plant and stem cell vocab
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
1. What are the three main tissues of plants?
Dermal tissue(outer protective layer)
ground-tissue (storage, support, secretion, photosynthesis)
vasular tissue(xylem, phloem)
2. What are the three main organs of plants?
roots(anchor, abosrot water/minterals)
stems(support, transport cellulose lining and turgor pressers for plant)
leaves(photosynthesis organ)
3. Draw, label and annotate a cross section of a root
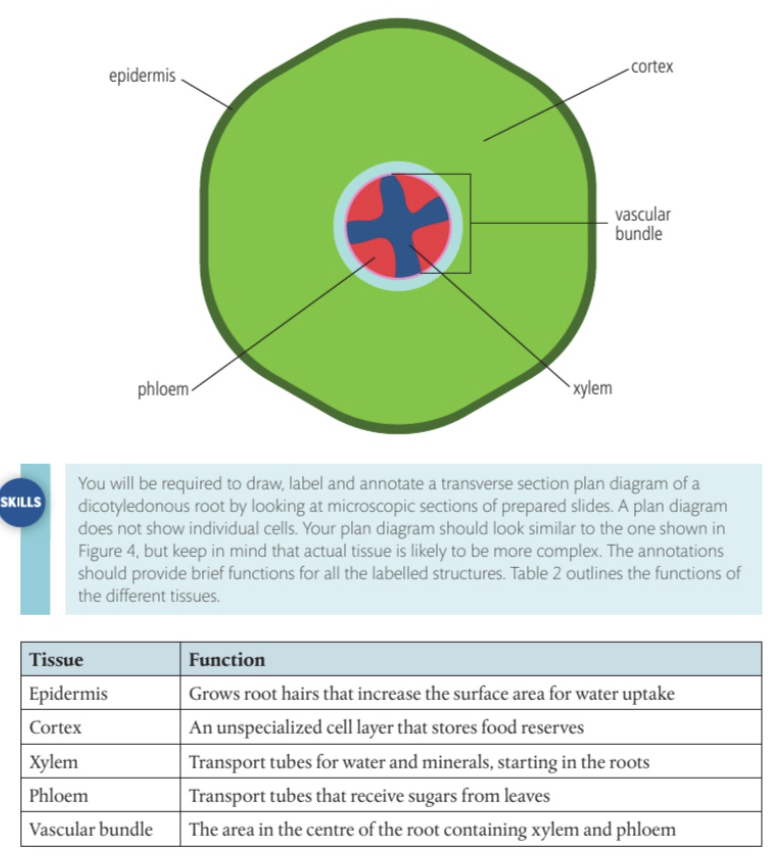
4. Draw, label and annotate a cross section of a stem
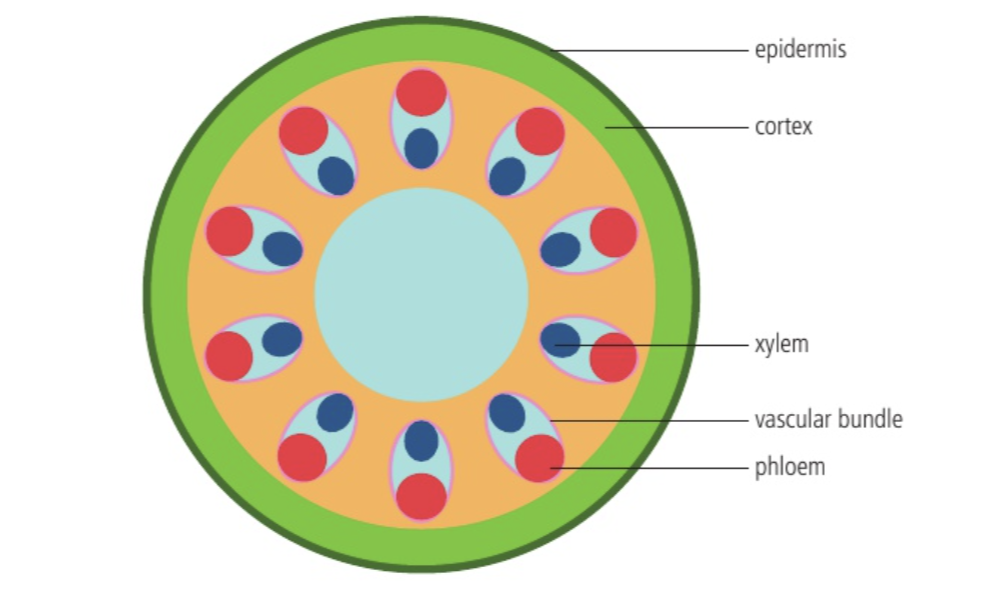

