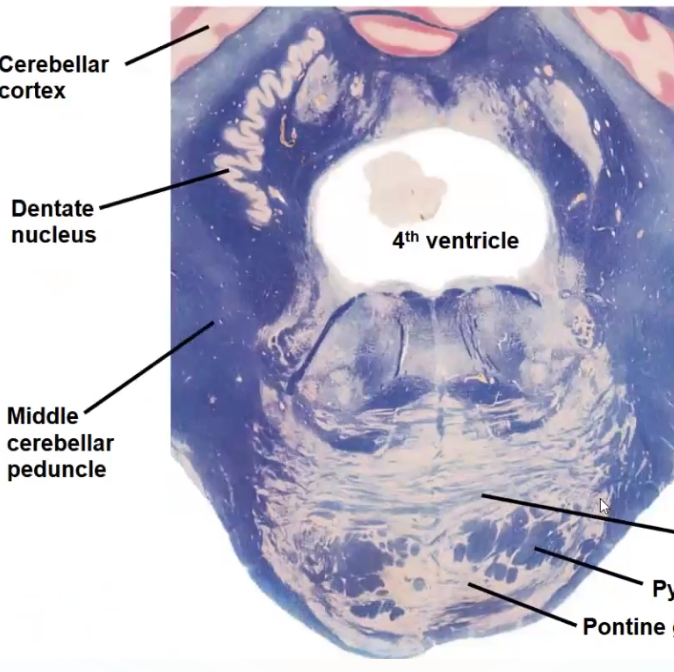
2. Forebrain, Thalamus and Basal Ganglia
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
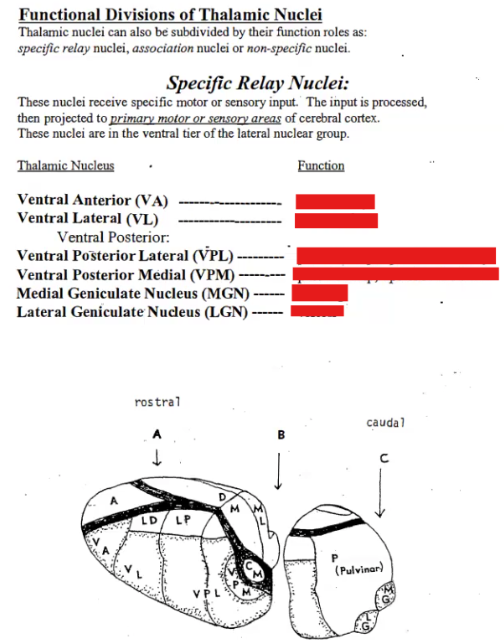
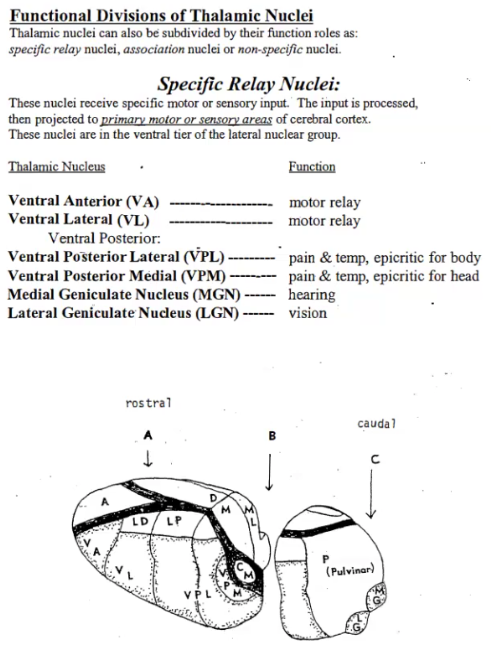
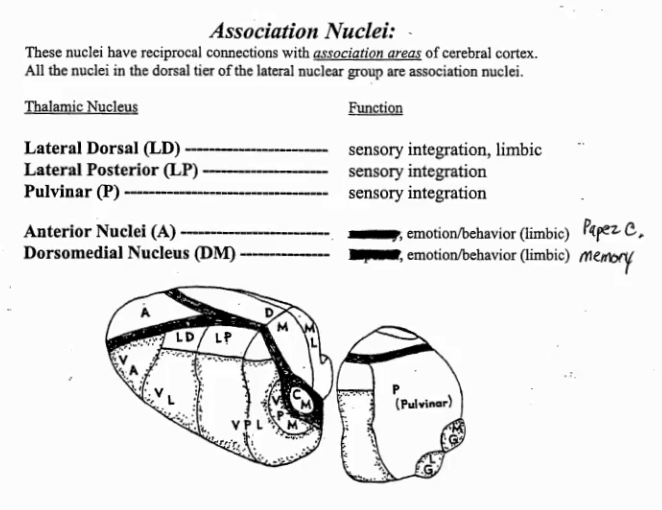
Label the function of each thalamic nucleus
The Thalamus is supplied by what arteries
Posterior communicating artery
Posterior cerebral artery
Anterior choroidal artery
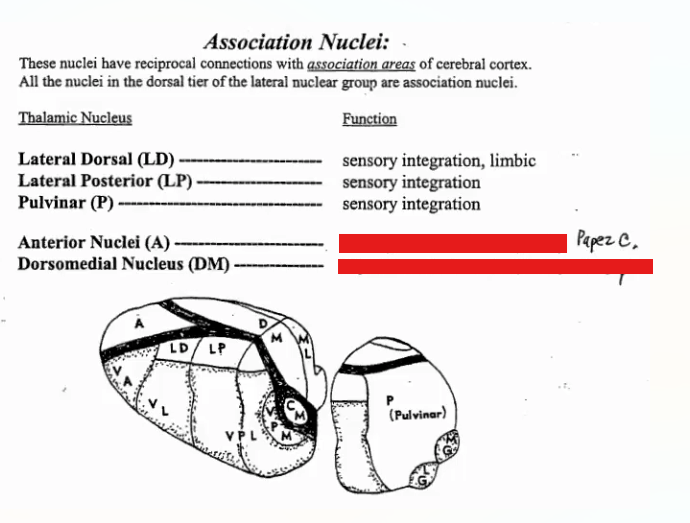
Function of Thalamic Association Nuclei
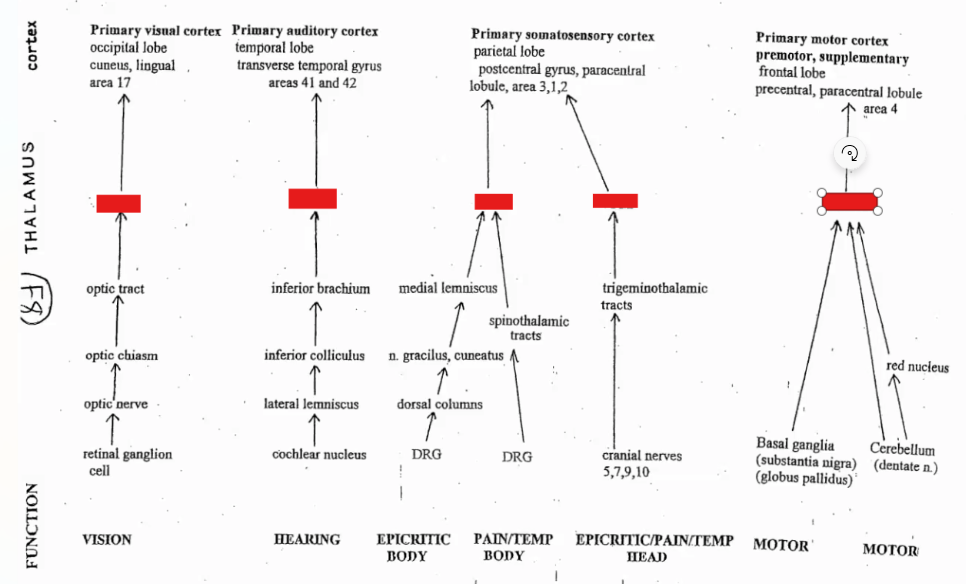
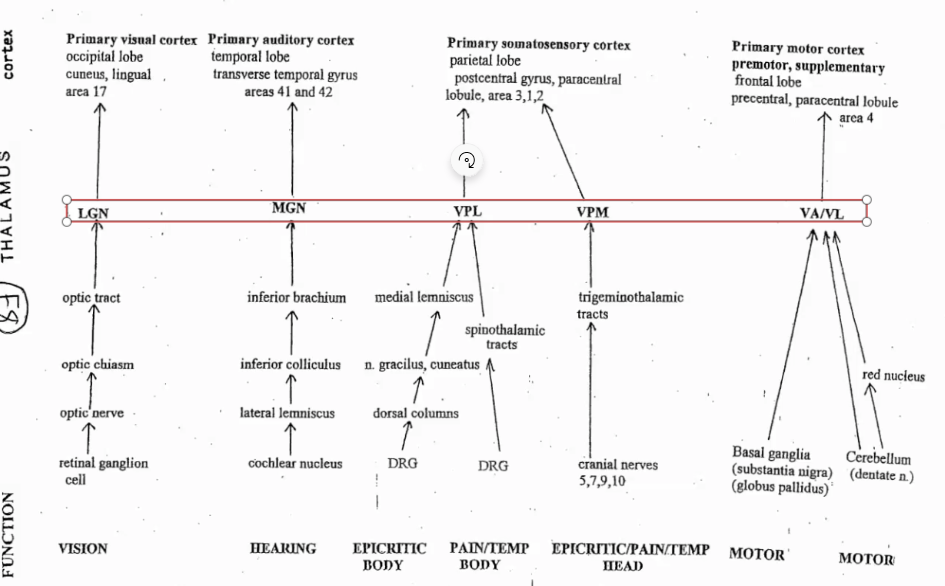
