WELLNESS and VACCINES
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Wellness Care Foundations
Illnesses are easier to prevent than treat
Prevention is for both the individual and the group
Felines hide illness better than dogs
78% of dog owners seek preventative care/year (AVMA)
47% of cat owners seek preventative care/year (AVMA)
Canine Life Stages
Puppy - Birth to sexual maturity
Junior - 6-12 months
Adult - 1-7 years, stopped growing
Mature - 7+ years
Senior - Last ¼ of life expectancy
Geriatric - life expectancy, stay here till death
Feline Life Stages
Kitten - Birth to sexual maturity
Junior - 7 months to 2 years
Adult - 3-6 years, stopped growing
Mature - 7-10 years
Senior - 11-14 years
Geriatric - 15+ years
Puppy and Kitten/junior wellness
Vet evaluation immediately upon acquistion
Physical exam
Spaying/Neutering at 4-6 months of age
Varies based on breed, size, and health
reduces health risks
Wellness visits every 3-4 weeks until 16 weeks old
Vaccines
Endo/Ecto Parasite treatment and prevention
Behavior/socialization
Adult dog/cat wellness exam
Annual to semiannual visits
Physical exam
Metabolic panel for baseline values
Dental care
Most need first dental prophylaxis between 3-5 years
Toy breeds and other individuals may need it sooner
Parasite control
Vaccines
Mature/Senior/Geriatric Wellness exam
Semiannual visits
Physical exam
Metabolic panel to look for changes
Behavior: Cognitive dysfunctions
Nutrition: don’t need as many calories
Parasite control
vaccines
Preventative Care
Grooming
Metabolic screening
Nutrition
Dental care
Exercise
Parasite control
Vaccinations
Fecal float
Heartworm test
Certain breeds are predisposed to certain diseases
Metabolic Screening
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
RBC, WBC, platelets
Chemistry
Indicated organ function
Urinalysis
helps evaluate renal health
Start screening between 3-5 years
or before anesthetic event
May need to start sooner depending on individual diseases or issues
Dental Care
Begins in puppy/kittenhood
Observe bite and eruption of adult teeth
Deciduous teeth fall out
Palate defect
Tooth brushing recommended as adult teeth erupt
Dental radiographs
Periodontal disease VERY common: 80-90% by age three
Importance of exercise
>50% of cats and dogs are overweight/obese in US
Shorter life span - as much as 2 years
Obesity linked to increases risk of disease
Cancer
Diabetes
Heart disease
Osteoarthritis
Bladder Stones
Anesthetic complications
Hypertension
Canine Exercise
Minimum 30 minutes/day
Depends on age, health, and breed
Reduces behavior issues
Prevents increased BCS
Puppies: More energy = more play
Adults: Depends on breed
Seniors: Decreased energy levels, weaker joints
Feline Exercise
Crepuscular animals
Hands are not toys!
Behavioral issues
Short sessions
15-20 minutes 2x/day
Avoid
String, thread, twine (foreign body)
RER
Resting Energy Requirement - energy required for a healthy animal at rest
MER
Maintenance Energy Requirement - calories needed/day to maintain weight
Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO) recognizes 4 catergories
Growth, Maintenance, Gestation/Lactation, All life stages
Considering Nutrition
Dogs are omnivores
Cats are obligate carnivores
NEED animal protein
Dog eating cat food?
vomiting, diarrhea, pancreatitis
Cats eating dog food
Deficiencies in Vit. A, Taurine, and fatty acids
Homemade diets
Hard to make nutritionally balanced
No scientifically-supported benefits
Why?
