ABI - Final Exam Assignments/IClickers
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
![<p><strong>IClicker: </strong>Michaelis-Menten kinetics depend upon a steady state assumption. Which of these statements are included in that assumption?</p><p>(A) [S] > [E]</p><p>(B) The substrate will become product at a constant rate.</p><p>(C) Rate of ES formation = Rate of ES breakdown.</p><p>(D) All of the above</p><p>(E) None of the above</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3de87eea-607f-473f-ab17-2bf284adbbe2.png)
IClicker: Michaelis-Menten kinetics depend upon a steady state assumption. Which of these statements are included in that assumption?
(A) [S] > [E]
(B) The substrate will become product at a constant rate.
(C) Rate of ES formation = Rate of ES breakdown.
(D) All of the above
(E) None of the above
(D) All of the above
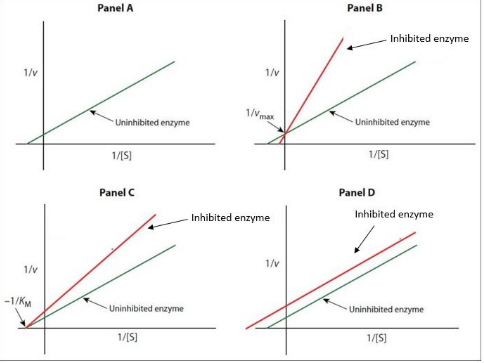
IClicker: Which panel best represents the changes to enzyme kinetics if you applied a noncompetitive inhibitor?
C
IClicker: Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitors like enalapril and lisinopril are competitive inhibitors with angiotensin I, which is converted to angiotensin II by ACE. In comparing the inhibitors in the reaction, the KI of enalapril is (1 × 10-9 M), and the KI of lisinopril is (7 × 10-5 M). Given the KI, which chemical is the most effective inhibitor?
(A) Enalapril
(B) Lisinopril
(A) Enalapril
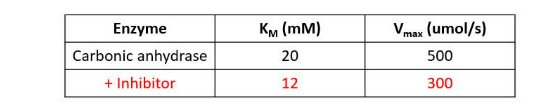
IClicker: In the table are enzyme kinetics for the enzyme carbonic anhydrase and the effect of its inhibitor.
By which form of inhibition is the inhibitor most likely working?
(A) Competitive
(B) Uncompetitive
(C) Noncompetitive
(B) Uncompetitive
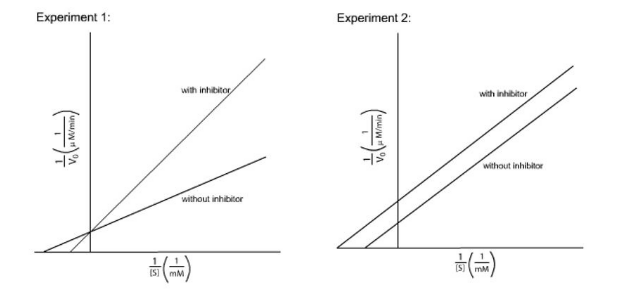
IClicker: The following figures show the Lineweaver-Burk plots of 2 different inhibitor experiments. Which experiment is using an uncompetitive inhibitor?
(A) Experiment 1
(B) Experiment 2
(C) Neither
(B) Experiment 2.
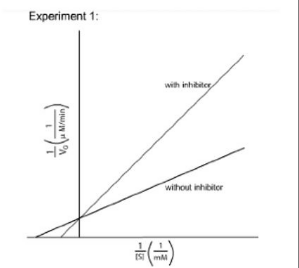
IClicker: In “Experiment 1,” an inhibitor is applied. The Lineweaver-Burk plot is below. What kind of inhibition is this, and what happens to Vmax?
(A) Competitive; Vmax increases
(B) Competitive; Vmax decreases
(C) Noncompetitive; no change in Vmax
(D) Competitive; no change in Vmax
(E) Noncompetitive; Vmax decreases
(D) Competitive; no change in Vmax
IClicker: Which rate constant(s) represent the formation of ES complex?
