science test revision task 4
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
metamorphic rock
A type of rock that forms from an existing rock that is changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions.
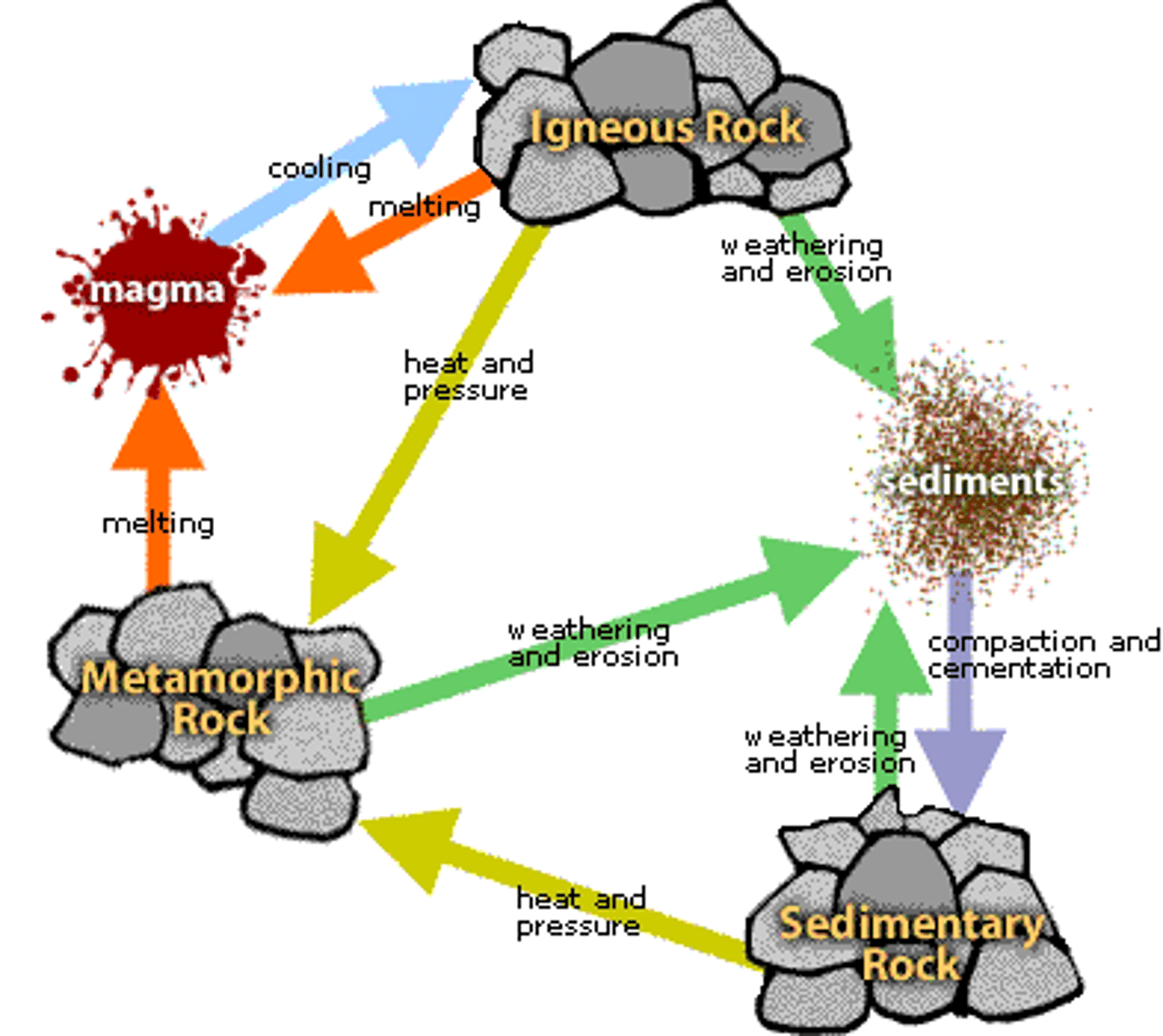
Rock cycle processes
Cooling and Hardening
Melting
Heat and Pressure
Compacting and Cementing
Weathering and Erosion
Lustre (Minerals)
How light reacts to the mineral:
Shiny
Glossy
Transparent
Metallic
Dull
streaky
Streak (Minerals)
The color of the mineral when is powdered
Leach mining system
A method of extracting metals from ore by dissolving them in a liquid, usually water or acid.
Fossils
Preserved remains of once-living organisms
body fossils
Hard parts of an organism, such as bone, teeth or shells, that has been preserved into a fossil
eg: dinosaur eggs
trace fossils
An imprint of an organism that has been filled mud and preserved
eg: footprints
resin fossils
a type of fossil formed when a small plant or insect becomes trapped and preserved in tree sap
eg: small bugs
igneous rock
a type of rock that forms from the cooling of molten rock at or below the surface
sedimentary rock
A type of rock that forms when particles from other rocks or the remains of plants and animals are pressed and cemented together
Cooling and hardening
when magma cools and hardens to make a igneous rock
melting
when igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic rock is heated up to form magma
heat and pressure
two forces that change the features of a igneous, sedimentary or metamorphic rock
compacting and cementation
when sediments are pressed together and chemically bind together to form a sedimentary rock
weathering and erosion
the process of breaking down rock and moving that rock
examples of igneous rocks
granite, pumice, obsidian, basalt
examples of sedimentary rocks
sandstone, shale, limestone
examples of metamorphic rocks
marble and quartzite
properties of igneous rocks
Origin: Intrusive/Extrusive
Texture: Glassy, Fine-grained, coarse-grained, porphyritic
Composition: What minerals are in it.
