AP Bio - Energy and Enzymes
1/35
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
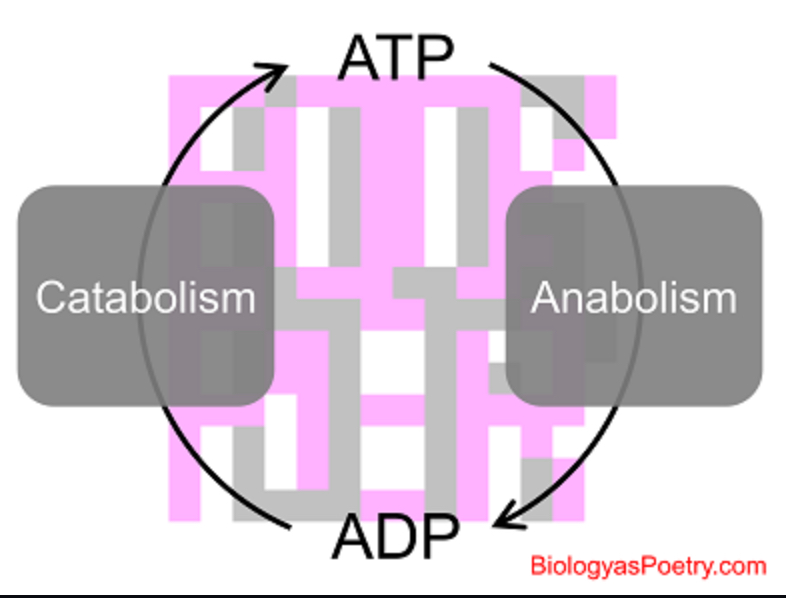
metabolism
The sum of the building & breaking reactions occurring in cells
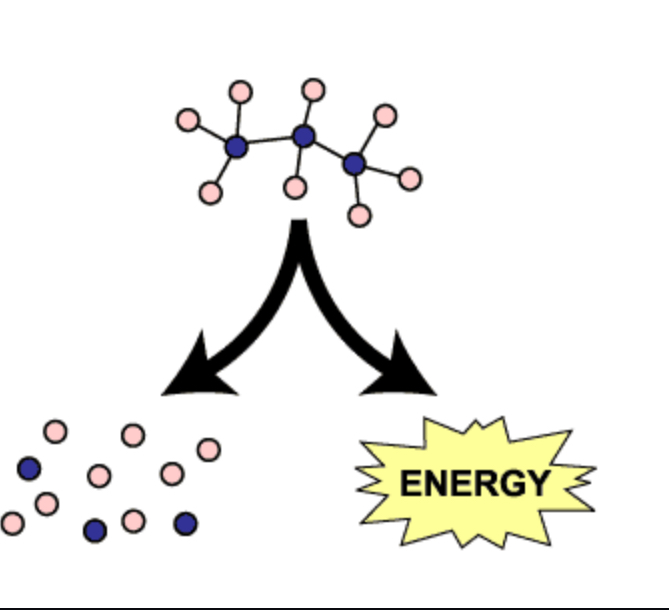
catabolic pathways
Series of reactions that release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds.
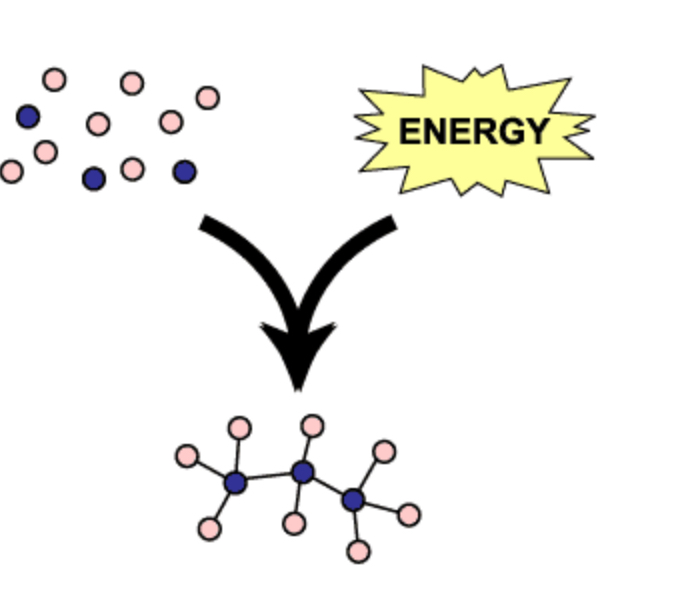
anabolic pathways
Series of reactions that consume energy to build complicated molecules from simpler ones.
thermal energy
Kinetic energy associated with the random movement of molecules or atoms. (heat)

potential energy
Stored energy.

