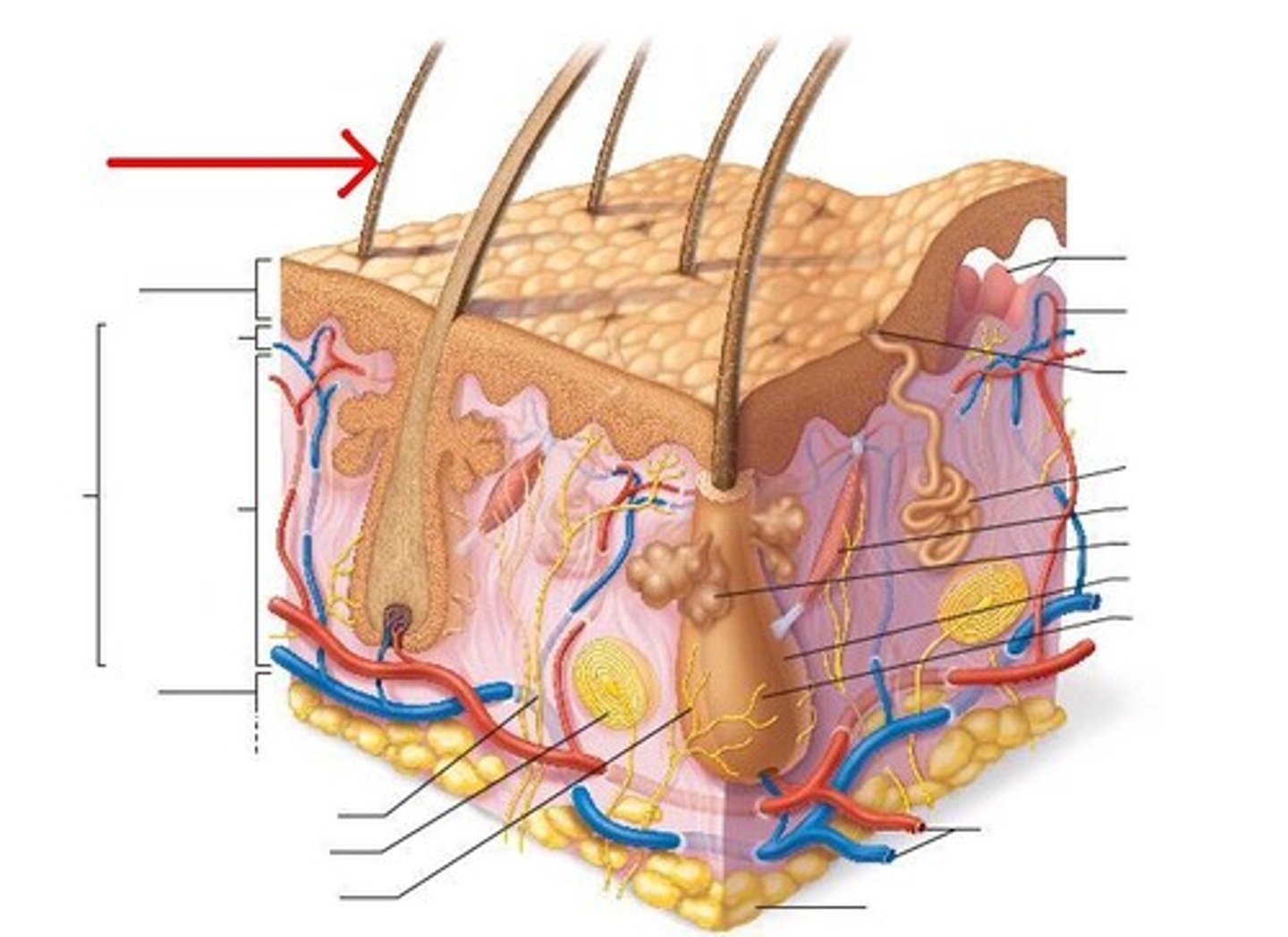
hair shaft
visible part of the hair
exocrine glands
Glands that secrete substances outward through a duct
first degree burn
Superficial burns through only the epidermis.
