Aquatic and Wetland Plants Lecture Material
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Why are aquatic ecosystems important?
habitat, refugia and food for aquatic organisms
Anthropocentric recreation
Environmental services: water filtration, algal control, erosion control
Economically important aquatic plants: rice, invasive aquatic plants
Definition of aquatic plants
Grow in/near water, evolved to exhibit various forms. Few are fully aquatic
Ephemeral aquatic areas
Are wet for only a portion of the year
How do we define aquatic community boundaries?
By using aquatic plants
Four types of aquatic plants
submerged, floating, emergent, shoreline
Submerged plants
Underwater for full life cycle, roots located in submerged soil at the bottom of water
Floating plants
Plants float on water’s surface, roots may float or be submerged in soil
Emerging plants
Plants with a large portion of their architecture elevated above water’s surface. Roots located in submerged soil
Shoreline plants
Found near the edge of a body of water. Tolerate periodic flooding, but their roots are not fully/continuously submerged
3
Mastered
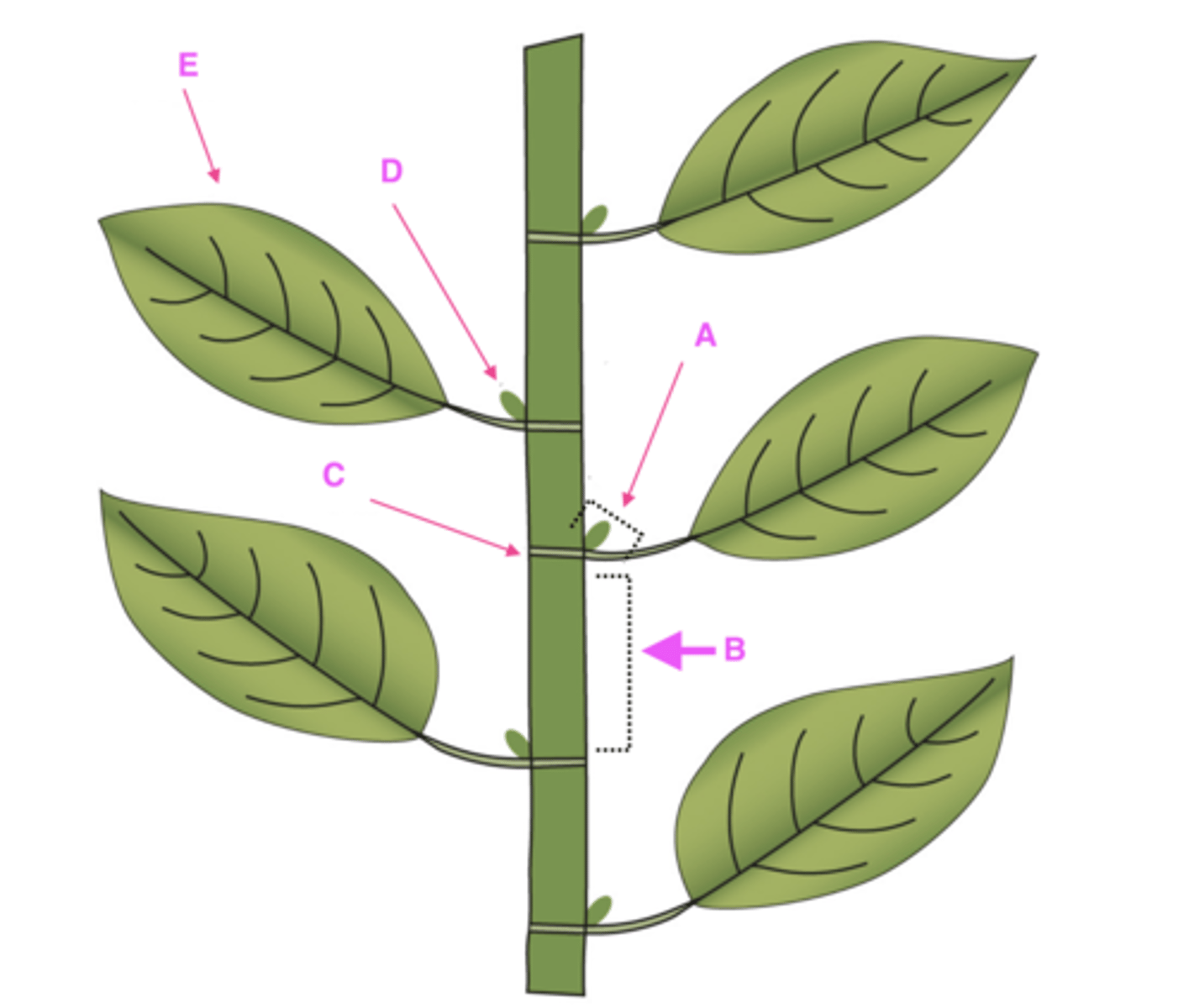
A. Leaf axil: point at which the leaf connects to stem or branch
B. Internode: area between nodes
C. Node: area of the stem where buds develop and form into stems/branches
D. Axillary bud
E. Leaf
Label structures A-E with proper plant architecture terminology.
