Neuroscience Methods
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
What does electrical activity in the brain indicate?
It is a good index of activity in neurons
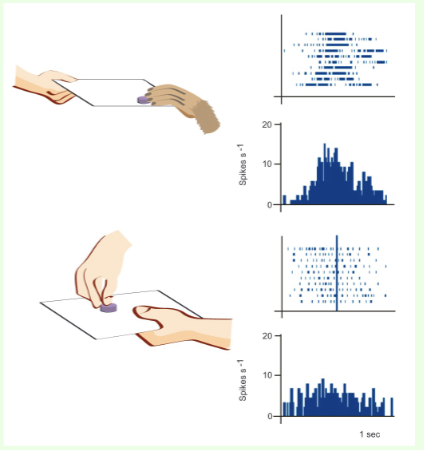
What is a single cell recording and what is it used for?
A technique where a microelectrode is placed close to an individual neuron to record the discharge of action potentials in the cell. Used to identify neurons that respond to particular stimuli
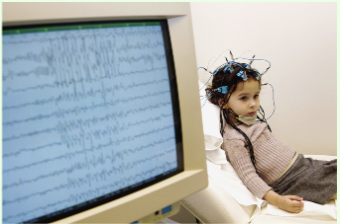
What does an electroencephalogram (EEG) measure?
It provides an amplified recording of waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain's surface
What are ERPs in the context of EEG?
Event-related potentials that are provoked by specific stimuli and have fine temporal resolution but low spatial resolution
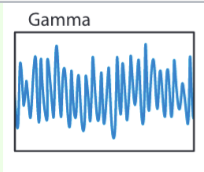
What frequency range are gamma waves?
26-42+ Hz, very high frequency
What state are gamma rays associated with?
conscious state or REM
Where in the brain are gamma rays?
thought to signal active exchange of information between cortical and other areas of the brain
What state are beta waves associated with?
Arousal or alertness
What parts of the brain are beta waves associated with?
most evident in frontal and usually seen on both sides of brain in symmetrical distribution
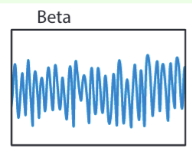
What frequency range are beta waves?
12 to 25, irregular low-amplitude
What is the frequency range for alpha waves?
7.5-13 Hz, synchronous waves
What are alpha waves associated with?
relaxed awake state
What mental states are theta waves associated with?
Transition between sleep and wakefulness, deep meditation, hynagonic state, creativity, and memory retrieval.
What frequency range are theta waves?
3.5-7.5 Hz, synchronous
What kind of frequency do delta waves have?
less than 4 Hz, low frequency, high-amplitude waves
What are delta waves associated with?
occurs during the deepest stages of sleep and loss of consciousness (e.g. coma)
What are “brain maps”?
color maps of brain functioning made from qEEG
What does magnetoencephalography (MEG) measure?
It measures magnetic fields created by the brain's electrical activity by placing up to 300 magnetically sensitive sensors on the scalp

What are the downsides to an MEG?
very expensive, must be carried out in room specially constructed to block all alien magnetic influences including earth’s magnetic field —> currently primarily used in medical diagnosis
What does a computed tomography CT (CAT) scan do?
It combines (with a computer) a series of x-ray photographs from different angles to create a composite representation of a slice through the brain or body
What does a positron emission tomography PET scan visualize?
It shows where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task (visual display of this brain activity) —> radioactive isotope decays into a nonradioactive atom after a minute
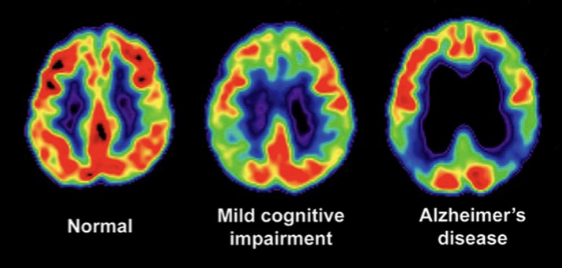
What are the downsides to a PET scan?
may be all sorts of activity going on in the brain that aren’t specific to task participant is performing, ways must be found to filter out background activity (e.g. subtraction paradigm: asking people to look at words flashed on a screen without responding, then asking then to say the words out loud)

How does a magnetic resonance imaging MRI work?
It uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images that distinguish among different types of soft tissue —> allows us to see structures within the brain
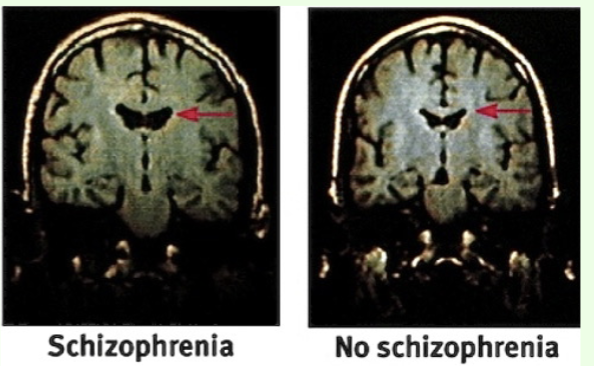
What does functional magnetic resonance imaging fMRI measure?
measures level of activity in different parts of the brain: can detect increases in blood oxygen providing a measure of blood flow and cognitive activity (oxygenated and deoxygenated blood respond differently to the magnetic
field)