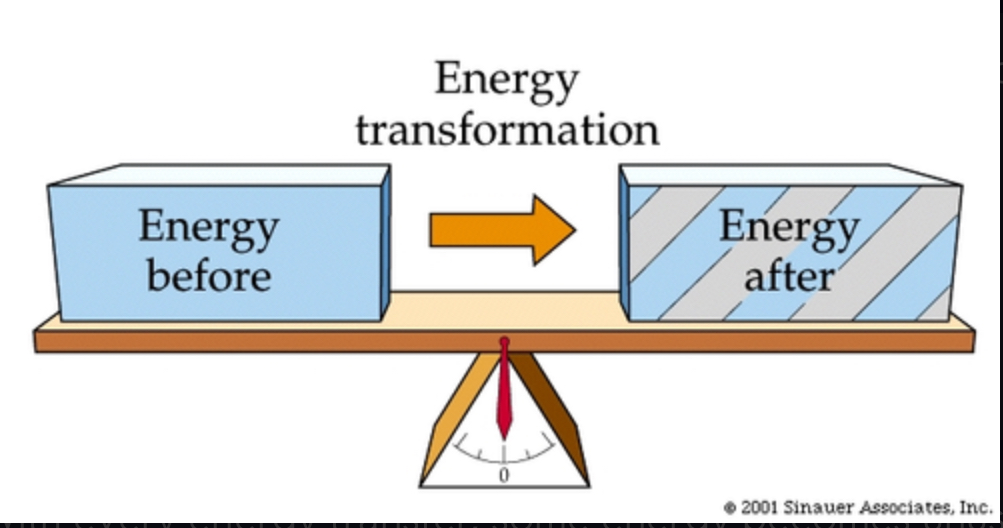
first law of thermodynamics
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
second law of thermodynamics
With every energy transfer, some energy becomes unusable. (Entropy of universe increases)
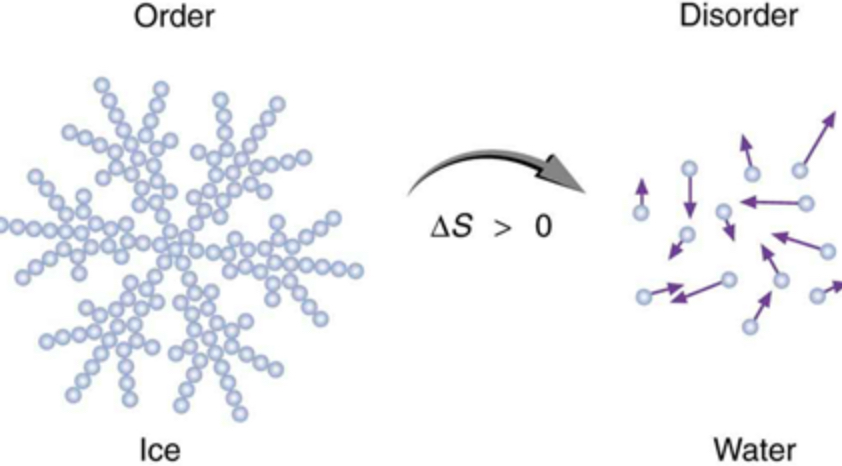
free energy
Measures the portion of a cell's energy that is available to do work (G)
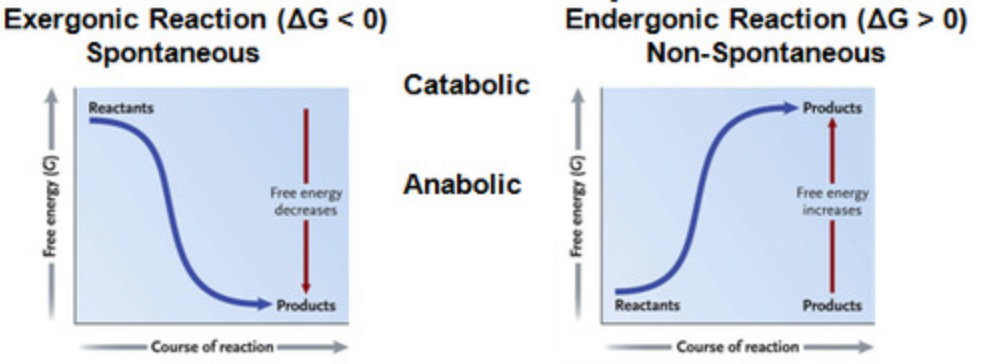
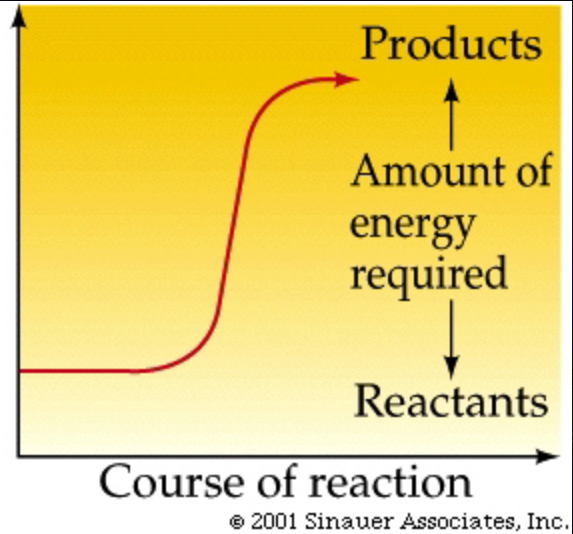
endergonic reaction
Reaction that absorbs free energy from its surroundings. Non-spontaneous! Energy REQUIRED. (+DG)