Promixal epiphysis
the end of a long bone that is closest to the body's center
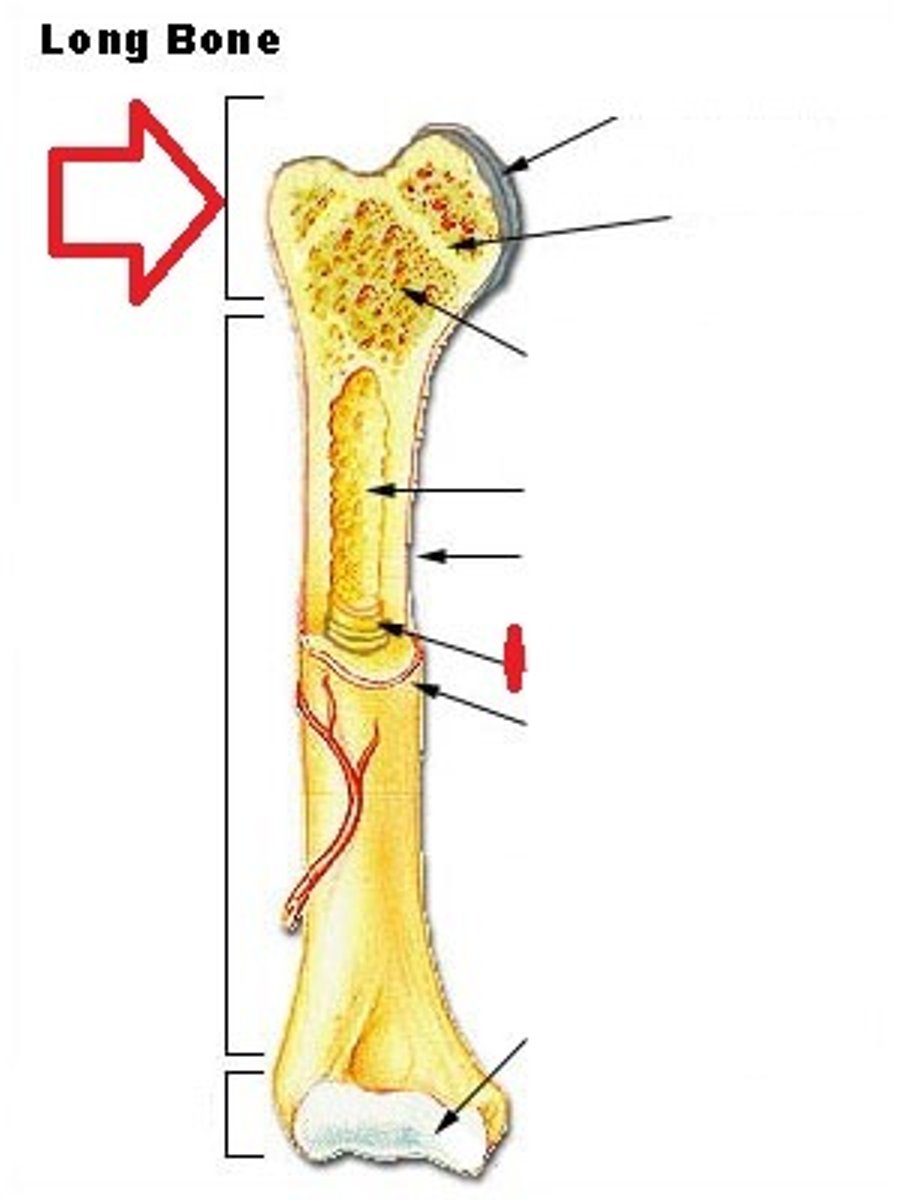
growth plate
the area just below the head of a long bone in which growth in bone length occurs; the epiphyseal plate.