(A) k1
(B) k2
(C) k-1
(A) k1
IClicker: A person with severe asthma has difficulty exhaling, causing CO2 accumulation. What condition occurs?
(A) Metabolic acidosis
(B) Metabolic alkalosis
(C) Respiratory acidosis
(D) Respiratory alkalosis
(C) Respiratory acidosis
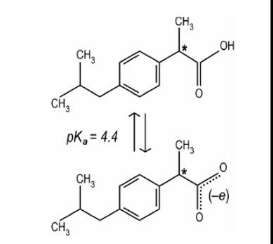
IClicker: A person takes ibuprofen (pKa = 4.4). It is best absorbed protonated. Is it more likely to be absorbed in the stomach (pH = 2.4) or the small intestine (pH = 6.4)?
(A) Stomach
(B) Intestine
(A) Stomach
IClicker: A clinical lab technician uses RT-qPCR to compare levels of SARS-CoV-2 virus in nasal swabs from two patients.
Ct values were: Sample A = 15; Sample B = 28.
Based on the q PCR results, assuming the same amount of nasal secretion was tested, which person has a greater viral load?
Sample A
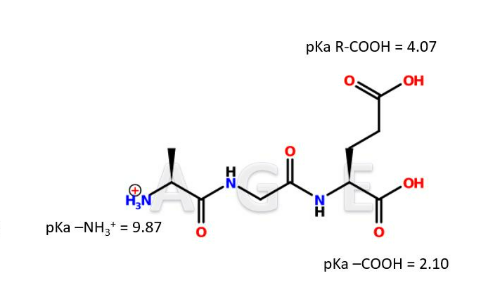
IClicker: To which pH do you think the tripeptide A-G-E is exposed in the image below?
(A) pH = 1
(B) pH = 3
(C) pH = 7
(D) pH = 9
(E) pH = 11
(A) pH = 1
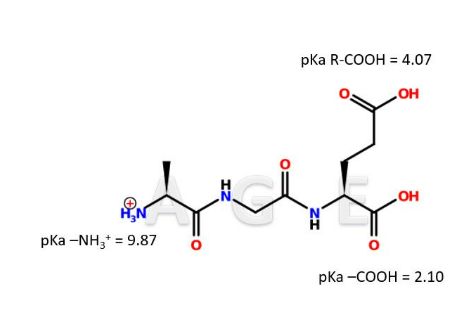
IClicker: What is the isoelectric point of the tripeptide A-G-E?
3.085
IClicker: When an inhibitor binds directly to the enzyme substrate complex but not to the free enzyme, this is best known as ____.
(A) Competitve Inhibition
(B) Uncompetitive Inhibition
(C) Noncompetitive Inhibition
(B) Uncompetitive Inhibition
IClicker: Uncompetitive inhibition leads to the following changes in enzyme kinetics:
(A) Increase in KM
(B) Decrease in KM
(C) Increase in KM and Vmax
(D) Decrease in KM and Vmax
(E) Vmax decrease and KM increase or decrease
(D) Decrease in KM and Vmax
IClicker: Organisms need to control their catalytic activities to coordinate metabolism, respond to environmental changes, to grow and to differentiate. The form of enzyme control in which an enzyme is stimulated or inhibited depending upon the activity of a kinase or phosphatase activating or inactivating that enzyme is BEST KNWON AS:
(A) Substrate availability
(B) Enzyme amount
(C) Feedback inhibition
(D) Covalent enzyme phosphorylation
(E) Isozyme specialized control
(D) Covalent enzyme phosphorylation
IClicker: What happens to enzyme kinetics in the presence of a positive allosteric effector?
(A) The sigmoidal curve shifts left.
(B) The sigmoidal curve shifts right.
(C) The enzymes Vmax decreases.
(A) The sigmoidal curve shifts left.
IClicker: A common theme of luminal phase digestion is:
(A) Dehydration reactions to break down large polymeric molecules into small polymers.
