Chemistry, matter and lab saftey
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/81
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
1
New cards
physical science
the study of matter and energy
2
New cards
chemistry
The study of the properties of matter and how matter changes
3
New cards
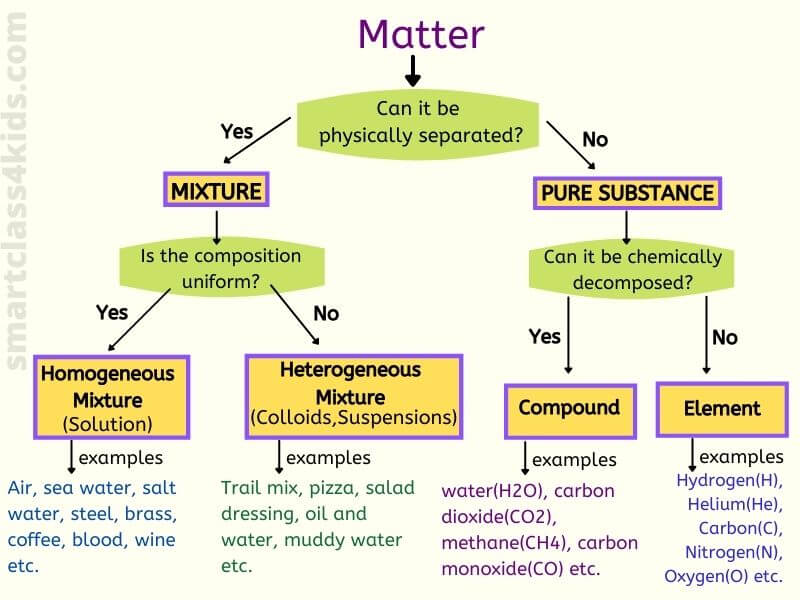
matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space
4
New cards
What is air
homogeneous mixture
5
New cards
elements
the simplest form of a pure substance it can't be broken down anymore
6
New cards
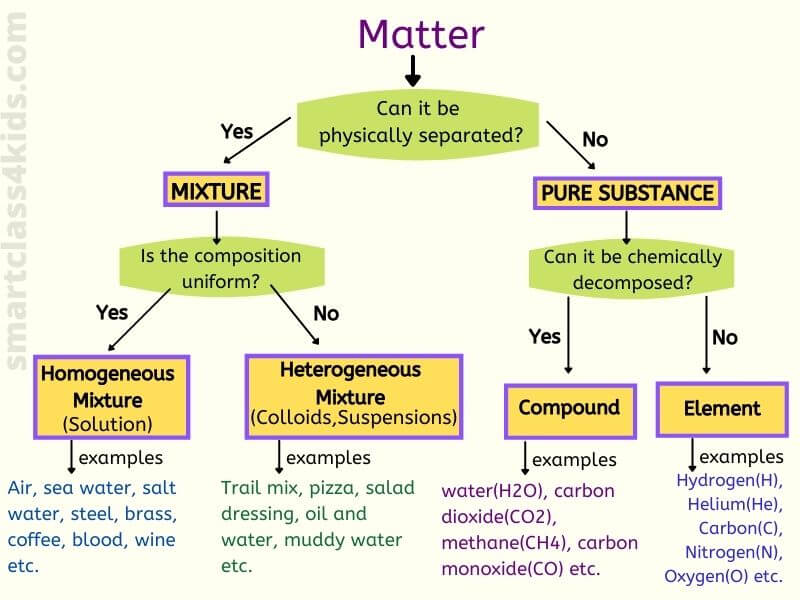
compounds
2 or more elements chemically combined
\-can be broken down by chemical means
\-can be broken down by chemical means
7
New cards
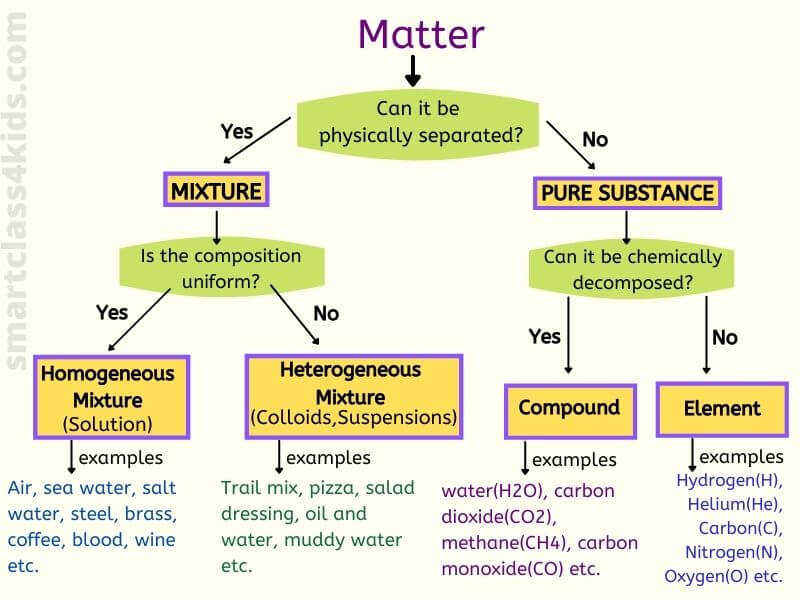
mixtures
A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined
8
New cards
heterogeneous
composed of different kinds not uniform
9
New cards
Homogeneous
the same throughout
10
New cards
solutions
A homogeneous mixture in which one or more substances are dissolved in another substance.