5. Draw, label and annotate a cross section of a leaf
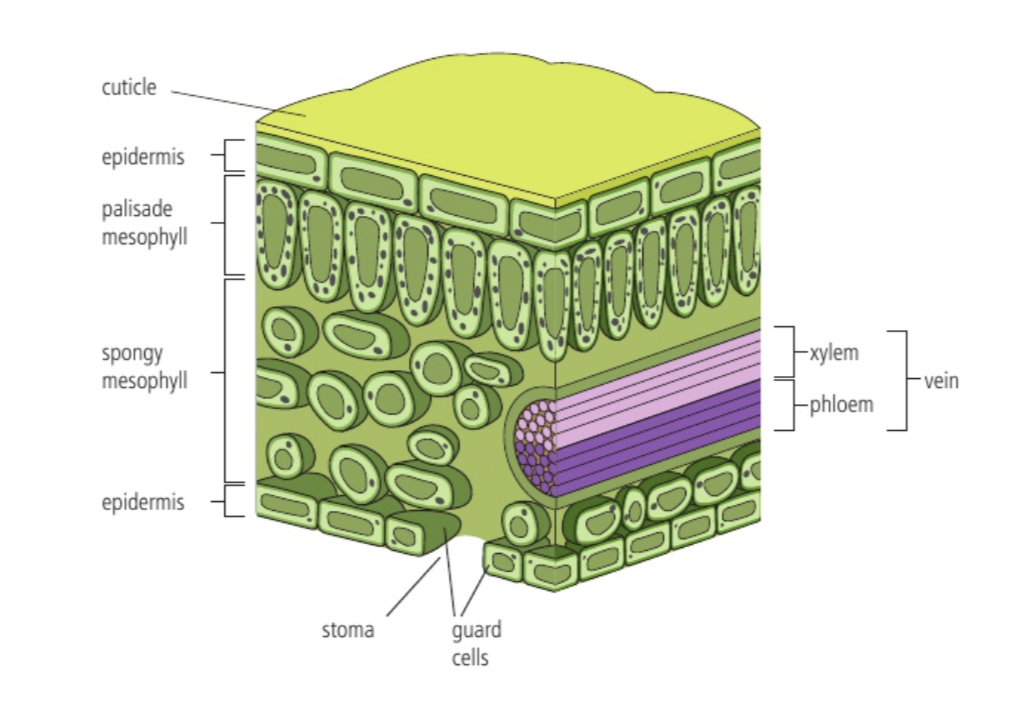
6. Draw, label and annotate a dicotyledonous flower
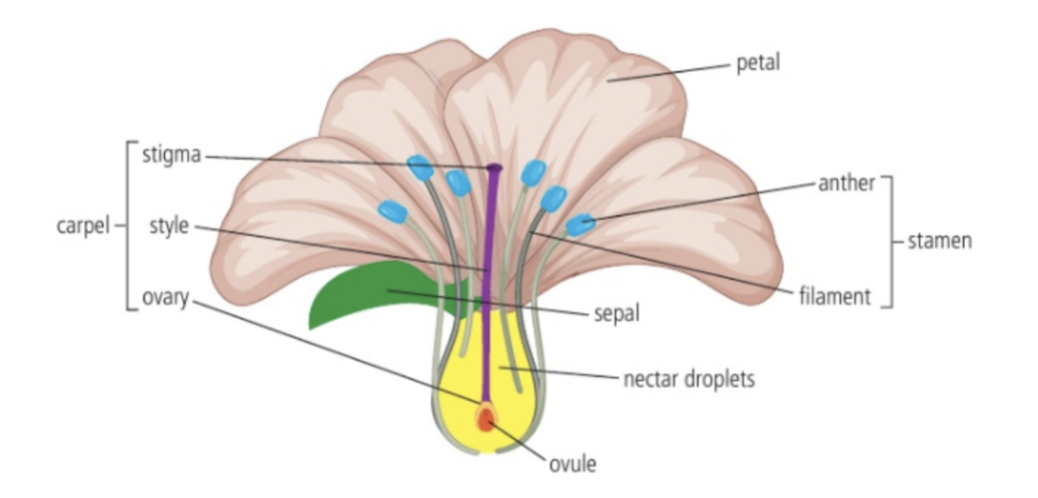
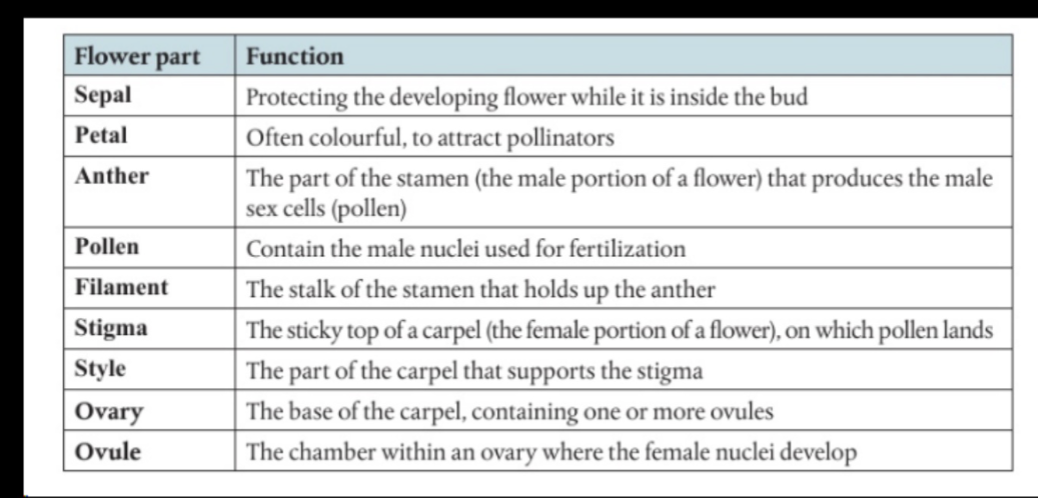
7. Label and annotate a seed
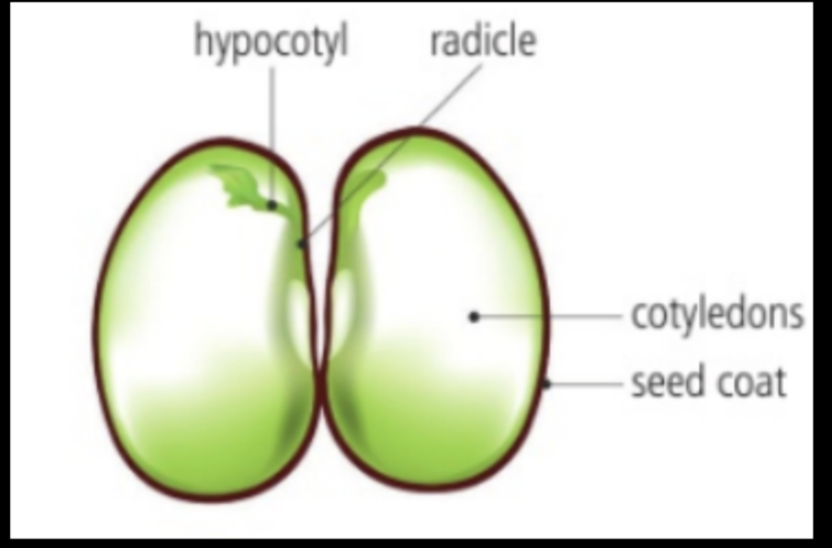
8. What is the xylem and what does it transport?
xylem is a transportation tube made of dead cells stacked up together with longing and pits to leave and enter
transports water and minerals up from roots to plants and leave
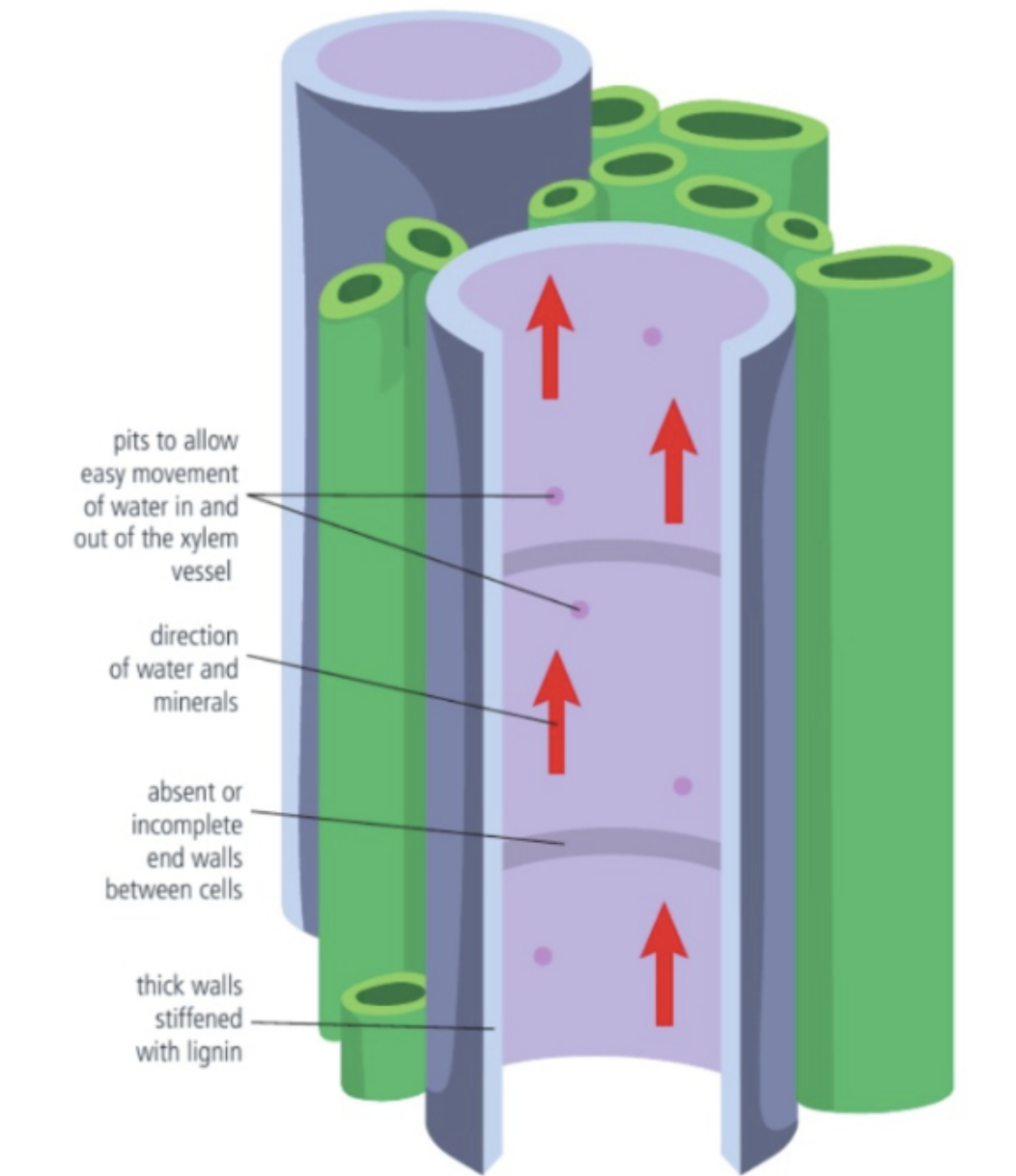
9. Draw and label the vessel elements of xylem and explain the importance of its structure to its function.
10. What is transpiration?
is the passive process on water loss from the leaves through transpiration pull
11. Describe the theory of how water moves up the plant during transpiration.
cohesion tension theory where water is pulled up through xylem tube so they all move upwards towards the leaf
there all cohesive to each other and al move up collectictly
water is pulled by the xylem tissue by capillary causing a negative pressure at zyelm tube that causes water to move up
12. Discuss how increasing temperature, light, humidity, and wind affect the transpiration rate in plants
TEMP: increases rates as it evaporates water and causes molecular water movement creating for more water loss
LIGHT: increases rate, simualrse guard cells to open stomata for photosysnteiss/respiration(co2 in and 02 out)
WIND: increases rate as wind removes water vapor at somata and increases for concernation gradient from high to low outside the leaves
HUMUDITY: decrease rate, as there already water molesutes outside lessens eh conceraton between inside and outside leaf
13. How do roots take up water?
though osmosis where water from soil moves to a lower concentration of the root hair cells and not xylem tissue
14. What are stomata and how do they function in gas exchange and water loss?
microscopic opening on lower surface of leaves, composed of two guard cells that open and close
open = co2 enter leaf and water vapor and 02 leave
15. What is phloem and what does it transport?
vasular tissue that tnraposrts sugar and amino acids (sap) from the leaves to other parts of plants up and down as sinks
