Urinalysis and Body Fluids MLS Review- | Quizlet
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
161 Terms
Urine Specimens- Random
use: routine urinalysis (UA)
collection: anytime
other: not ideal since urine may be dilute or contaminated
Urine Specimens- First am
use: Routine UA
collection: upon awakening
other: best for screening- most concentrated
Urine Specimens- 2 hr postprandial
use: Diabetes mellitus monitoring
collection: 2hr after eating
other: best for detecting glycosuria
Urine Specimens- 24-hr
use: Quantitative chemistry tests
collection: Discard 1st void on day 1 & note time.
Collect all urine for next 24 hr, including first void at same time on day 2
other: Improper collection is common source of error. Refrigerate or keep on ice. Preservatives required for some tests.
Urine Specimens- Clean Catch
use: routine, culture
collection: Cleanse external genitalia & collect midstream in sterile cup
other: less contamination. do culture before UA
Urine Specimens- Catheterized
use: culture
collection: catheter inserted into urethra
other: avoids contamination
Urine Specimens- Suprapubic aspiration
Use: culture
collection: needle inserted through abdomen into bladder
other: avoids contamination
Normal Daily Urine Volume
600ml - 2000ml (average 1,200-1,500mL)
Normal Day to Night ratio (urine)
2:1-3:1
exocrine function of kidney
elimination of metabolic waste products
Diuresis
increase urine production
Polyuria
excessive production of urine
Adult: >2,500mL daily
Children: 2.5-3mL/kg/day
Oliguria
Decreased urine output
Adult: <400mL/day
Children: <0.5mL/kg/hr
Infants: <1mL/kg/hr
Anuria
no urine production
Normal Urine color
yellow due to urochrome
Dilute urine color
colorless, pale yellow
Concentrated Urine color
Dark yellow, amber
Bilirubin urine color
Amber, orange, yellow-green; yellow foam on shaking
Urobilin Urine Color
Amber, orange; no yellow foam on shaking
Homogentisic acid
Normal on voiding; brown or black on standing
Myoglobin
Red; brown on standing
Blood/hemoglobin
pink or red when fresh; brown on standing
Porphyrin
port-wine stains
Drug medications, food
green, blue, red, orange
Pseudomonas infection (urine color)
green, blue-green
Changes in Unpreserved Urine at Room Temperature >2 hr: turbidity
increases due to multiplication of bacteria, precipitation of amorphous crystals
Changes in Unpreserved Urine at Room Temperature >2 hr: pH
increases due to the conversion of urea to ammonia by bacteria
Changes in Unpreserved Urine at Room Temperature >2 hr: Glucose
decreases due to the metabolism by bacteria
Changes in Unpreserved Urine at Room Temperature >2 hr: ketones
decreases due to volatilization of acetone, breakdown of acetoacetate by bacteria
Changes in Unpreserved Urine at Room Temperature >2 hr: Bilirubin
decreases due to the oxidation of biliverdin
Changes in Unpreserved Urine at Room Temperature >2 hr: Urobilinogen
decrease due to oxidation of urobilin
Changes in Unpreserved Urine at Room Temperature >2 hr: WBCs, RBCS, Casts
decreases due to lysis in dilute or alkaline urine
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: pH
(normal, principle and significance)
normal range: 4.5-8
principle: double indicator system
Significance: acid-base balance, management of urinary tract infection (UTI)/renal calculi
protein/meat diet creates what type of pH
acidic pH
vegetarian diet create what type of pH
alkaline
pH 9 explains what
improperly preserved specimen
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Protein (normal, principal, significance)
normal range: negative-trace
principle: protein error of indicator
significance: possible renal disease (Kidney Disease); nephrotic syndrome
which protein is most sensitive to the reagent strip
albumin
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Glucose (normal, principle, significance)
normal range: negative
principle: Double sequential enzyme
significance: possible diabetes mellitus
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Ketones (normal, principle, significance)
normal: negative
principle: sodium nitroprusside rxn
significance: increase fat metabolism (uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, vomiting, starvation, low carb diet, strenuous exercise)
Ketones reagent strip is most sensitive to
acetoacetic acid
Ketones reagent strip is less sensitive to
acetone
ketones reagent strip doesn't react with
beta-hydoxybutyric acid
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Blood (normal, principle, significance)
normal: negative
principle: Pseudoperoxidase activity of hgb
significance: Hematuria, hemoglobinuria, myoglobinuria
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Bilirubin (normal, principle, significance)
normal: negative
principle: Diazo reaction
significance: Liver disease, biliary obstruction
what is the only type of bilirubin excreted in the urine
only conjugated bilirubin
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Urobilinogen (normal, principle, significance)
normal: 0.2-1
principle: Ehrlich's aldehyde rxn or diazo rxn
significance: Liver disease, hemolytic disorders
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Nitrite (normal, principle, significance)
normal: negative
principle: Greiss reaction
significance: UTI
some bacteria reduce nitrates to
nitrites (1st am specimen best)
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Leukocyte estrase (normal, principle, significance)
normal: negtaive
principle: Leukocyte esterase rxn
significance: UTI
Chemical Urinalysis by Reagent Strip: Specific Gravity (normal, principle, significance)
normal: Random specimen: 1.003-1.030
principle: pKa change of polyelectrolyte
significance: Indication of kidney's concentrating ability & state of hydration. increase in diabetes mellitus due to glucose. decrease in diabetes insipidus due to decrease ADH
Increase/False Positive w/ pH
improperly preserved specimen
Decrease/false negative w/ pH
acid runover from protein square
increase/false positive w/ protein
highly buffered alkaline urine, prolonged dippin, contaminated container, increased SG
decrease/false negative w/ protein
proteins other than albumin
increase/false positives w/ glucose
contrition w/ peroxide or bleach
decrease/false negative w/ glucose
unpreserved specimen
increase/false positive w/ ketones
red pigments, dyes and some meds
decrease/false negative w/ ketones
improper storage. Acetone is volatile. Bacteria break down acetoacetic acid
What will cause an increased/false positive w/ blood?
Menstruation, oxidizing agens, bacterial peroxidase, ascorbic acid
decreased/false negative w/ blood
unmixed specimen
what will cause an increased/false positive with Bilirubin?
highly pigmented urine
decreased/false negative w/ bilirubin
exposure to light.
increased/false positive w/ urobilinogen
highly pigmented urine
decreased/false negative w/ urobilinogen
improperly preserved specimen
what will casue increased/false positive with nitrite?
Highly pigmented urine, improperly preserved specimen (contaminating bacteria produce nitrites)
decreased/false negative w/ nitrite
non-nitrate reducing bacteria
what will cause an increased/false positive with leukocyte esterase?
Highly pigmented urine, vaginal discharge
decreased/false negative w/ leukocyte esterase
increase glucose, protein, ascorbic acid and SG; antibiotics; reading too soon
increased/false positive w/ SG
increased SG
decreased/false negative w/ SG
Alkaline urine
Microalbumin test
detects albumin in low concentrations (not detected by most urine dipsticks- which is why its done on chemistry instrument)
Sulfosalicylic acid (SSA) test
detects all proteins, including Bence Jones proteins
Bence Jone Proteins
are rarely found in urine. If they are, it is usually associated with multiple myeloma. An abnormal result may also be due to: An abnormal buildup of proteins in tissues and organs (amyloidosis)
Clinitest
detects reducing substances (method: copper reduction)
Acetest
detects ketones (method: Sodium nitroprusside reaction)
Ictotest
detects bilirubin (diazo reaction)
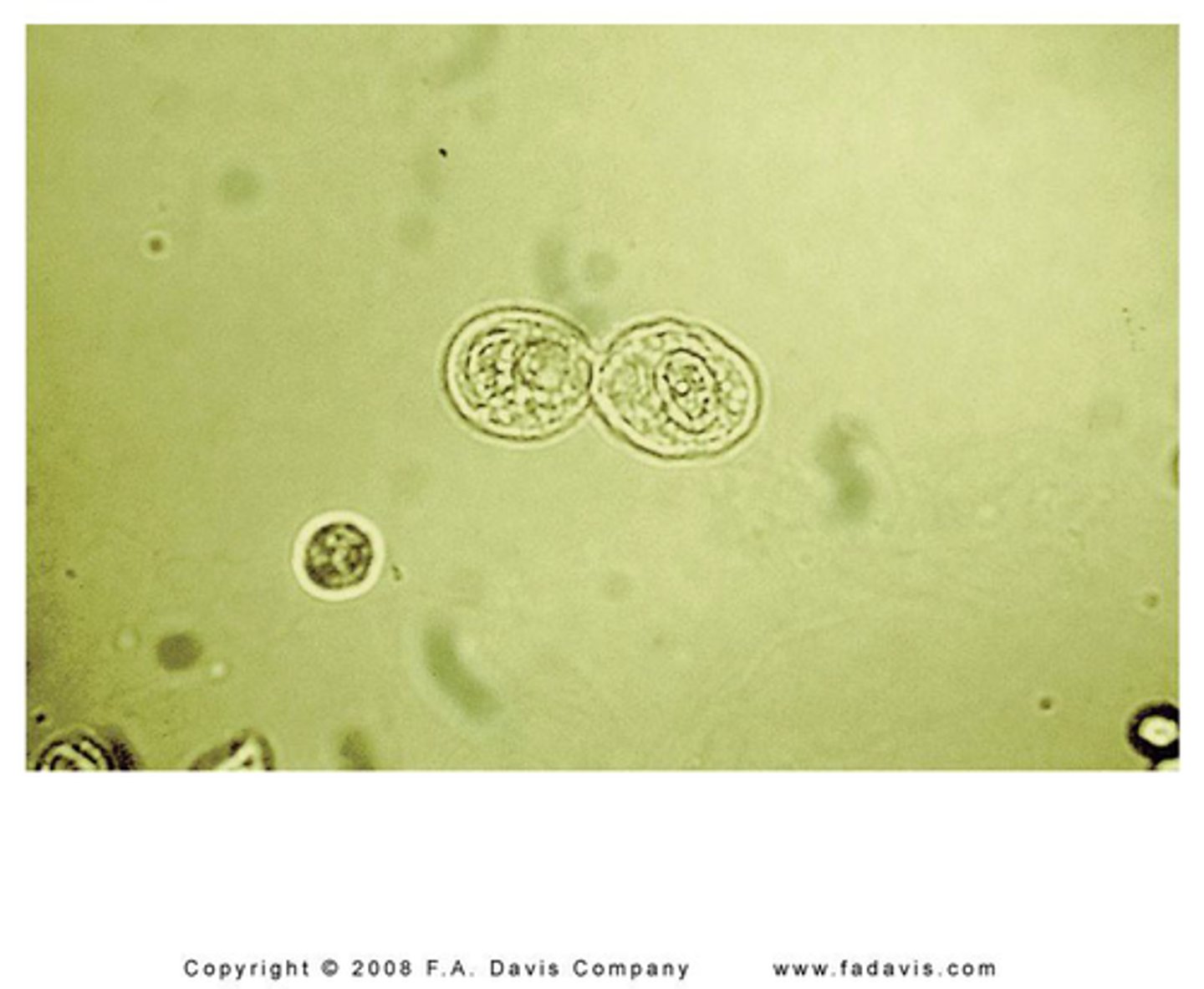
Squamous epithelial cells (not clinically significant)
increased numbers usually seen in urine from females. May obscure RBCs & WBCs. Reduced by collecting midstream clean-catch specimen.
