Dairy Cattle
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What are the four routes of income for dairy farms?
- Milk
- Sale of young stock
- Sale replacement heifers
- Embryo sales
List some expenses of dairy farms.
- Feed (50-60%)
- Labor
- Calf and heifer-raising
- Utilities
- Veterinary services
- Pharmaceuticals
- Equipment maintenance
The breeding period starts around ________ months of age or ________ days in lactation. The weaning period starts when?
- 12
- 45-60
- 2-3 months
Dairy cows fear _________ but become accepting of a ______________. They are __________ animals.
- Novelty
- Routine
- Social
The flight zone is affected by what two things?
1) Size of animal enclosure
2) Previous contact with people
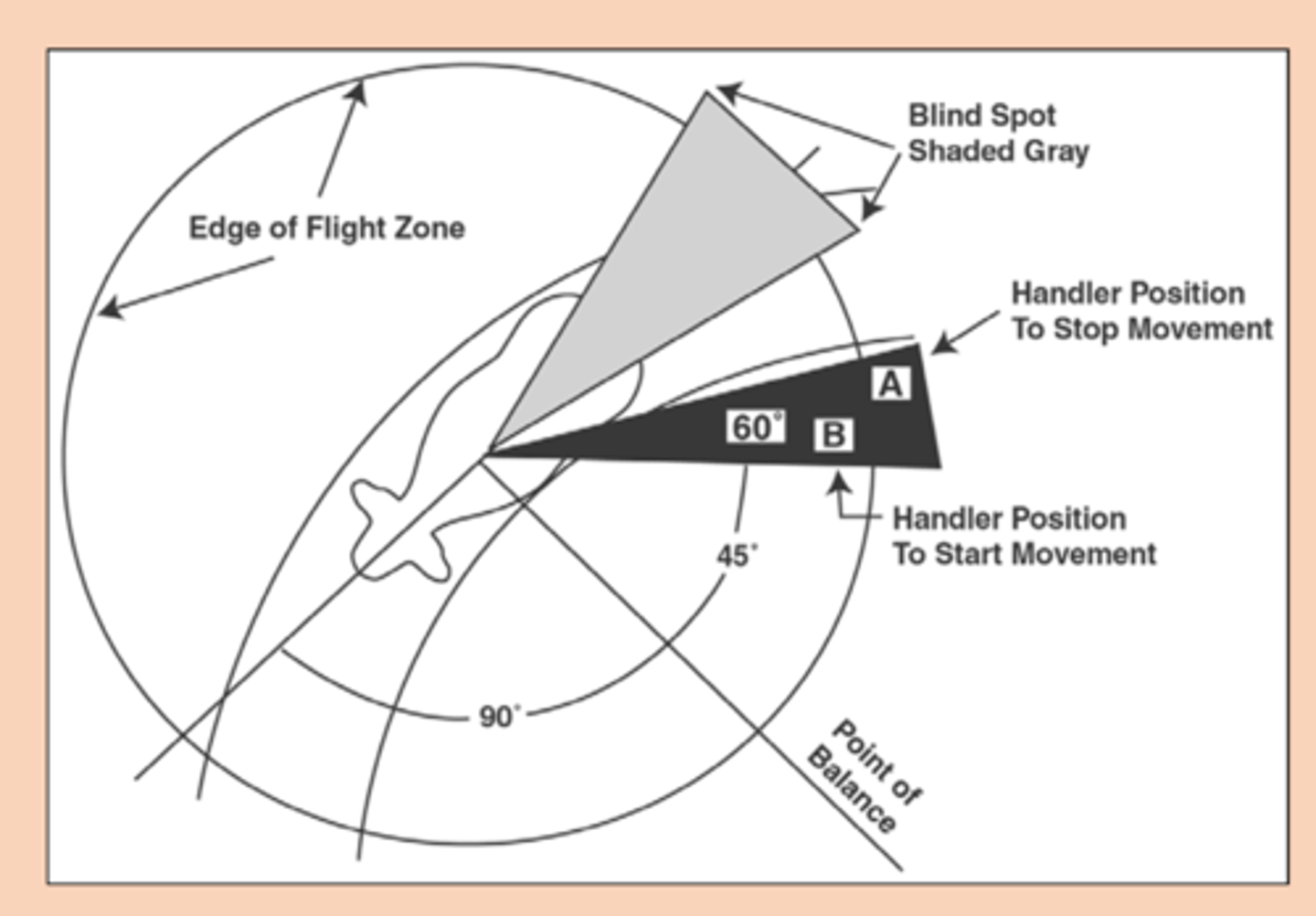
How can one encourage forward movement?