(B) Dehydration reactions to break down small polymer molecules into lone/free monosaccharides, amino acids, and fatty acids.
(C) Hydrolysis reactions to break down large polymeric molecules into small polymers.
(D) Hydrolysis reactions to break down small polymer molecules into lone/free monosaccharides, amino acids, and fatty acids.
(C) Hydrolysis reactions to break down large polymeric molecules into small polymers.
IClicker: In which phase of lipid assimilation are triglycerides broken down into monoglycerides?
(A) Emulsification
(B) Hydrolysis
(C) Micelle formation
(D) Absorption
(B) Hydrolysis
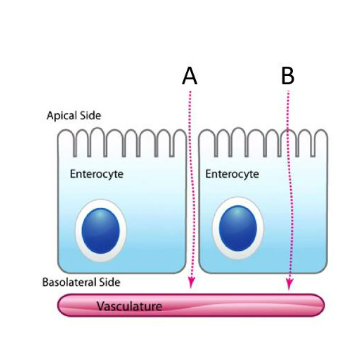
IClicker: Which arrow represents paracellular transport?
(A)
IClicker: Cellular respiration requires glucose to go through glycolysis. This is followed by several steps. Which statement below is FALSE?
(A) Glycolysis occurs in the mitochondrion.
(B) The Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) occurs in the mitochondrion.
(C) Electrons acquired in the citric acid cycle can be transferred to the electron transport chain.
(D) Cellular respiration is aerobic and thus requires oxygen.
(A) Glycolysis occurs in the mitochondrion.
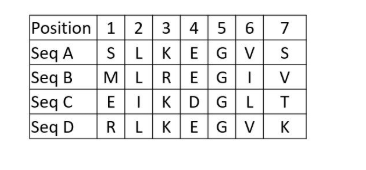
IClicker: Here is an example alignment of a small run of amino acids:
Which position represents an amino acid that could be potentially be conservatively subsituted?
(A) Position 1
(B) Position 3
(C) Position 5
(D) Position 7
(B) Position 3
IClicker: The Bohr Effect is physiologically important because it ensures that hemoglobin releases oxygen in ____ environments such ____, where metabolic activity produces ____ and ____.
(A) alkaline; lungs; CO2; H2O
(B) acidic; tissues; CO2; H+
(C) acidic; lungs; O2; H+
(D) alkaline; tissues; O2; CO2
(B) acidic; tissues; CO2; H+
IClicker: Which of the following is true about enzyme catalysis?
(A) Enzymes change ΔG of the reaction.
(B) Enzymes make endergonic reactions exergonic.
(C) Enzymes increase the rate without altering ΔG.
(D) Enzymes consume ATP in all reactions.
(C) Enzymes increase the rate without altering ΔG.
IClicker: Glucose uptake in intestinal epithelial cells is considered secondary active transport because glucose moves ___ its concentration gradient, coupled to ____ moving down its gradient, where the gradient is maintained by ____.
(A) up; Na+; Na+/K+ ATPase
(B) down; Na+; Na+/K+ ATPase
(C) up; K+; Na+/K+ ATPase
(D) down; Na+; glucose transporter
(A) up; Na+; Na+/K+ ATPase
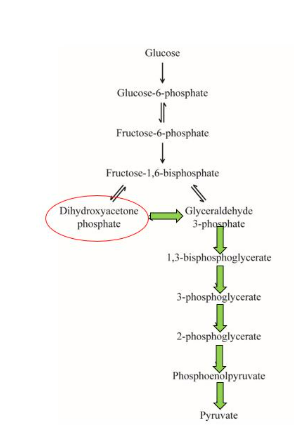
IClicker: What is the NET energy gain when 1 mol of dihydroxyacetone phosphate is converted into 1 mol of pyruvate?
(A) 2 mols of NADH + 2 mols of ATP
(B) 2 mols of NADH + 4 mols of ATP
(C) 1 mol of NADH + 1 mol of ATP
(D) 1 mol of NADH + 2 mols of ATP
(E) 1 mol of NADH + 4 mols of ATP
(D) 1 mol of NADH + 2 mols of ATP
IClicker: Phosphofructokinase is allosterically ___ by high concentrations of ___.