11
New cards
collid
heterogeneous mixture whose particles never settle
12
New cards
pure substance
A substance is made of only one kind of matter and has definite properties.
13
New cards
homogenous uniform
uniform but has indefinite properties
14
New cards
solid
Definite shape and volume
15
New cards
liqued
the state of matter that has a definite volume but not a definite shape
16
New cards
gas
A state of matter with no definite shape or volume
17
New cards
plasma state of matter
high temperature state with charged particles
18
New cards
what happens when a substance changes states?
it absorbs or releases energy
19
New cards
solid to liquid
melting
20
New cards
liquid to solid
freezing
21
New cards
liquid to gas
evaporation
22
New cards
solid to gas
sublimation
23
New cards
gas to liquid
condensation
24
New cards
melting point
The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid
25
New cards
boiling point
The temperature where substance boils or condenses
26
New cards
Density
ratio of mass to volume, dose not matter how much there is of object
27
New cards
density formula
D\=m/v
28
New cards
physical property
a characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance
29
New cards
examples of physical properties
Color, odor, mass, density, specific heat, malleability, ductility, conductivity, melting point, boiling point, magnetism.
30
New cards
Ductility
The ability to be pulled into thin wires
31
New cards
Malleability
The ability of a metal to be molded into thin sheets.
32
New cards
chemical properties
Characteristics that cannot be observed without altering the substance
33
New cards
examples of chemical properties
flammability, reactivity, corrosiveness, oxidation
34
New cards
intensive property
sane for substance no matter how much there is ex: color, texture, hardness, Density
35
New cards
extensive property
a property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample Ex: mass, value, energy
36
New cards
volume
The amount of space an object takes up
37
New cards
Quantitative
Data that is in numbers
38
New cards
qualitative
Data in the form of words and visual observations
39
New cards
physical change
A change in a substance that does not involve a change in the identity of the substance ex: state, solubility, size ,shape ( 4 s's)
40
New cards
chemical change
A change in matter that produces one or more new substances ex: burning, rusting, baking
41
New cards
beaker
used to hold liquids
42
New cards
Graduate cylinder
A measuring device is used to measure the volume of a liquid. very accurit
43
New cards
test tube
used for holding, mixing, heating small amounts
44
New cards
watch glass
Used as a cover or sample plate
45
New cards
tongs
tool used to pick up hot glassware
46
New cards
Erlenmeyer flask
used to hold liquids, has narrow neck to prevent splashes
47
New cards
scoopula
Used to transfer solids
48
New cards
funnel
for pouring liquid or other substance through a small opening
49
New cards
wire gauze
used to support a container (such as a beaker or flask) during heating
50
New cards
ring stand
Used as a support; Rings and clamps attach to the stand
51
New cards
Bunsen burner
used to heat substances
52
New cards
iron ring
to fasten to the ring stand as a support for apparatus
53
New cards
evaporating dish
Used to evaporate liquids from a mixture
54
New cards
googles
should be worn over eyes the whole lab
55
New cards
pipettes
Accurately measure small volumes of liquid (usually between 0-10mL)
56
New cards
Eyedropper
allows you to add a small amount of liquid, one drop at a time
57
New cards
hot plate
a lab tool used to heat substances
58
New cards
utility clamp
used to hold laboratory glassware
59
New cards
Volumetric Flask
used to make known concentrations of a solution of a specific volume
60
New cards
Filter Paper
Used to separate a solid from a liquid
61
New cards
sparker
used to light bunsen burner
62
New cards
crucible tongs
used to pick up and hold small items
63
New cards
test tube clamp
clamp used to hold hot test-tube
64
New cards
balance
measures mass in grams
65
New cards
ceramic triangle
A triangular-shaped device that can be placed on an iron ring to hold a crucible
66
New cards
what should you do before a lab?
1. Read lab the night before
2. ask questions before lab starts
67
New cards
when should you get help from the teacher?
1. If there's an emergency ( glass breaking, injury, spill)
2. if a chemical gets on someone
68
New cards
what should you never do in the lab?
1. eat or drink
2. preform unauthorized experiments
3. leave a flame unattended
69
New cards
3 clothing requirements for lab
1. closed toed shoes
2. wear goggles
3. tie back long hair
70
New cards
what should you do at the end of every lab?
clean up and wash hands
71
New cards
how long to use the eye wash
squeeze and run over eyes for 15 minutes
72
New cards
what should you do before using glassware?
check that its clean and has no cracks
73
New cards
what should you do before washing hot glassware?
wait for it to cool down or else it might crack.
74
New cards
if you are using heated glass what should you use to pick it up
tongs
75
New cards
what should you do if you don't finish the lab
talk to the teacher
76
New cards
when should Google be worn
whenever chemicals or heat or glassware is used
77
New cards
when should you read lab instructions
the night before
78
New cards
what should you do if there's a fire drill
turn of flames and cover opened containers
79
New cards
should solids go in the sink
NO
80
New cards
should you lick chemicals in the lab
NO
81
New cards
physical changes examples
state of matter, solubility, size, shape
82
New cards
chemical change indicators
color
bubbles
smoke
oder change
temp change without added/removed heat
bubbles
smoke
oder change
temp change without added/removed heat