Complete the pathways with the nucleus it reaches to
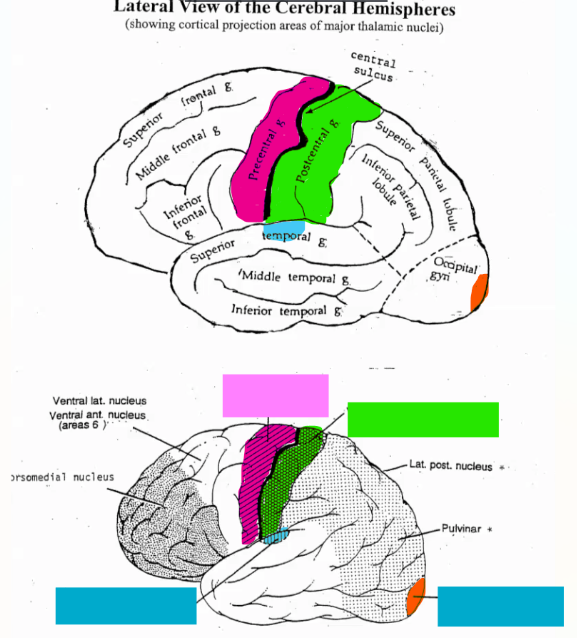
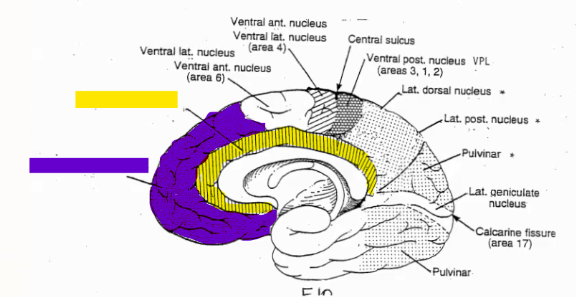
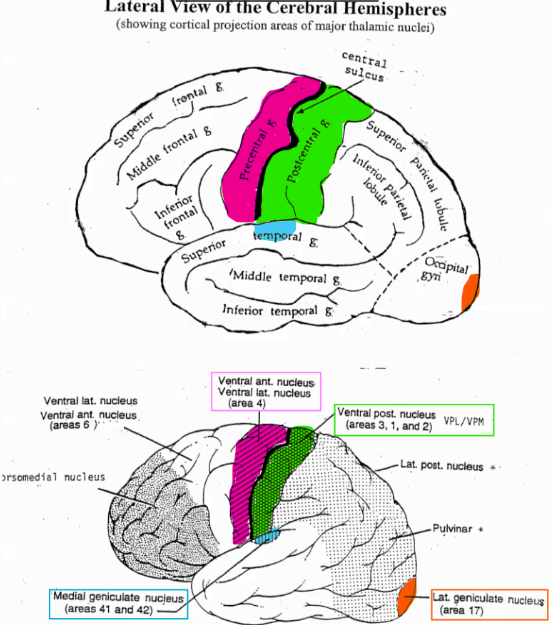
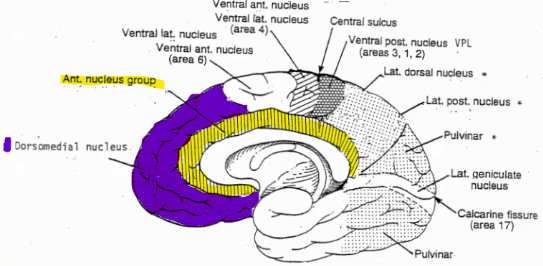
Each region of the brain receives information from a different thalamic nucleus, label it
Functions of the hypothalamus
Homeostasis
Thermal regulation
Endocrine System Control
Autonomic System control
What structures make up the limbic system
Cingulate Gyrus
Parahippocampal gyrus
Subcallosal gyrus
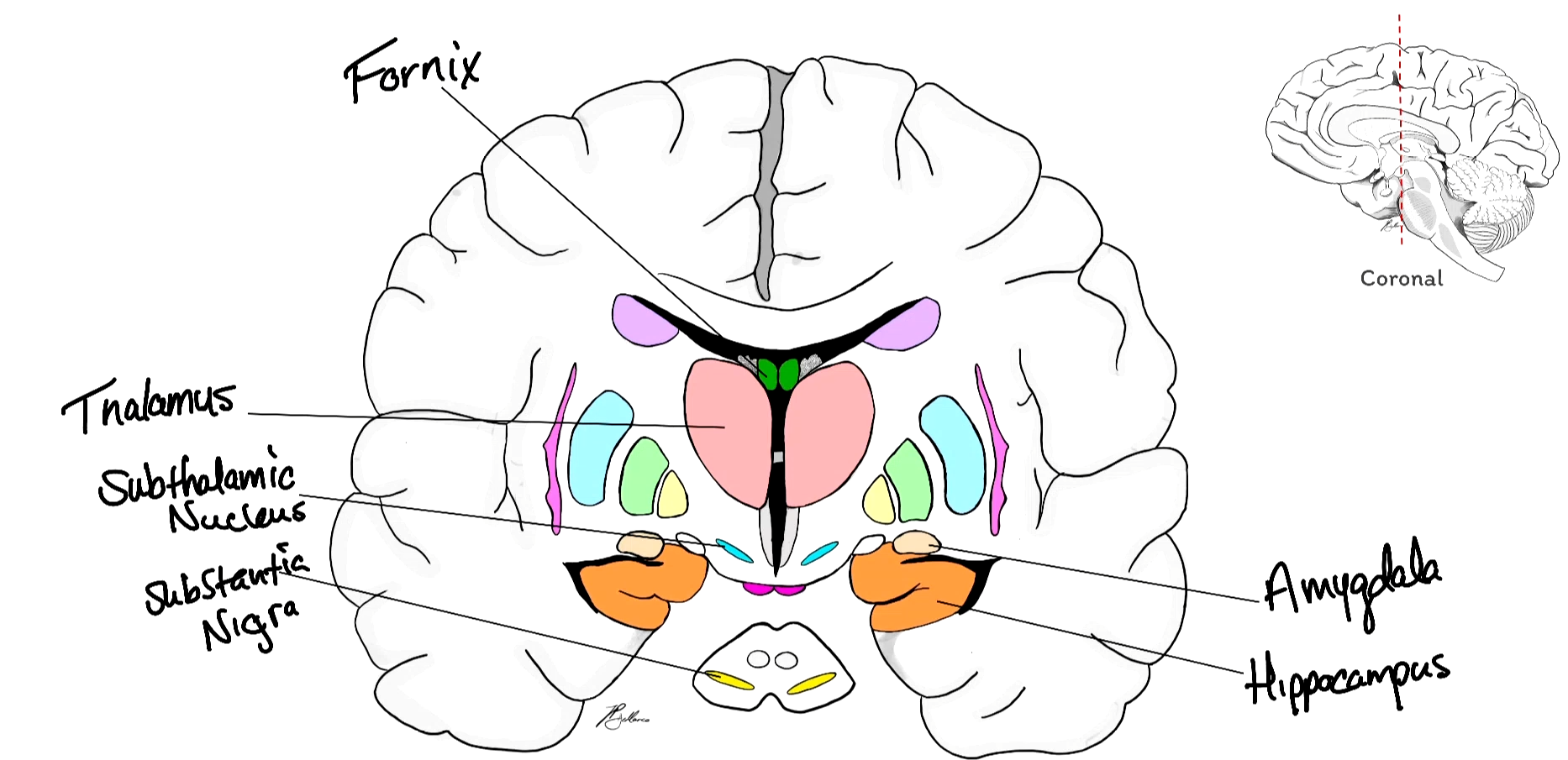
Fornix
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Amygdala