I. Activated; ATP | II. Inhibited; ATP | III. Inhibited; ADP | IV. Activated; ADP
(A) I, III
(B) II, III
(C) II, IV
(D) I, IV
(E) None of the above.
(C) II, IV
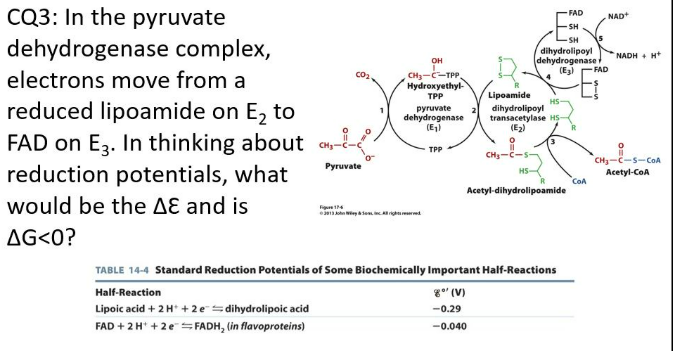
IClicker: In the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, electrons move from a reduced lipoamide on E2 to FAD on E3. In thinking about reduction potentials, what would be the ΔE and is ΔG < 0?
(A) ΔE = -0.040 V - (-0.290 V) = 0.250 V; No
(B) ΔE = -0.040 V - (-0.290 V) = 0.250 V; Yes
(C) ΔE = -0.290 V - (-0.040 V) = -0.250 V; Yes
(D) ΔE = -0.290 V - (-0.040 V) = -0.250 V; No
(B) ΔE = -0.040 V - (-0.290 V) = 0.250 V; Yes
IClicker: Which of the following is FALSE regarding the regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase?
(A) Its activity is slowed by a high [ATP]/[ADP] ratio.
(B) Its activity is slowed by a high [NAD+]/[NADH].
(C) Its activity is activated by Ca2+.
(D) Its activity is slowed by excess acetyl-CoA.
(B) Its activity is slowed by a high [NAD+]/[NADH].

IClicker: In electron transport, cytochrome c will transfer an electron to (thus reducing) CuA within complex IV.
What is ΔE? Is this reaction happening spontaneously?
(A) ΔE = 0.245 V - 0.235 V = 0.010 V, yes
(B) ΔE = 0.245 V - 0.235 V = 0.010 V, no
(C) ΔE = 0.235 V - 0.245 V = -0.010 V, yes
(D) ΔE = 0.235 V - 0.245 V = -0.010 V, no
(A) ΔE = 0.245 V - 0.235 V = 0.010 V, yes
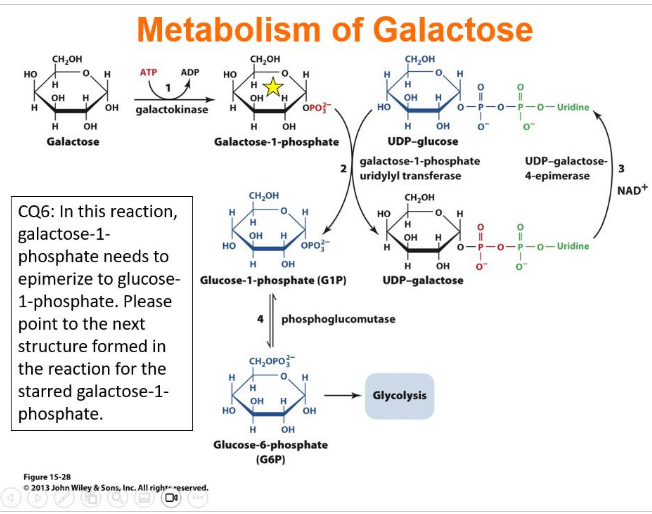
IClicker: In this reaction, galactose-1-phosphate needs to epimerize to glucose-1-phosphate. What is the next structure formed in the reaction for the starred galactose-1-phosphate?