description: 40-50 μm. Flat. Prominent round nucleus.
origin: lower urethra, vagina
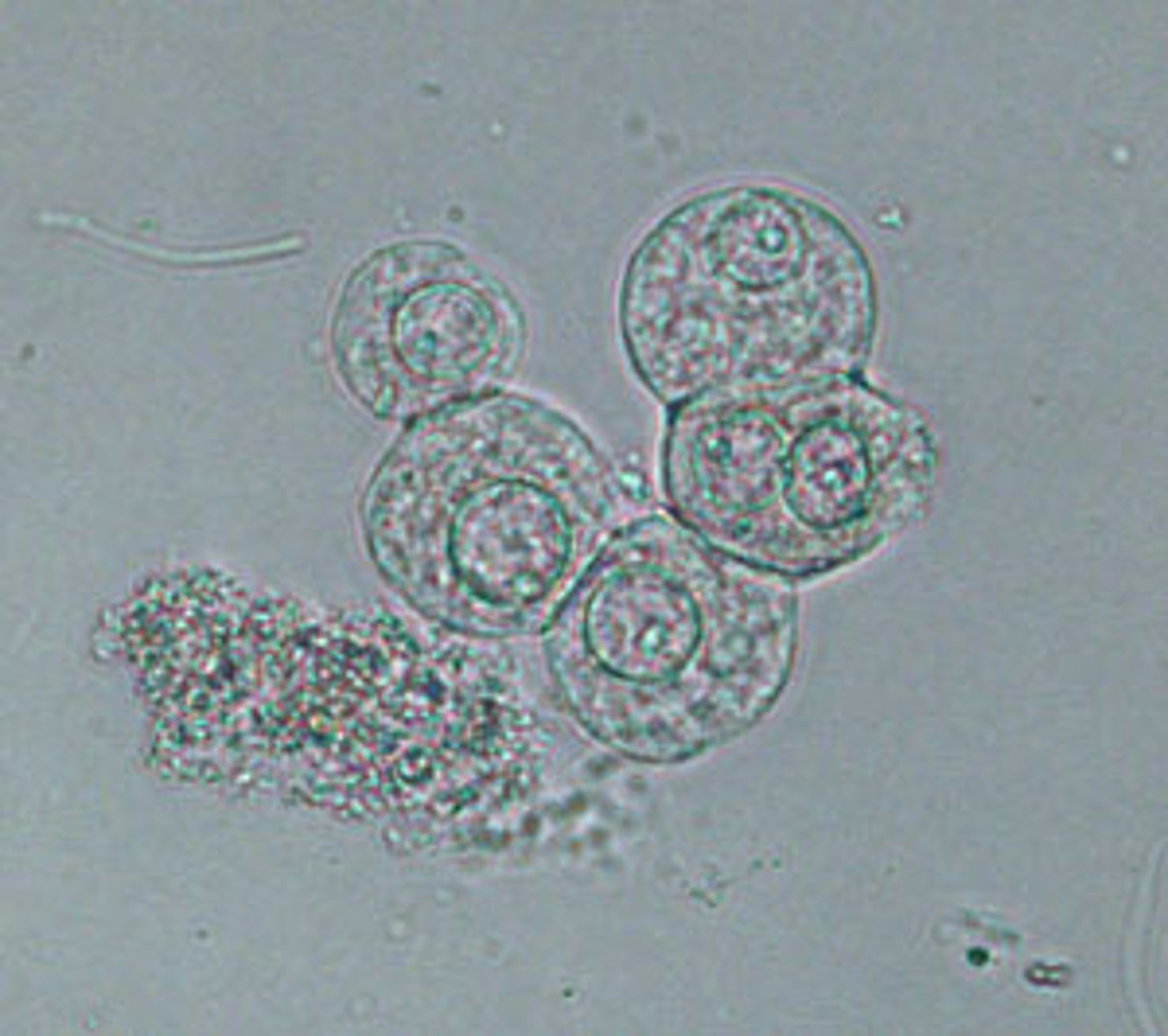
Transitional epithelial cell
May form clumps
description: 20-30μm. Spherical, pear-shaped, or polyhedral. Round central nucleus
origin: Renal pelvis, ureters, bladder, upper urethra
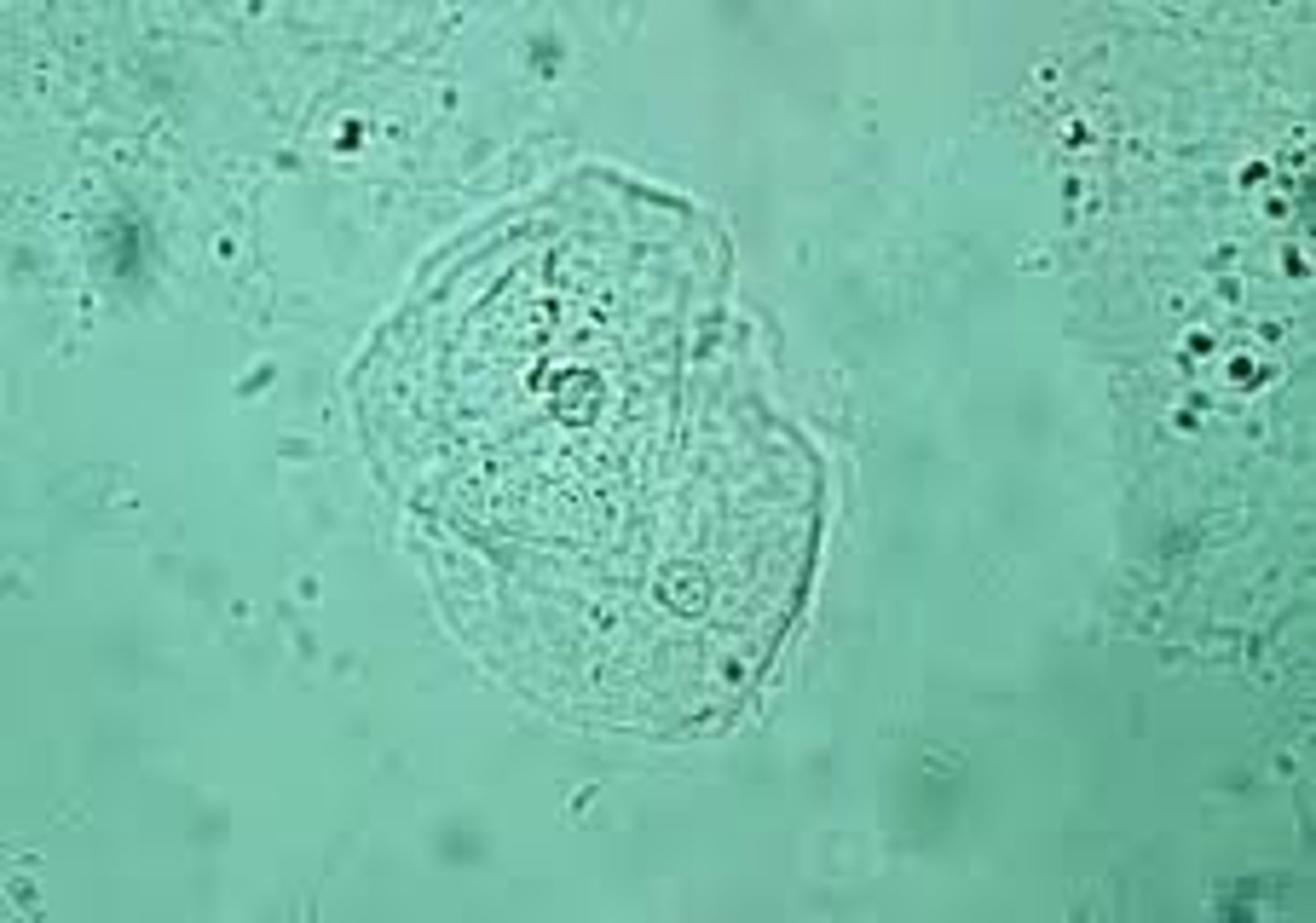
Renal tubular epithelial cells
Slightly larger than a WBC (12 μm).
