Brain Anatomy
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
11/4/2024
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
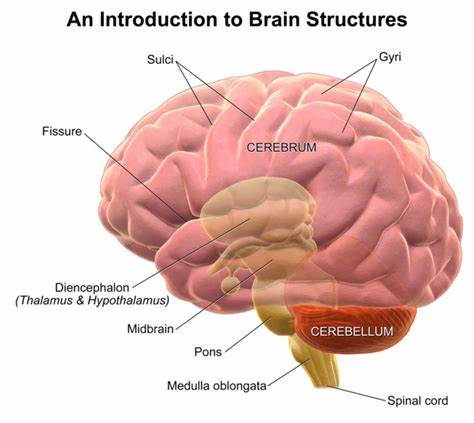
The Cerebrum
largest part of the human brain
location of all conscious processes
surface features: gyri & sulci
cerebral cortex is the outer surface
subcortical structures are found below the cortex
aka the forebrain
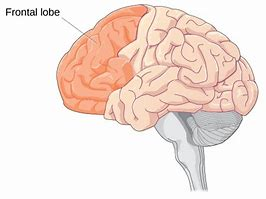
The Frontal Lobe
responsible for thinking and creativity
houses the motor area (voluntary movement and activity)
higher level cognitive functions- prefrontal cortex
critical thinking, puzzling, decision making
Broca’s area- language production
Olfactory cortex
sense of smell
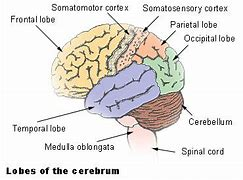
Parietal Lobe
memory of objects and their uses, directions
contains the sensory area (aka somatosensory cortex)
processes information from the body’s senses and receptors
Gustatory cortex
sense of taste
The Motor and Sensory Cortex
primary motor cortex- dedicated to voluntary movement
maps out specific body parts along a central sulcus
sensory cortex- processes information regarding touch, temperature, and pain
organized topographically to mirror the body
The Temporal Lobes
control hearing, speech, memory, emotion, and some langauge
location of auditory cortex
Wernicke’s area = speech comprehension
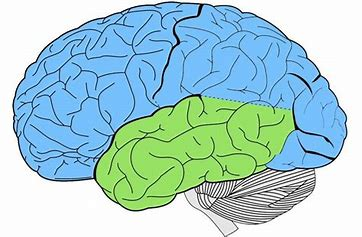
The Occipital Lobe
receives visual nerve impulses and turns them into images
Primary visual cortex
interprets visual information through connection to the eyes
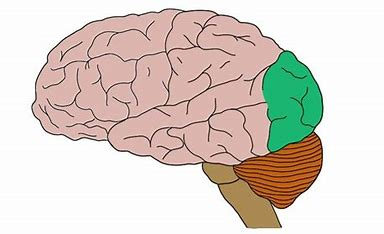
The Insular Lobe
located beneath the other four lobes, interior of the brain
related to behavior and feelings
specifically desires, cravings, and addiction
visceral association area
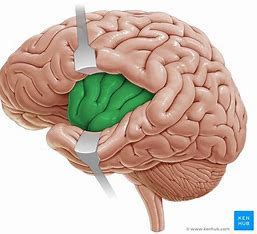
The Cerebellum
second largest portion of the brain
controls movement, posture, and balance
completes the initiation of action from the cerebrum
has a role in learning and memory
Arbor vitae
The Diencephalon
Thalamus
relay station for sensory impulses to the cerebral cortex
Hypothalamus
regulates homeostasis
Pituitary gland
posterior area produces hormones
Also contains optic tracts and pineal gland
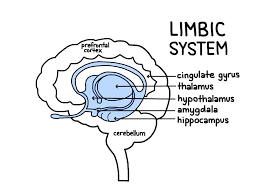
The Limbic System
Responsible for processing emotion and memory
Hippocampus
essential for learning and memory
Amygdala
The experience of emotion and tying emotion to our memories
Hypothalamus
homeostasis and bridge between nervous and endocrine systems
The Brain Stem
connection between the brain and spinal cord
divided into three parts
midbrain
pons
Medulla oblongata
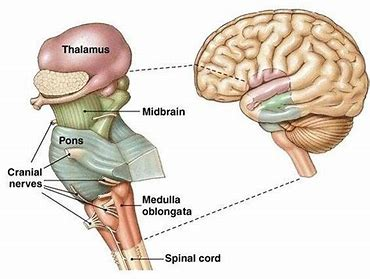
The Brain Stem made up of
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla oblongata
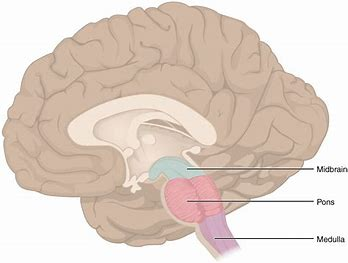
Midbrain
controls vision
hearing
eye movement
body movement
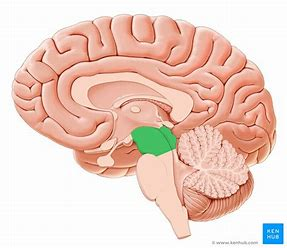
Pons
motor control and sensory analysis-linked to cerebellum
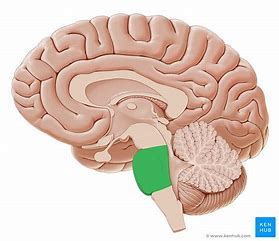
Medulla oblongata
controls vital body functions = breathing, heart rate, blood pressure regulation, swallowing, etc
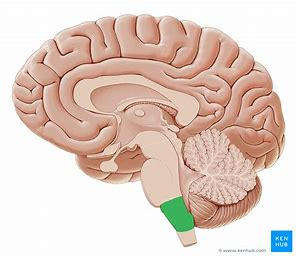
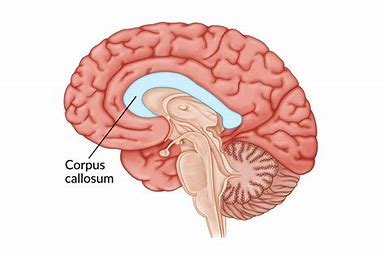
The Corpus Callosum
thick band of neural fibers that connect the two hemispheres of the brain
allows for communication and passage of information
each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body
Thalamus
acts as the brain's relay station, processing and transmitting sensory information to the appropriate areas of the cerebral cortex.
Amygdala
a small, almond-shaped cluster of nuclei located deep within the temporal lobe, involved in emotional processing, memory, and the regulation of fear responses.
Hippocampus
a critical structure for memory formation and spatial navigation, located in the medial temporal lobe.
Cerebral Cortex
the outer layer of the brain, responsible for higher-level functions such as thought, reasoning, and voluntary movement.