Picky eaters
Concerns over recalls
More expensive
Nutrition deficiency/excess can lead to: Malnutrition, Obesity, Muscle loss, Congestive heart failure, Vision loss, Skin problems, Weakened bones and joints
Raw Diets
Discouraged by American Veterinary Medical Association
Raw food more likely to be contaminated with:
Salmonella spp. - severe diarrhea
Listeria monocytogenes - mortality rate 20-30% in humans
MDR Escherichia coli - diarrhea, vomiting
Public health risk
If client is feeding raw:
Discourage allowing their dogs to lick their faces
WEAR GLOVES when working with patient
3 things raw food are likely contaminated with
Salmonella spp. - severe diarrhea
Listeria monocytogenes - mortality rate 20-30% in humans
MDR Escherichia coli - diarrhea, vomiting
Ectoparasites
Fleas, Ticks, Ear mites
Fleas
Lifecycle: 21-28 days
Females lay up to 50 eggs/day (2000 in a life time)
Difficult to treat homes
Time consuming
Can take months
Clinical signs: Scratching, hair loss, Anemia
MOST COMMON ectoparasite
Ticks
Carry many diseases
5 common species in US
4 life stages: Egg → Larva → Nymph → Adult
Ticks feed on mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians
About 900 species of ticks
Common ticks
Deer tick, Lone Star tick, Rocky Mountain Wood tick, American Dog tick, Brown dog tick
Tick borne diseases
Lyme Disease:
Bacterial infection
Expanding red rash
Deer tick
Tick paralysis
Immune system reaction
Component in tick saliva
Neuromuscular/Respiratory
Ehrlicia
Bacterial infection
lone star and deer ticks
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Lone star and American dog tick
Babesia
Blood parasite
Flu-like symptoms
Ear Mites
Highly contagious!
Live on cats, dogs, rabbits, and ferrets
5 Life Stages
3 weeks from egg to adult
Live for 2 months
Entire lifecycle on host animal
SECOND most common ectoparasite
Zoonotic
Ectoparasites Preventatives
Many varieties to choose from
Comes in topical, oral, and collar
recommend based on client preference
Heartworm has an injectable version
Some have more coverage than others
NEVER use dog flea/tick products on cats
Can happened in cats if given dog flea/tick product
Pyrethrin Toxicity
Heartworm disease
Transmitted via mosquitos
6-month life cycle from larva to adult
Advanced = caval syndrome
Clinical signs
Appear when disease is advanced
Lethargy
Coughing
Anemia
Ascites
Damage to heart and lungs
Helminth Parasites
“Worms”
Many zoonotic
Dangerous for young animals/people
Can cause issues with:
Respiratory system
Integumentary system
Neurological system
Circulatory
Prevention:
Deworm pets regularly
Control fleas
Perform fecal floats
Feed cooked food
remove/dispose of feces
Diagnosed with fecal float
Tapeworms
Large, flat, segmented worm
Larval fleas eat tapeworm eggs
Dipylidium caninum - dog/cat tapeworm
Zoonotic
Taenia psisiformis - rabbit tapeworm
Not zoonotic
Worldwide distribution
Clinical Signs: Weight loss, Dull hair coat, Scooting
Whipworms
Trichuris Vulpis - dog
T. Campanula, T. serrata - cat
Uncommon
Species specific - above not zoontic
Ingest blood from cecum
Clinical signs:
Mucoid diarrhea
Weakness
Dehydration
Roundworms
Zoonotic!
Toxocara sp. (ascarids)
Life cycle from 14-80 days
Depends on species
Live for 4 months
Primarily causes disease in puppies
Transmission
Ingestion of eggs from environment
Trans-mammary
In-utero
Live in the intestine
Hookworms
Zoonotic!
Ancylostoma sp.
Live in intestine
Feed on blood
causes anemia
Transmission via:
ingesting eggs
Trans-mammary/transplacental
Grooming feet
Treatment of Helminths
PREVENTION!
Prophylactic deworming recommended
Medications
Many options
Most common
Pyrantel
Praziquantel
Fenbendazole
Protozoal Parasites
Single celled-organisms
Common diseases caused by:
Coccidia
Giardia
BOTH are zoonotic
Both live in the intestines
Treat with anti-protozoal meds
Coccidia
Most common genus is Isospora
Four infect dogs
Two infect cats
Sexual and asexual reproduction
Species specific
Transmission Via:
Feces
SEVERE diarrhea
Mostly effects puppies and immunocompromised adults
Giardia
6 distinct species
Found in contaminated
Water
Soil
Food
Feces
Worldwide, children <5 years over-represented
Clinical Signs:
Diarrhea
Nausea
Abdominal pain
Malabsorption of nutrients
Vaccinations
Stimulates body’s response against disease
Build resistance to specific infections
Improves immune system
Safe and effective
Preventative healthcare
Encourages veterinary-client relationship
Antigen
Killed or weakened form of virus or bacteria. Trains the immune system to recognize and fight a pathogen
Adjuvants
Helps boost the body’s immune response to an antigen
Preservatives
ensures vaccine stays safe
Stabilizaers
Protects vaccine during transport
What’s in a Vaccine?