Round. Eccentric round nucleus
significance: Tubular necrosis, toxins, viral infections, renal rejection
differentiate WBCs from renal tubular epithelial cells by
Add 2% acetic acid to visualize nucleus & differentiate from WBC
Oval Body Fat (located in renal tubules)
Renal tubular epithelial cell containing fat
droplets.
significance: Tubular necrosis, toxins, viral infections, renal rejection
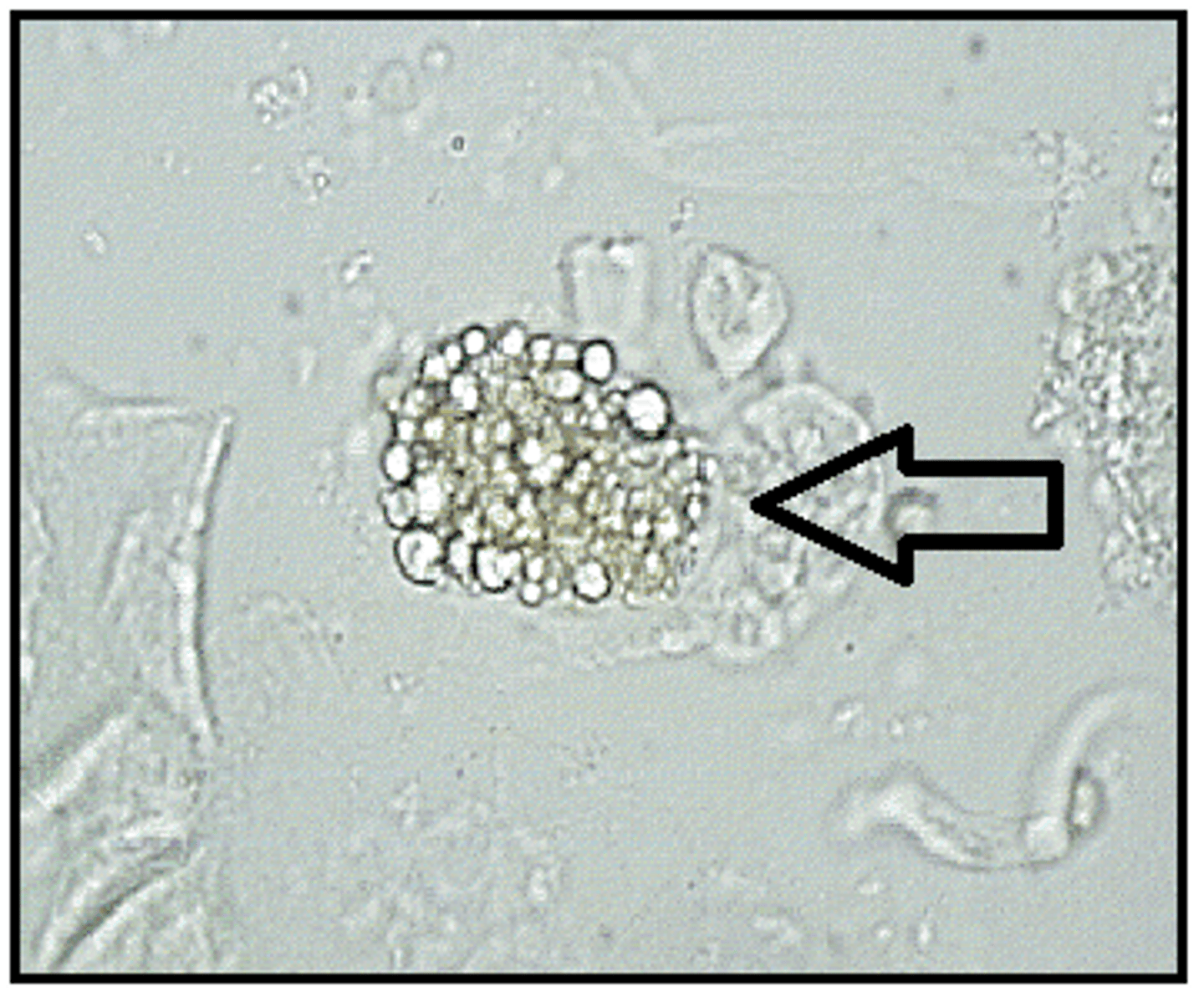
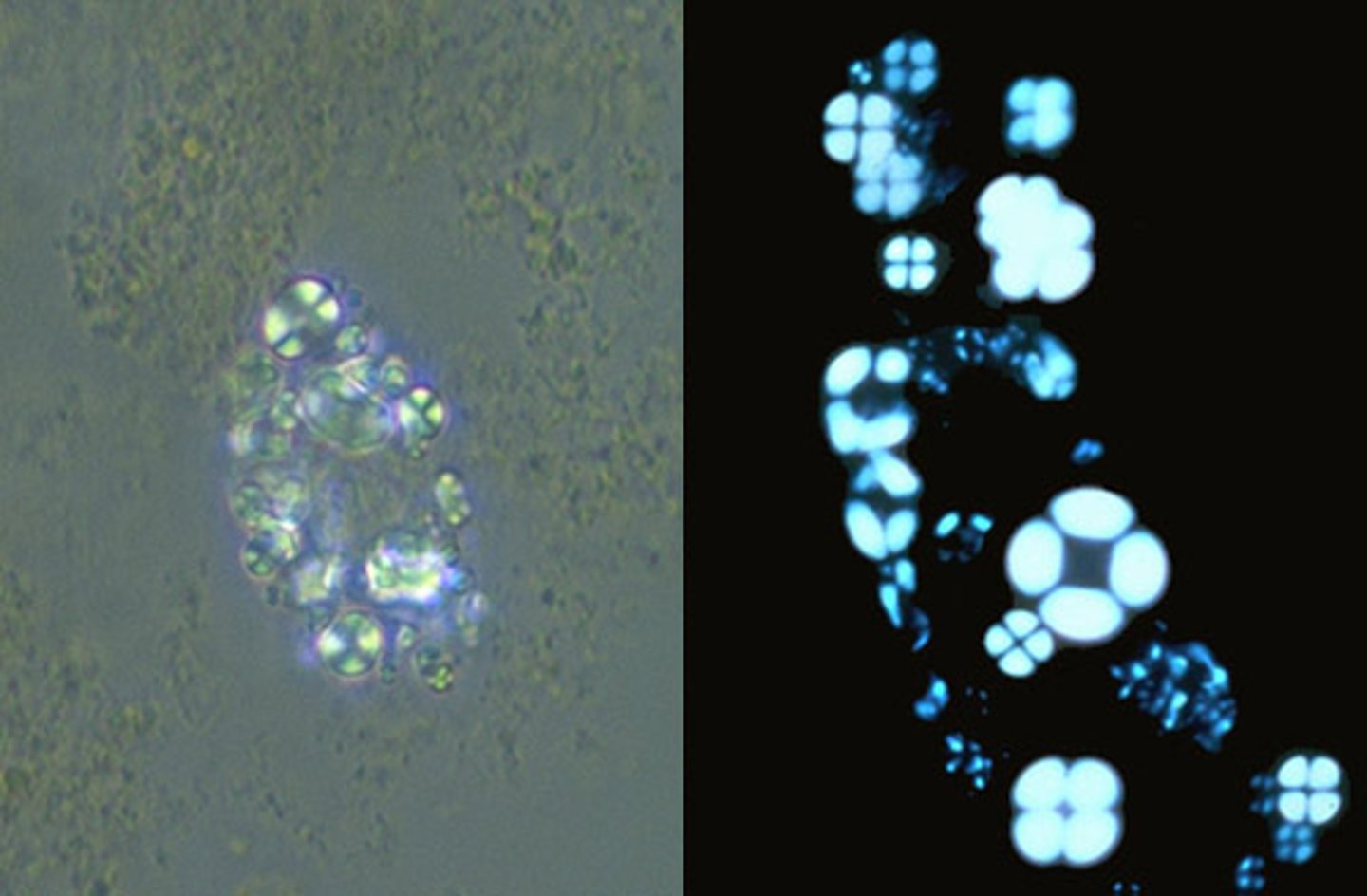
Oval Body Fat polarized
Maltese crosses with polarized light
WBC in urine
granular appearance
origin: Kidney, bladder, or urethra
clinical significance: Cystitis, pyelonephritis, tumors, renal calculi.
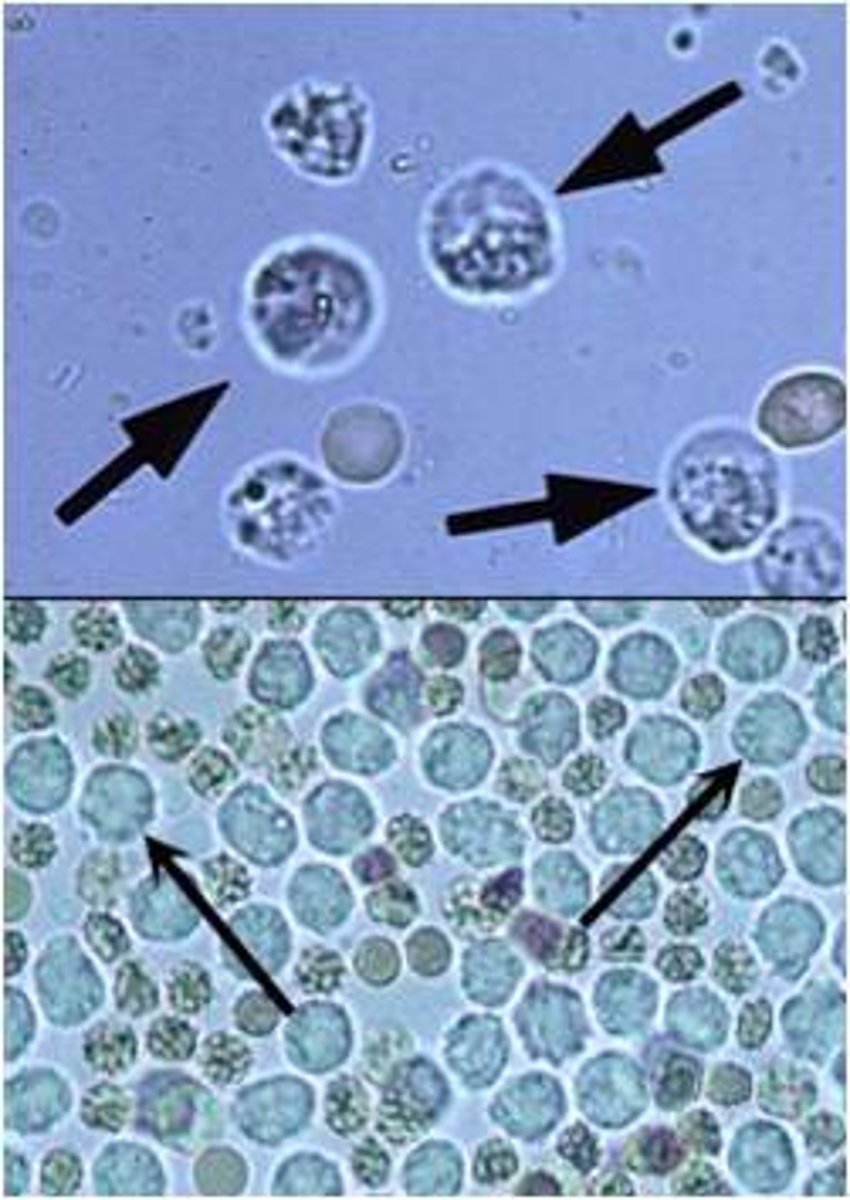
clumps of WBCs could indicate (normal range)
0-8/HPF; clumps could indicate acute infection
Glitter cells
WBC with Brownian movement of granules. Stain faintly or not at all.