UDP-Galactose
IClicker: If your cells have a need for ___ and ___, then they will shunt ___ into the Pentose Phosphate Pathway.
(A) NADH; fructose-6-P; ribose-5-P
(B) NAD+; ribose-5-P; glucose-6-P
(C) NADP+; ribose-5-P; fructose-6-P
(D) NADP+; ribose-5-P; glucose-6-P
(E) NADPH; ribose-5-P; glucose-6-P
(E) NADPH; ribose-5-P; glucose-6-P
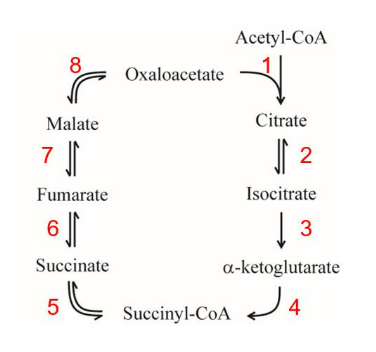
IClicker: Which are steps that directly produce high energy products or produce electron carriers that can be used to generate ATP?
(A) 1, 3, and 4
(B) 1 and 5
(C) 3, 4, 6, and 8
(D) 5, 6, and 8
(E) 3, 4, 5, 6, and 8
(E) 3, 4, 5, 6, and 8
IClicker: Under standard state conditions, which enzyme of the citric acid cycle has the largest positive ΔG0'?
(A) Malate dehydrogenase
(B) Citrate synthase
(C) Aconitase
(D) Isocitrate dehydrogenase
(A) Malate dehydrogenase
IClicker: The reaction of the Krebs Cycle catalyzed by ___ requires an enzyme bound flavin coenzyme (FAD).
(A) Isocitrate dehydrogenase
(B) α-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
(C) Succinyl-CoA synthetase
(D) Succinate dehydrogenase
(D) Succinate dehydrogenase
IClicker: How many NADH are produced when one acetyl group is oxidized in the Kreb’s cycle?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(C) 3
IClicker: Which of the following would decrease activity of the Kreb’s cycle overall?
(A) High concentration of NADH
(B) High concentration of Ca2+
(C) High concentration of ATP
(D) High concentration of citrate
(D) High concentration of citrate
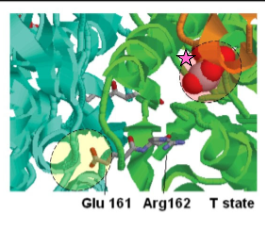
IClicker: In this image, you are looking at two sites on glycolytic enzyme PFK. In the image, PFK is in the T-state, so it’s not active. What is the likely molecule bound to the site with the pink star?
(A) ADP
(B) ATP
(C) NADH
(B) ATP
IClicker: Which enzyme catalyzes the reaction that is coupled to the reaction converting malate to oxaloacetate?
(A) Fumarase
(B) Citrate synthase
(C) Aconitase
(D) Isocitrate dehydrogenase
(B) Citrate synthase
IClicker: Which 2 molecules cause product inhibition for the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
(A) ATP and Pyruvate
(B) Acetyl-CoA and NAD+
(C) Acetyl-CoA and NADH
(D) ATP and Acetyl-CoA
(C) Acetyl-CoA and NADH

IClicker: Regulation of the citric acid cycle is based upon mass action. Thus, when the muscle is at rest, levels of ___ and ___ will be high while levels of ___ and ___ will be low.
(A) NAD+, oxaloacetate, NADH, malate
(B) NADH, malate, NAD+, oxaloacetate
(C) NAD+, malate, NADH, oxaloacetate
(D) NADH, oxaloacetate, NAD+, malate
(B) NADH, malate, NAD+, oxaloacetate
Extra Credit Practice: True or False. Given the equation ΔG = ΔH - TΔS, one could say a reaction that is exothermic and becomes less ordered is always spontaneous.
True.
Extra Credit Practice: True or False. The hydrophobic effect is driven primarily by attractive forces between nonpolar molecules.