Hippocampus
Corpus callosum
Septum pellucidum
Functions of the limbic system
Olfaction
Autonomic functions
Emotions, memory and behavior
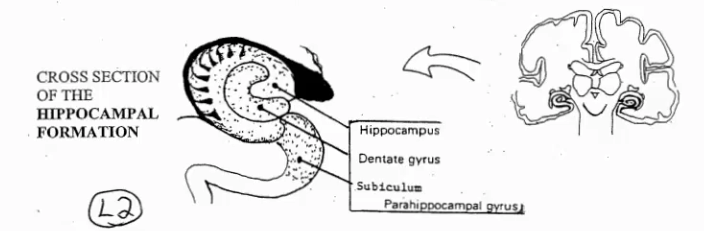
What is the hippocampal formation and what are its 3 layers
It is a 3-layered cortex in the temporal lobe responsible for memory formation and learning
Hippocampus (outside), Dentate gyrus (inside) and Subiculum (under)
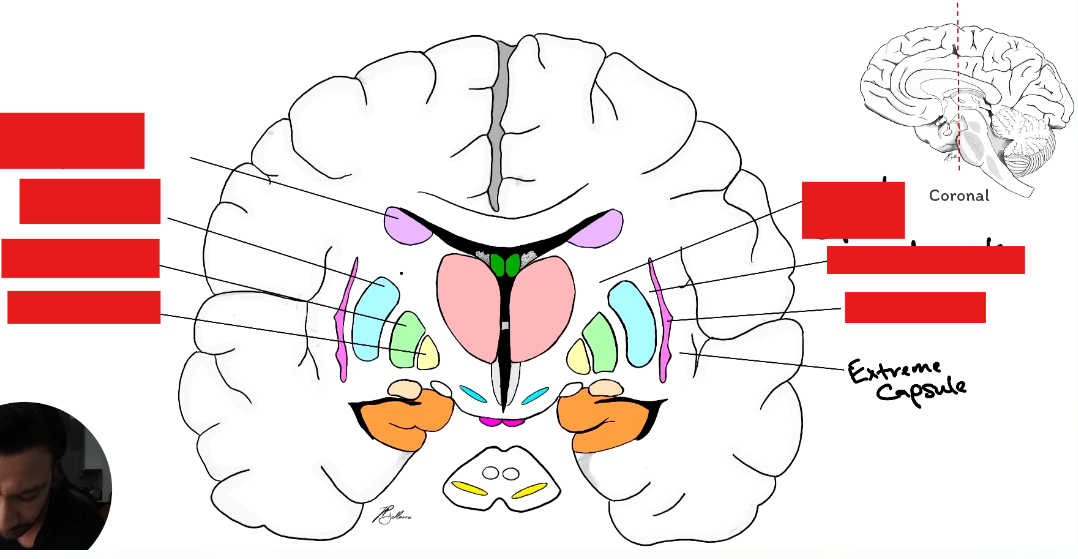
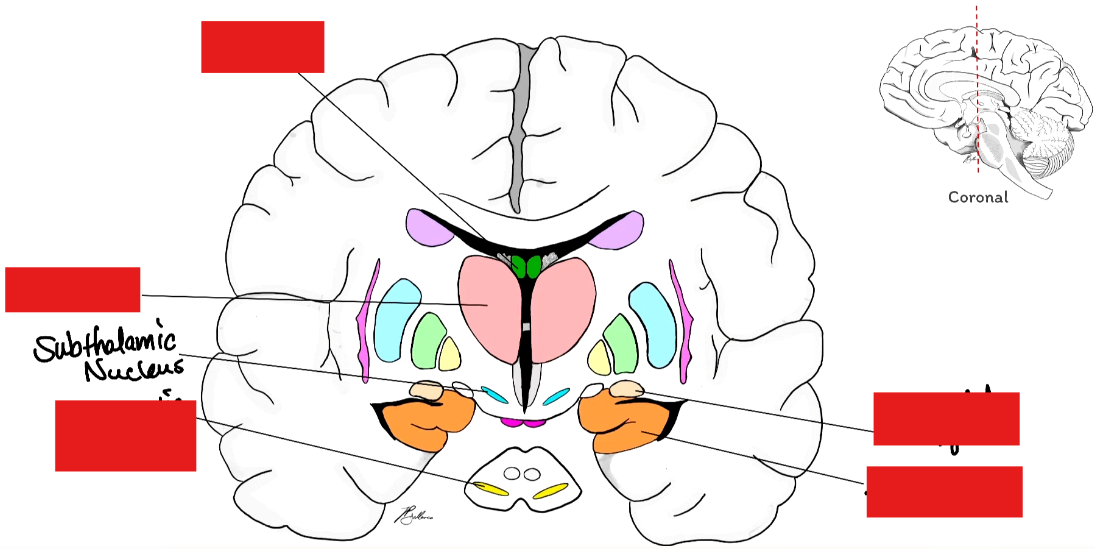
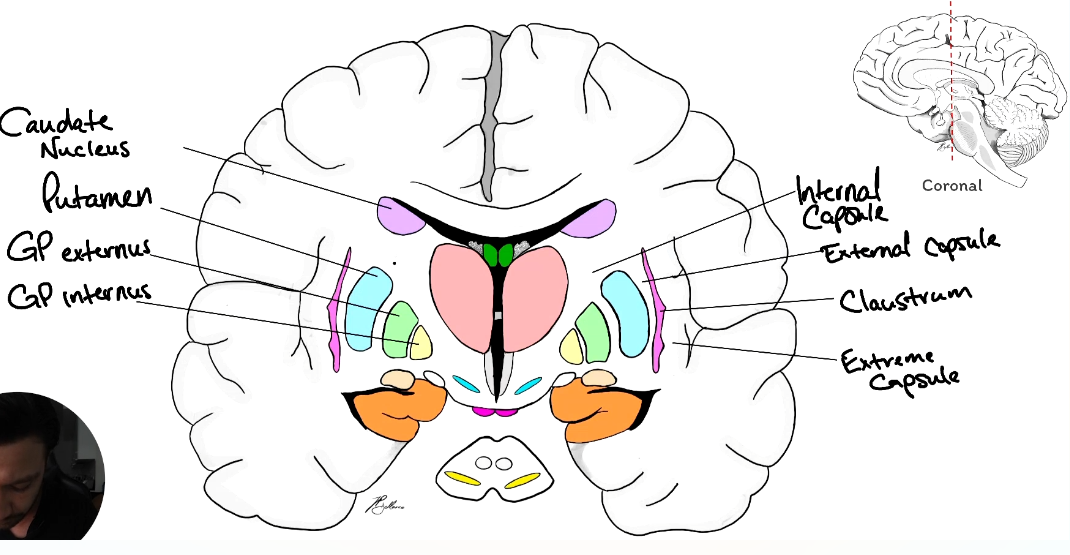
Label the Basal Ganglia
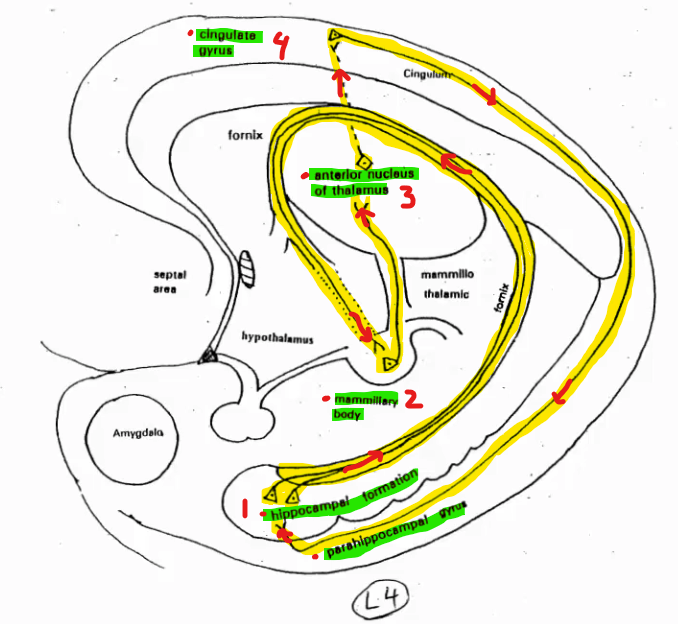