origin: Kidney, bladder, or urethra
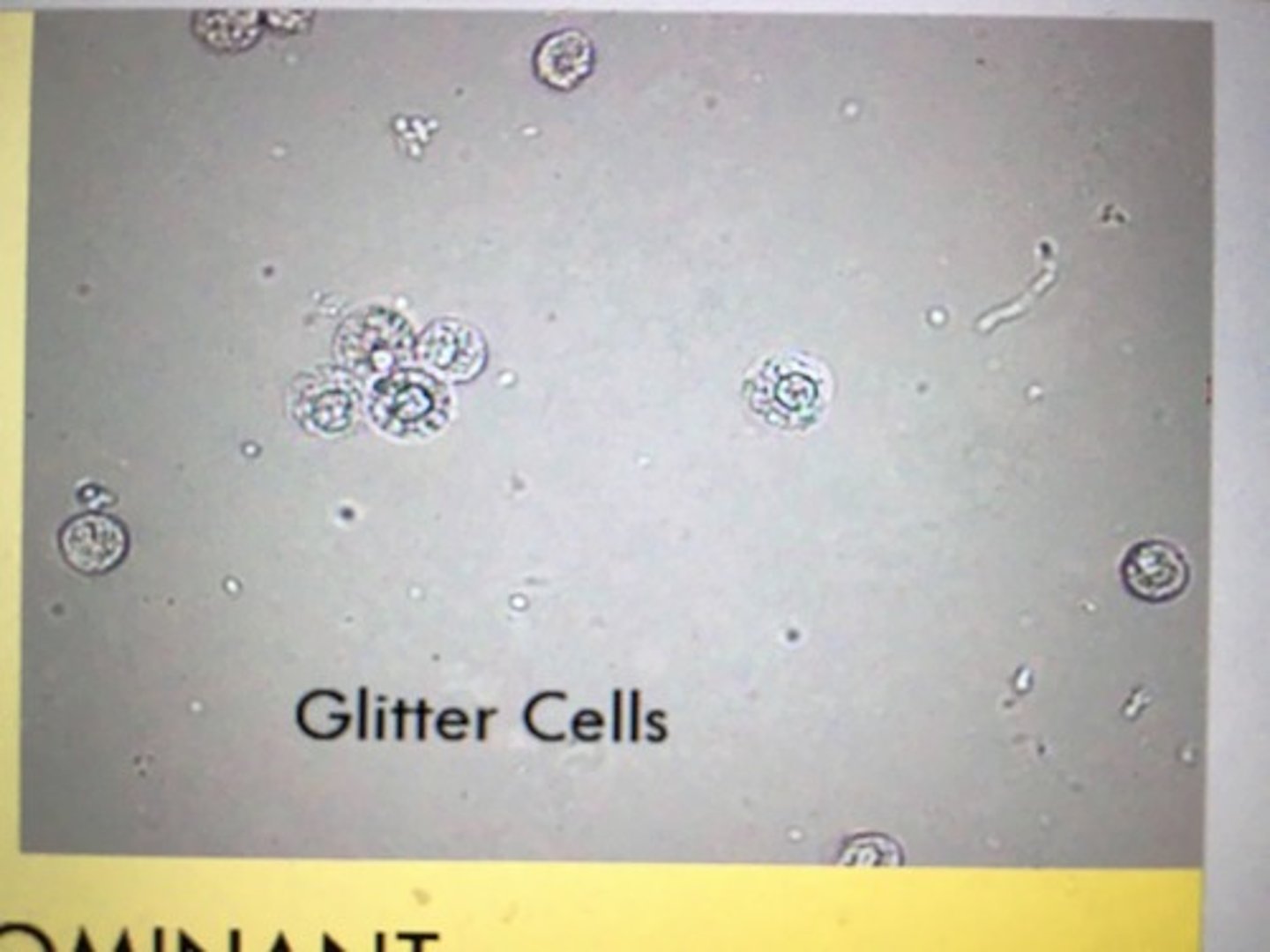
glitter cells is seen in
hypotonic urine
Red Blood Cells in urine
Biconcave disk, about 7 μm. Smooth. Non-nucleated.
significance: Infection, trauma, tumors, renal calculi. Dysmorphic RBCs indicate glomerular
bleeding.
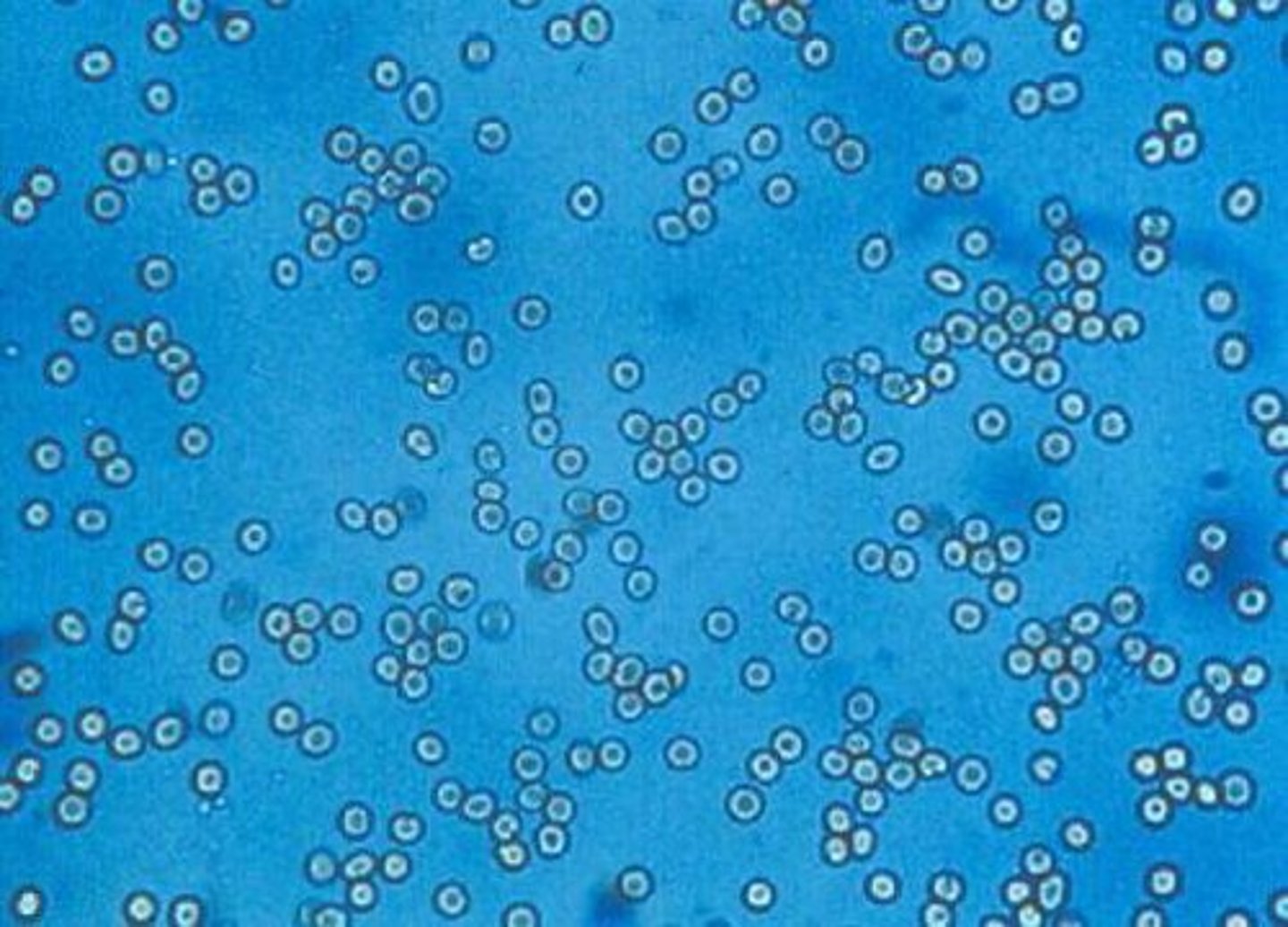
blood in hypotonic/hypertonic urine + normal range
Normal: 0-3/HPF. Crenate in hypertonic urine. Lyse in hypotonic urine & with 2% acetic acid.
crenated RBCs in urine
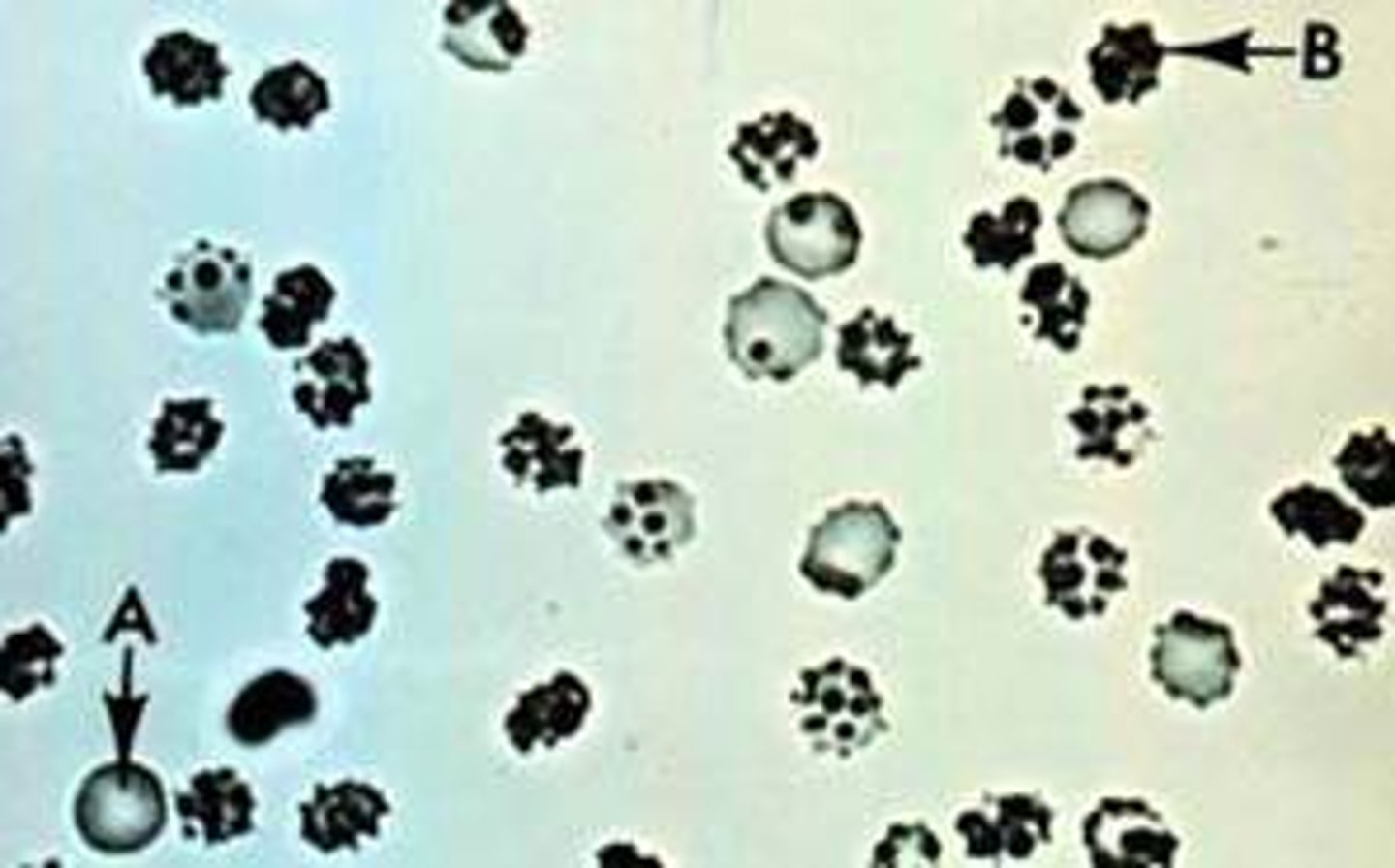
Amorphous urates (normal crystals)
found in acidic urine; irregular granules;
Form pink precipitate in bottom of tube. May obscure significant sediment. Dissolve by
warming to 60oC.