- Enter flight zone behind point of balance; move back and forth parallel to direction of desired movement (Point A and B)
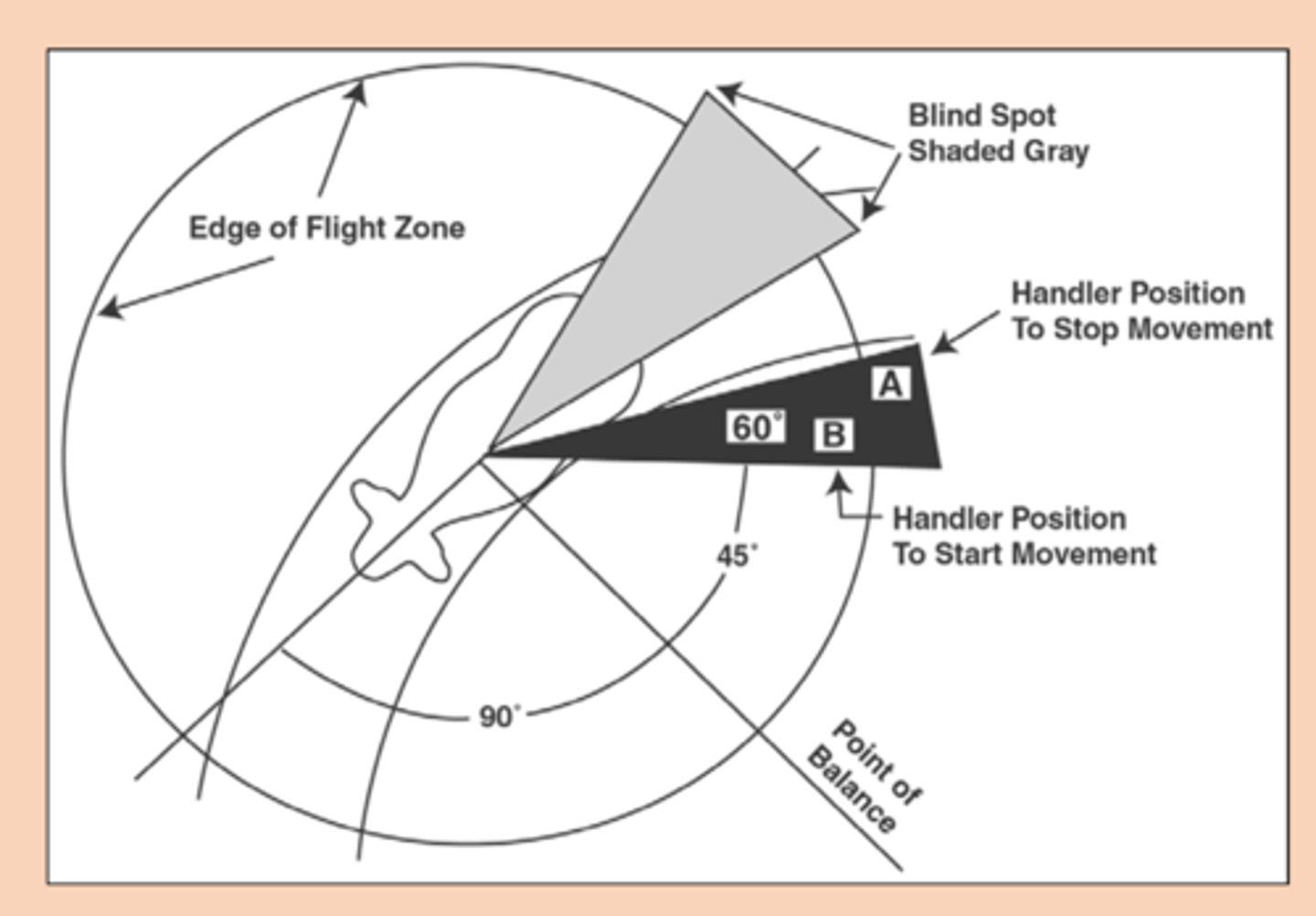
How can one encourage backwards movement?