The Papez Circuit
Function
Describe the route
Connects the structures of the limbic system
Hippocampal formation > Mammillary Body > Anterior Nucleus of Thalamus > Cingulate Gyrus Parahippocampal gyrus > Repeat
Motor Functions of the Cerebellum
Motor Functions of basal ganglia
Maintains posture, maintains muscle tone, motor coordination
Posture reflexes, initiation and execution of motor reflexes
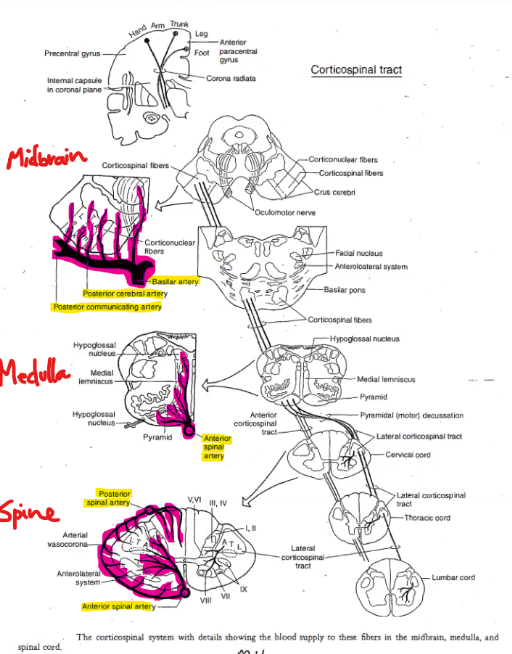
What are the arteries supplying the following
Midbrain
Medulla
Spinal Cord
Midbrain: posterior communicating artery, posterior cerebral artery, basilar artery