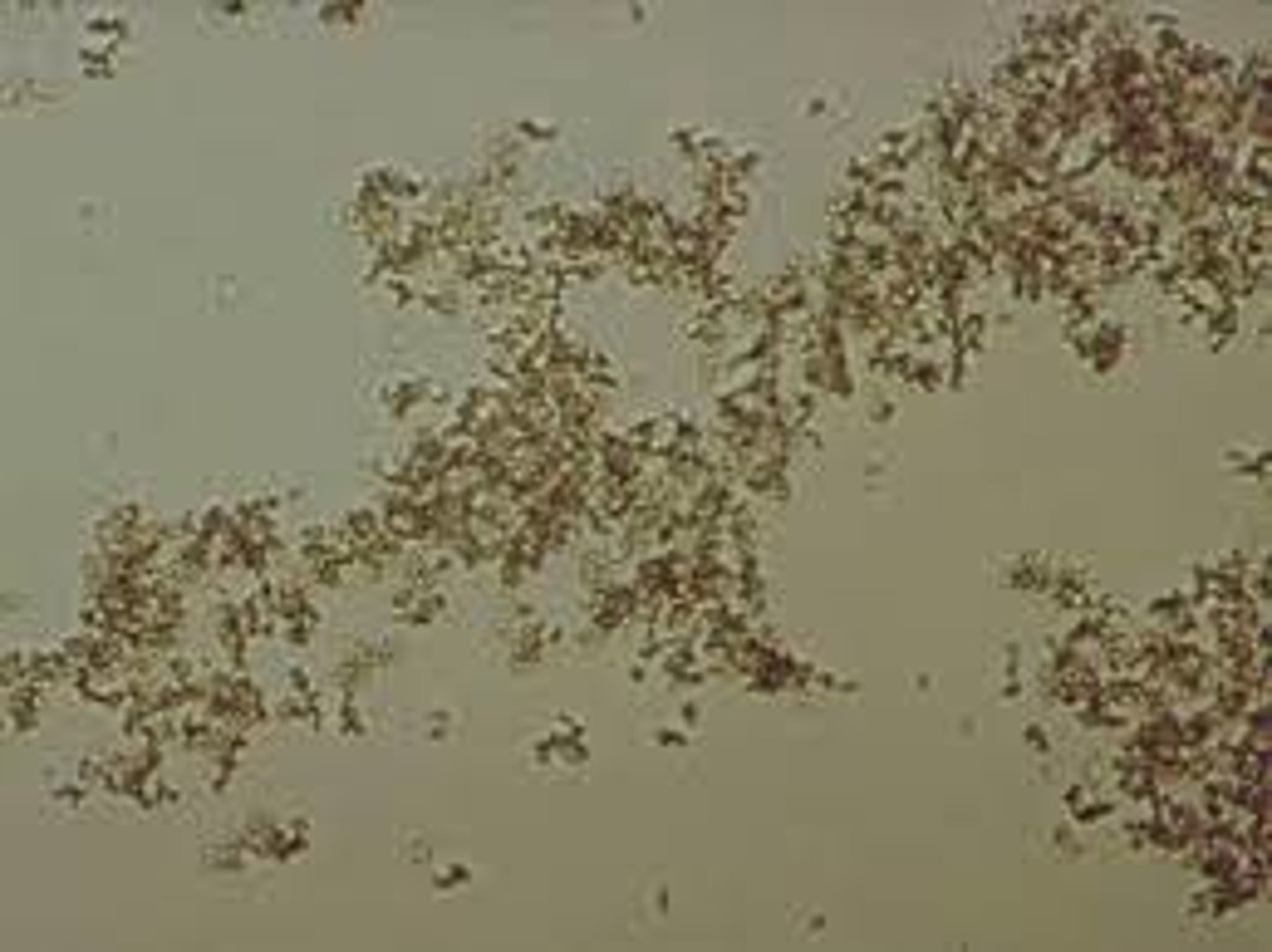
Uric Acid (normal crystal)
found in acidic urine: Pleomorphic. 4-sided, 6-sided, star-shaped, rosettes, spears, plates. Colorless, red-brown, or yellow.
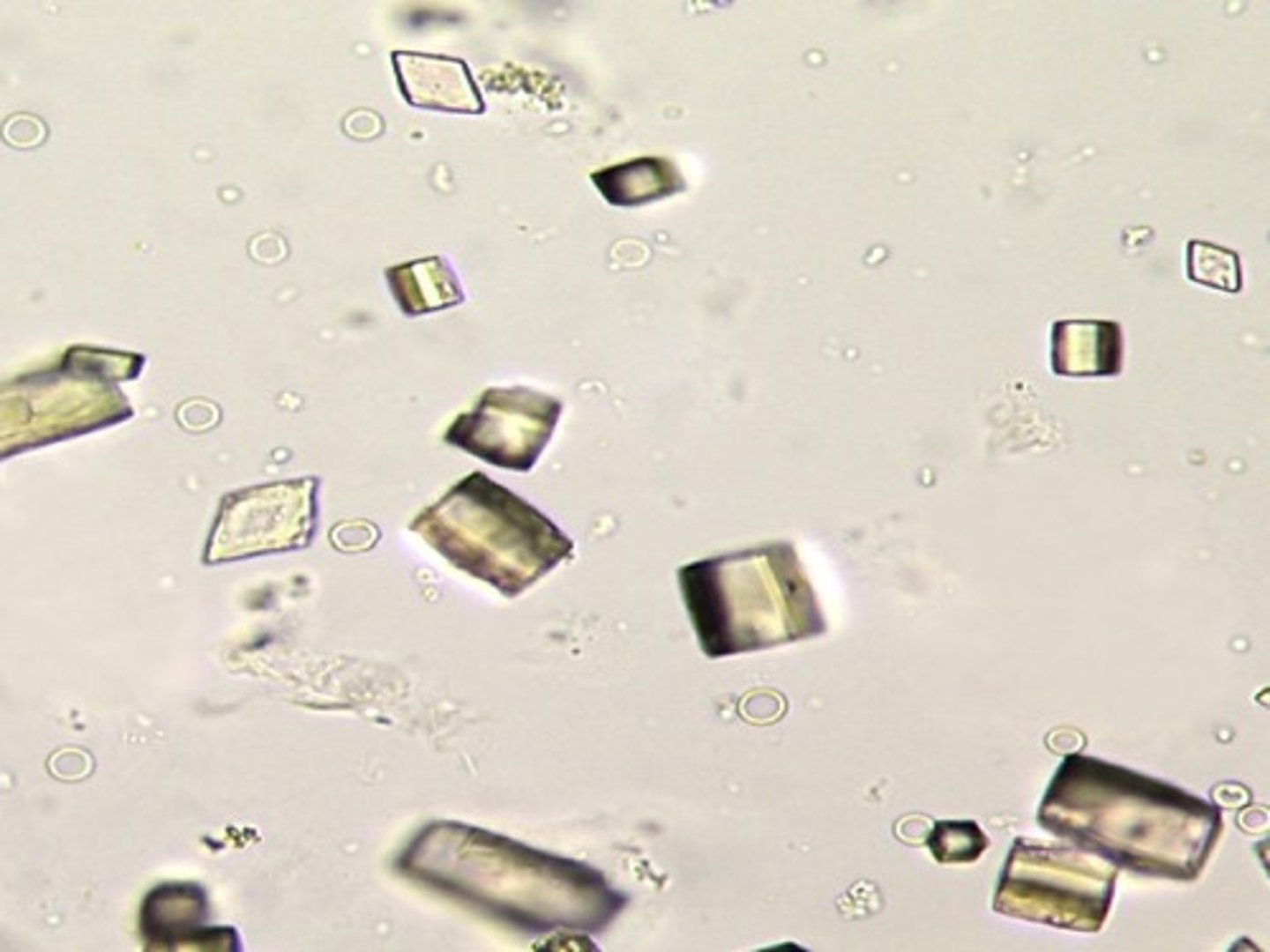

Calcium oxalate (normal crystal)
occasionally found in slight alkaline urine; Octahedral (8-sided) envelope form is most common. Also dumbbell & ovoid forms. (stems from oxalate-rich foods)
