2.1 homeostasis, hormones
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
define homeostasis
the maintenance of a constant internal environment
list the basic principles (steps) of homeostasis
change in internal environment (stimulus) → receptor + control centre → corrective mechanism → negative feedback
define and describe a hormone
a chemical substance, produced by a gland, carried by the blood, which alters the activity of one or more specific target organs.
explain what is meant by an endocrine gland
they are ductless glands that transport their secretions through the bloodstream
the islets of Langerhans pancreas is an endocrine gland which secretes insulin and glucagon
explain the importance of maintaining a constant blood glucose level
for tissue respiration (energy)
explain how the blood glucose concentration is regulated by insulin as a homeostatic mechanism
Stimulus: BGC increases
Receptor + control centre: Islets of Langerhans detect stimulus
Hormone secretion (effector): Islets of Langerhans (β-cells) secrete more insulin into the bloodstream
Corrective mechanism:
permeability of cell surface membrane to glucose increases, more glucose is absorbed by the cells
respiration rate of cells increases
liver and muscle cells absorb more glucose in the same way and converts excess glucose to glycogen for storage
BGC decreases
explain how the blood glucose concentration is regulated by glucagon as a homeostatic mechanism
Stimulus: BGC decreases
Receptor + control centre: Islets of Langerhans detect stimulus
Hormone secretion (effector): Islets of Langerhans (α-cells) secrete more glucagon into the bloodstream
Corrective mechanism:
liver converts stored glycogen to glucose
glucose enters the bloodstream
BGC increases
describe type 2 diabetes mellitus
target cells in the body do not respond well to insulin (body’s resistance to insulin) / insufficient production of insulin → persistently higher than normal BGC
symptoms:
slow/difficult healing of wounds
thirst
weight loss
frequent urinatino
glucose in urine
persistently high BGC
identify the risk factors of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Obesity/overweight
Age
Family history (diabetes can be inherited)
Unhealthy blood lipid levels
Sedentary lifestyle
identify ways to manage type 2 diabetes mellitus
maintain healthy body weight
avoid being inactive for long time
engage in more active physical activities
eat healthily:
consume food low in calories and high in fibre (eg fruits & veg)
which is not a function of the liver?
conversion of glucose to glycogen
storage of glycogen
secretion of insulin
synthesis of proteins from amino acids
secretion of insulin (pancreas)
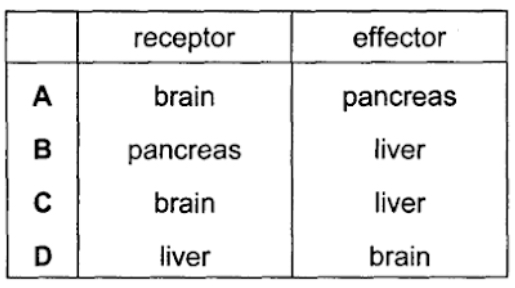
in the control of blood glucose level, which organs are the receptor and effector?
B) receptor: pancreas | effector: liver
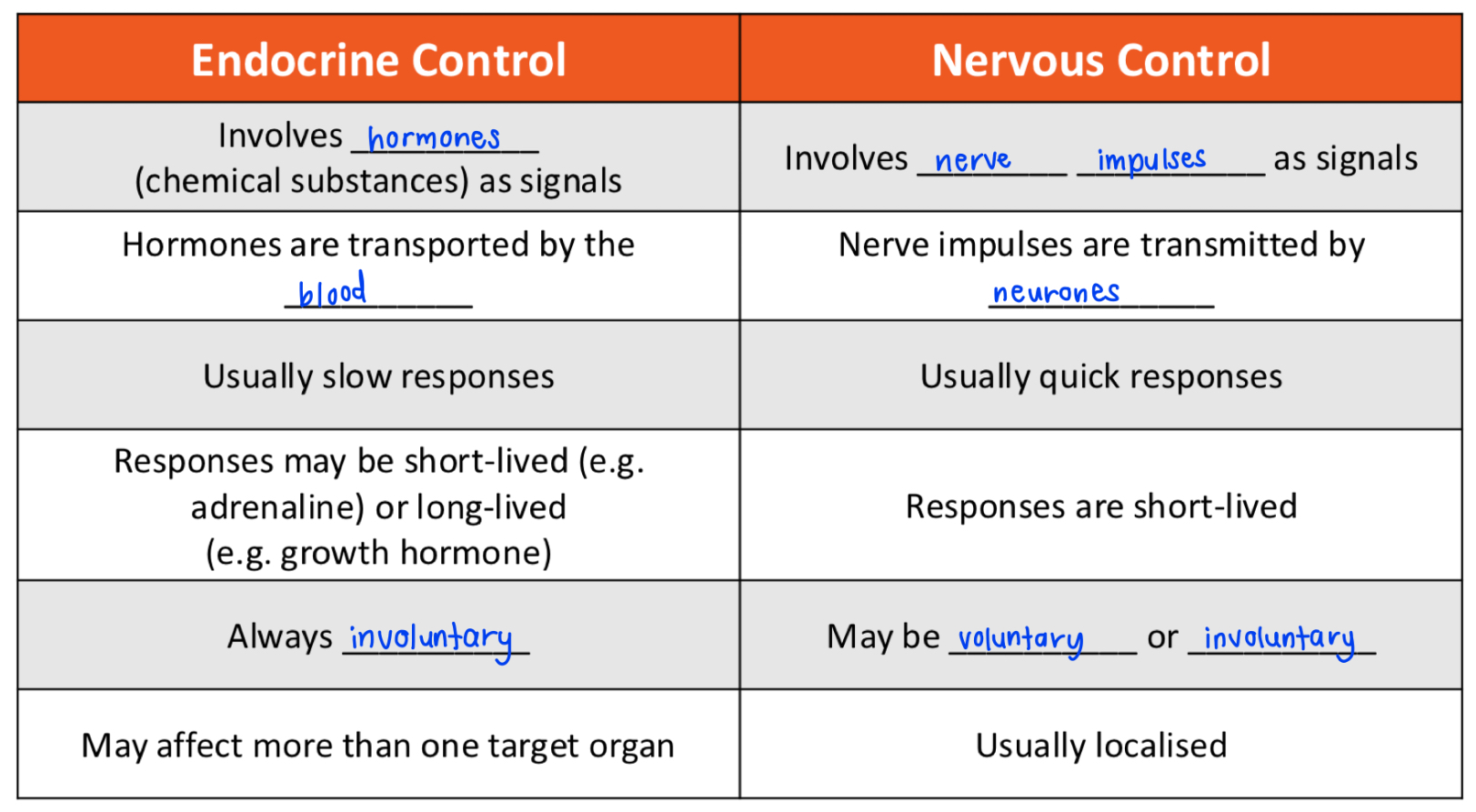
compare and contrast the nervous and endocrine systems (control) — (also under nervous system)
endocrine involves hormones as signals; nervous involves nerve impulses as signals
endocrine — hormones are transported by blood; nervous — nerve impulses are transmitted by neurones
endocrine — usually slow responses; nervous — usually quick responses
endocrine — always involuntary; nervous — may be voluntary / involuntary
endocrine — may affect more than one target organ; nervous — usually localised