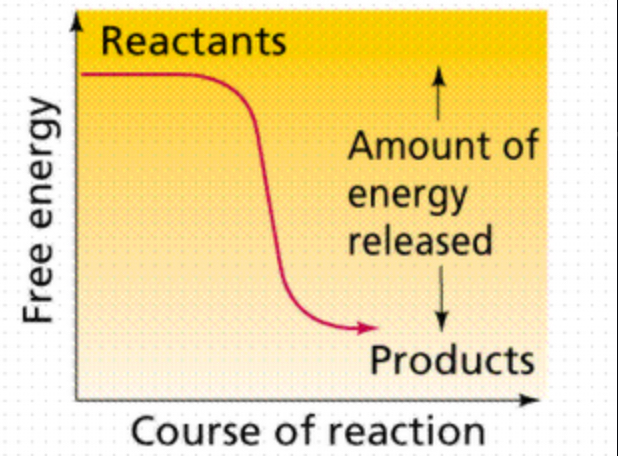
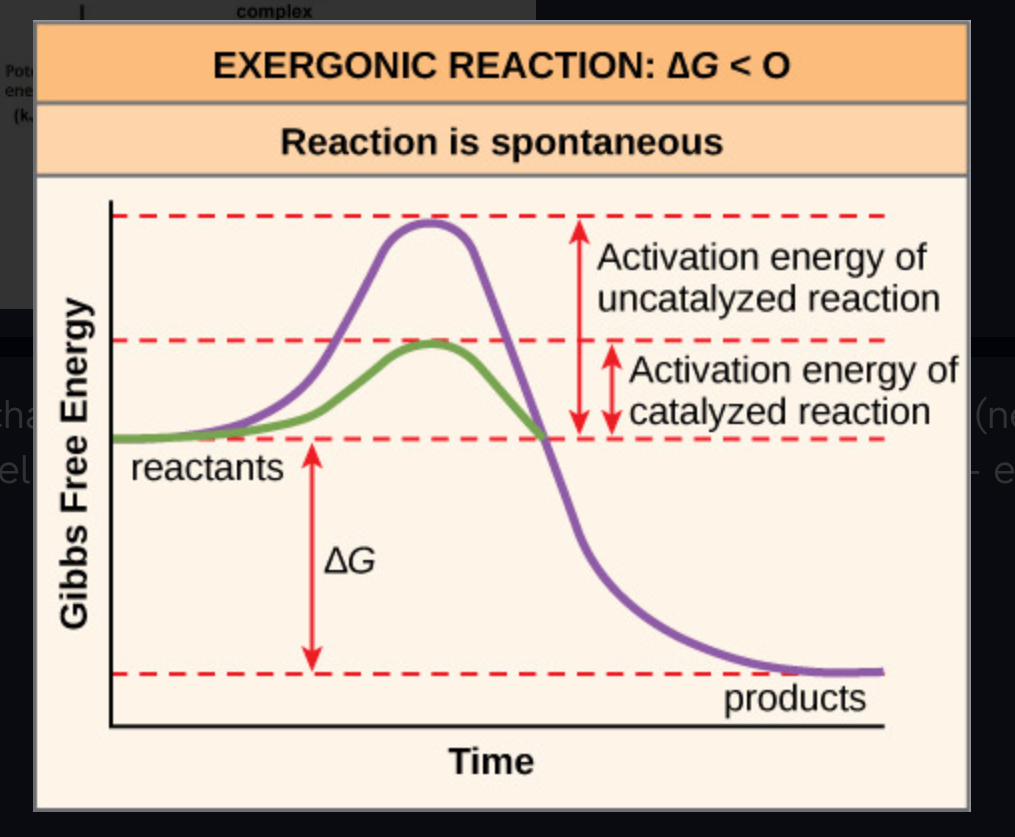
exergonic reaction
Reaction that proceeds with a net release of free energy. Spontaneous - ENERGY RELEASED. (-DG)
energy coupling
Capturing energy from an exergonic reaction and passing it to an endergonic one. Usually done with ATP.
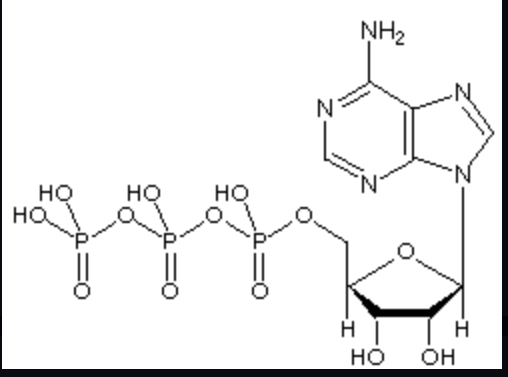
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
Composed of a sugar ribose, nitrogenous base adenine, and a chain of three phosphate groups bonded to it.