Medulla: anterior spinal artery
Spinal Cord: anterior and posterior spinal arteries
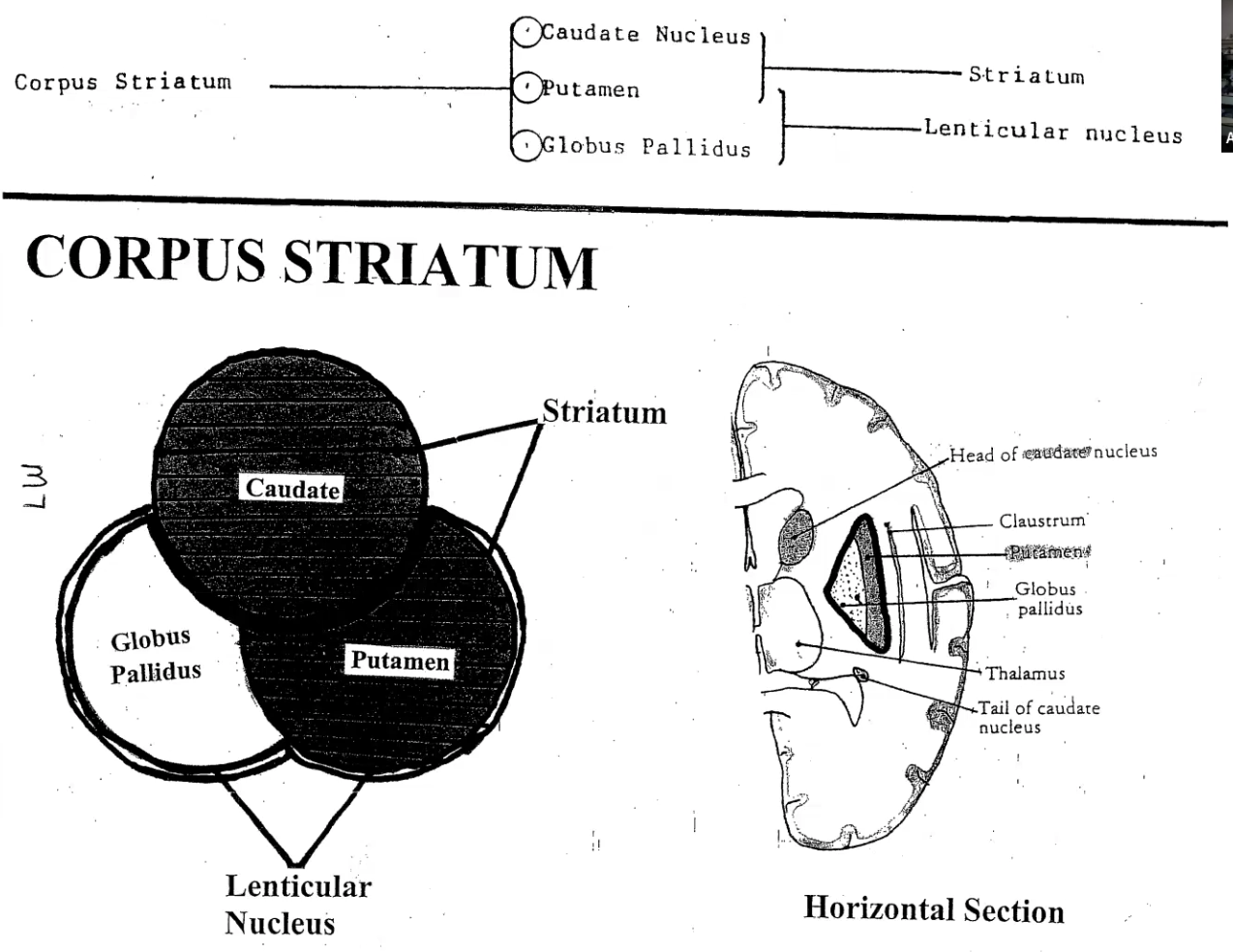
Name the structures that make up the
Corpus Striatum
Striatum
Lenticular Nucleus
Corpus Striatum: Caudate Nucleus, Putamen, Globus Pallidus
Striatum: Caudate Nucleus and Putamen
Lenticular Nucleus: Putamen and Globus Pallidum
The substantia nigra is the ______ nucleus in the midbrain
It is an _________ motor nucleus
Degeneration of the substantia nigra results in __________ _______
The substantia nigra is the largest nucleus in the midbrain
It is an extrapyramidal motor nucleus