False
Extra Credit Practice: True or False. A weak acid is a useful buffer within the range of one pH unit of its pKa.
True
Extra Credit Practice: In your equine medicine clinical rotation in veterinary school, you see a horse with a pleural pneumonia. This is a lung infection (pneumonia) that spreads to the lining of the lungs (pleura). With that infection comes inflammation known as pleurisy that causes sharp chest pain with breathing, this causing the horse's breathing to be slower and shallower than normal. When you check arterial blood gas bloodwork of the horse, you find that the blood pH is lower than normal. This is likely a ___________________.
(A) Metabolic acidosis
(B) Metabolic alkalosis
(C) Respiratory acidosis
(D) Respiratory alkalosis
(C) Respiratory acidosis
Extra Credit Practice: As a veterinarian, you see a dog with a fungal rhinitis. In order to treat the rhinitis, you have to sedate the dog and then carefully add an antifungal. The antifungal needs to stay protonated and thus uncharged (HA) so that it can penetrate the tissue membranes and act intercellularly. The tissue pH = 7.4. Which works better: ketoconazole (pKa = 6.4) or itraconazole (pKa 3.4)?
(A) Ketoconazole
(B) Itraconazole
(C) Both work equally well.
(A) Ketoconazole
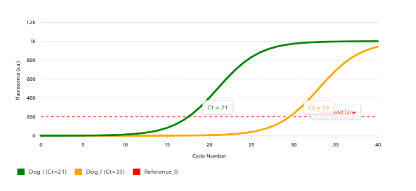
Extra Credit Practice: Two dogs show signs of fever and jaundice. RT-qPCR of urine was performed to look for leptospira bacteria in Dog I, which produced a Cycle Threshold value of 21. RT-qPCR of urine from Dog J produced a Cycle Threshold value of 33. Which dog is more likely to positive?
(A) Dog I
(B) Dog J
Dog I
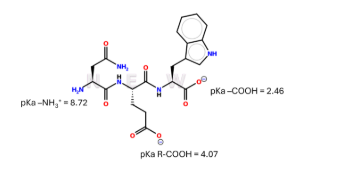
Extra Credit Practice: The tripeptide was placed in a solution with a certain pH that led to the image you see above. Given the pKas and what you see for the ionizable functional groups above, within which pH was the tripeptide placed in:
(A) pH = 1
(B) pH = 3
(C) pH = 6
(D) pH = 12
(D) pH = 12
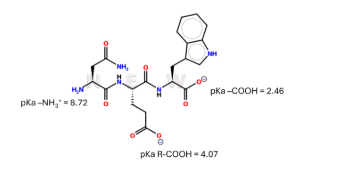
Extra Credit Practice: The pl of this tripeptide is:
(A) 3.23
(B) 5.59
(C) 6.40
(A) 3.23
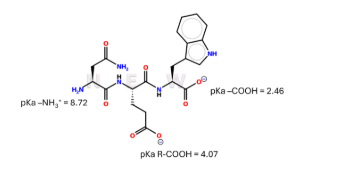
Extra Credit Practice: The charge of the peptide at pH 7 is:
(A) -2
(B) -1
(C) 0
(D) +1
(E) +2
(B) -1
Extra Credit Practice: Here is an example alignment of a small run of amino acids:
Position | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
Seq A | M | L | K | E | G | V | S |
Seq B | M | L | R | E | G | I | V |
Seq C | M | I | K | D | G | L | T |
Seq D | M | L | K | E | G | V | K |
In the alignment, which of the following positions is demonstrating conservative substitution?
(A) Position 1
(B) Position 3
(C) Position 5
(D) Position 7
(B) Position 3
Extra Credit Practice: Which statement correctly distinguishes secondary from tertiary structure?
(A) Secondary structure depends on side-chain interactions; tertiary does not.
(B) Secondary structure involves backbone hydrogen bonding; tertiary involves side-chain interactions.
(C) Both involve multiple subunits.