- Move in front of point of balance
List some methods of dairy cattle restraint.
- Halter
- Head lock
- Restraints that divert attention
- Casting restraints
What are restraints that divert attention?
- Tail restraint
- Nose lead
What are two methods for casting?
- Rope squeeze or Half-hitch method
- Running "W" or criss-cross method
What 3 things are involved in a pre-examination routine?
1) Inspection of holding/housing facility
2) Evaluate animal before restraint
3) Assess animal's gait
What is the BCS score range in dairy cattle?
1-5
Where should one auscultate the heart in dairy cattle?
- Ventral part of thorax between 3rd and 6th ribs
What is a normal HR in dairy cattle?
- 60-84 BPM
Where should one auscultate the lungs in dairy cattle? What should one observe?
- Caudal border of 11th rib
- Observe rate and effort
What is a normal RR in dairy cattle?
- 12-36
In dairy cattle, what should one auscultate in addition to the lungs and heart?
- Rumen
When examining the udder, what should one do?
- Strip every teat and evaluate milk
- Evaluate udder consistency
What is a normal temperature in a dairy cow?
- 101-102.8
In dairy cattle, products labeled for SQ or IM administration should be administered where?
- In the neck region
In dairy cattle, injections should be spaced how far apart?
- At least 4 inches apart
No more than what volume of product should be administered per IM or SQ injection site?
- 10 mL
What are two sites for blood collection in dairy cattle?
1) Jugular vein
2) Coccygeal vein ("tail vein")
What are some popular areas for dairy production in the U.S.?
- Midwest
- California
- New England
Why is the Midwest such a popular area for dairy production?
- Feed is produced there
Lately, there has been more ____________ of the dairy industry. There are more __________ dairies and less _________ dairies.
- Consolidation
- Large
- Small
Milk is the #______ commodity in Oregon.
- 4
Jersey milk is higher in ____________, making it better for products like ____________.
- Components
- Cheese
What is the most popular dairy breed in the U.S.?
- Holstein
What are the 4 primary types of dairies?
1) Conventional (all feed is provided in the facility)
2) Grazing (Majority of forage is consumed during growing season)
3) Combination (grazing + conventional; conventional in winter, grazing in summer)
4) Organic
Majority of larger operations are what type of dairy?
- Conventional
What type of dairy are most small operations?
- Grazing
Which type of dairy is equally present amongst large and small operations?
- Organic
What are the types of housing systems? Describe them.
1) Open-dry lot: Essentially a dirt pen with shading
2) Loose housing: Multiple animal area
3) Free-stall barn: Each cow has access to a bedded stall
4) Pasture: What it sounds like
What type of housing system does the OSU dairy use?
- Free-stall
What are the types of parlors? Describe their characteristics.
- Parallel: More affordable, but can't milk as many cows per hour.
- Herringbone: Can fit slightly more cows than parallel.
- Rotary: Milks the most cows per hour; Used to be very expensive but are becoming more accessible
Cows are creatures of ___________.
- Habit
Do all cows milk at the same pace?
- No
Majority of cows are done milking after __________ loops in a rotary system.
- One
The income from milk is based on what?
- Volume (paid per 100 lb)
- Components
- Quality (SCC)
Milk pricing is set by the ___________ and is influenced by ___________.
- Government
- Supply
What is the primary expense on a dairy farm?
- Feed
High levels of SCC indicate what?
- Possible mastitis
When young stock are sold by dairy farms, they are often what used for what?
- Bull calves used for meat
Once a dairy cow calves, she is referred to as what?
- Fresh cows
A cow in the late stage of her dry-period is referred to as what?
- Close-up
A cow in the early stage of her dry-period is referred to as what?
- Far-off
What is the most sensitive/high "disease risk" period for a dairy cow?
- Immediately after calving (fresh)
Milk production peaks at what phase of the production cycle?
- At the end of early lactation, beginning of middle lactation
What are calves fed after separation from the cow?
