Reproduction
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
reproductive endocrine organs
hypothalamus
pituitary gland
ovary
testes
HPG axis
hypothalamus releases GnRH
anterior pituitary gland releases gonadotropins (FSH and LH)
gonads release sex steroid hormones
sex steroid hormones inhibit secretion and responsiveness to GnRH (negative feedback)
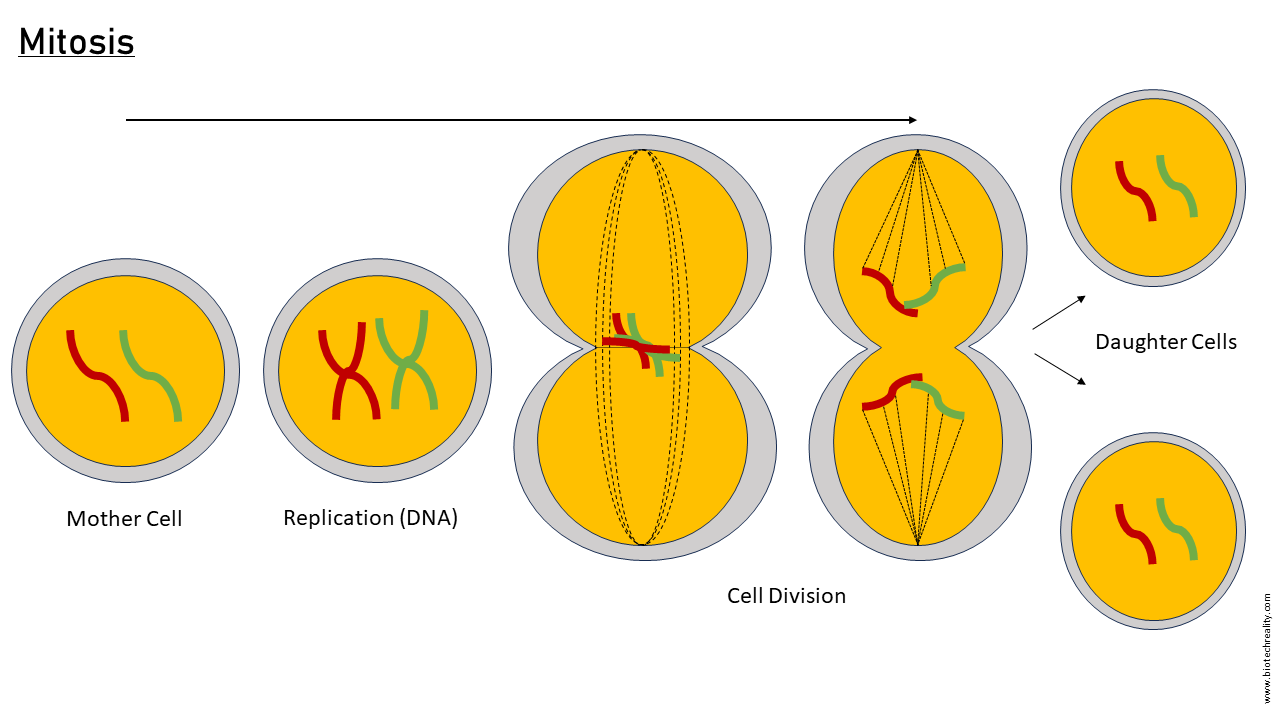
mitosis
produces diploid cells
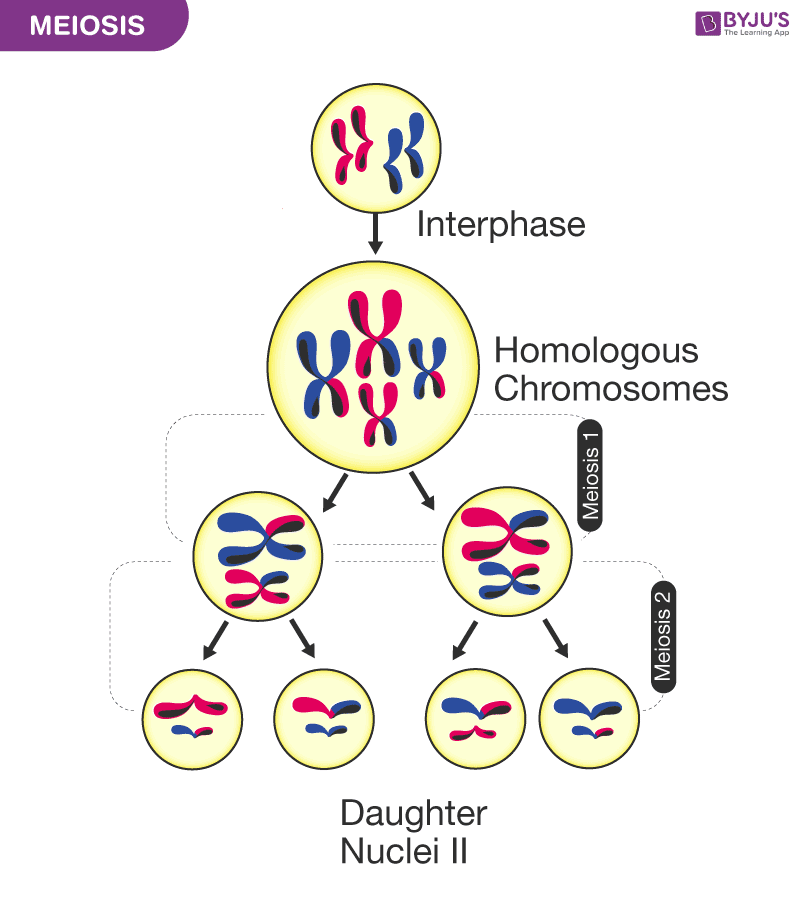
meiosis
produces haploid cells
zygote
ovum is fertilized by sperm in Fallopian tube
testis-determining factor (TDF)
transcription factor located on Y-chromosome (SRY gene) that determines if testes will develop; occurs in the first 40 days following fertilization
X-chromosome inactivation
in females, one X-chromosome is inactivated
intersex
reproductive or sexual anatomy does not fit typical definitions of male or female
causes: reduced or loss of function in TDF, TDF translocation to X-chromosome, androgen insensitivity
placenta
formed by embryo after implantation in uterine wall
gestation
developmental milestones tracked across three trimesters
first trimester
~8 weeks
external genitalia begin to emerge (determines sex)
male = testosterone or dihydrotestosterone (DHT) present
female = testosterone or DHT absent
second trimester
weeks 13-25
typical first movement (weeks 16-20)
lungs start to produce surfactant (week 29)
third trimester
weeks 13-25
most organs developed
weight gain
full term
38 weeks after conception
intersex females
too much androgen exposure
not enough Wnt4 exposure
aromatase deficiency
masculinization
intersex males
testicular feminization (ex: testosterone, testosterone receptors, problem with 5α-reductase)
puberty
process of sexual maturation, triggered by high pulsatile LH
females: > 8 years
males: > 10 years
thelarche
start of breast development
menarche
first menstruation
menstrual cycle
drives maturation and release of oocyte about once a month
spermatogenesis
spermatogonia → spermatozoa in ~74 days
menopause
ovarian follicles are depleted
change/loss of hormones
transition from high estrogen state to low estrogen state (hot flashes)
loss of estrogen protection (heart, vasculature, bone mass)
hypogonadal
occurs in males by ~70 years
ovaries
produce oocytes and release estrogen and progesterone
Fallopian tubes
transport sperm to ovum and fertilized ovum to uterus
endometrium
layer of glands and blood vessels lining uterus
shed during menstruation
myometrium
uterine smooth muscle
contracts during child birth (parturition)
oogenesis
primary oocyte in immature follicle
FSH stimulates growth
secondary follicle (develops fluid vesicles)
meiosis → secondary oocyte + polar body
only one follicle matures to ovulation each cycle