16. How does active translocation move phloem sap in plants?
xylem realizes water into sieve tubes and water will move from high pressure of xylem to low pressure of phloem by osmosis that causes sap into sieve tube allowing it to expand and move water with sugars along tube
17. What are sources and what are sinks in plants?
sources: leaf cell that produces sugar through photosynthesis
sinks= root cell sues these products for growth and development
18. Compare and contrast phloem and xylem
notes ples
19. What are meristems?
located at tips of shoots and roots regions that allow plant to conunisouly grow throughout life
20. What are the roles of apical meristems and lateral meristems in plant growth?
apical= primary growth of lenghthnenign at tops of shoots and roots that produce new leaves and flowers
lateral= secondary growth widening occurs at cambium and prodcuces bark on trees
21. Describe the processes of pollination, fertilization and seed dispersal and the roles of insects, animals, water and wind in these processes.
notes
22. What factors affect seed germination?
notes
23. What is phototropism?
notes
24. What are the roles of auxin and expansion in the mechanism of phototropism?
phythrome produced in growing tips fo shoots roots and growth buds of plants
enter phloem tissue and move though plan within phloem sap
when sunlight overhead the IAA molecules produced by apical meristem are evenly distributed in shoot though when sunlight only shade son side the IAA molecules move the far side and elongate causing it to bend towards light
enters cells with diffusion requires auxin efflux carriers to exit(active transport?)
25. What is the role of gibberellin in seed germination?
cures synthesis of amaysle breaking down starches into maltose allowing seed to access energy needed to grow
26. What is the role of the plant hormone cytokinin?
produced in root growing region, transported in xylem fluid best plant growth is when growing tips of shoots and roots have access to both cytokines and snail causes increase in cell divisiion
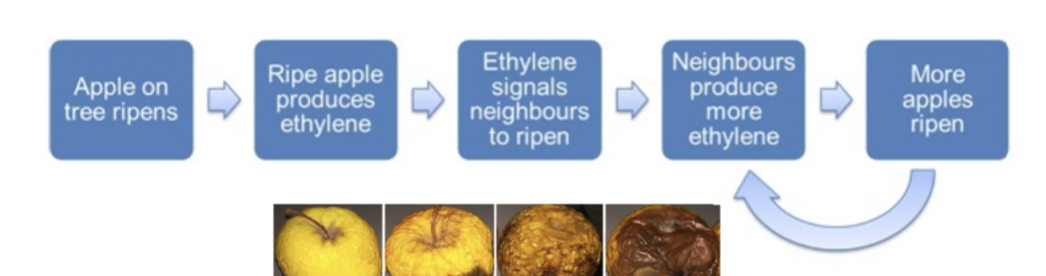
27. Explain the process of fruit ripening.
28. What are stem cells? + 29. What are the two unique properties of stem cells?
uspecilaized cells that can
self renewal and continosutly divide and replicate
recreate functional tissue and differetatite into specialized cells
30. Make a chart describing the four different types of stem cells.
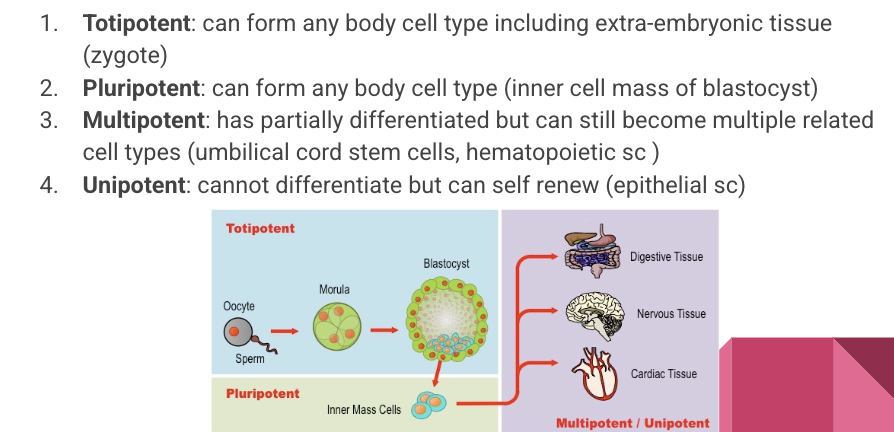
31. Describe how bone marrow and hair follicles are stem cell niches
because they present in high numbers due to regular proliferation also demonstrate differenration
rest check stem cells slide, SA:V slides, and notes especially on last question