chemistry - rates of reaction & energy changes: rates of reaction (7.1 - 7.8)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
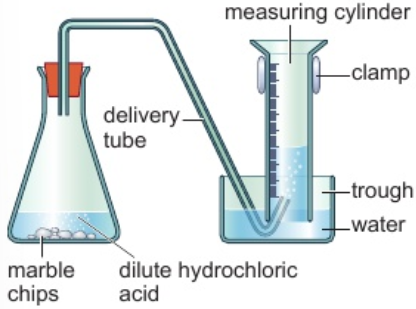
7.1 core practical: effects of changing conditions of reaction on rates of chemical reactions - measure production of gas (reaction between hydrochloric acid & marble chips)
set up apparatus shown in diagram
measure 40cm3 dilute hydrochloric acid into conical flask
add 5g small marble chips to flask
immediately stopper flask & start stop clock
record total volume of gas produced every 30 secs until reaction finished
repeat experiment using 5g larger marble chips
smaller chips = larger surface area = faster rate of reaction
7.1 core practical: effects of changing conditions of reaction on rates of chemical reactions - observe colour change (reaction between sodium thiosulfate & hydrochloric acid)
place 50cm3 sodium thiosulfate into 300cm3 conical flask
measure 5cm3 dilute hydrochloric acid in test tube
clamp conical flask in water bath at certain temp. & record temp.
place test tube in rack in same water bath
after 5 mins remove flask & place on white piece of paper marked with cross
add acid to thiosulfate & start stop clock
look down from above, stop clock when cross disappears
record this time & record final temp. of mixture
repeat at 3 or 4 other temps. between 20°C & 50°C
higher temp. = more frequent successful collisions = faster rate of reaction
7.2 practical methods for determining rate of given reaction
measure changes in:
conc.
mass/volume of reactants/products
e.g. measure mass of reactant used if product is gas: do experiment on weighing scales, measure how much mass lost
e.g. measure volume of product formed if product is gas: collect gas produced in gas syringe, shows volume gas produced
rate of reaction formulas
amount of reactant used/time
amount of product formed/time
units: g/s; cm3/s
7.3 what do particles have to do for reaction to occur & why?
collide with enough energy
successful collision - energy helps break bonds, atoms rearranged to make products
activation energy
minimum amount of energy needed by colliding particles for reaction to occur
7.3 frequency &/or energy of collisions effect on rate of reaction & why
frequency &/or energy of collisions increased = rate of reaction increased
more collisions/more particles with activation energy required = more reactions
7.4 change in temperature effect on rate of reaction
temperature increased = rate of reaction increased
reactant particles speed up & have more energy = more frequent collisions, more particles have enough energy to react when collide
7.4 change in concentration effect on rate of reaction
concentration of solution increased = rate of reaction increased
more reacting particles in same volume = more frequent collisions
7.4 change in surface area:volume of solid effect on rate of reaction
surface area:volume ratio of solid increased = rate of reaction increased
decrease size of solid pieces, keep total volume of solid same
more surface area for collisions to occur = more frequent collisions
7.4 change in pressure (reactions involving gases) effect on rate of reaction
pressure of gases increased = rate of reaction increased
reactant particles closer together = more frequent collisions
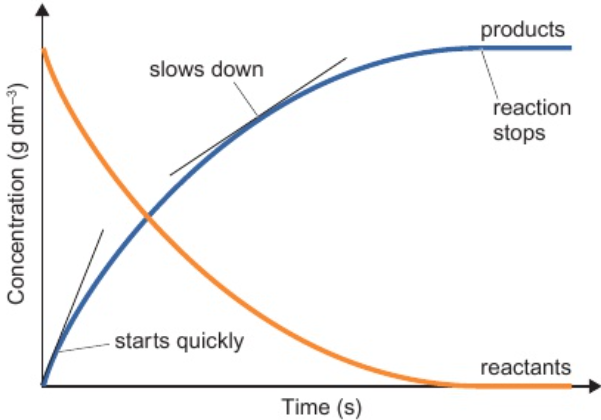
7.5 graphs of mass/volume/concentration of reactant/ product against time
gradient indicates rate of reaction: steeper gradient = faster rate of reaction
7.6 catalysts
substances that speed up rate of reaction
don’t alter products of reaction
not chemically changed themselves
in mass at end of reaction
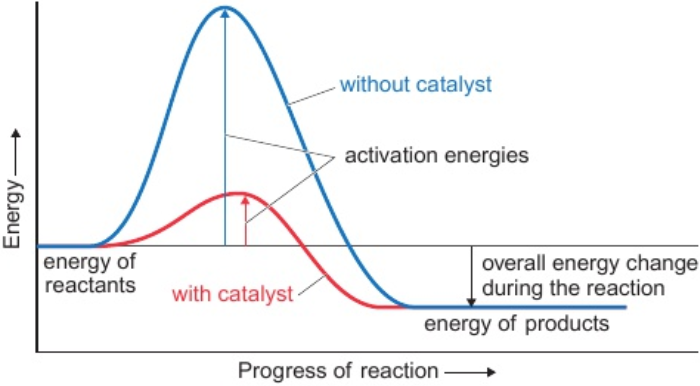
7.7 adding catalyst effect on rate of reaction & why (activation energy)
increases rate of reaction
provides alternative reaction route - requires less activation energy
7.8 what are enzymes? (b... c...)
biological catalysts
7.8 what are enzymes used in production of?
alcoholic drinks