Minerals
Minerals are naturally occurring chemical substances
that make up igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic
rocks
Ores
minerals that are mined because they contain useful metals or nonmetals
Examples of Minerals
calcium, potassium, sodium, magnesium
Examples of Ores
iron and aluminum
difference between a mineral and an ore
An ore is always a mineral but a mineral is not always an ore. Ores are big amounts of minerals.
Color (Minerals)
Colour of the mineral, different minerals can have same colours and same minerals can have different colours
Hardness (Minerals)
How hard or soft the mineral is. Harder minerals can scratch softer minerals
Cleavage (Minerals)
The angle/s in which the mineral breaks
importance of an ore in the world economy
ores contain metals crucial to industry and trade
eg: copper is used in electrical wiring
Rock Cycle Diagram
mould fossil
fossil formed when a living thing decomposes underneath sediment, creating a cavity in the shape of the dead organism
eg: skeleton
fossil formation process
1. The animal dies.
2. Soft parts of the animal's body, including skin and muscles, start to rot away. Scavengers may come and eat some of the remains.
3. Before the body disappears completely, it is buried by sediment - usually mud, sand or silt. Often at this point only the bones and teeth remain.
4. Many more layers of sediment build up on top. This puts a lot of weight and pressure onto the layers below, squashing them. Eventually, they turn into sedimentary rock.
5. While this is happening, water seeps into the bones and teeth, turning them to stone as it leaves behind minerals.
Mantle
Layer beneath the Earth's crust
Asthenosphere
Upper portion of the mantle behaving plastically
Core
Very dense center of the Earth
Metamorphic Rocks
Changed by heat and pressure within Earth
Geology
Study of rocks and Earth's structure
Geologist
Scientist who studies rocks
Crust
Outermost solid layer of Earth
Rock Cycle
Model explaining rock formation processes
Igneous Rocks
Formed from red hot melted rock
Sedimentary Rocks
Formed from sediments or minerals solidifying
Weathering
Processes breaking rocks into smaller pieces
Erosion
Transport of broken rock material
Deposition
Settling of broken rock material
Biological Weathering
Living organisms breaking down rock
Chemical Weathering
Chemical reactions breaking down rock
Physical Weathering
Mechanical forces breaking down rock
Wind
Carries fine rock particles, causing erosion
Temperature Change
Causes rock to expand and contract, leading to cracks
Glaciers
Frozen rivers slowly carving rocks
Agents of Erosion
Water, wind, gravity, or ice moving rock particles
Prospectors
Search for precious minerals
Delta
Landform at a river's mouth from sediment deposition
Igneous Rock Formation
Complete melting and recrystallization
Metamorphic Rock Formation
Partial melting and recrystallization
Compaction and Cementation
Process forming sedimentary rock from compacted sediment
Melting and Crystallization
Solid rock melting and forming new crystals
Igneous rock
Formed from magma or lava crystallization
Extrusive igneous rocks
Formed at or near the Earth's surface
Intrusive igneous rocks
Formed from magma cooling below the surface
Crystals
Interlocking mineral structures in igneous rocks
Magma
Molten rock beneath the Earth's surface
Lava
Magma that reaches the Earth's surface
Rapid cooling
Leads to small or no crystals in igneous rocks
Slow cooling
Allows crystals to grow larger in igneous rocks
Texture
Smoothness or roughness of a rock's surface
Colour
Linked to minerals present in the rock
Basalt
Dark-coloured extrusive igneous rock
Dolerite
Intrusive igneous rock with larger crystals
Granite
Intrusive igneous rock composed of quartz, feldspar, and biotite
Obsidian
Dark volcanic glass formed from rapidly cooled lava
Pumice
Light extrusive igneous rock with gas bubbles, floats on water
Scoria
Dark extrusive igneous rock denser than pumice, sinks in water
Uses of igneous rocks
Include building materials, concrete, road surfaces, and ornaments
Shearing
Process where rocks slide sideways due to pressure
Recrystallisation
Chemical change in rocks forming new minerals
Tectonic Plates
Massive plates in Earth's crust that can collide or move apart
Metamorphism
Process of forming metamorphic rocks due to heat and pressure
Foliation
Movement of minerals into layers or bands in rocks
Contact Metamorphism
Alteration of rock mostly by heat, often due to hot magma intrusion
Dynamic Metamorphism
Alteration of rock mostly by pressure, occurs in small areas
Ore Mineral
Contains a metal or valuable material, extracted from rocks
Native Metal
Metal found in nature as a pure element
Hydrothermal Fluids
Superheated solutions carrying dissolved minerals
Mining
Process of removing resources from the ground
Processing
Extracting and enriching minerals from ore
Rehabilitation
Restoring mining sites to original or usable conditions
Tailings
Toxic waste materials from mining or processing plants