All ingredients of a vaccine play an important role in ensuring a vaccine is safe and effective.
Antigen, Adjuvants, Preservatives, Stabilizers
Are Vaccines Necessary
Yes! Prevention is always better than treatment
Much cheaper to vaccinate than treat
Benefits outweigh risks
Protects people and other animals
Rabies required BY LAW!
Not always 100% effective
Types of Vaccines
Attenuated (live, modified live, live attenuated)
Inactivated (killed)
Recombinant (Polysaccharide, conjugate, viral-vectored)
Toxoid
Attenuated vaccine
Long duration of immunity
More likely to prevent both infection and disease
Requires careful storage and handling
Refrigeration
Administer promptly after reconstitution
EXAMPLES: most canine distemper viruses, parainfluenza, parvovirus, adenovirus-2
Inactivated vaccine
Stable products that cannot induce disease
Shorter duration of immunity than attenuated
Require an adjuvant to induce sufficient immunity
May require more frequent dosing
May be associated with adverse reactions
Protects against disease, but no infection
EXAMPLE: rabies, influenza, lyme, some Lepto, parenteral bordatella vaccines
Recombinant vaccine
Laboratory-made vaccines
Uses the gene of a pathogen inserted into a virus, bacterial plasmid, single protein alone or with antigens
Antigens are purified and used as active ingredient in vaccine
Significant variability in terms of immunity and frequency of booster doses
EXAMPLES: canarypox virus-vectored canine distemper, some lyme vaccines
Toxoid Vaccines
Creates immunity to the toxin produced by the organism rather than the organism itself
Shortest duration of immunity of all vaccines
Do not prevent infection
EXAMPLES: Western diamond back rattlesnake toxoid, tetanus toxoid
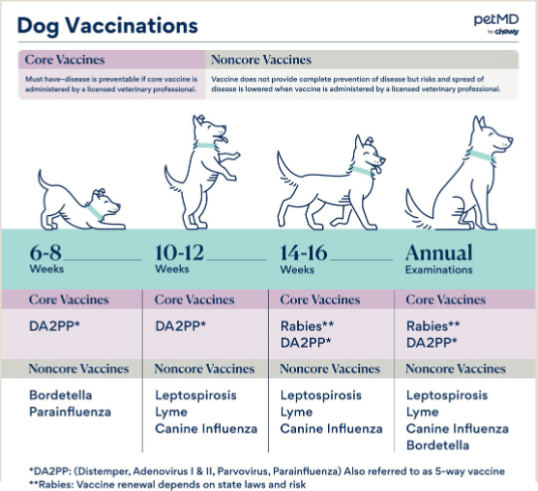
Canine CORE vaccines
DHPP
Canine distemper, Infectious hepatitis, Parvovirus, Parainfluenza, Leptospirosis (new in 2024), rabies
Canine Distemper
Caused by paramyxovirus (closely related to measles)
Highly contagious and potentially lethal
Spread through:
o Direct contact with infected animal or object
o Airborne exposure
o PlacentaTwo stages
All dogs at risk, especially unvaccinated puppies <4 months old
Raccoons, foxes, skunks, wolves, coyotes
Not zoonotic
No cure, treat symptomatically
Infectious Hepatitis
Infectious Hepatitis
Caused by an adenovirus
Spread via consumption of infected:
o Nasal discharge
o Saliva
o Urine
o FecesTargets liver, spleen, lung, kidneys, and intravascular space
Can be caused by accumulation of copper
Not zoonotic
Parvovirus
EXTREMELY contagious (full isolation mandatory)
Unvaccinated dogs and puppies at high risk
Transmitted via infected feces but can live in the environment for extended periods
Breeds at higher risk:
◦ Rottweilers, pitbulls, dobermans, GSDs, English Springer SpanielClinical signs:
◦ Vomiting, hemorrhagic diarrhea, hypotension
Parainfluenza
Highly contagious viral lung infection
Component of canine infectious respiratory complex
Shares similarities with distemper
Excreted from respiratory tract
Unrelated to canine influenza
Most common pathogenic agent of tracheobronchitis
Leptospirosis
Caused by spriochete bacteria Leptospira
Zoonotic! Barrier Isolation!
