JC History - Early Christian Ireland
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
1
New cards
Pre-Christian Ireland
-Dominated by Celtic culture (language, laws, religion)
-Coincided with iron age
-Romans didn't conquer Ireland
-Druids controlled Celtic religion (pagan religion)
-Coincided with iron age
-Romans didn't conquer Ireland
-Druids controlled Celtic religion (pagan religion)
2
New cards
3
New cards
Iron age
Iron replaced bronze as the main metal for weapons + tools
4
New cards
Druid
spirtural figures simaller to Celtic priest with a foucos on nature and earth
5
New cards
Pagan religion
Believed in many gods
6
New cards
The coming of Christianity to Ireland
-Christians were in Ireland by early 5th century
-Some came from Roman Britain where they had been captured in raids by Irish warriors
-Others were Irish people who converted to Christianity after contact with British Christians
-The pope sent missionaries to visit the Irish Christians
-Palladius was the first missionary
-St Patrick was the most famous missionary
-Some came from Roman Britain where they had been captured in raids by Irish warriors
-Others were Irish people who converted to Christianity after contact with British Christians
-The pope sent missionaries to visit the Irish Christians
-Palladius was the first missionary
-St Patrick was the most famous missionary
7
New cards
Palladius
-First missionary sent to Ireland
-431 AD
-A bishop sent to 'the Irish who believe in Christ'
-431 AD
-A bishop sent to 'the Irish who believe in Christ'
8
New cards
St Patrick
-Born in Roman Britain
-Was captured at the age of 16 by Irish raiders
-He was a slave for 6 years + tended to sheep in the West of Ireland
-He escaped + returned to Britain
-He later became a priest + a bishop then returned to Ireland as a missionary
-Was captured at the age of 16 by Irish raiders
-He was a slave for 6 years + tended to sheep in the West of Ireland
-He escaped + returned to Britain
-He later became a priest + a bishop then returned to Ireland as a missionary
9
New cards
Ireland after missionaries
-Ireland was largely Christian after the 6th century
-This caused significant changes to Irish culture + society
-It replaced the pagan religion
-Celtic festivals were replaced with Christian ones
-This caused significant changes to Irish culture + society
-It replaced the pagan religion
-Celtic festivals were replaced with Christian ones
10
New cards
St. Patrick's Confession
-An account written by St Patrick
-It includes brief details about his life
-It explains why he did certain things + defends his name against any attacks
-The Book of Armagh in Trinity contains the earliest copy of the confession
-It includes brief details about his life
-It explains why he did certain things + defends his name against any attacks
-The Book of Armagh in Trinity contains the earliest copy of the confession
11
New cards
When were monasteries in Ireland built?
Early 6th century
12
New cards
first monastery built
inis mór founded by st enda on the aran islands around 500 AD
13
New cards
Who founded the monasteries
St íta
St Brigid
St Enda in the Aran Islands
St Finian of Clonard
St Ciarán of Clonmacnoise
St Brendan of Clonfert
St Brigid
St Enda in the Aran Islands
St Finian of Clonard
St Ciarán of Clonmacnoise
St Brendan of Clonfert
14
New cards
monks
men who deicaded themselfs to a religiuos oder and to live in a monastey
15
New cards
What happened in monasteries
-Centres of learning + culture
-Bible studied
-Manuscripts written
-Art made with metal + stone work
-Visitors welcome
-Pray
-Bible studied
-Manuscripts written
-Art made with metal + stone work
-Visitors welcome
-Pray
16
New cards
Manuscripts definition
handwritten texts
17
New cards
beehive hut
small stone hut shaped like a beehive where a monk slept
18
New cards
Monks lives
-Simple lives
-Strict rules
-Abott in charge
-Produced their own food
-They wore long tunics with woollen cloaks, and shoes or sandals
-Strict rules
-Abott in charge
-Produced their own food
-They wore long tunics with woollen cloaks, and shoes or sandals
19
New cards
How do historians + archaeologists know about Clonmacnoise?
1. Begin investigation with questions
2. Research sources for evidence to answer questions
2. Research sources for evidence to answer questions
20
New cards
Where was Clonmacnoise?
On the river Shannon, south of present day Athlone
21
New cards
Clonmacnoise: How old was it + who founded it?
-St Ciaran founded it in 549 AD
22
New cards
Clonmacnoise: Did many people live here?
-Clonmacnoise was a large urban area
-There was a fair green where fairs were held
-It was a large site
-A large population lived between the first + second rings around the monastery
-There was a fair green where fairs were held
-It was a large site
-A large population lived between the first + second rings around the monastery
23
New cards
Clonmacnoise: What did they work at?