What does the BOLD signal refer to?
difference between oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, known as the blood oxygen level dependent contrast used in fMRI
fMRI or PET more used?
fMRI has superseded PET in many domains
What is the goal of voxel-based morphometry (VBM)?
To reveal differences in regional brain volume and tissue concentration across groups using structural MRI scans
event-related fMRI
-able to measure the BOLD signal associated with individual rapidly occurring neural events
-Which areas of brain show increased activation when one is viewing a picture
that is subsequently well remembered vs. one that is simply judged familiar or not remembered at all?
-study done in fMRI scanner
-Parahippocampus and the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex correlated with levels of memory performance for individual events
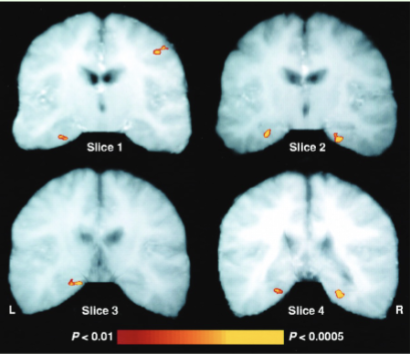
How does VBM work?
-Each brain is superimposed on a template, then the brain image is smoothed
so that each voxel (3 dimensional pixel) represents the average of itself and its neighbors
-image volume then compared across brains at every voxel
What is a famous VBM study?
London taxi cab study, posterior hippocampi of London taxicab drivers were significantly larger than that of controls

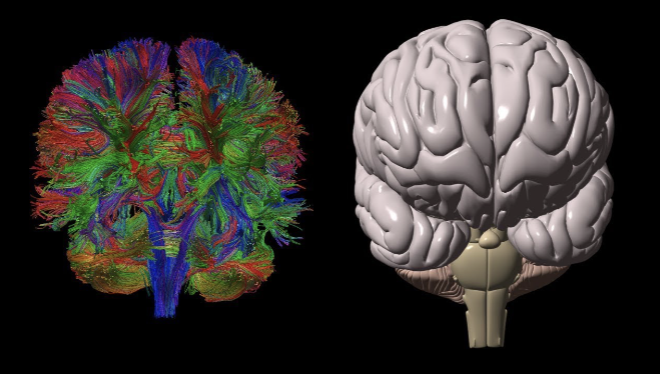
What does diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) analyze?
It measures the hindrance of water diffusion due to local tissue boundaries, special type of MRI
what does fractional anistropy FA do?
-DTI-derived quantitative measure of the directional dependence of water diffusion
-reflects anatomical features of white matter, such as axon caliber, fiber density, and myelination
What does fractional amplitude of low frequency fluctuations (f/ALFF) measure?
It measures spontaneous fluctuations in BOLD-fMRI signal intensity for a given region of the resting brain.
-Electrophysiological studies suggest that low-frequency oscillations arise from
spontaneous neuronal activity
-Grit has been found to be negatively associated with the f/ALFF in the dmPFC
-actual significance unknown