Degeneration of the substantia nigra results in Parkinson’s Disease
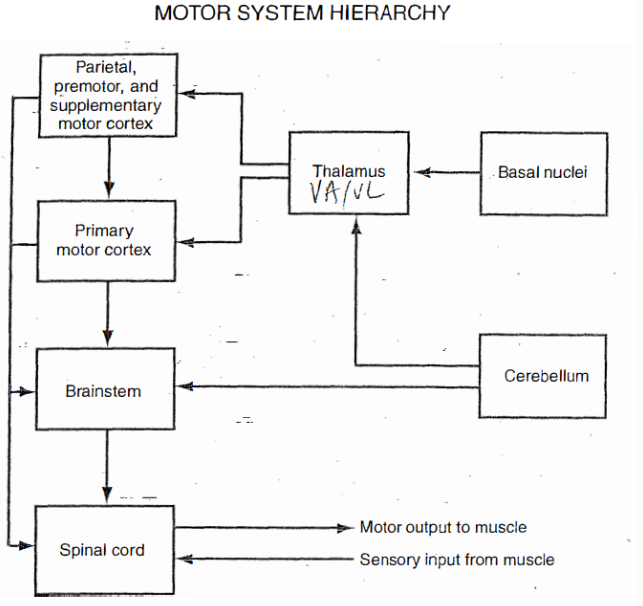
Main Circuit of the Basal Ganglia
cerebral cortex > striatum > Globus Pallidus > Thalamus (VA nucleus) > repeat
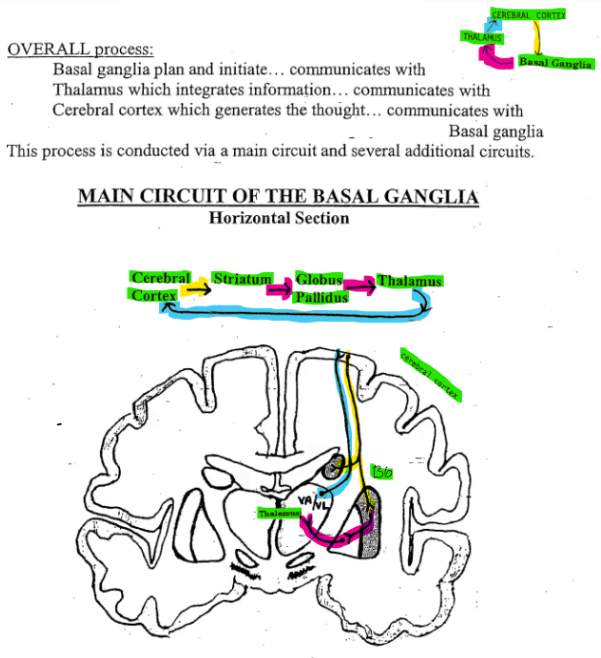
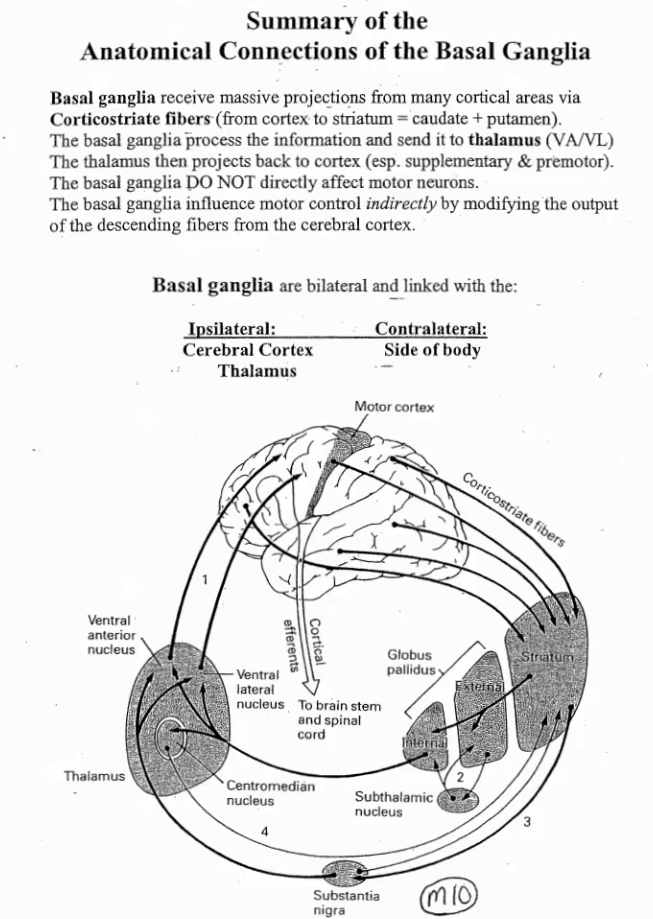
The Basal Ganglia receive massive projections from many cortical areas via ________ ______
The Basal Ganglia process the information and send it to the ________
The thalamus then projects back to the _____
The Basal Ganglia do not directly affect _____ neurons