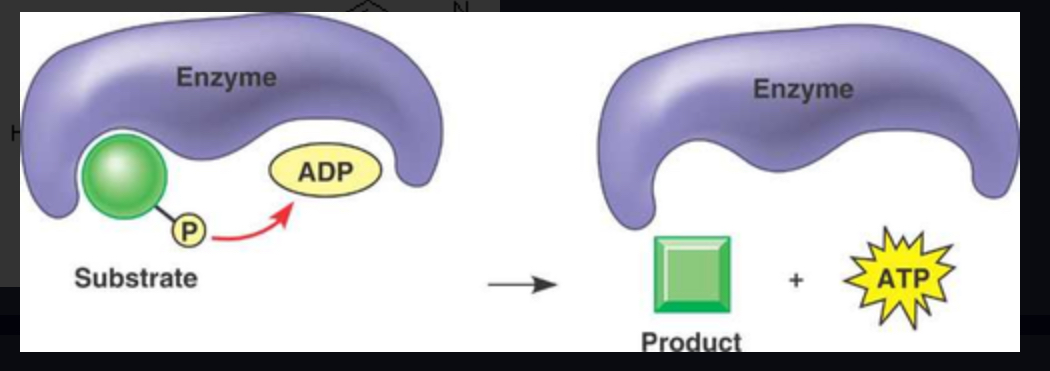
phosphorylation
The metabolic process of adding a phosphate group into an organic molecule.
catalyst
Any chemical agent that speeds up a reaction. Written above the arrow in a chemical equation
enzyme
Protein catalyst that speeds up reactions in our body. Typically end in "ase" (ex. Peroxidase, Lipase)

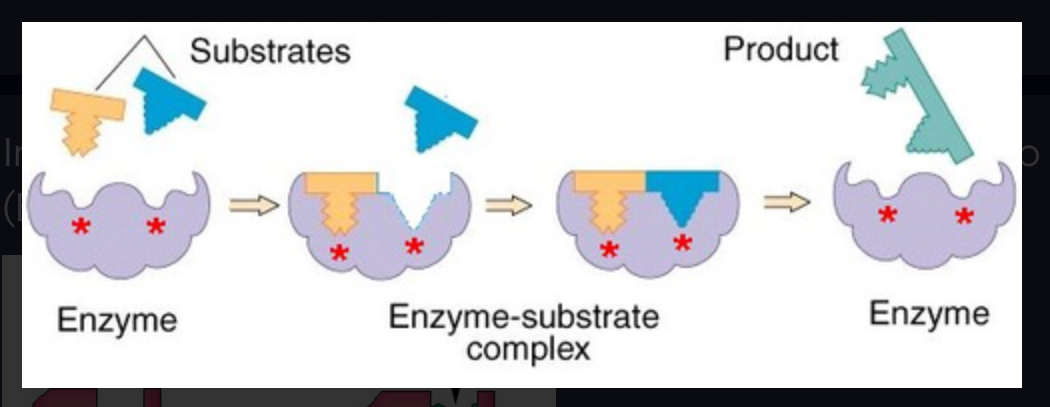
enzyme-substrate complex
When an enzyme binds to its substrate, it forms this:
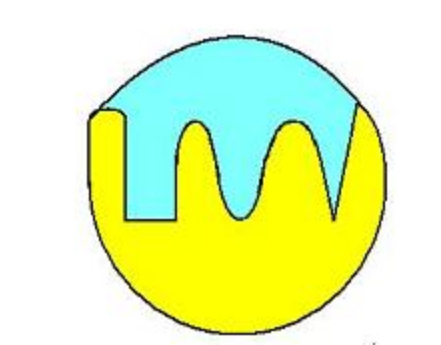
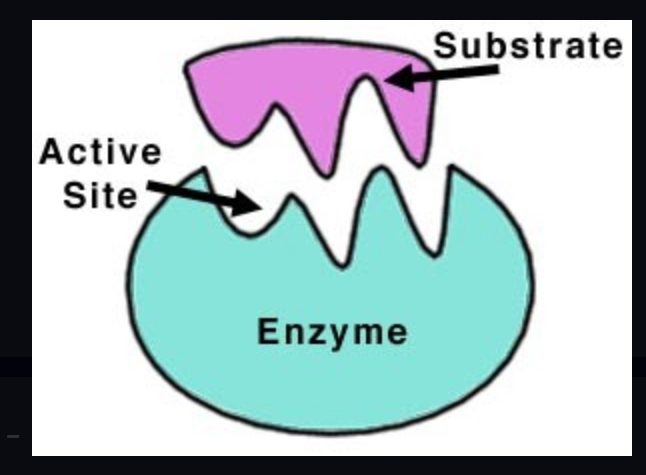
active site
A pocket or groove on the surface of the enzyme where a substrate can bind.