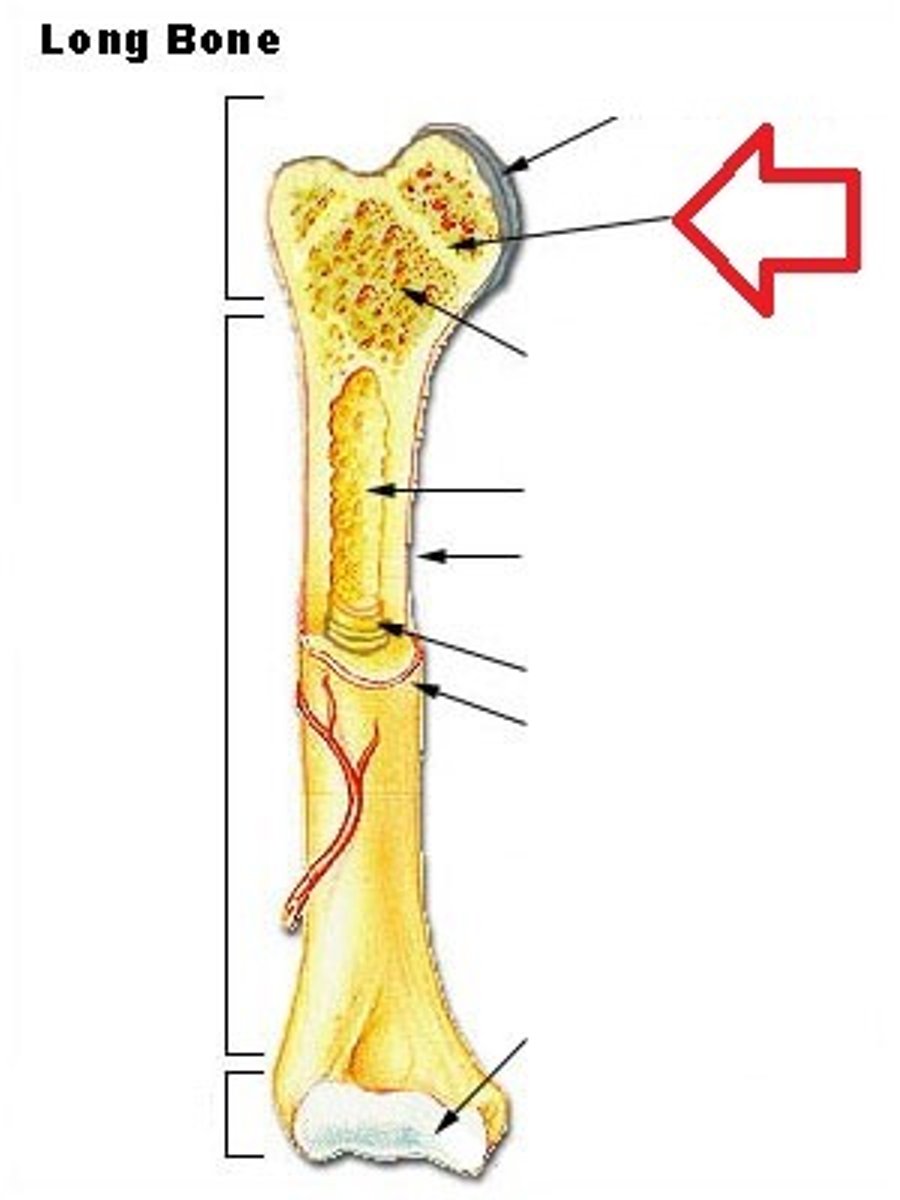
marrow
a soft fatty substance in the cavities of bones, in which blood cells are produced
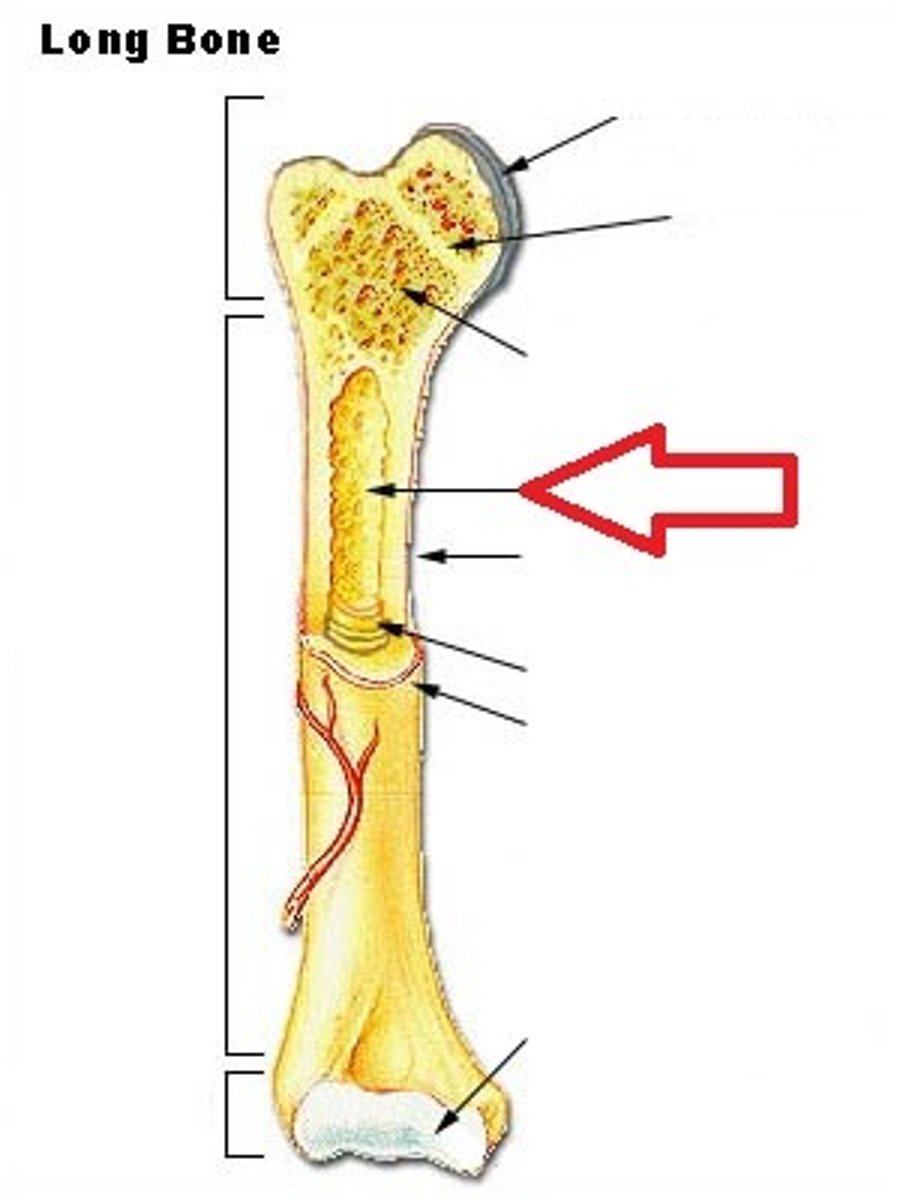
Periostium
tough, tight-fitting membrane that covers bone's surface
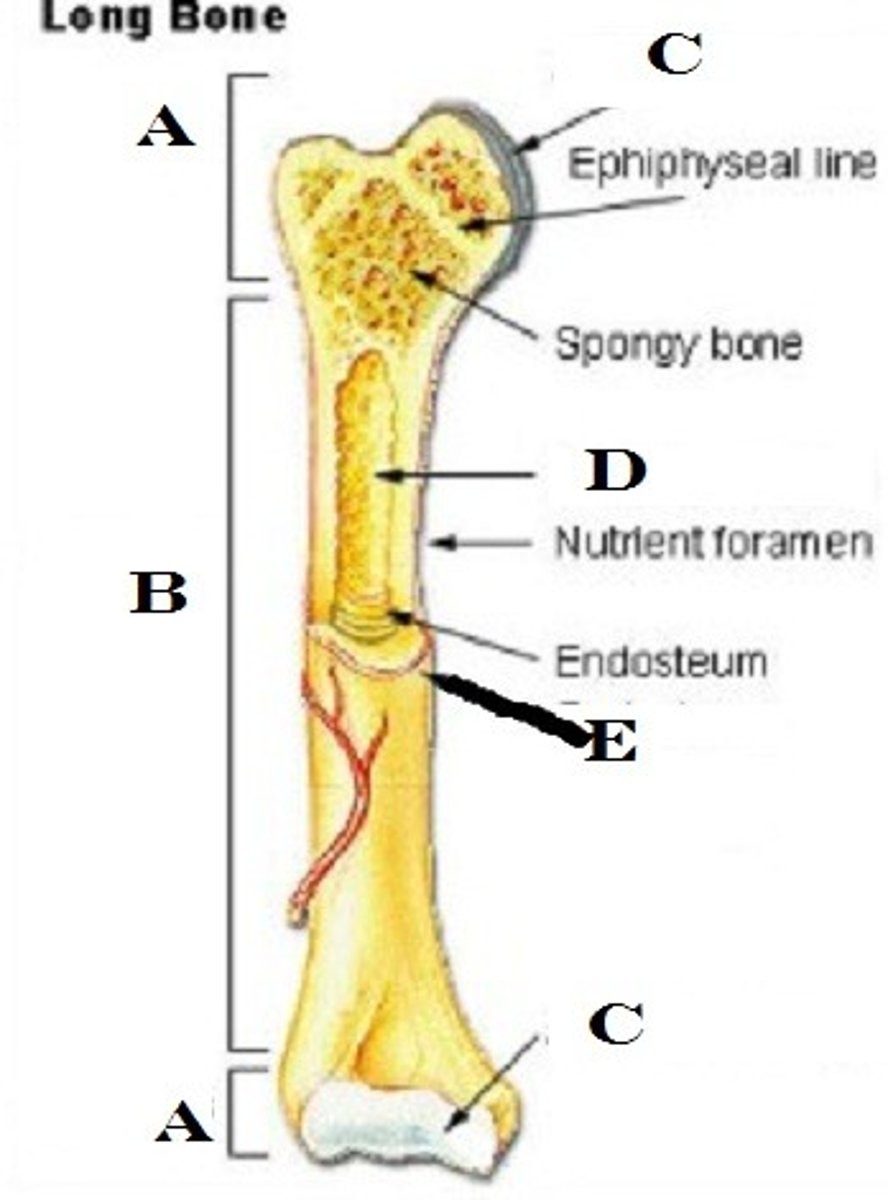
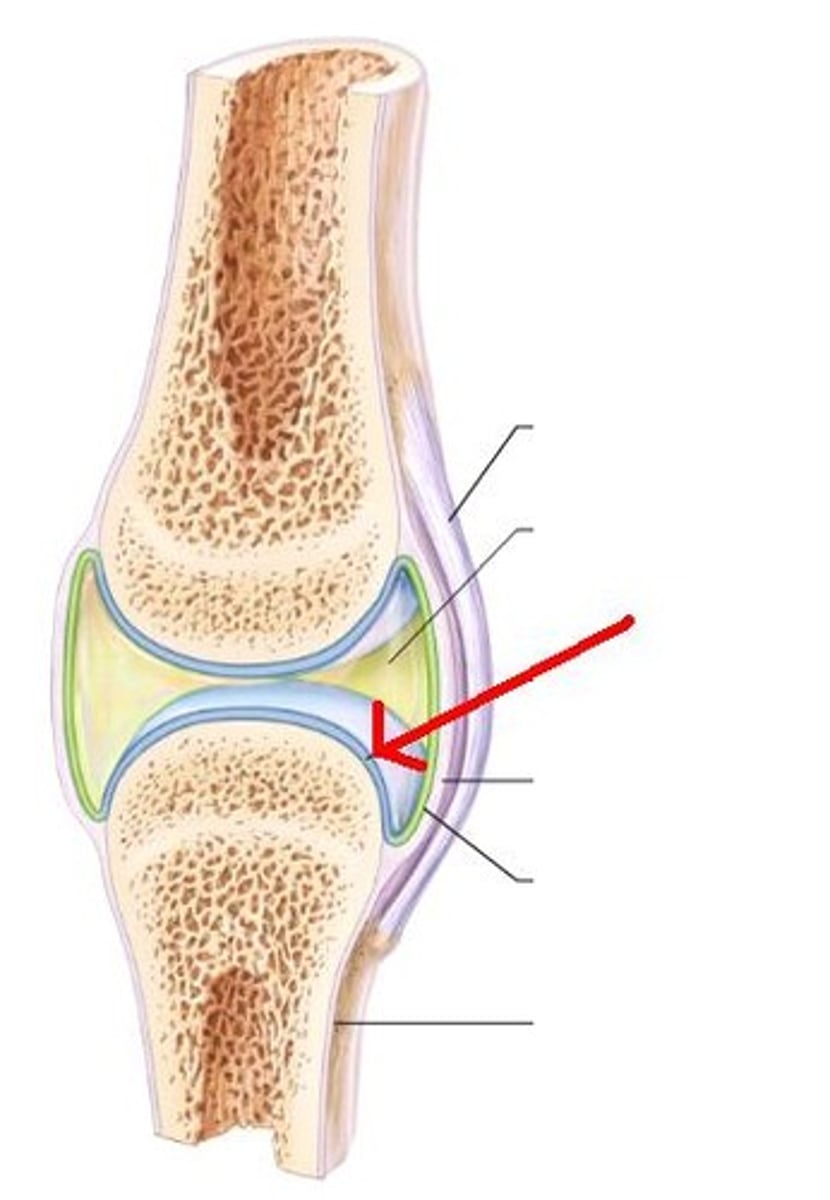
hyaline cartilage
Translucent bluish white cartilage consisting of cells embedded in an apparently homogeneous matrix, present in joints and respiratory passages, and forming most of the fetal skeleton
canaliculi
Hairlike canals that connect osteocytes in their lacunae to each other and the central canal
DNA vs RNA
DNA is the genetic material found in the nucleus of a cell. It replicates prior to cell division to ensure every body cell is identical. DNA provides instructions for building every protein in the body. By contrast, RNA is mostly found outside the nucleus and carries out the instructions for generating proteins as dictated by DNA
4 stages of mitosis
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
prophase
first and longest phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate and take up positions on the opposite sides of the nucleus
anaphase
the third phase of mitosis, during which the chromosome pairs separate and move toward opposite poles
telophase
the final phase of cell division, between anaphase and interphase, in which the chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and two nuclei are formed.