LH causes mature (Graafian) follicle to rupture, releasing oocyte (ovulation)
if fertilized by sperm, second meiotic division occurs (zygote)
if no fertilization, corpus luteum degenerates and menstruation occurs
follicular phase
days 1-13
days 1-4 = menstruation
days 5-13 = proliferative FSH, then estrogen
ovulation
~day 14
LH surge
luteal phase
days 15-28
progesterone and estrogen from corpus luteum
expansion of endometrial lining and glands
GnRH release
influenced by stress, emotion, and rigorous athletic activity (low body fat, decreased leptin)
amenorrhea
loss of menstruation
acrosome reaction
contact of acrosome (head of spermatozoa) to zona pellucida (ovum)
fusion occurs, exocytosis to release acrosome enzymes
inner acrosomal membrane fuses, enters ovum
creates calcium wave in ovum
in ovum, induction of second meiotic division and changes to block other sperm
now a zygote (diploid)
travels to uterus for implantation
human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
mimics LH
prevents menstruation
maintains uterine lining for pregnancy until placenta secretion of progesterone
placental hormones
hCG
hCS
progesterone
estrogen
labor
stimulated by oxytocin and prostaglandins
childbirth
fetal CRH (from placenta), ACTH, and corticosteroids are important
lactation
suckling/baby’s cry
ascending sensory signal
hypothalamus
decreased dopamine
anterior pituitary
prolactin
milk production
posterior pituitary
oxytocin
milk ejection reflex
hormonal actions during pregnancy
promote implantation
dampen mother’s immune system (limit reaction to fetal antigens)
myometrial quiescence (prevents mestruation)
hCG (first 8-10 weeks)
progesterone (by 8 weeks)
parturition
estrogen (females)
increases…
blood volume by 40% in third trimester
stroke volume by 30%
heart rate by 15%
tidal volume by 50%
renal blood flow by 40%
production of clotting proteins (late in pregnancy)
antibodies for passive immunity (IgG in late pregnancy, IgA after birth)
human chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS)
opposes insulin which minimizes hypoglycemia to protect energy source for fetus
increases lipolysis, FFA, glucose, and ketones
burden on mother, increases susceptibility to gestational diabetes
preeclampsia-eclampsia
pregnancy-induced hypertension, proteinuria, and edema
common cause of maternal death
treating hypertension may cause placental insufficiency
dysmenorrhea
painful menstruation and cramping in lower abdomen
primary: abnormally high prostaglandin production (endometrium) causes excessive contractions
secondary: to pelvic disease (ex: endometriosis → extrauterine “ectopic” endometrial tissue)
treatments reduce hormone fluctuations
abnormal vaginal bleeding