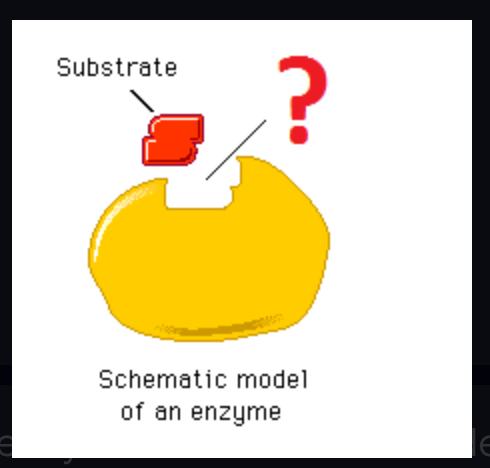
induced fit model
States that the enzyme and substrate undergo conformational changes to interact fully with one another (as opposed to "Lock & Key")
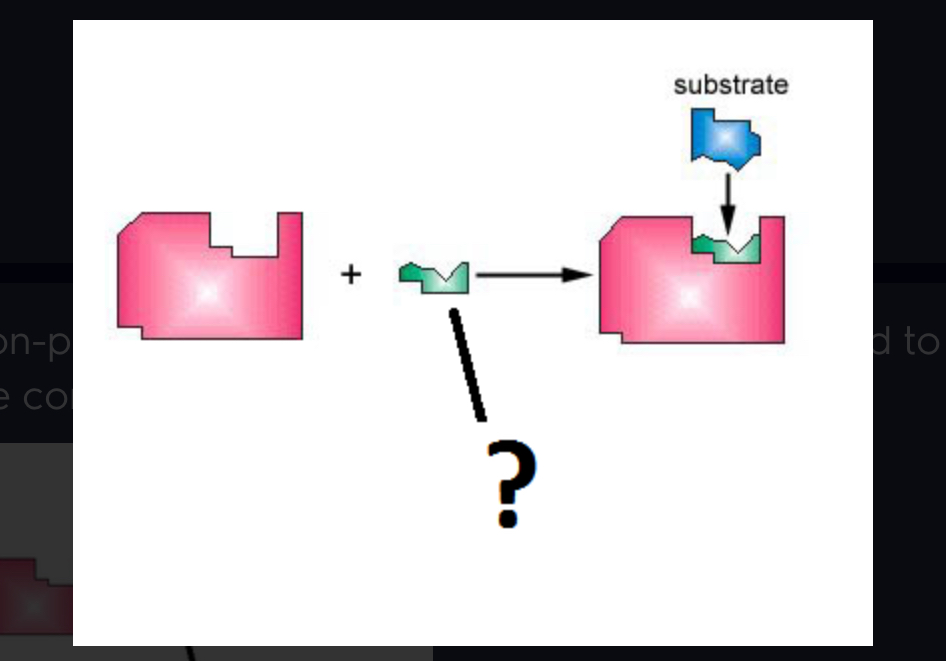
cofactor
Inorganic metal ion helpers that bind to enzymes to help to assume correct shape (Ex. Zn).
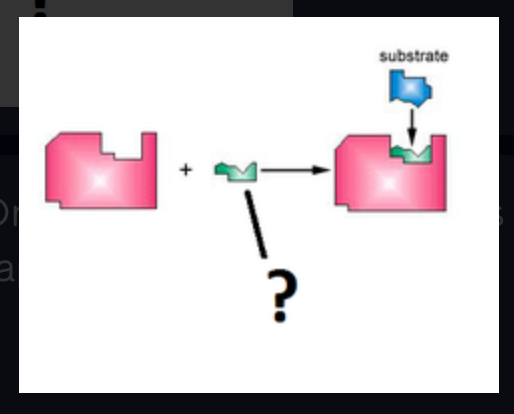
coenzyme
Non-protein Organic helpers like vitamins that bind to enzymes to help them assume the correct shape. (Ex. Vitamin A)
competitive inhibitors