(B) Secondary structure involves backbone hydrogen bonding; tertiary involves side-chain interactions.
Extra Credit Practice: How does increased H⁺ concentration affect hemoglobin?
(A) Stabilizes the R state and increases O₂ binding
(B) Stabilizes the T state and promotes O₂ release
(B) Stabilizes the T state and promotes O₂ release
Extra Credit Practice: Why is sucrose non-reducing?
(A) It contains no hydroxyl groups.
(B) Both anomeric carbon are involved in the glycosidic bond.
(C) It has a ketone group only.
(B) Both anomeric carbon are involved in the glycosidic bond.
Extra Credit Practice: What is the main structural difference between cellulose and amylose?
(A) Cellulose has α-linkages; amylose has β-linkages
(B) Cellulose has β-linkages; amylose has α-linkages
(C) Cellulose is branched; amylose is linear.
(B) Cellulose has β-linkages; amylose has α-linkages
Extra Credit Practice: True or False. The uptake of glucose in an intestinal epithelial cell considered a form of secondary active transport because of the coupling of glucose transport to the movement of 2 Na+ ions down their concentration gradient, where the Na+ gradient is a result of active transport.
True
Extra Credit Practice: How does an enzyme affect the activation energy of a reaction?
(A) It increases ΔG‡
(B) It decreases ΔG‡
(C) It changes ΔG of the reaction.
(B) It decreases ΔG‡
Extra Credit Practice: True or False. Increasing substrate concentration beyond saturation will further increase Vmax.
False
Extra Credit Practice: True or False. Absorption can occur effectively even if digestion does not take place.
False
Extra Credit Practice: True or False. Membranous-phase enzymes are free-floating in the intestinal lumen.
False
Extra Credit Practice: Chylomicrons leave enterocytes through the basolateral membrane, enter intestinal lymphatics, and reach the bloodstream via the thoracic duct.
True
Discussion 7 Assignment: True or false. The catalytic activity of an enzyme can be regulated by controlling the amount of the enzyme available and by structural alterations of the enzyme that influence substrate binding.
True
Discussion 7 Assignment: True or false. If you have an abundance of substrate such that [S] is much greater than [E], then [ES] remains constant because the enzyme will have so much substrate with which to bind as it catalyzes the S → P reaction. This situation is considered a steady state situation for the ES complex, and the substrate will become product at a constant rate.
True
Discussion 7 Assignment: When a substance binds to the enzyme active site and to the enzyme-substrate complex, this is best known as:
(A) Competitive Inhibition
(B) Uncompetitive Inhibition
(C) Noncompetitive Inhibition
(C) Noncompetitive Inhibition
Discussion 7 Assignment: In noncompetitive inhibition, it leads to the following change's in enzyme kinetics:
(A) KM increase; Vmax = no change
(B) KM and Vmax decrease
(C) KM increase or decrease; Vmax decrease
(C) KM increase or decrease; Vmax decrease
![<p><strong>Discussion 7 Assignment: </strong>Assuming steady state, the rate of breakdown of the enzyme-substrate complex could be described as:</p><p>(A) k<sub>2</sub> [ES]</p><p>(B) k<sub>1</sub> [ES]</p><p>(C) k<sub>-1</sub> [ES] + k<sub>2</sub> [ES]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b60d0c45-f417-4928-8ab3-c490f9e40aa8.png)
Discussion 7 Assignment: Assuming steady state, the rate of breakdown of the enzyme-substrate complex could be described as:
(A) k2 [ES]
(B) k1 [ES]
(C) k-1 [ES] + k2 [ES]
(C) k-1 [ES] + k2 [ES]
Discussion 7 Assignment: The type of enzyme inhibition in which Vmax is unaffected is ______.
(A) Competitive Inhibition
(B) Uncompetitive Inhibition
(C) Noncompetitive Inhibition
(A) Competitive Inhibition
Discussion 7 Assignment: In the small intestine, which layers form a viscous coating that traps molecules near the apical membrane?
Glycocalyx and mucus.