What is functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS)?
A noninvasive optical imaging technique measuring changes in hemoglobin (Hb) concentrations within the brain.
How does fNIRS compare to fMRI?
higher temporal resolution but inferior spatial resolution and penetration depth
Advantages of fNIRS?
robustness to motion, lower cost, small size/portable —> ideal candidate for multimodality studies
-can effortlessly be combined with fMRI, EEG, TMS, tDCS
and many other imaging modalities
What is repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS)?
It sends an intense pulse of magnetic energy through a coil placed on the skull, resulting in electrical firing of neurons beneath scalp (can briefly enhance or disrupt neural activity)
What are the reported effects of rTMS on depression?
It can reduce symptoms of depression in about 30-40% of patients without side effects (when applied to left prefrontal cortex, and sometimes right)
-treatment performed on wide-awake patients for 20-30 min daily, 2-4 weeks
-stimulation may energize left frontal lobe, relatively inactive during depression, cause nerve cells to form new functioning circuits
What else can TMS treat?
also FDA approved for treatment of OCD
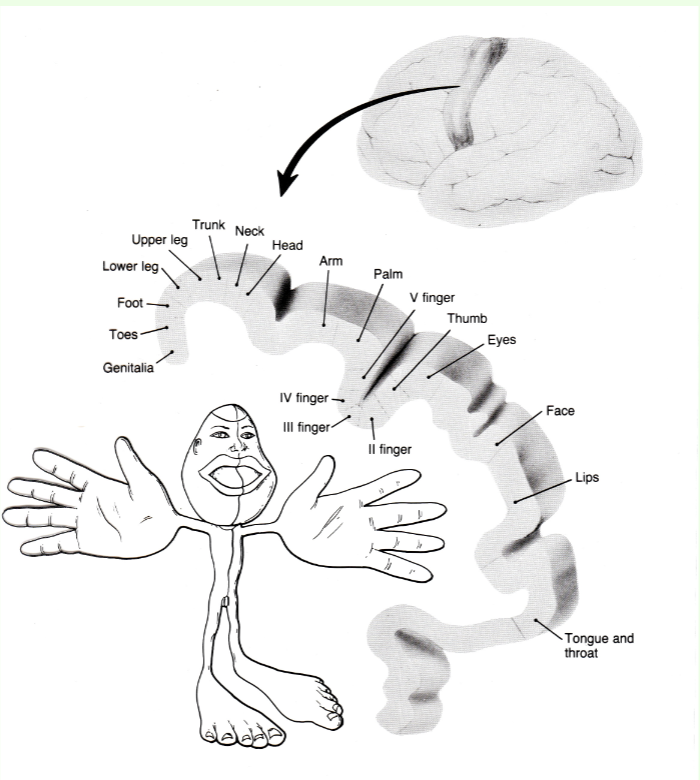
Penfield studies
electrical stimulation of association areas of brain during open brain surgery, patient fully conscious (body mapped onto brain, some limbs bigger because more sensitive
What happens during electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)?
A jolt of electricity (through electrode on no-speech dominant hemisphere of scalp) is applied to trigger a brief seizure while the patient is under anesthesia and paralyzed muscles
-usually 3 treatments per week, 2-4 weeks
How does ECT benefit (on a neurological level) those with depression?
-increases release of norepinephrine or by calming neural centers overactive in depression
-stimulates neurogenesis and new synaptic connections within hippocampus and amygdala
What are advantages to ECT?
-it can relieve symptoms much faster (within a few days) than antidepressants
-70% of ppl with depression that don’t respond to other treatments find relief
-credited with saving many from suicide
-ECT is sometimes used in interim period before antidepressant drugs become effective in suicidal patients (may be court-mandated in certain cases)
What are some disadvantages of ECT?
Potential for brain damage in prolonged and excessive use —>long-lasting memory impairments
-high relapse rates.
What is Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for depression?
-weak current is applied to the scalp on the left side of dorsolateral prefrontal
-safer than ECT
How does deep brain stimulation work for depression?
neurosurgical procedure, places a neurostimulator (brain pacemaker) that sends electrical impulses (through implanted electrodes) to specific targets in the brain.
What does optogenetics enable researchers to do?
It allows control of neuron activity (can activate neurons by particular wavelength of light) using light-sensitive opsin proteins or can cause neuron to produce flash of light of particular wavelength when activated
-can be used for precise identification of specific neurons and neural networks
-can be used in future for treatment of depression, chronic pain, seizures, restoration of vision to blind
How does optogenetics work?
-insert opsin genes into neurons
-causes neuron to manufacture light-sensitive opsin proteins and incorporate them into the membrane
What was demonstrated using optogenetics in mice?
Researchers could activate specific neurons to induce memories or perceptions of environmental stimuli.
-produced hallucinations in mice
-mice trained to lick pipe if they saw vertical stripe
-identified neurons in visual cortex that switched on in response to vertical shapes
-mice in darkness, vertical stripes neurons switched on with optogenetics
-mice licked pipe!
-neuroscientists tagged neurons associated with certain memory (fear of stove)
-artificially induced neurons to fire to make new associations between events and environments with no ties to reality (fear of park)
another example of optogenetics study
-changed songs that young zebra finches sing by implanting new memories in their brains
What is a challenge when interpreting neuroimaging data?
Noise in the system, especially with large voxel sizes leading to distorted signals.
Everyone’s brain is slightly different, distortions can occur when data are normalized to allow comparison across participants
-smaller voxel —>higher spatial resolution but lower signal strength, often necessary to increase the voxel size to capture small fluctuations in
the BOLD signal
-increases the range of different types of brain tissue occurring in each voxel, distorting signal
How does EEG measure the electrical activity of populations of neurons?
electrodes attached to skull, wired up to a computer. each electrode sensitive to electrical activity of thousands of neurons (closest neurons make largest contribution). coordinated activity of neural populations seen as waves at different frequencies
why are EEGs useful?
useful in clinal contexts for diagnosing epilepsy and tumors, most widespread and least expensive technique for studying electrical activity of a large population of neurons