Reduce the productivity of enzymes by blocking substrates from entering active sites.

noncompetitive inhibitors
Impede enzymatic reactions by binding to a site other than the active site (usually bind to an allosteric site)
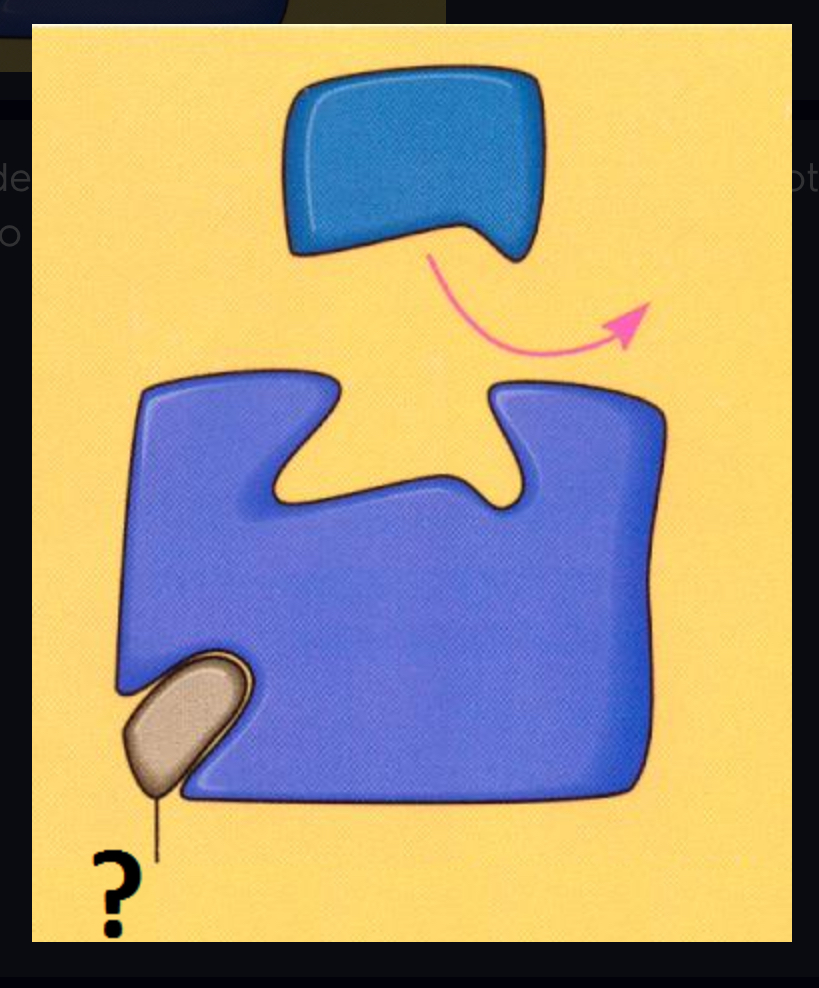
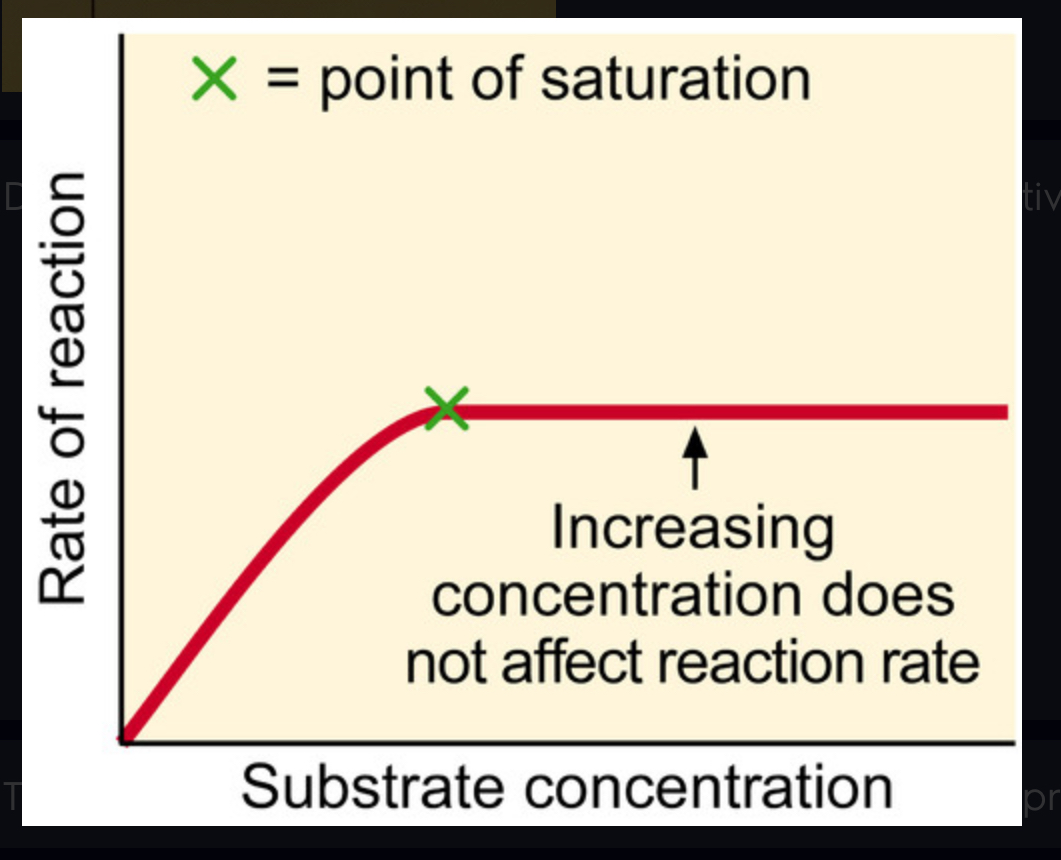
saturated
Describes an enzyme's maximum activity when every active site is being used.
substrate
The reactant that an enzyme binds with. It becomes the product(s)
Chemical Energy
Potential energy trapped in molecular bonds of macromolecules.