- Milk replacer
- Stored milk from cows
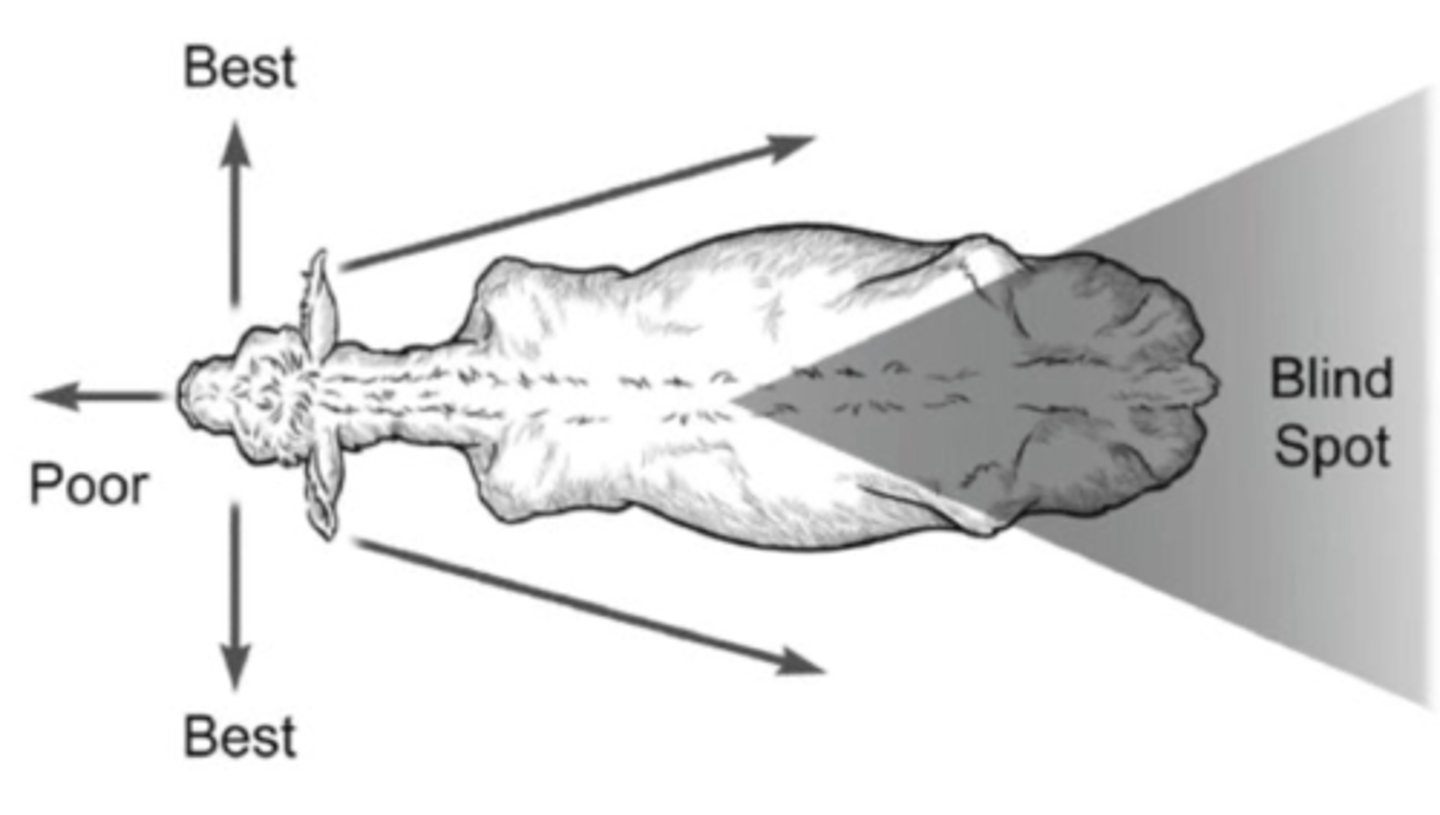
The cow has better __________ vision, meaning they have _________ vision directly in front of them and ________ vision immediately to their side.