Discussion 7 Assignment: True or False. Digestion and absorption are the same physiological process.
False
Discussion 7 Assignment: True or False. The brush border is composed of microvilli on the apical membrane of enterocytes. True
True
Discussion 7 Assignment: True or False. The tight junctions between enterocytes are impermeable to water and small ions.
False
Discussion 8 Assignment: True or False. The breast muscles of the domesticated chicken and turkey have greater amounts of mitochondria compared to leg muscles of the same birds.
False
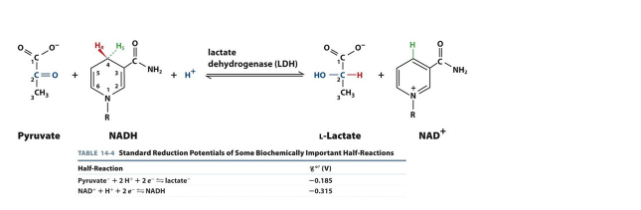
Discussion 8 Assignment: In homolactic fermentation, pyruvate is reduced to lactate in order to regenerate NAD+. In thinking about reduction potentials, what would be the ∆Ɛ?
(A) 0.500 V
(B) 0.130 V
(C) -0.130 V
(D) -0.500 V
(B) 0.130 V
Discussion 8 Assignment: True or False. In the liver, fructose can bypass phosphofructokinase (PFK) and thus disrupt fuel metabolism so that glycolytic flux is directed toward lipid synthesis in the absence of a need for ATP.
True
Discussion 8 Assignment: The enzyme controlling the flux of glycolysis in the muscle is _____. It has two conformational states T and R.
Phosphofructokinase.
Discussion 8 Assignment: When glycolysis is active, the substrate for the flux-controlling enzyme (PFK) is:
Fructose-6-phosphate.
Discussion 8 Assignment: When the allosteric effector ___ is found in its effector site of PFK, the substrate F6P fails to bind the enzyme because ____ is facing into the substrate-binding site
ATP; Glu161
Discussion 8 Assignment:
Discussion 8 Assignment: True or false. In a mammal, when considering the fate of pyruvate after glycolysis under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate must be converted to a reduced end product lactate in order to reoxidize the NADH produced by the GAPDH reaction.
True
Discussion 8 Assignment: Pyruvate enters the PDH complex and when all is said in done with the complex, the following are generated:
Acetyl-CoA, NADH, and carbon dioxide.
Discussion 8 Assignment: ADP will act as an inhibitor for _____ which itself is an inhibitor of the PDH complex; thus, inhibition of the inhibitor leads to activation of the PDH complex.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase
Discussion 8 Assignment: Within the Krebs Cycle there is one enzyme that is embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane which has a covalently bound FAD+ that will transfer electrons directly to into the electron transport chain. This enzyme is ___.
Succinate dehydrogenase.
Discussion 8 Assignment: One major regulatory mechanism for the Krebs Cycle is based in the law of mass action. When muscles are at rest and thus are not requiring oxidative phosphorylation, in the mitochondria, you will find the following two molecules with high concentrations:
Malate & NADH
Discussion 8 Assignment: You are examining the following reaction:
Succinate + FAD → Fumarate + FADH2
Reduction potentials for the 2 half-reactions are:
(A) Fumarate + 2H+ + 2e- → succinate E°’ = 0.030 V
(B) FAD + 2H+ + 2e- → FADH2 E°’ = -0.180 V
From the reaction listed at top, ____ is being reduced and is thus the electron acceptor, and ____ is being oxidized and is thus the electron donor.
FAD; Succinate.
Discussion 8 Assignment: The Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Multienzyme Complex has one cofactor that is bound to a lysine on E2 that swings around to accept the hydroxyethyl from one cofactor bound to E1 so that the hydroxyethyl can undergo transesterification reaction so that the acetyl group is transferred to CoA. This swinging cofactor is ________________.
(A) TPP
(B) NAD+
(C) Zn+ ion
(D) FAD+
(E) Lipoamide
(E) Lipoamide