ABCDE rule for skin cancer
asymmetry, border, color, diameter, evolving
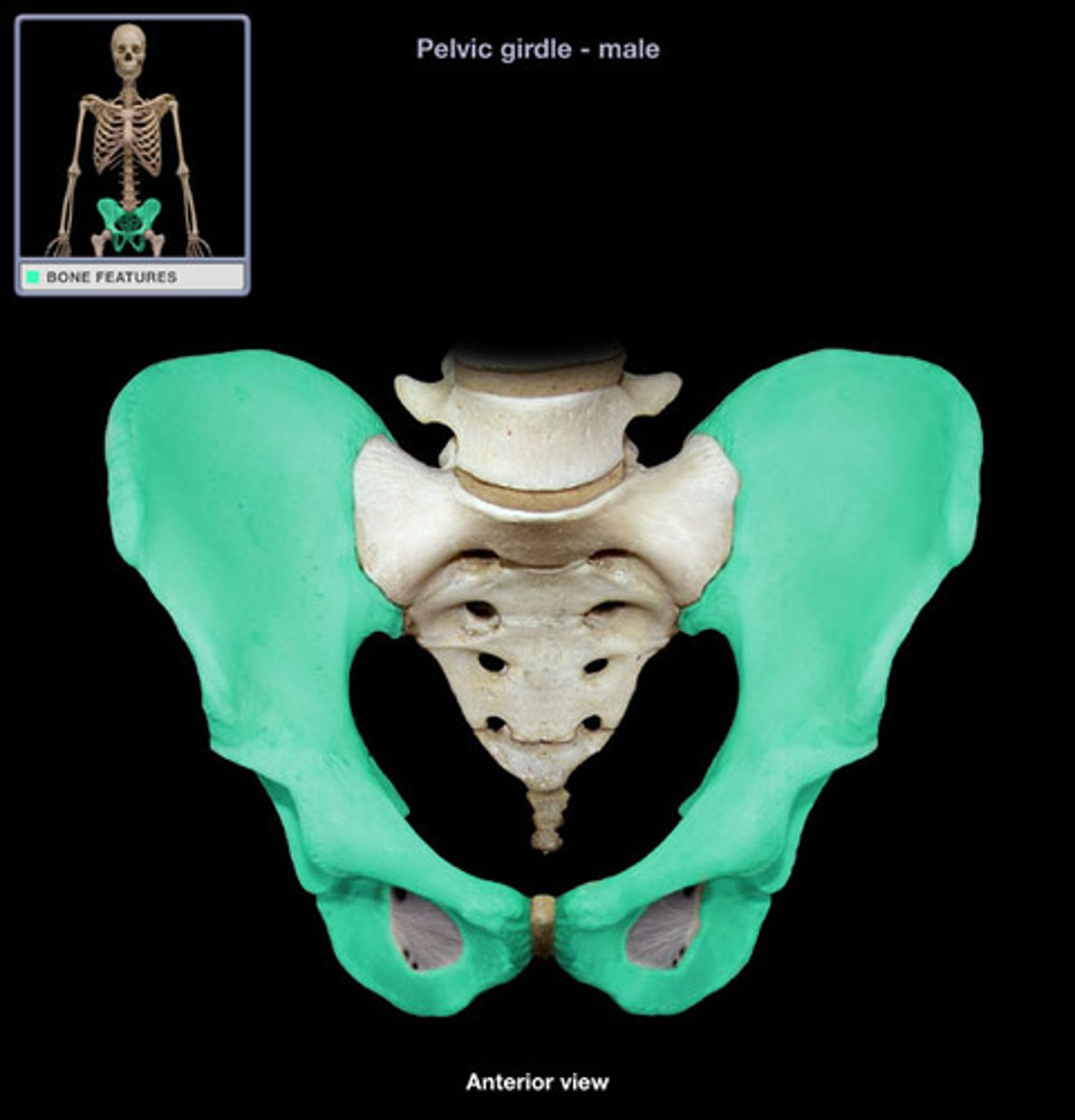
female vs male pelvis
1. has a larger and more circular inlet
2. is shallower than the male pelvis
3. has bones that are lighter and thinner than male pelvis bones
4. has a shorter and less curved sacrum
5. has a more rounded pubic arch because the angle of the pubic arch is greater
6. has shorter ischial spines that are also farther apart
importance of calcium ions in skeletal muscle contraction
Calcium ions are necessary for myosin heads to attach to binding sites on actin filaments. As the action potential travels into the muscle cell, it stimulates the sarcoplasmic reticulum surrounding each myofibril to release its stored calcium ions into the sarcoplasm. The calcium ions trigger the binding of myosin heads to actin filaments and the initiation of the sliding of filaments.