large intestine+liver - GI disorders
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
main functions of large intestine (colon)
store faecal material
regulates its release to external environment
involved in water and electrolyte reabsorption
what are the roles of bacteria found in the large intestine
digesting bile acids
provides environment for bacteria that are important in synthesising certain vitamins
good bacteria provides barrier to invasive microbes
what vitamins do the bacteria in large intestine synthesise
vitamin B
vitamin K
calcium
iron
what effect does bad bacteria in the large intestine have
obesity - high concentrations of bad bacteria in obese patients
inflammation - plays major role in development of IBD and colitis
what is the main functions of the liver
processing nutrients from food
providing bile acids and alkaline fluid for absorption of fats and neutralisation of gastric acids
conjugation, degradation and excretion of waste products of metabolism
detoxification of poisonous substances
true or false: liver can regenerate new cells
true
but this function can be limited due to prolonged bad lifestyle choices
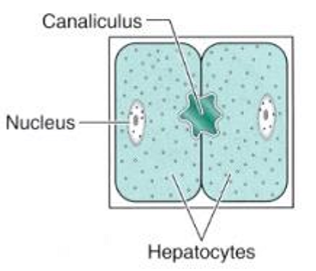
structure of liver: what are canaliculi
minute tubules which are grooves in surfaces between 2 liver cells
what does the bile contain
electrolytes
HCO3- ions
function of bile
to neutralise gastric acid
helps in digestion of dietary fats
what pigment is the breakdown product of haemoglobin
bilirubin
what can impaired liver function lead to digestive problems. what does this include
immune disorders
abnormal absorption of fats
impaired blood sugar levels - hypogycaemia
gall stones
haemorrhoids
constipation, bloating
acid reflux
impaired liver function can also lead to nervous system disorder. what can the change in mood result in
depression
anxiety
anger
poor concentration
cognitive ability
migraine
what are the different types of liver diseases
hepatitis - A,B,C
liver fibrosis/cirrhosis
primary liver cancer
hereditary disease
alcoholic liver disease
what are the 2 most common inherited liver disease
haemochromatosis
alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency
what is haemochromatosis
excess iron absorbed from the diet and deposited in the liver
what is alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency
alpha 1 antitrypsin is a liver protein important for normal lung function - a lack of this would cause compromised lung function
what is hepatitis
chronic condition that lasts less than 6 months
inflammation of the liver
what causes hepatitis
group of viruses known as hepatitis viruses
toxic substances e.g. alcohol, meds, organic solvent
true or false: hepatits is never a self limiting condition
false - can be a self limiting condition
if not self limiting, what can hepatitis progress to become
1) fibrosis
2) cirrhosis
symptoms of hepatitis
asymptomatic
leads to jaundice, anorexia, malaise
diarrhoea
vomiting
symptom of hepatitis - jaundice
yellowish pigmentation of skin, conjunctival membranes over sclerae (whites of eyes) and other mucous membrane
what is hepatitis - jaundice caused by
hyperbilrubinemia - high bilirubin levels
what can hyperbilirubinemia cause
increased level of bilirubin in extracellular fluid
conc higher than 2.5mg/dl leads to jaundice
how is hepatitis A transmitted
by mouth
e.g. direct contact, poor personal hygiene, unsafe sexual practices, street drug use
how is hepatitis B transmitted
through sex and blood
e.g. hemodialysis, exposure to blood, needle stick injury, sexual activity with multiple partners, IV drug use