The Basal Ganglia receive massive projections from many cortical areas via Cortico-striate fibers (from cortex to striatum)
The Basal Ganglia process the information and send it to the Thalamus
The Thalamus then projects back to the cortex
The Basal Ganglia do not directly affect motor neurons
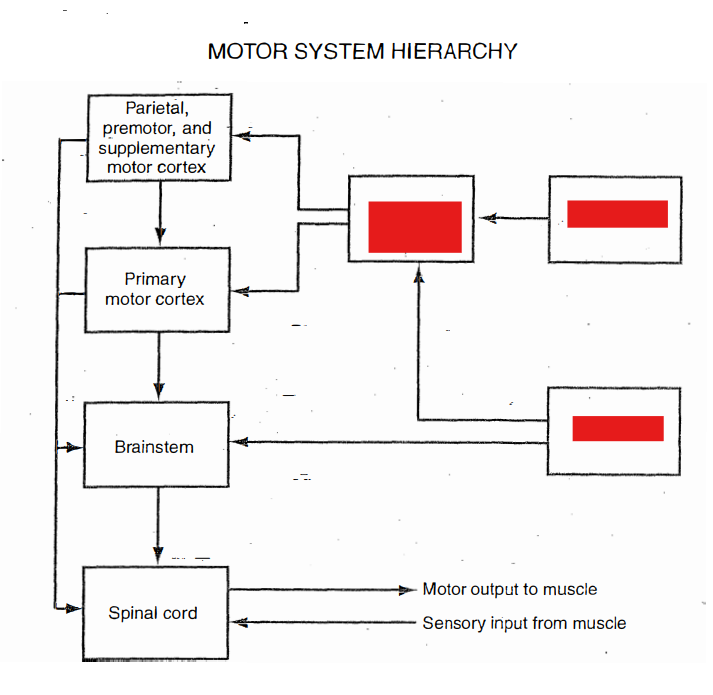
Label
Parkinson’s Disease
Results from
Symptoms
What else can induce similar effects (parkinsonism)
Degradation of dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra
Shuffling gait, Bradykinesia, Akinesia, Tremors, Rigidity
Drugs or head trauma

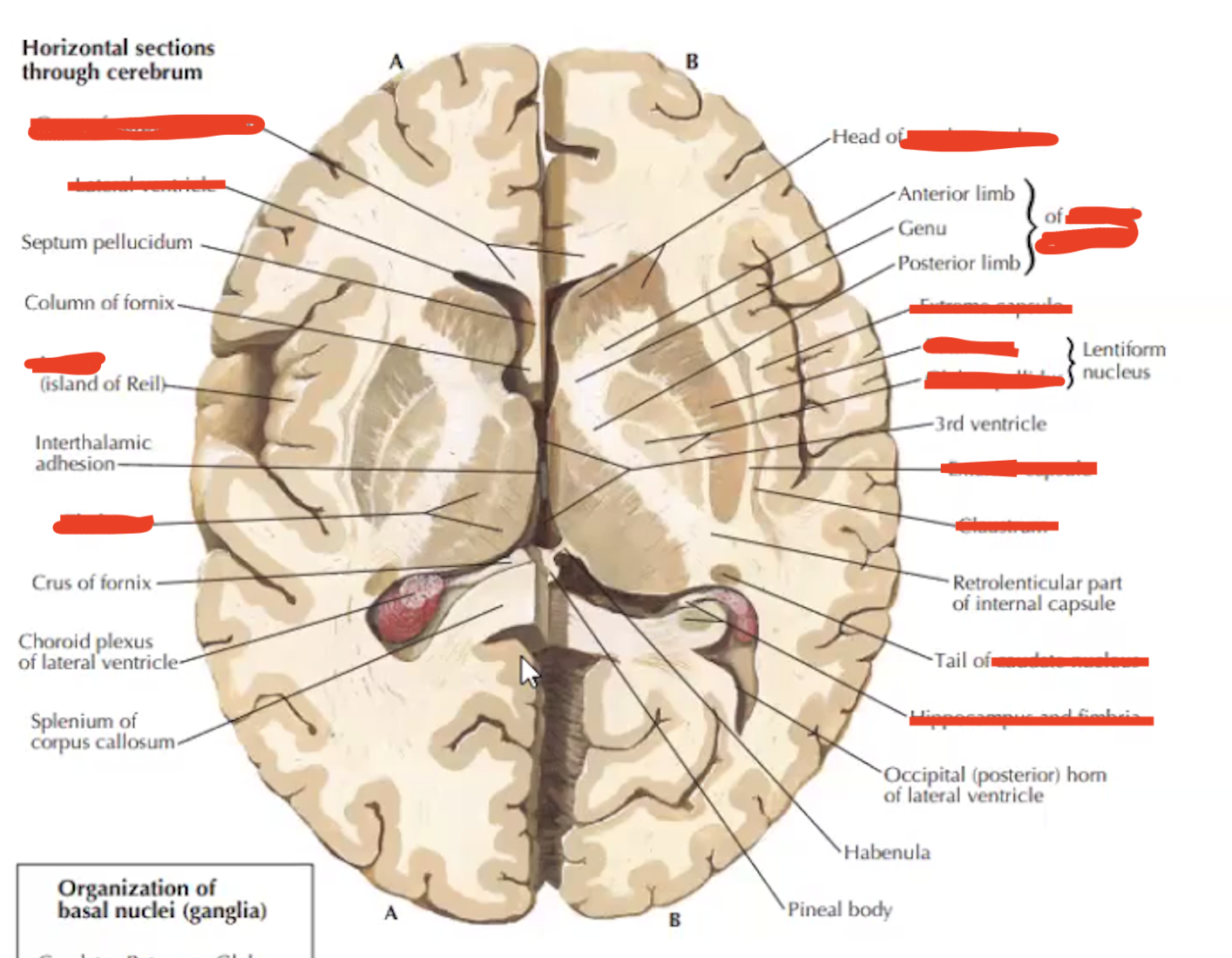