-Clonmacnoise was a major centre of Christian art + learning
-Annals of Clonmacnoise + other manuscripts were produced in the scriptorium
-There is evidence of craftwork, animal slaughtering, metalworking, stone cutting + farming
-Annals of Clonmacnoise + other manuscripts were produced in the scriptorium
-There is evidence of craftwork, animal slaughtering, metalworking, stone cutting + farming
24
New cards
Clonmacnoise: What connection did the monastery have with the river?
-Traders could sail up + down the river
-Remains of a wooden bridge on the river Shannon were found. The timber dated back to 804AD
-Remains of a wooden bridge on the river Shannon were found. The timber dated back to 804AD
25
New cards
Clonmacnoise: Why was this location chosen for the monastery?
-It is the junction of the north-south route on the navigable River Shannon with the Eiscir Riada (Great Road) - a great glacial deposit - which was the main east-west route across Early Christian Ireland
26
New cards
Clonmacnoise: Was there only 1 wall around it?
-8th century manuscripts say there was 2 or 3 rings
-Excavation of a ditch showed at 2nd ring
-An aerial photo showed a 3rd ring
-Excavation of a ditch showed at 2nd ring
-An aerial photo showed a 3rd ring
27
New cards
Clonmacnoise: What use was made of the buildings?
-A cathedral was built in 909AD
-The annals also make reference to other churches + high crosses
-A round tower was built in 1124AD
-Postholes in other round towers show that wooden steps were built up to the high door
-The annals also make reference to other churches + high crosses
-A round tower was built in 1124AD
-Postholes in other round towers show that wooden steps were built up to the high door
28
New cards
Annals
historical records
29
New cards
round tower
a bell tower and a safe place for people (and teruses) if the monasterys came under attach
30
New cards
Scriptorium
A room in a monastery for writing or copying manuscripts
31
New cards
Refectory
dining hall
32
New cards
Dormitory
A room for sleeping
33
New cards
Oratory
Where monks prayed
34
New cards
layout of irish monastry photo
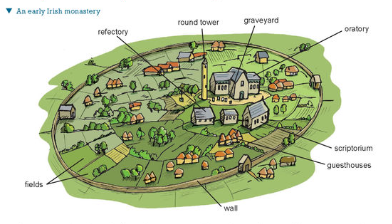
35
New cards
Technology used to investigate Clonmacnoise
-Geographical survey
-Virtual reality
-Underwater archaeology
-Virtual reality
-Underwater archaeology
36
New cards
Examples of other Monasteries
-Clonard
-Kells
-Cork
-Clonfert
-Glendalough
-Armagh
-Skellig Michael
-Kells
-Cork
-Clonfert
-Glendalough
-Armagh
-Skellig Michael
37
New cards
Monastic towns
-Towns with many lay people living around the monastery
-Centres of economic activity
-Centres of economic activity
38
New cards
Lay people
a non-ordained member of a church.
39
New cards
Remote Monasteries
-Out of the way monasteries away from towns
E.g. Skellig Michael
E.g. Skellig Michael
40
New cards
Skellig Michael
-A monastery built on an island off the West coast of Co. Kerry
-Monks lived in small stone beehive huts (carbelled roofs) beside a small stone church
-Monks lived in small stone beehive huts (carbelled roofs) beside a small stone church
41
New cards
Round towers
-Stone towers built in big monasteries
-25 to 40m tall
-4 windows on top floor facing north, south, east + west
-Used as belfries to call the monks to services
-Also used to hide valuables during attacks
-25 to 40m tall
-4 windows on top floor facing north, south, east + west
-Used as belfries to call the monks to services
-Also used to hide valuables during attacks
42
New cards
Belfries
The tower or steeple in which bells are hung to call monks to services
43
New cards
Work in a monastery
-Prayer was the main activity
-They prayed 6-8 times a day
-Farm work: ploughing, milking, harvesting + grinding corn
-Lay monks helped
-Monasteries were famous for their great works of art
-They prayed 6-8 times a day
-Farm work: ploughing, milking, harvesting + grinding corn
-Lay monks helped
-Monasteries were famous for their great works of art
44
New cards
What was the contribution of Christianity to Ireland?