how is hepatitis C transmitted
spread by blood
e.g. hemophilia, hemodialysis, organ transplant, tattooing
true or false: there are no vaccines to protect against hepatitis A and B
false - there are vaccines to protect against hep A and B
there are no vaccines available for hep C,D,E
which types of hepatitis can cause long lasting problems like liver cirrhosis and cancer
hep B,C,D
what is liver fibrosis
scarring process that represents liver’s response to injury
common outcome in chronic liver disease
liver damage causes liver stellate cells to be over active, what can this trigger
triggers extracellular matrix synthesis to increase
true or false: fibrosis can be reversed of the trigger factor and inflammation is controlled
true
what can liver fibrosis lead to
cirrhosis
what is liver cirrhosis
replacement of liver tissue by fibrosis, scar tissue and regenerative nodules, leading to loss of liver function
true or false: cirrhosis can develop independently without fibrosis
false - cirrhosis is always developed from fibrosis
lifestyle advice for treatment of liver cirrhosis
prevent further damage to liver
consume balanced diet
multivits
avoid drugs
avoid alcohol
what are the complications of cirrhosis
oedema
ascites
how to treat oedema and ascites
reduce salt in diet by using diuretics as they promote the elimination of salt and water into urine
which hepatitis indicate liver cancer
hep B and C
what to do to detect liver cancer earlier on
screen yearly or biyearly with ultrasound examination
what is the only curative treatment for end stage cirrhosis
liver transplant
what is fatty liver disease caused by
large vacuoles of triglyceride fat accumulation in liver cells or abnormal retention of lipids
true or false: fatty liver disease is considered as ‘benign’
true
true or false: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with diabetes
false - assocaited with obesity which can be inlammatory leading to cirrhosis
symptoms of fatty liver disease
dull or nagging pain in abdominal area
weakness, nausea
bloating
high cholesterol
high bp
weight gain
yellowness in skin
risk factors of fatty liver disease
diabetes mellitus
protein malnutrition
hypertension cell toxicity
what are the causes of fatty liver disease
taking certain meds
gastric bypass surgery
high cholesterol
high triglycerides in blood
how can fatty liver disease be treated
only treated naturally though diet and exercise
what is alcoholic liver disease
overconsumption of alcohol which damages liver

diagnostics of liver disease

what are the main treatments for constipation
Bulk forming laxatives
Osmotic laxatives
Stimulant laxatives
Stool softeners
what are the main treatments for diarrhoea
Loperamide
Morphine
Adsorbents
Bismuth
Bulk forming agents
what is vomiting (emesis)
ejection of gastric contents through mouth
what is the advantage of vomiting
protects stomach as it removes toxic substances from the body
how is vomiting controlled
controlled by the vomiting centre and chemoreceptor trigger zoon in the brain
chemoreceptor trigger zone is permeable, what does this mean for drugs used to treat vomiting
can be affected by drugs circulating systemically that do not cross blood brain barrier
what drugs affect vomiting
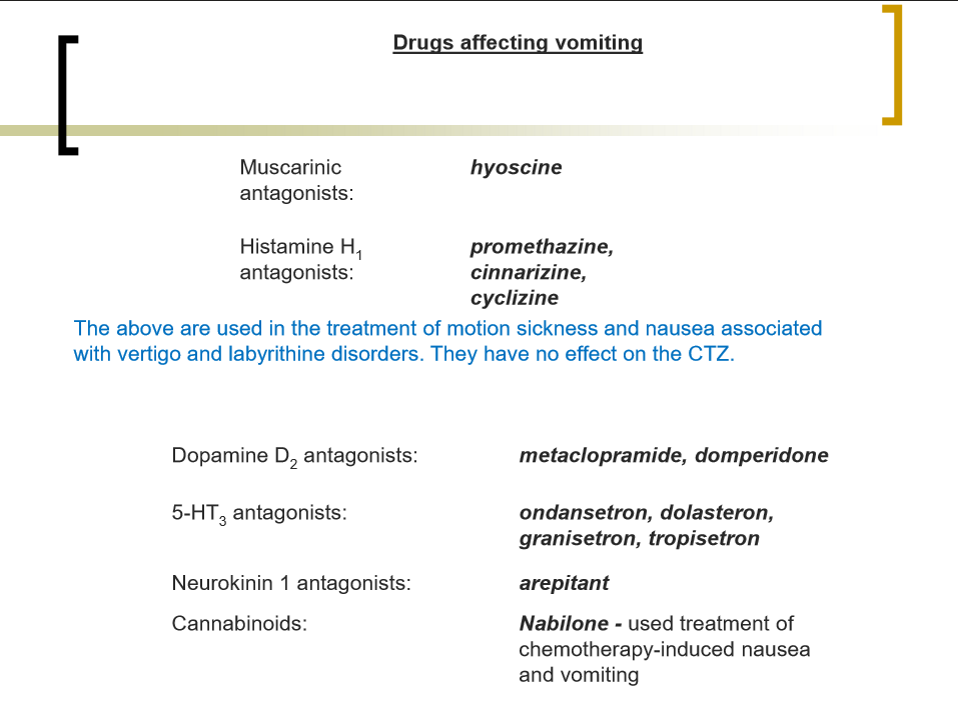
what are the main neurotransmitters involved in the vomiting reflex
Ach, 5-HT,, histamine, dopamine and substance P and its is the receptors they act on that provide targets for most commonly used anti-emetic drugs (anti-vomiting drugs)