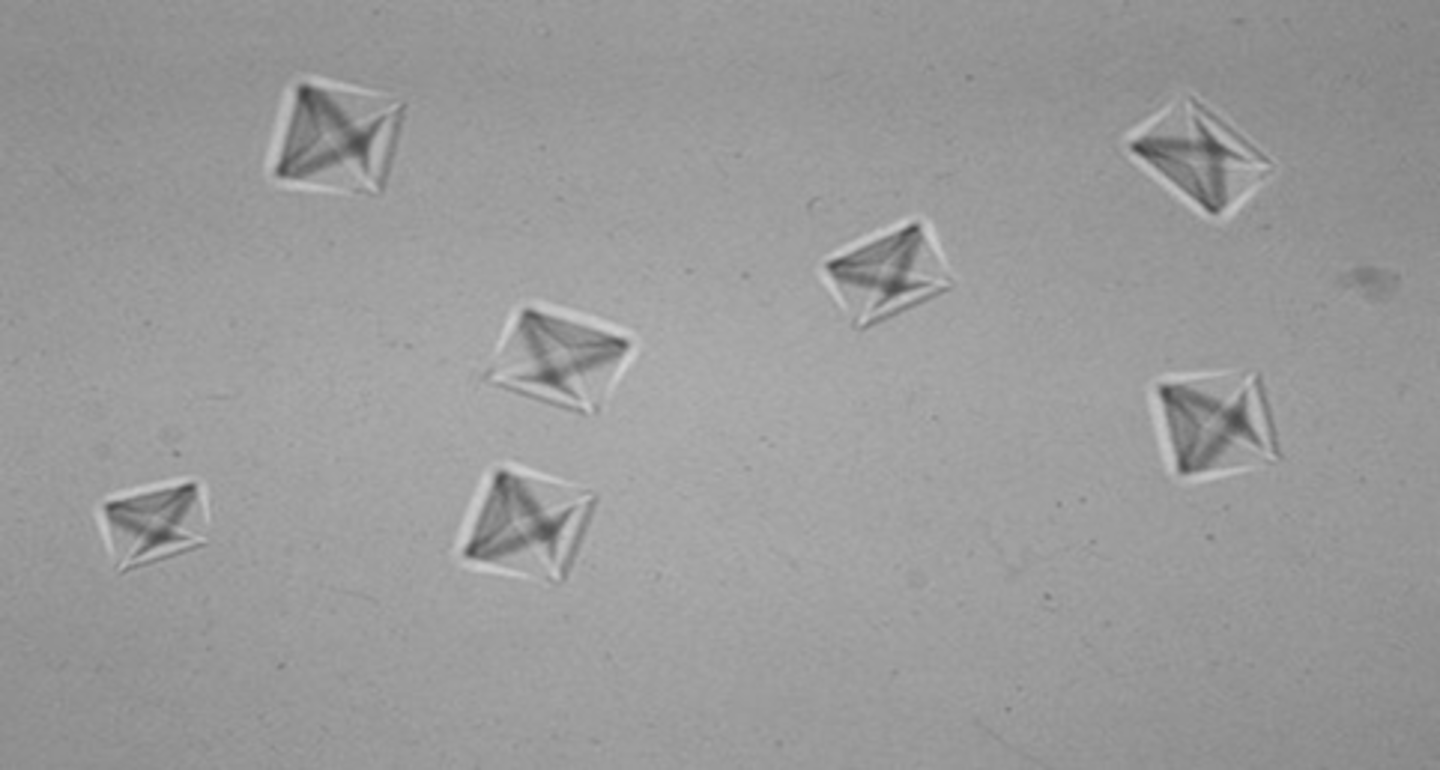
Amorphous phosphates (normal crystal)
found in alkaline urine; irregular granules
Form white precipitate in bottom of tube. Dissolve with 2% acetic acid.
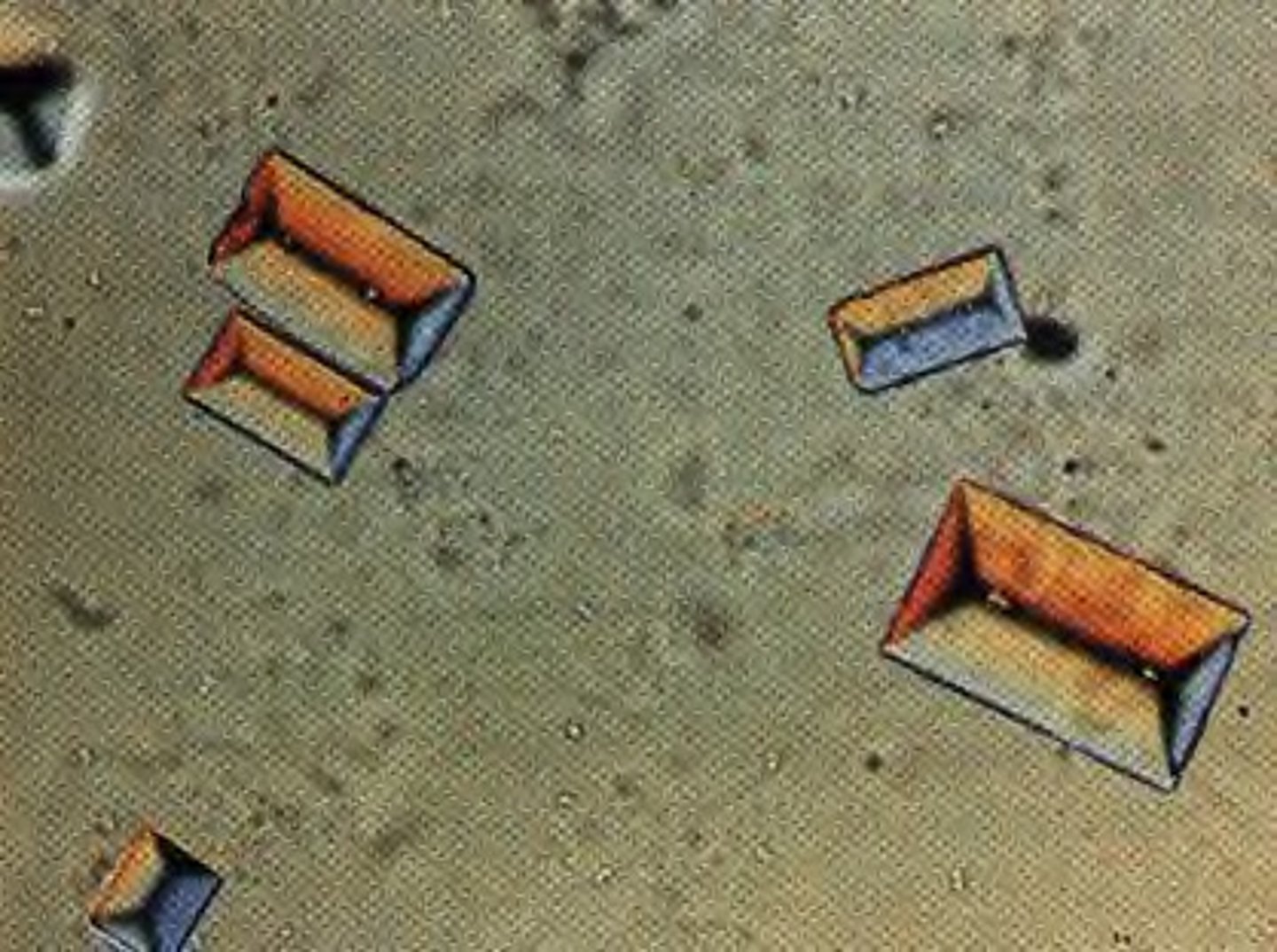
triple phosphate (normal crystal)
colorless prisms resembling "coffin lids" in alkaline urine
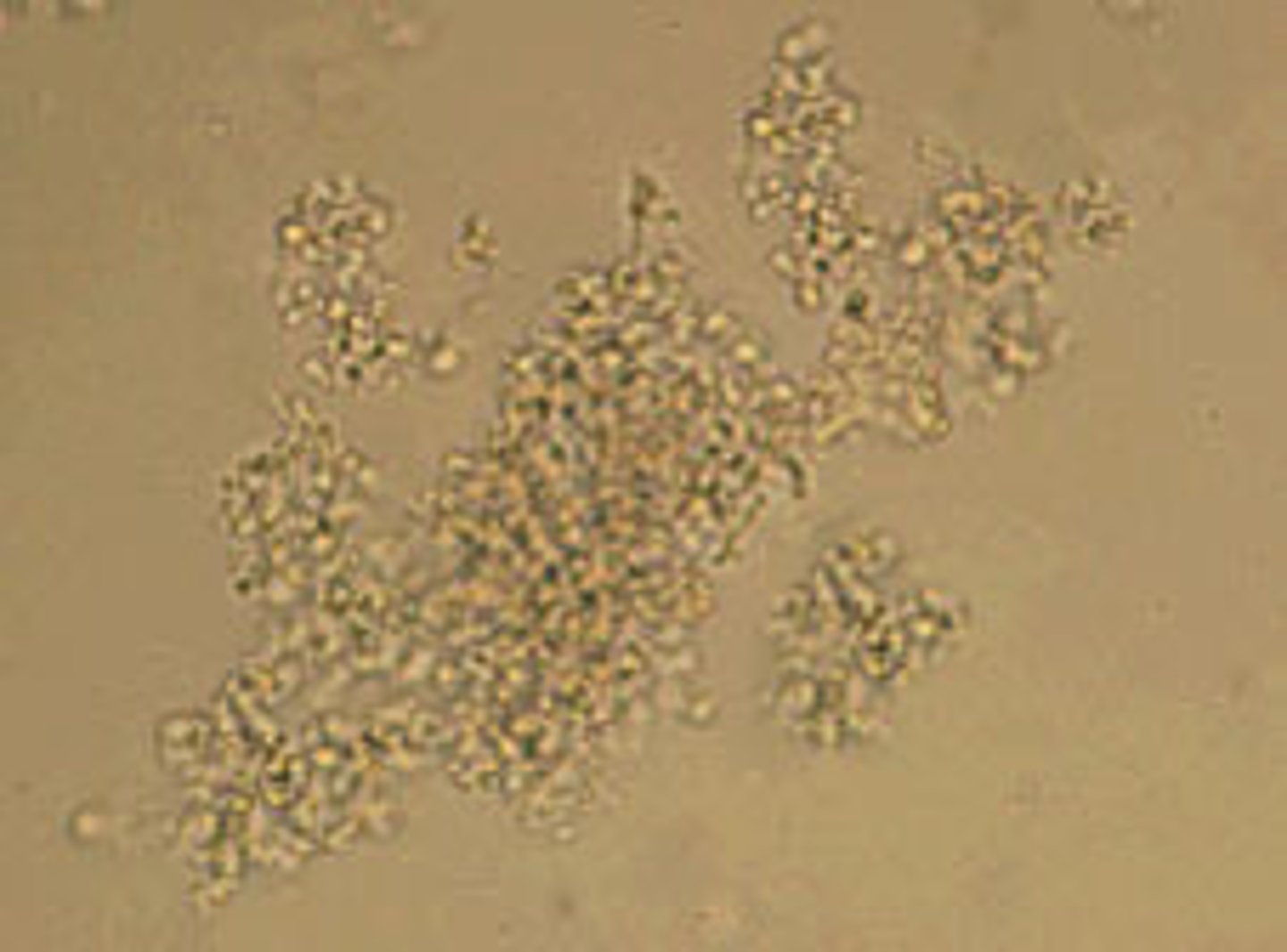