o Contain urine in collection system if possibleFound in soil and water
o Common in areas with high annual rain fall4 common strains
o Leptospira canicola, L. icterohaemorrhagiae, L. pomona, L. grippotyphosaLeads to kidney and liver failure
Antibiotics and supportive care
Rabies
FATAL viral infection affecting the CNS
Caused by both rabies virus and lyssavirus
Spread through:
o Saliva, scratches, direct contact with mucosaTwo stages
o Furious (encephalitic)
o ParalyticZoonotic
o 59k people/year
Canine Non-Core Vaccines
Lyme, Bordatella, Canine influenza, Toxoids depend on environment
Lyme
Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria
Transmitted via ticks
o Most commonly deer tick in midwest
o Different species globally – not all carry lymeZoonotic!
Treated with antibiotics
Common clinical signs:
o Painful/swollen joints
o Mild fever
o Hyporexia
Bordatella
Bordatella bronchiceptica – HIGHLY CONTAGIOUS!
Spreads through:
o Direct contact (licking, nuzzling)
o Air
o Contaminated fomites (you)Component of canine infectious respiratory complex
Common in dogs in daycare, boarding, etc.
Clinical signs:
o Lethargy, mild fever, cough
Canine Influenza
Caused by viral influenza virus –
Type A
o H3N8 and H3N2Highly contagious
Very similar to parainfluenza
Component of canine infectious respiratory complex
Transmitted via:
o Direct contact, coughing, fomitesTreatment is supportive care
Canine Vaccine Schedule
Feline CORE Vaccines
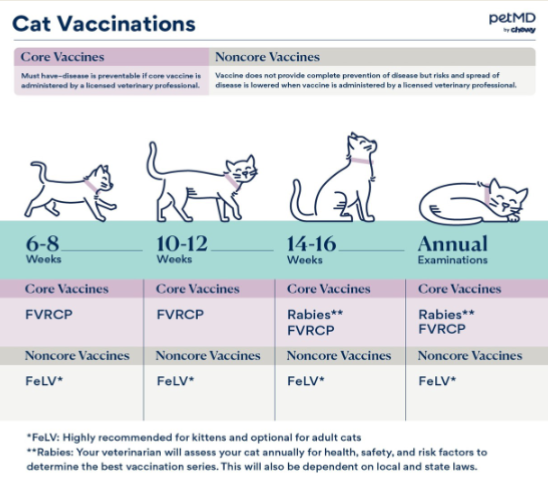
FVRCP
Feline viral rhinotracheitis, calcivirus, panleukopenia
Rabies
FeLV (in some cases)
Rhinotracheitis
Highly contagious – barrier isolation!
Caused by herpesvirus type-1
Called "cat flu/URI/herpes"
Usually not serious except in kittens
Can lead to respiratory compromise
Very common
Component of feline respiratory disease complex
Calicvirus
Highly contagious – barrier isolation!
Caused by a virus in the Caliciviridae family
Similar to rhinotracheitis
o Oral ulceration commonTransmitted via aersol droplets and fomites
Component of feline respiratory disease complex
Panleukopenia
Caused by a parvovirus
Highly contagious – often fatal
Kittens are most commonly affected
Transmitted through:
o Infected feces, respiratory secretions, and fomitesRoaming animals at higher risk of exposure
FeLV
Feline Leukemia Virus caused by a retrovirus
ONLY a core vaccine for kittens <1 year and outdoor cats
Transmitted via saliva and nasal secretions
Most common infectious disease in cats
Clinical signs:
o Anorexia, weight loss, poor coat condition, fever, diarrhea, gingivitis, seizuresWeakens immune system, but some cats become immune
Cats can live normal lives
No Vaccine FIV
Feline Immunodeficiency Virus - "Kitty aids"
Retroviral infection
Transmitted via bite wounds from infected cat
- Commonly seen in intact males with outdoor accessNo cure, but average lifespan
o If they don't also have FeLVFound worldwide
FIV
Feline Immunodeficiency Virus
Feline Vaccine Schedule
Vaccine Reactions
Can happen to any animal
Most Common:
Hyperthermia
Hives
Vomiting
Diarrhea
Lethargy
Tenderness
Pain at injection site
Can become an emergency!
Anaphalaxis may occur
Group at greatest risk
Small breed young adults (1-3 years old)
Most reactions occur the same day