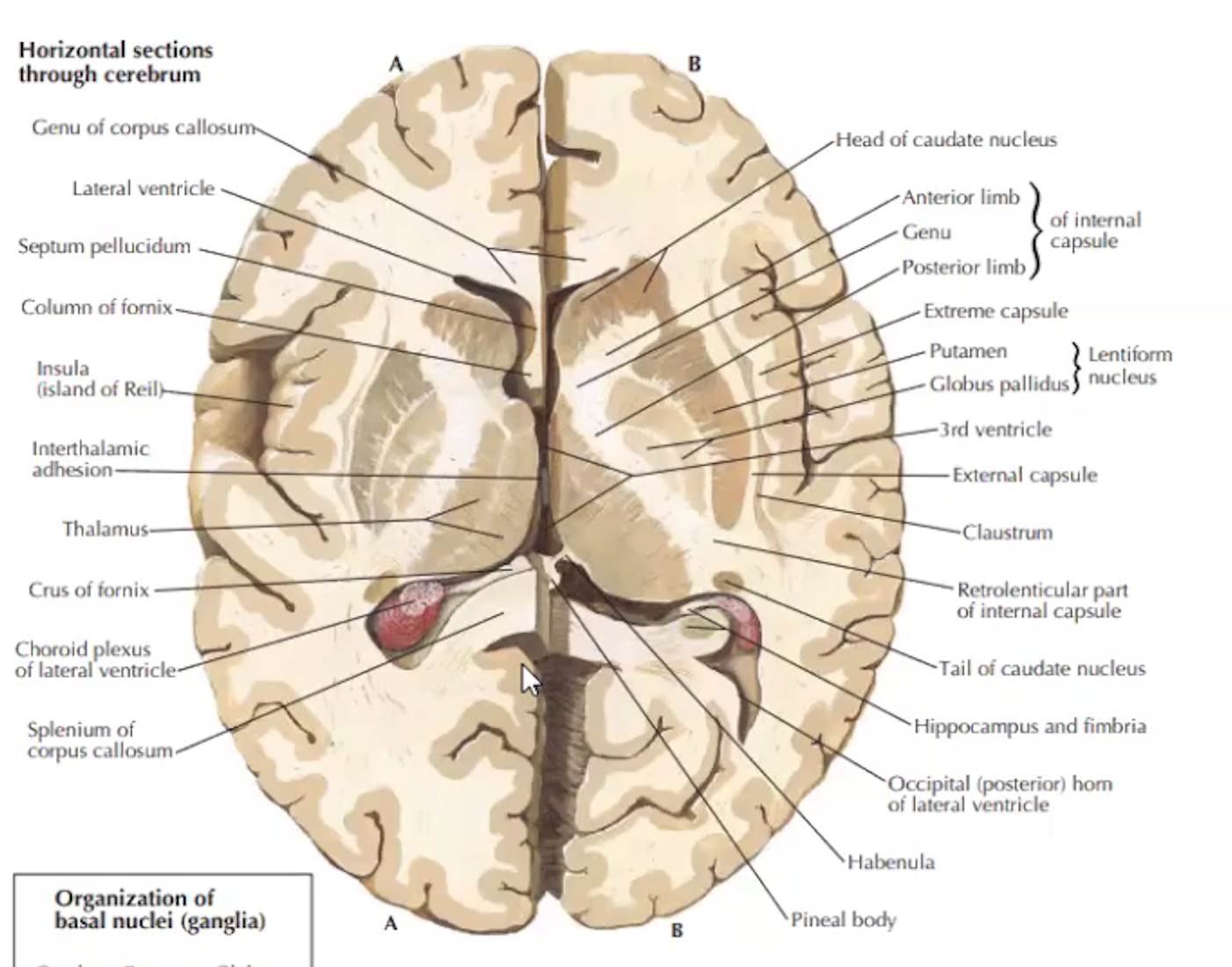
Label horizontal section
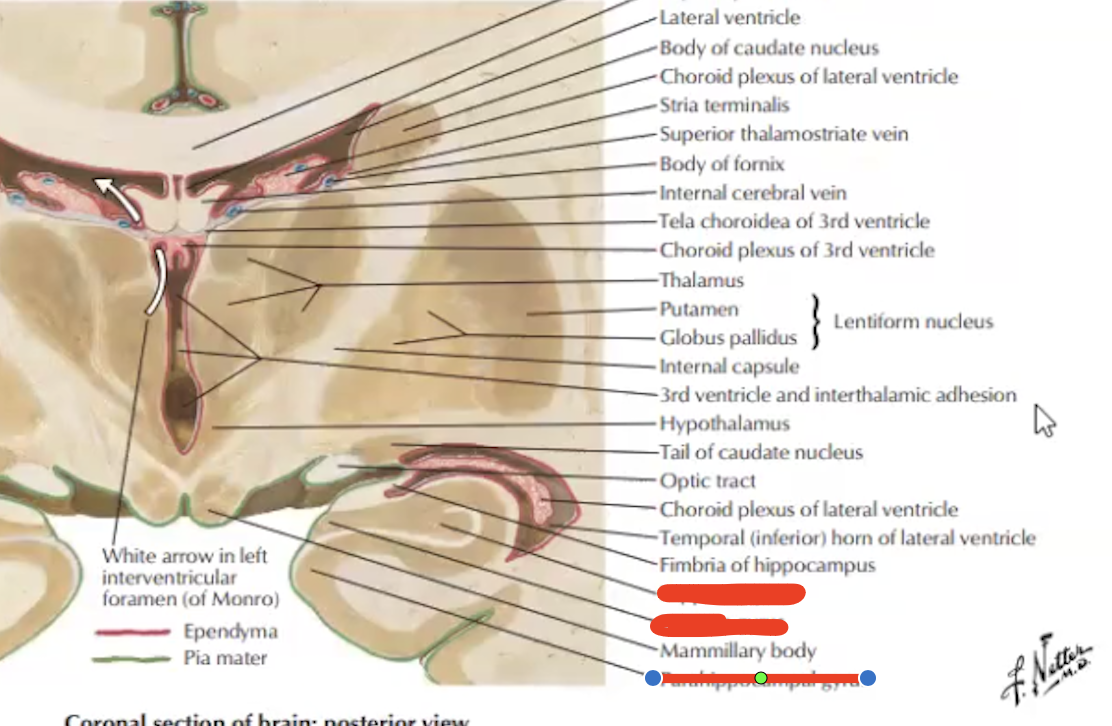
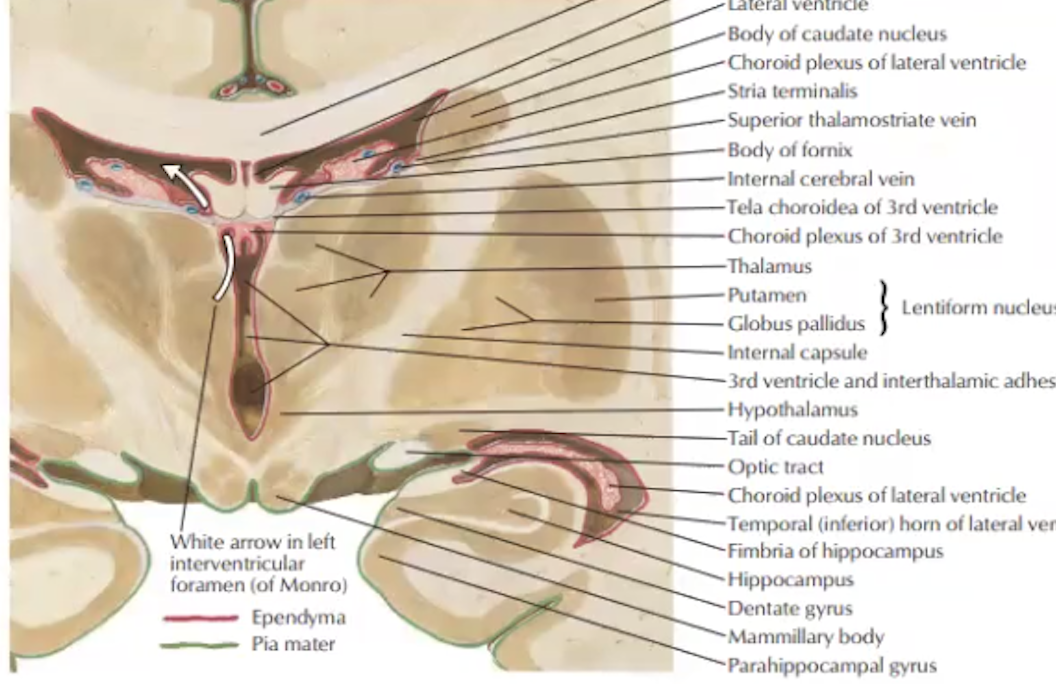
Label
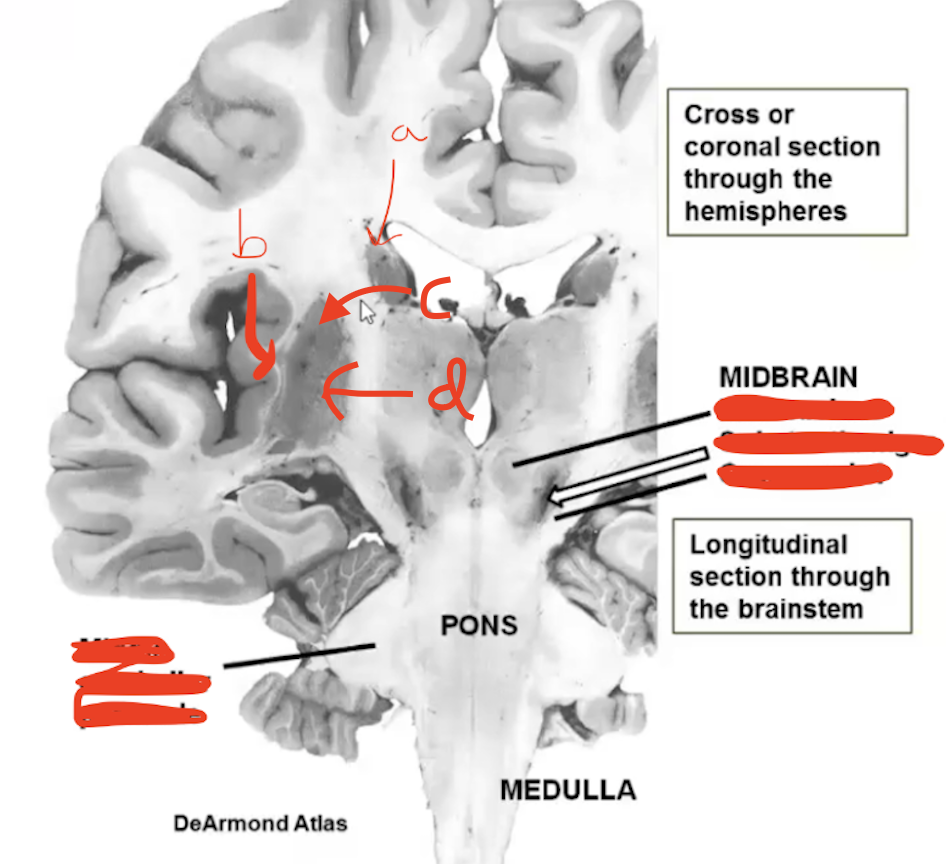
Label
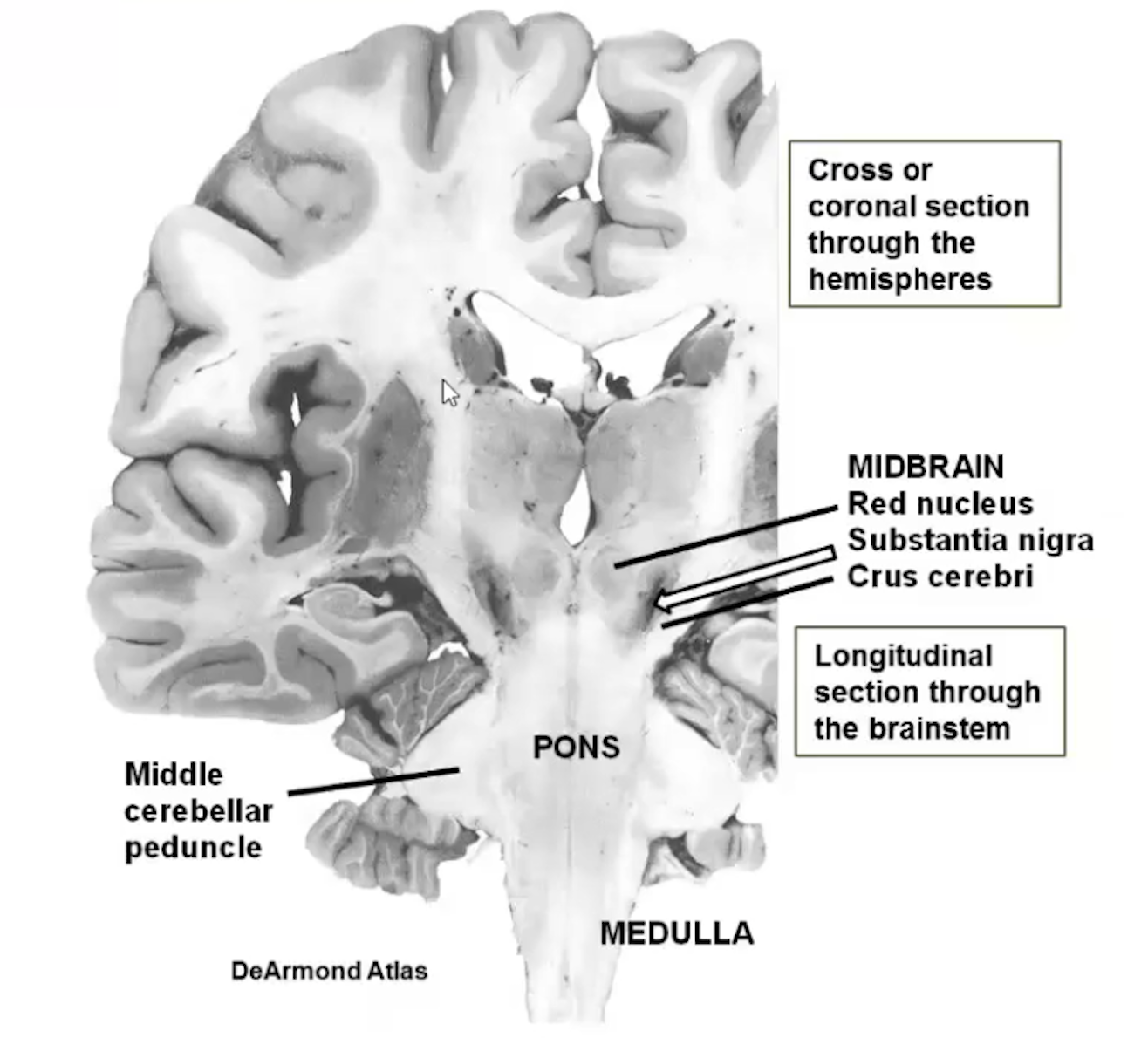
a. Head of caudate nucleus
b. Claustrum
c. Putamen
d. Globus Pallidum
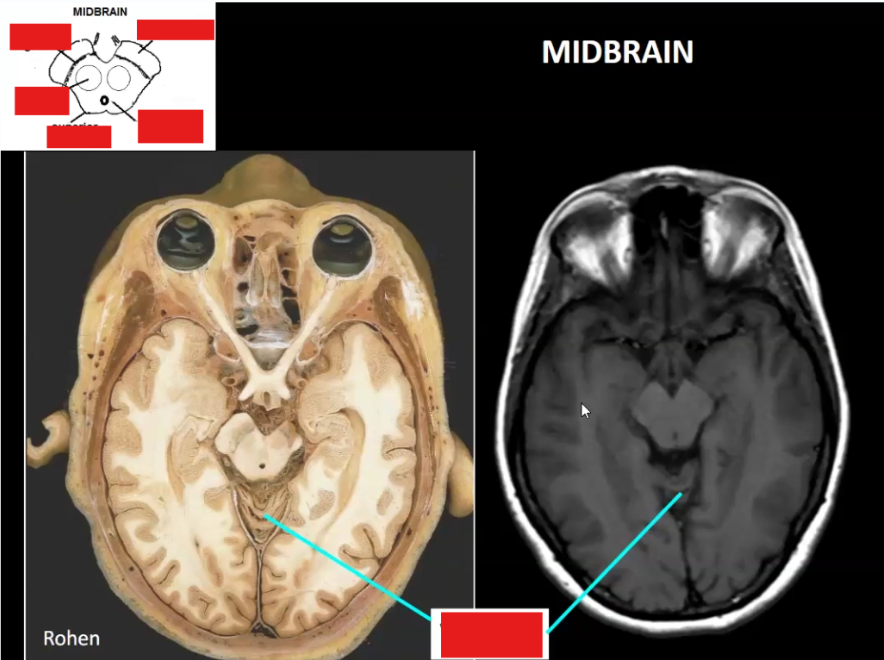
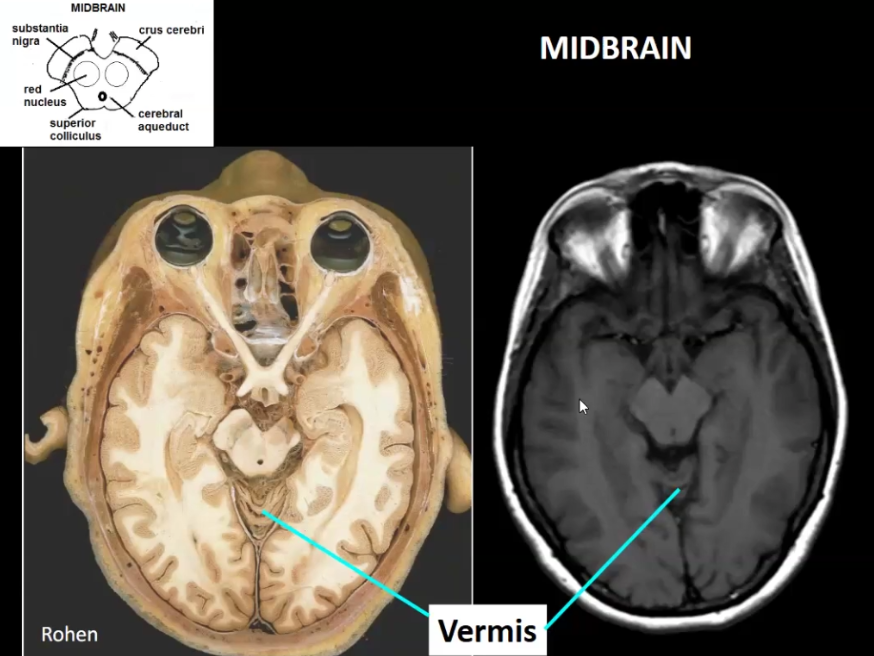
Label
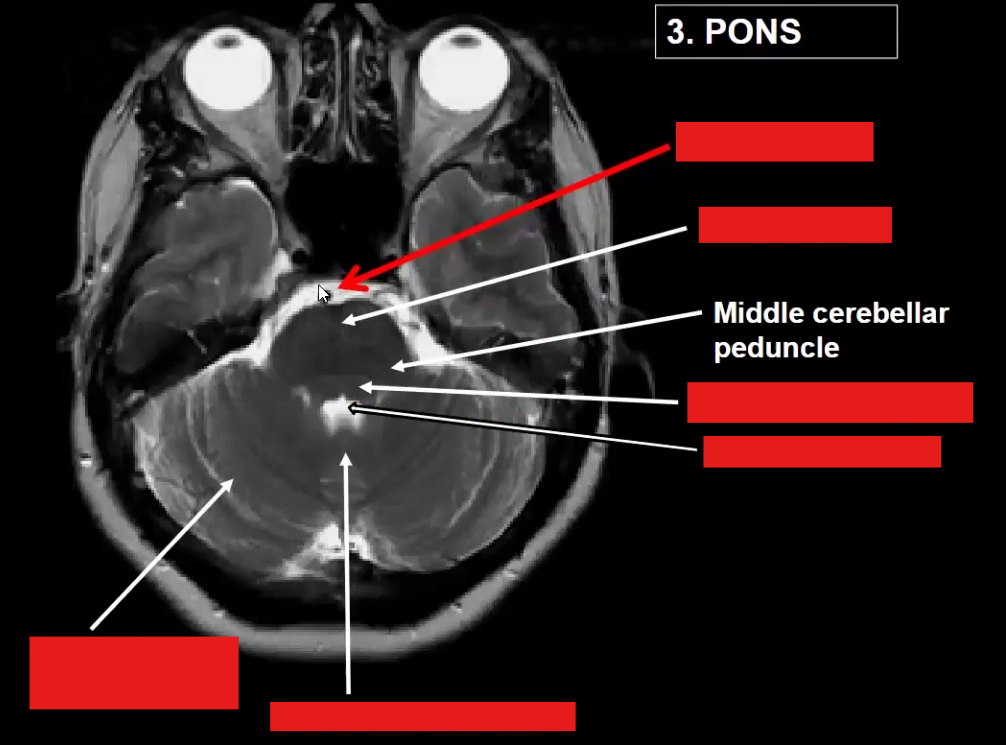
Label
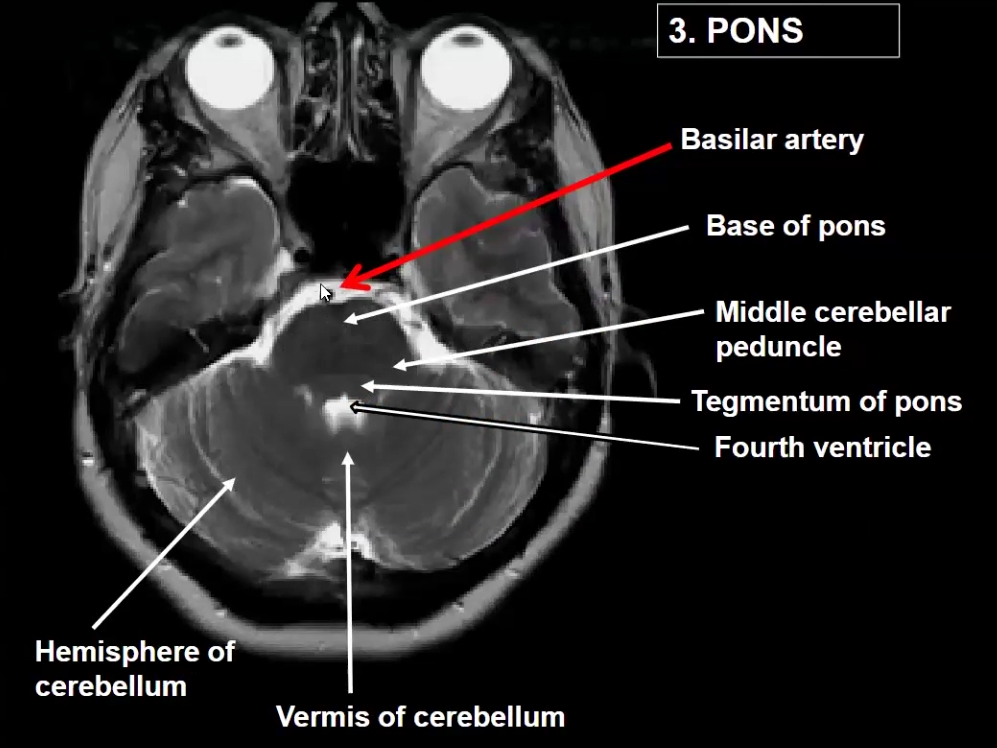
Label
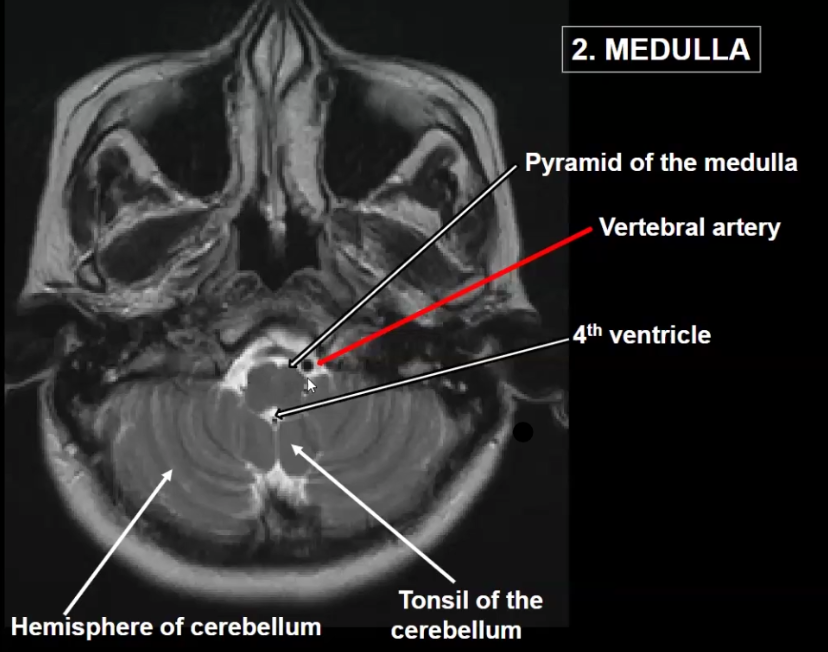
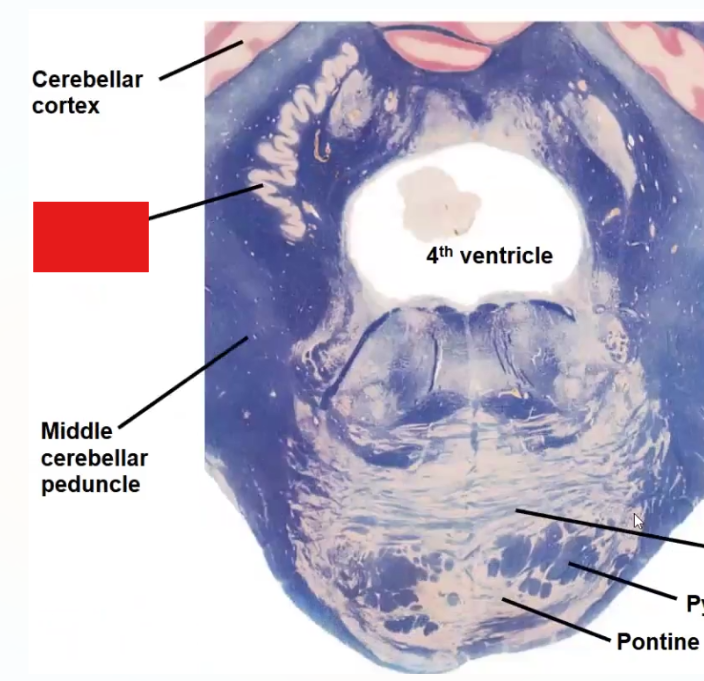
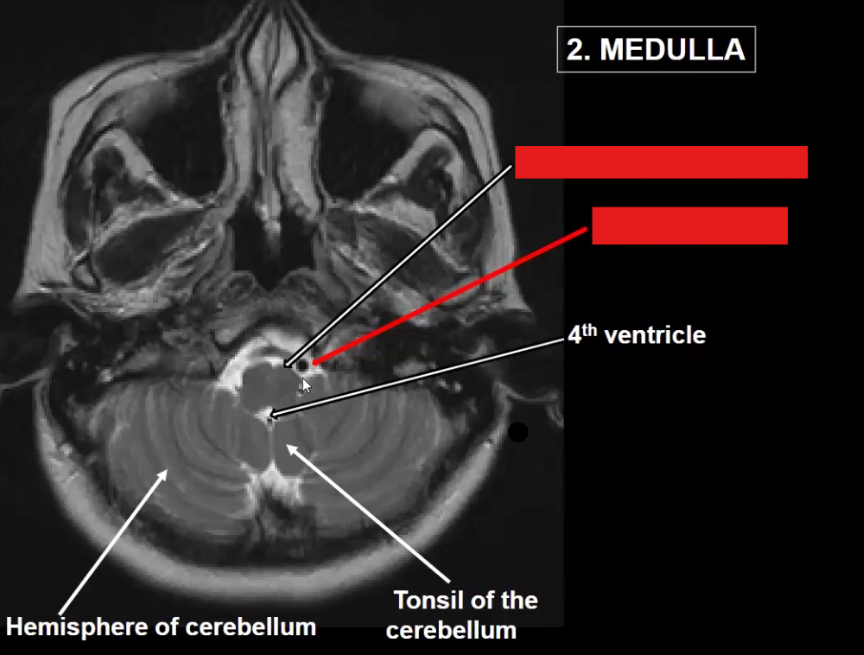
Label