Ammonium biurate crystals (normal crystal)
-Yellow brown "thorny apples"
-will convert to uric acid when acetic acid is added
-Alkaline pH
-Old specimen
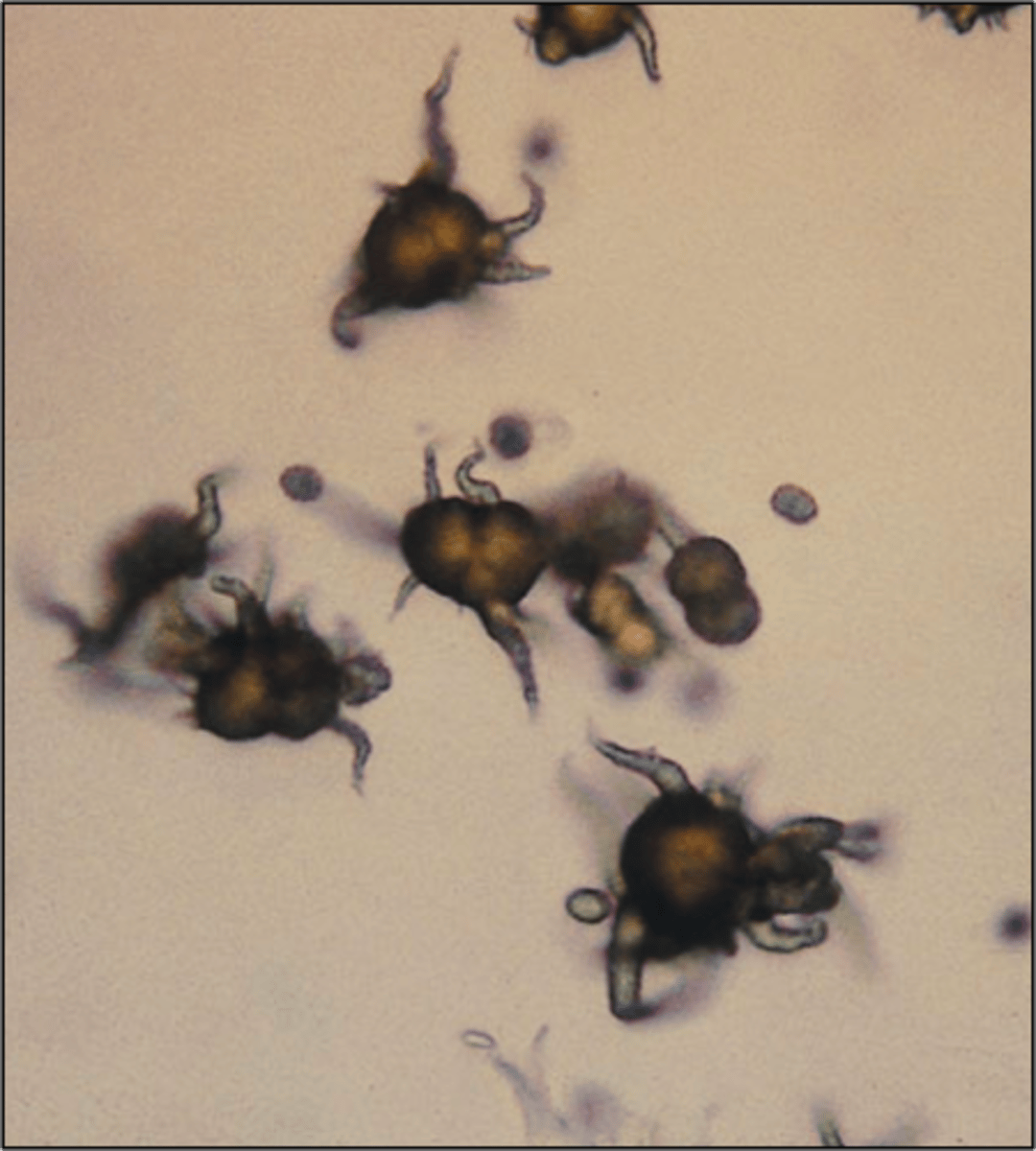
calcium phosphate (Normal)
Needles, rosettes, "pointing finger"; Only needle form seen in alkaline urine.
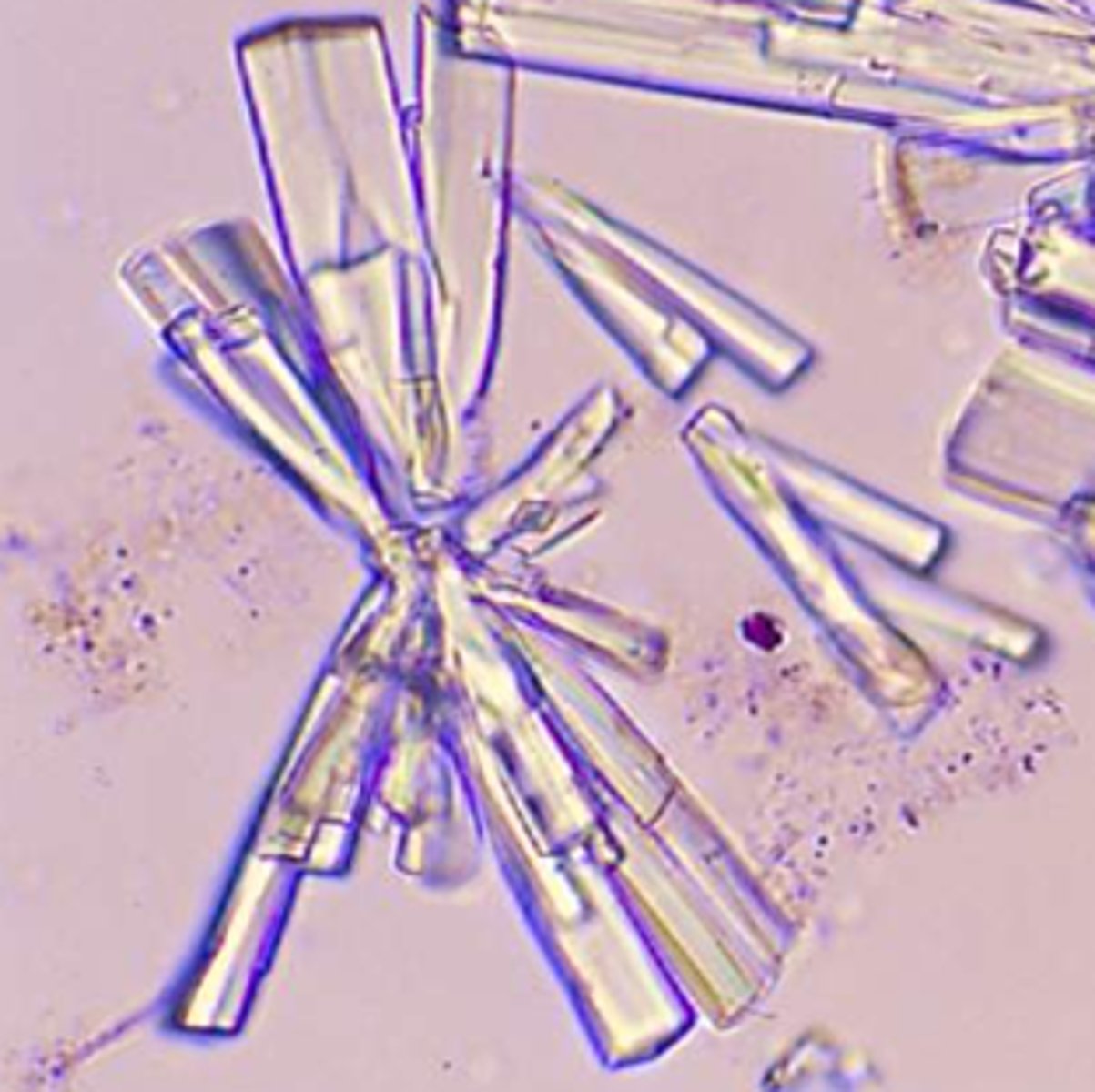

calcium carbonate (normal crystals)
found in alkaline urine; Colorless dumbbells or aggregates