-Reading + writing
-Contribution to art
-Contribution to Europe
-Contribution to art
-Contribution to Europe
45
New cards
Reading + writing
-Christianity brought reading + writing to Ireland
-First reading + writing was in Latin (language of the Catholic Church)
-Later it was in Irish (vernacular language)
-Early missionaries taught reading + writing
-These changes brought Ireland into written history
-It brought the learning of Roman scholars + early church writers to Ireland
-This was used to make laws
-First reading + writing was in Latin (language of the Catholic Church)
-Later it was in Irish (vernacular language)
-Early missionaries taught reading + writing
-These changes brought Ireland into written history
-It brought the learning of Roman scholars + early church writers to Ireland
-This was used to make laws
46
New cards
Ogham stones
-First form of writing was done on the sides of stones
-Lines carved represented words
-The ogham alphabet consisted of 20 letters based on the Latin alphabet
-Christianity made full use of the Latin language to write manuscripts
-Lines carved represented words
-The ogham alphabet consisted of 20 letters based on the Latin alphabet
-Christianity made full use of the Latin language to write manuscripts
47
New cards
Contribution to art
-Manuscripts
-High crosses
-Metalwork
-High crosses
-Metalwork
48
New cards
Manuscripts
\-Early manuscripts were written in Latin + later ones were written in Irish
\-Some recorded early Irish history
\-Some monks called scribes had skills in writing + illuminating religious books
\-They practiced on wax tablets
\-They copued manuscripts in a scriptorium onto vellum or parchment
\-They used reeds or quills + ink (made of minerals, plants + leaves)
\
\-Some recorded early Irish history
\-Some monks called scribes had skills in writing + illuminating religious books
\-They practiced on wax tablets
\-They copued manuscripts in a scriptorium onto vellum or parchment
\-They used reeds or quills + ink (made of minerals, plants + leaves)
\
49
New cards
Examples of manuscripts
1. Annals of Clonmacnoise - written in Clonmacnoise, original copy lost but a copy was made in the 17th century
2. Cathach - psalms in Latin on vellum, oldest manuscript in Ireland, kept in the Royal Irish Academy
3. Book of Durrow - a copy of the Gospels of Matthew, Mark, Luke + John in Latin, it is copied on vellum + housed in Trinity
4. Book of Kells - copy of the 4 gospels in Latin, copied on vellum + housed in Trinity
5. Book of the Dun Cow - Lebor na hUidre is a vellum manuscript with stories + legends from Ancient Ireland, it was written in Clonmacnoise, it is the oldest manuscript written in Irish + is held in the Royal Irish Academy
2. Cathach - psalms in Latin on vellum, oldest manuscript in Ireland, kept in the Royal Irish Academy
3. Book of Durrow - a copy of the Gospels of Matthew, Mark, Luke + John in Latin, it is copied on vellum + housed in Trinity
4. Book of Kells - copy of the 4 gospels in Latin, copied on vellum + housed in Trinity
5. Book of the Dun Cow - Lebor na hUidre is a vellum manuscript with stories + legends from Ancient Ireland, it was written in Clonmacnoise, it is the oldest manuscript written in Irish + is held in the Royal Irish Academy
50
New cards
High crosses
-Minks carved high stone crosses
-Has scenes from the Bible on them
-Taught people about Christianity
-Has scenes from the Bible on them
-Taught people about Christianity
51
New cards
Metalworking
-Monks produced silver chalices, croziers + brooches
-They were decorated with gold, amber + enamel
-The intricate gold writing is called filigree
-Their designs are influenced by the Celts
-They were decorated with gold, amber + enamel
-The intricate gold writing is called filigree
-Their designs are influenced by the Celts
52
New cards
Contribution to Europe
-Irish monks founded monasteries abroad
-They made manuscripts in the Irish style + converted tribes to Christianity
-It is considered the 'Golden age' in Irish learning
Examples:
-St Colmcille founded Iona monastery in Scotland
-St Columbanus founded monasteries in France, Switzerland + Italy
-They made manuscripts in the Irish style + converted tribes to Christianity
-It is considered the 'Golden age' in Irish learning
Examples:
-St Colmcille founded Iona monastery in Scotland
-St Columbanus founded monasteries in France, Switzerland + Italy
53
New cards
St. Patrick's Day
-National holiday
-Irish national identity
-Parades are tourist attractions
-Brings the Irish diaspora together
-Irish national identity
-Parades are tourist attractions
-Brings the Irish diaspora together
54
New cards
Rules of St Columbus
-Must obey superiors
-Rule of silence must be obeyed
-No gorging or drunkenness, must eat coarse food
-Satisfied with few possessions
-Keep company with many
-Rule of silence must be obeyed
-No gorging or drunkenness, must eat coarse food
-Satisfied with few possessions
-Keep company with many
55
New cards
Casula
A cloak worn by early Christian monks.
56
New cards
Tonsure
A part of a monk's or priest's head left bare on top by shaving off the hair
57
New cards
Matins
morning prayers
58
New cards
Vespers
evening prayer
59
New cards
Cloisters
Covered walkway