- Monocular
- Poor
- Best
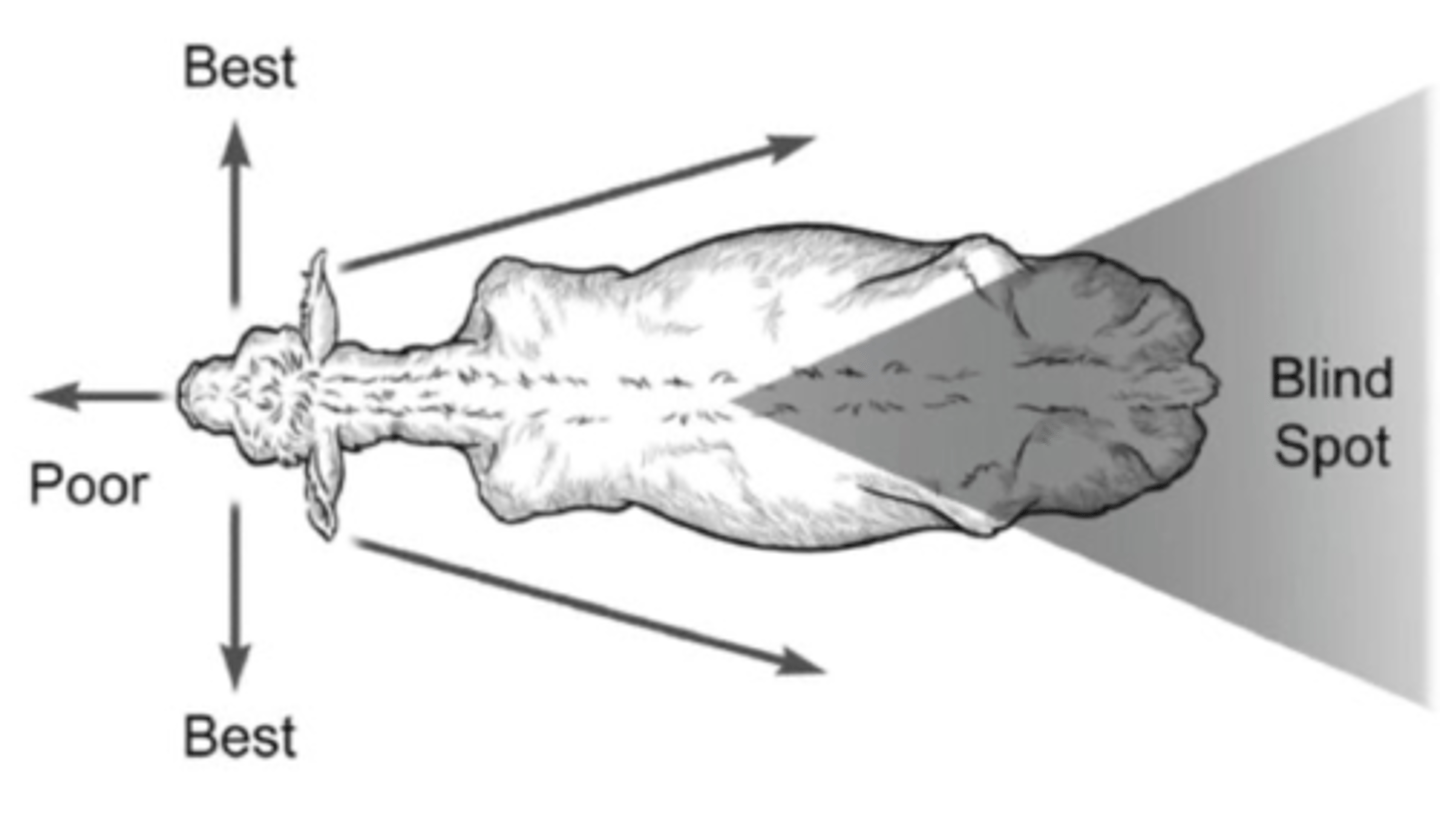
Where is the cow's blind spot?
- Directly behind them
What should be available when cows exit the parlor, particularly for fresh cows? Why?
- Feed
- They are in a negative energy balance when fresh
In open-stall systems, beds must be what? What can happen otherwise?
- Long enough for cow to lay and stand comfortably
- Lameness
Maternity pens should not be ___________.
- Crowded
How many cows should be present in a calving pen?
- One
When an animal crosses their limbs while moving, this indicates _______________.
- Lameness
Much of a physical exam is simply ________________.
- Observational
How does one collect urine in dairy cows?
- Stroke the area below the vulva
When does one measure urine pH often in dairy cows? Why?
- Cows in late lactation which are about to calve
- They are being fed a diet which puts them at a higher risk for acidosis to prevent hypocalcemia