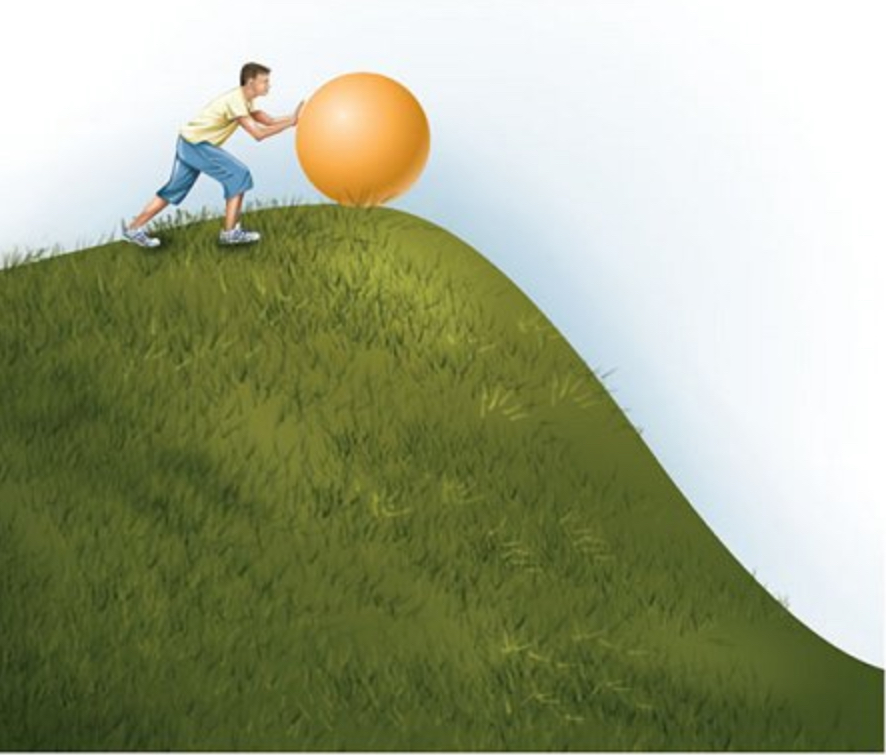
activation energy (Ea)
the initial energy needed to start a chemical reaction
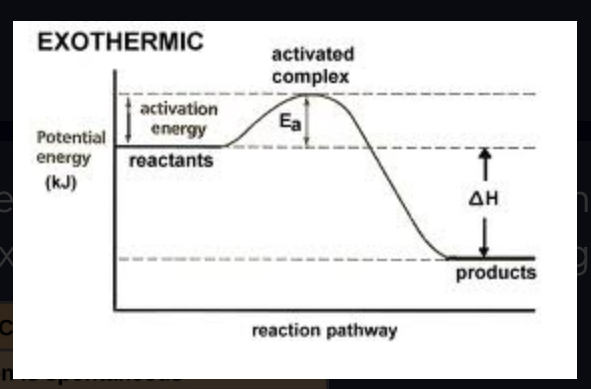
Delta G
change in free energy (FINAL - INITIAL) Can be + or - (negative means energy released - exergonic / positive means energy gained - endergonic)
homeostasis
A tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state; the regulation of any aspect of body chemistry, such as blood glucose, around a particular level
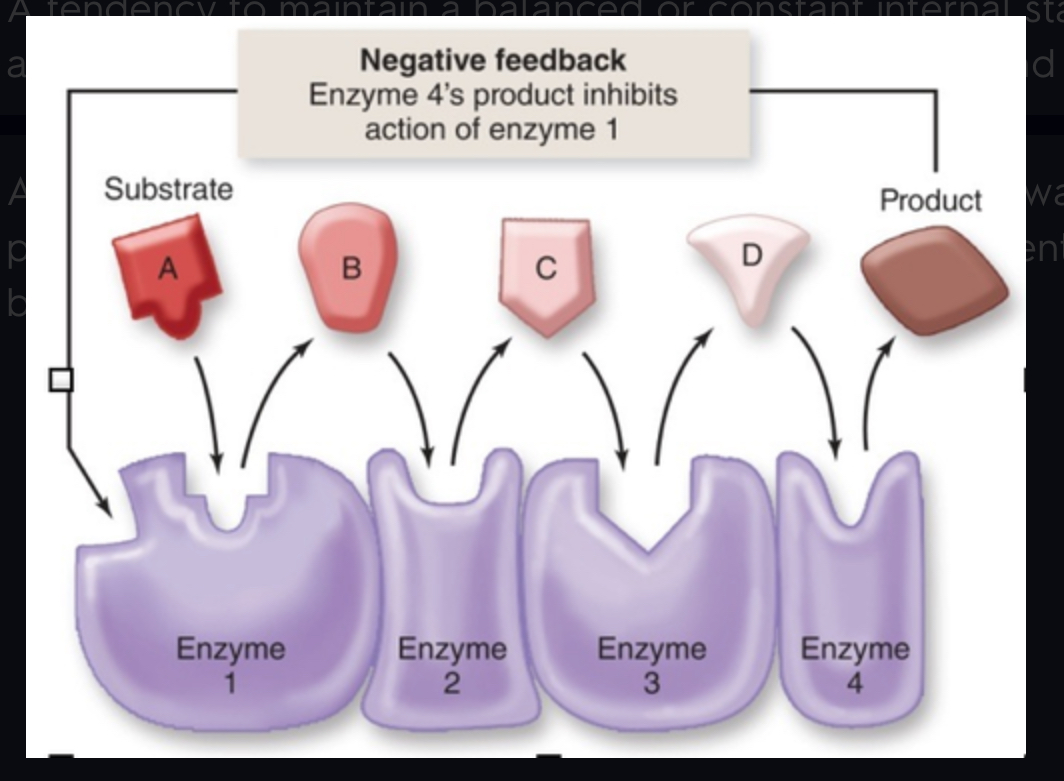
negative feedback inhibition
A primary mechanism of homeostasis, in metabolic pathways it is where the final product behaves as an inhibitor of the pathway to prevent too much product from being made