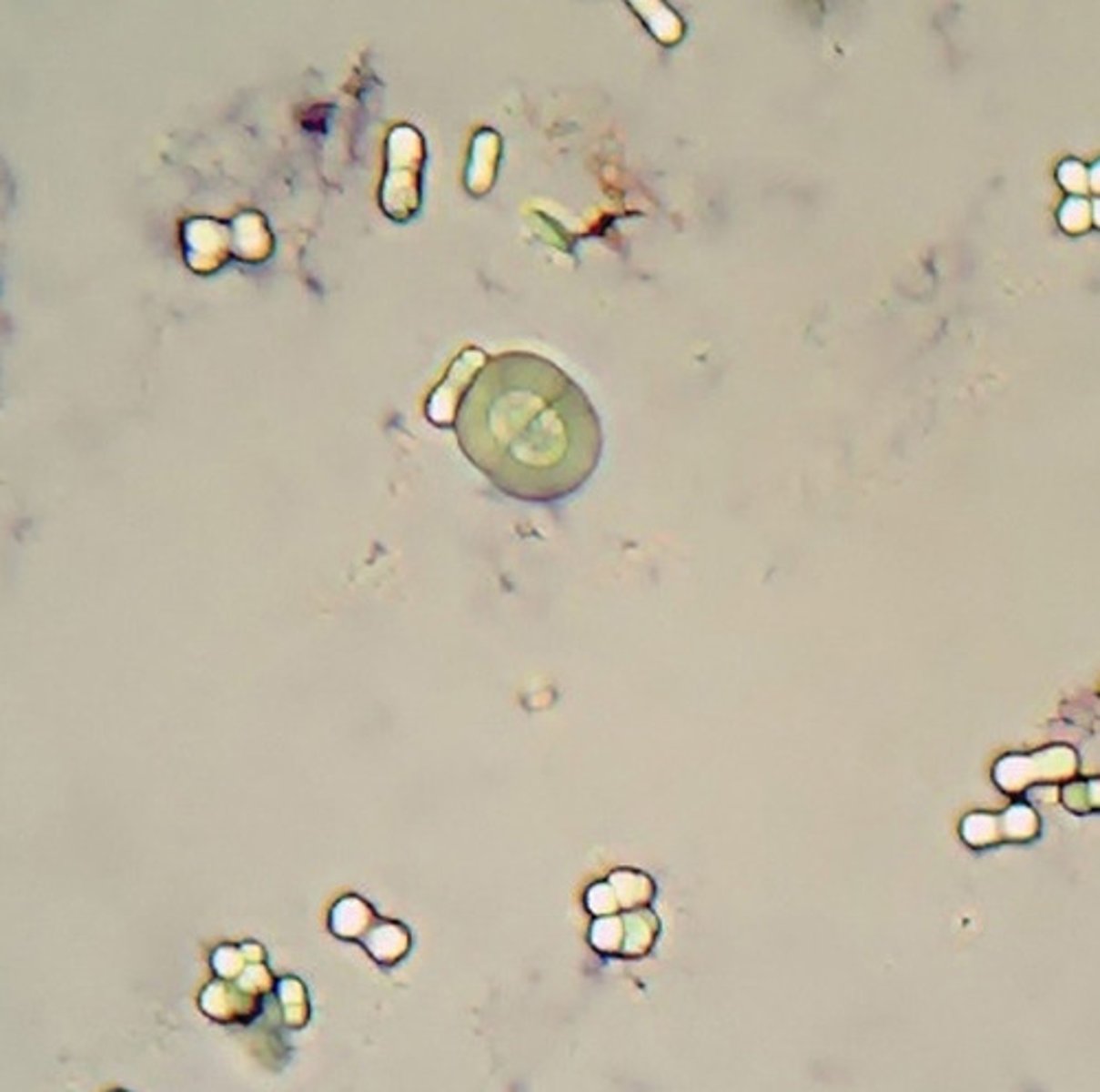
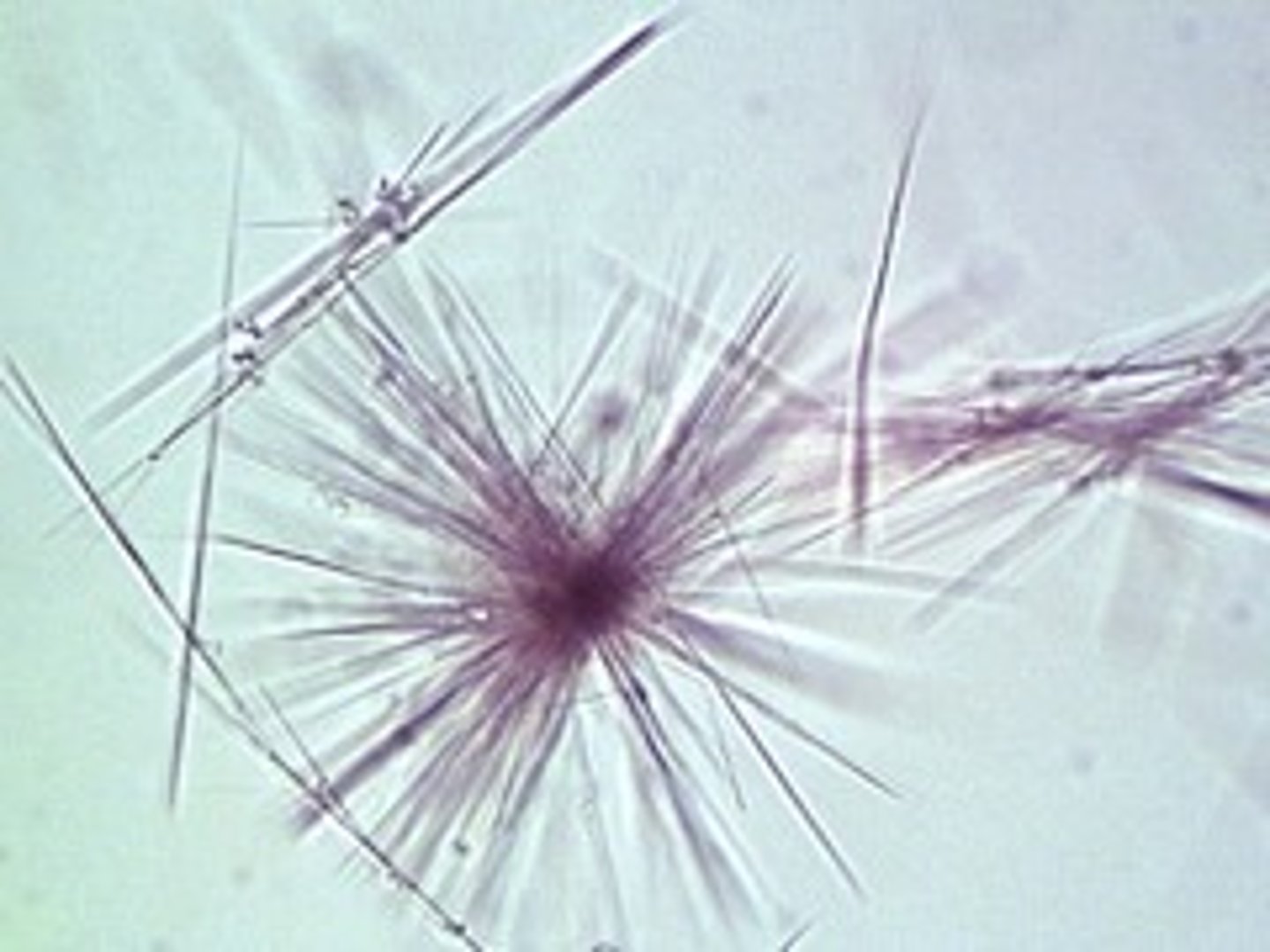
Leucine crystals in urine (abnormal crystals)
Fine yellow needles in sheaves or rosettes; seen in severe liver disease
often seen w/ tyrosine
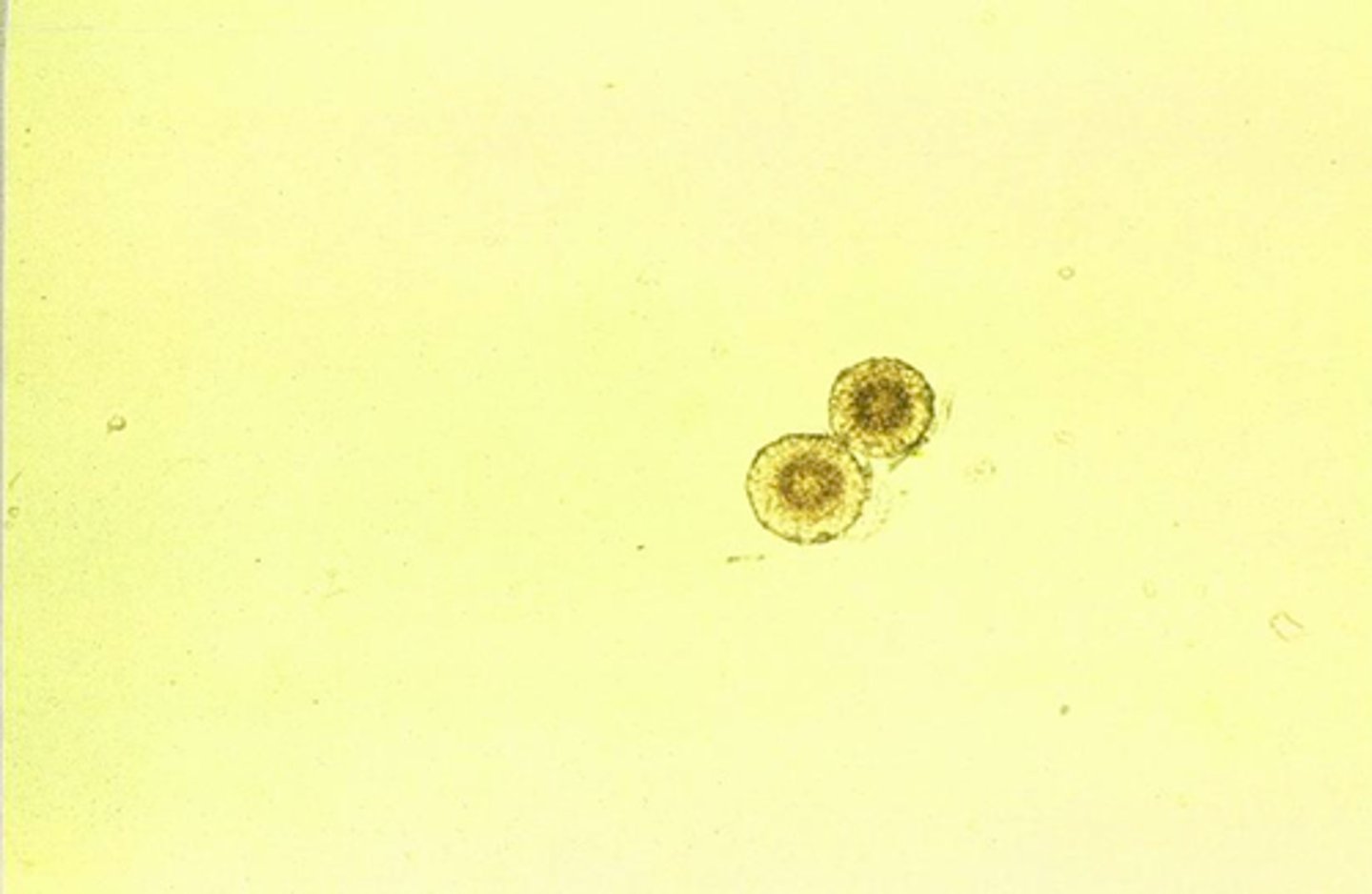
Tyrosine crystals (abnormal crystals)
Fine yellow needles in sheaves
or rosettes; Severe liver disease
Often seen with leucine.