structural lesions (ex: endometrial polyps)
cancers (uterine, cervical, endometrial)
infertility
inability to achieve pregnancy for > 1 year
source can be either male or female
ovarian dysfunction
tubal or pelvic dysfunction (ex: endometrial scarring)
epididymis
sperm maturation
vas deferens
transports sperm from testes to urethra
prostate
secretes prostate fluid for semen
testes
testosterone release and sperm production
~2°C below body temperature
semen
male reproductive fluid
suspension of spermatozoa
penis
voids urine
ejaculates semen
seminiferous tubules
sertoli cells → respond to FSH
site of spermatogenesis
secretes inhibin → negative feedback to inhibit FSH release
interstitial tissue
leydig cells → respond to LH
secretes testosterone which stimulates meiosis of spermatogonia
estrogen (males)
at least part of negative feedback
bone mass
fusion of epiphyseal plates (bone)
aromatase
converts testosterone into estradiol
spermatogenesis
spermatogonia (diploid)
mitosis → spermatogonia + primary spermatocyte
primary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis
after two meiotic divisions → four haploid spermatids
maturation of spermatids
develop flagellum
develop acrosome (cap with digestive enzymes for penetrating ovum)
transported to epididymis
flagellum matures, becomes motile
erectile tissue
corpus cavernosa and corpus spongiosum
during arousal, fills with blood, causing erection
PNS activates nitric oxide release
vasodilation of penile vasculature fills corpi
pressure of corpi limit venous outflow, trapping blood
SNS stimulates ejaculation (expulsion of semen from penis)
erectile dysfunction
difficulty in developing or maintaining an erection
treatment with PDE inhibitors (ex: sildenafil)
inhibits phosphodiesterase → reduces breakdown of cGMP → extends inhibition of calcium channel → extends relaxation
pre-testicular infertility
abnormal hypothalamus (GnRH) or anterior pituitary (LH, FSH) function, typically genetic
anabolic steroid use
testicular infertility
varicocele (dilates scrotal veins) → abnormal temperature, blood flow impairs spermatogenesis
chromosomal structure abnormalities → low or no sperm (ex: Klinefelter syndrome)
toxins, smoking, or temperature
post-testicular infertility
ductal obstruction, caused by genetic abnormality, surgery, inflammation, or infection
benign prostatic hyperplasia
non-malignant growth
enlargement of prostate
common with age
one-third of men over 65 years
symptoms: compression of urethra (urinary retention), increased bladder pressure, painful urination, nocturia, difficulty starting urination
treatments: relax bladder and prostate smooth muscle
α1-adrenergic receptors (ex: prazosin)
PDE5 inhibitors (ex: sildenafil)
5α redcutase inhibitors (ex: finasteride)