EL1 - Lecture 3 Phonological processes
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
By Vzu Nguyen
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
the study of sound systems in languages | âm vị học | _ examines how sounds function in a particular language.
phonology [n.] /fəˈnɑːlədʒi/
related to the system of sounds in a language | thuộc về âm vị học | The _ rules of English determine how sounds change in different contexts.
phonological [adj.] /ˌfəʊnəˈlɑːdʒɪkəl/
related to the physical production of speech sounds | thuộc về ngữ âm | The International _ Alphabet (IPA) represents speech sounds.
phonetic [adj.] /fəˈnetɪk/
the study of speech sounds and their physical properties | ngữ âm học | _ focuses on how sounds are produced and perceived.
phonetics [n.] /fəˈnetɪks/
related to phonemes, the smallest units of sound that distinguish meaning | thuộc về âm vị | English has a _ contrast between /p/ and /b/.
phonemic [adj.] /fəˈniːmɪk/
the smallest unit of sound that can change meaning in a language | âm vị | The sounds /p/ and /b/ are different _ in English.
phoneme [n.] /ˈfəʊniːm/
a pair of words that differ by only one sound | cặp tối thiểu | "Bit" and "Pit" form a _ in English.
minimal pair [n.] /ˌmɪnɪməl ˈpɛr/
a variation of a phoneme that does not change meaning | tha âm | The English /t/ has different _ in "top" and "stop."
allophone [n.] /ˈæləfəʊn/
a different form of a linguistic element | biến thể | The flap /ɾ/ is a _ of /t/ and /d/ in American English.
variant [n.] /ˈvɛriənt/
marks added to letters to indicate pronunciation details | dấu phụ | The tilde (~) in Spanish ñ is an example of _.
diacritics [n.] /ˌdaɪəˈkrɪtɪks/
the process of producing a sound with airflow through the nose | sự mũi hóa | In French, vowels before "m" or "n" often undergo _.
nasalisation [n.] /ˌneɪzələˈzeɪʃən/
the process of pronouncing a normally voiced sound without vocal cord vibration | vô thanh hóa | The final /d/ in "bad" undergoes _ in rapid speech.
devoicing [n.] /dɪˈvɔɪsɪŋ/
capable of forming a syllable | thuộc về âm tiết | In English, the /n/ in "button" is _.
syllabic [adj.] /sɪˈlæbɪk/
a phonological process where a sound is produced further forward in the mouth | tiền vị hóa | In some accents, "goose" undergoes _ to sound more like "geese."
fronting [n.] /ˈfrʌntɪŋ/
a burst of air released when pronouncing certain consonants | hơi bật | The English /p/ in "pin" is pronounced with _.
aspiration [n.] /ˌæspəˈreɪʃən/
the release of a stop consonant through the nose | phát âm qua mũi | The /d/ in "hidden" has a _ in rapid speech.
nasal release [n.] /ˈneɪzl rɪˈliːs/
a phonetic process where a sound is articulated further back | hậu vị hóa | In some dialects, /s/ is pronounced with _.
retracting [n.] /rɪˈtræktɪŋ/
a stop consonant pronounced without an audible release | không nhả hơi | The /p/ in "stop" is often _ in casual speech.
unreleased [adj.] /ʌnˈriːliːst/
the release of a stop consonant through the sides of the tongue | phát âm bên | The /d/ in "paddle" can have a _.
lateral release [n.] /ˈlætərəl rɪˈliːs/
the process of producing a sound with airflow through the nose | sự mũi hóa | In French, vowels before "m" or "n" often undergo _.
nasalization [n.] /ˌneɪzələˈzeɪʃən/
the articulation of a consonant with the tongue against the teeth | xát hóa răng | In some accents, /t/ and /d/ undergo _.
dentalization [n.] /ˌdɛntələˈzeɪʃən/
the duration of a speech sound | độ dài âm | In some languages, vowel _ distinguishes word meaning.
length [n.] /leŋθ/
the process of articulating a sound with the back of the tongue raised toward the velum | hóa ngạc mềm | The English "dark L" in "pull" is an example of _.
velarization [n.] /ˌviːlərɪˈzeɪʃən/
the process of rounding the lips while articulating a sound | tròn môi | The English /k/ in "queen" undergoes _.
labialization [n.] /ˌleɪbiəlaɪˈzeɪʃən/
Phonemes
• A phoneme is the _______ ________ ___ ________ which can __________ two words.
• This is the smallest amount by which these two words could differ and still remain distinct forms. Any smaller subdivision would be impossible because English doesn’t subdivide /p/ or /b/. Therefore, /p/ and /b/ are considered two phonemes.
smallest segment of sound, distinguish
• Pair of words such as ‘pit’ and ‘bit’, ‘pit’ and ‘pet’, ‘back’ and ‘bag’ which differ by only one phoneme in identical environment are known as ________ ______.
• One way to ________ ____ _________ of any language is to look for minimal pairs.
minimal pairs, identify the phonemes
• There are ____ phonemes in English: _____ consonants and ____ vowels.
• Each phoneme is meaningless in isolation. It becomes __________ only when it is _______ ____ other phonemes.
• Problem:
– A letter can be represented by _______ _______.
– A phoneme can be represented by _________ letters or ___________ of letters.
=> Phonemes form a set of abstract units that can be used for noting down the sound of a language systemmatically and unambiguously.
44, 24, 20, meaningful, combined with, different sounds, different, combinations
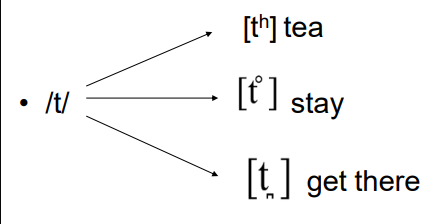
• Allophones are the ________ ___ ________ that occur in speech.
• Reasons: the way a phoneme is pronounced is conditioned by the ________ _______ it or by its _________ in the word.
For example: /t/
variants of phonemes, sounds around, position
Concept | Explanation | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Phonemes | Phonemes are _______-___________ sounds, and substituting one for another results in a word with a different meaning. | /p/ vs. /b/: "pat" vs. "bat" (changing the phoneme changes the meaning of the word). |
Allophones | Allophones are variations of a single phoneme, and substituting them _____ ____ _________ the meaning, only the pronunciation. | /p/ in "spin" (unaspirated) vs. /p/ in "pin" (aspirated) – both are the same phoneme /p/ but pronounced differently. |
meaning-distinguishing, does not change
Concept | Explanation | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Phonemic Symbols | These symbols represent __________, and the number of phonemic symbols matches the number of phonemes in the language. | In RP (BBC English), there are 44 phonemic symbols. Example: /p/, /b/, /t/, /d/, /k/, /g/ |
Phonetic Symbols | These symbols represent _________ and are used to give an accurate label for an allophone or to depict sounds with greater precision, often using diacritics. | Example: [pʰ] (aspirated /p/) vs. [p] (unaspirated /p/) or [ɾ] for the tapped /r/ sound in "butter" in some accents. |
phonemes, allophones
Concept | Explanation | Examples |
|---|---|---|
________/ Broad Transcription | Represents each phoneme with one phonemic symbol, capturing only the basic sounds of the language without extra detail. | /kæt/ for "cat" (no distinction between aspirated/unaspirated sounds or vowel quality). |
_________/ Narrow Transcription | Provides detailed information about the exact quality of sounds, including aspiration, length, nasalization, and other phonetic features using diacritics. | [kʰæt] for "cat" (shows aspiration on /k/), [kæn] for "can" (shows nasalization of the vowel). |
Phonemic, Phonetic