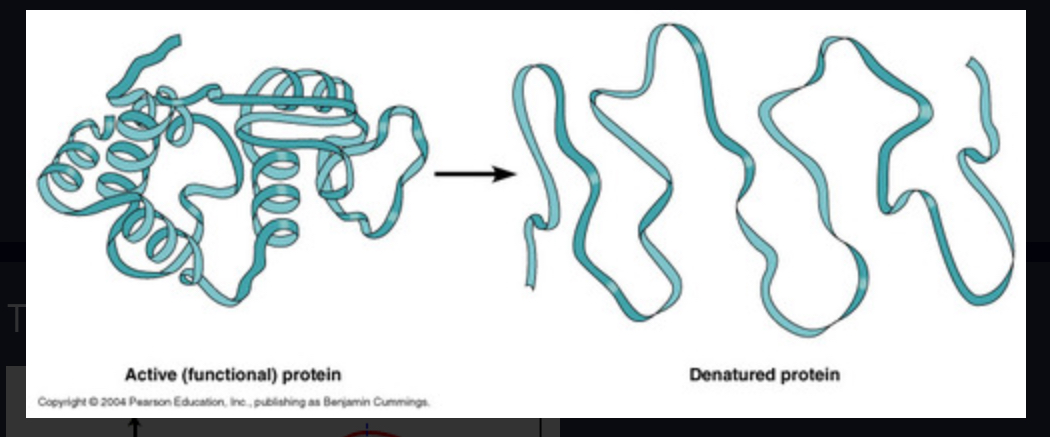
Denatured
Change the shape of an enzyme so that it can no longer speed up a reaction. (involved UNFOLDING of tertiary structures)
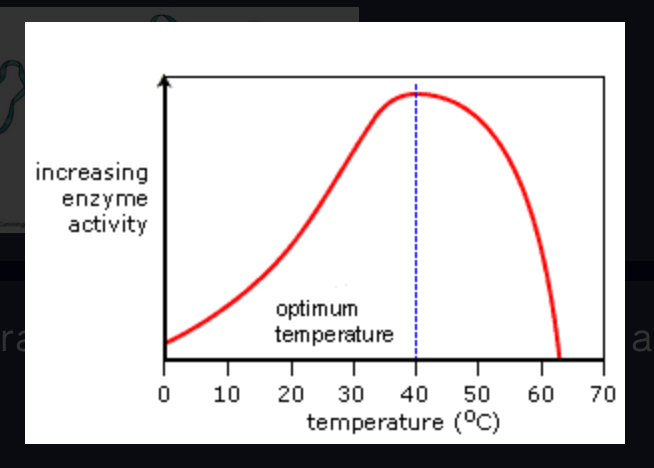
optimum temperature
The temperature at which an enzyme is most active
Optimum pH
the pH at which an enzyme is most active
-ase
forms names of enzymes
Rate formula for enzyme activity
(amount 2 - amount 1)/(time2 - time1)
Phosphorylation
the addition of a phosphate group to a molecule (ex. ADP --> ATP
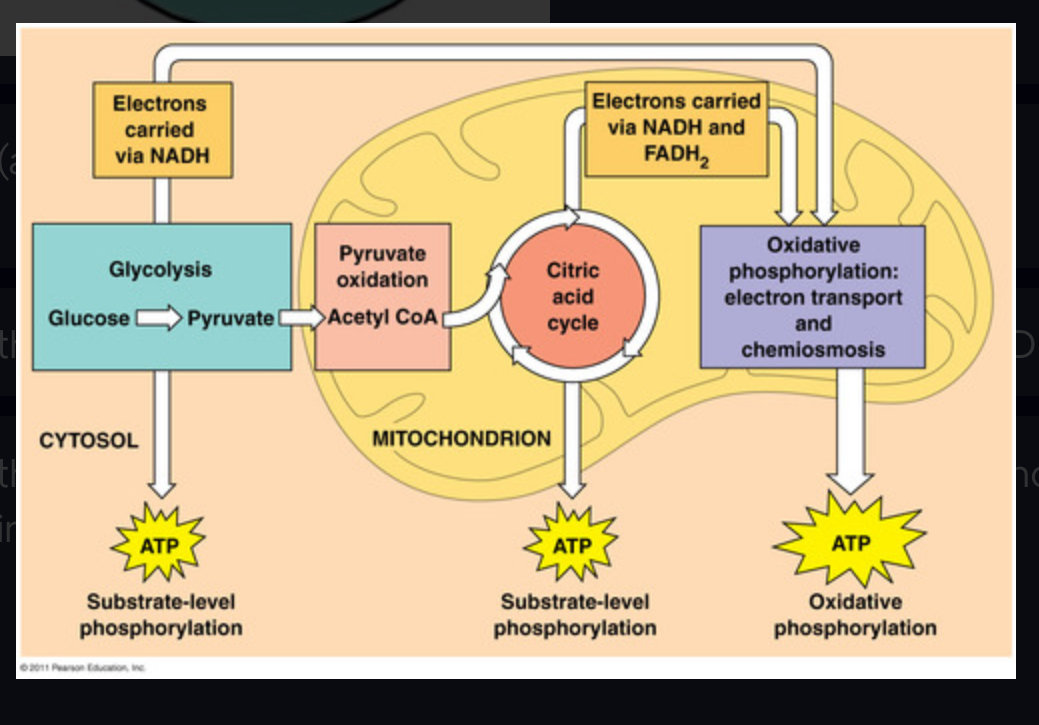
cell respiration
the controlled release of energy from organic compounds to produce ATP. (usually in mitochondria)