4
Mastered
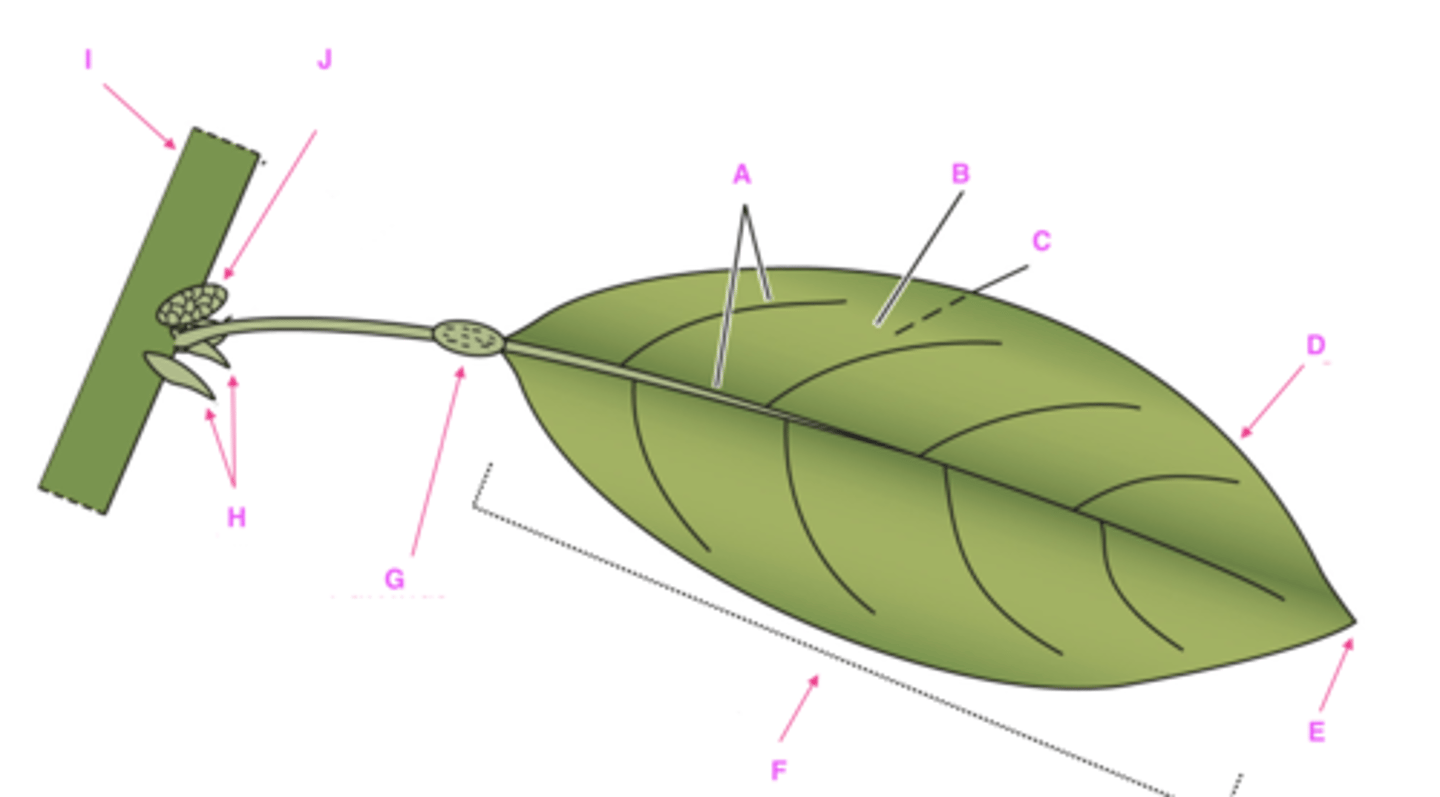
A. Veins
B. Adaxial surface (top, facing stem)
C. Abaxial surface (bottom, away from stem)
D. Margin (edge of leaf)
E. Apex (tip of leaf)
F. Blade
G. Pulvinus (joint-like thickening at base of leaf/leaflet, helps move the leaf)
H. Stipules
I. Stem
J. Bud
Label structures A-J with proper leaf components.
5
Mastered
Acicular: needle shaped
What shape is this leaf?

6
Mastered
Falcate: sickle-shaped
What shape is this leaf?
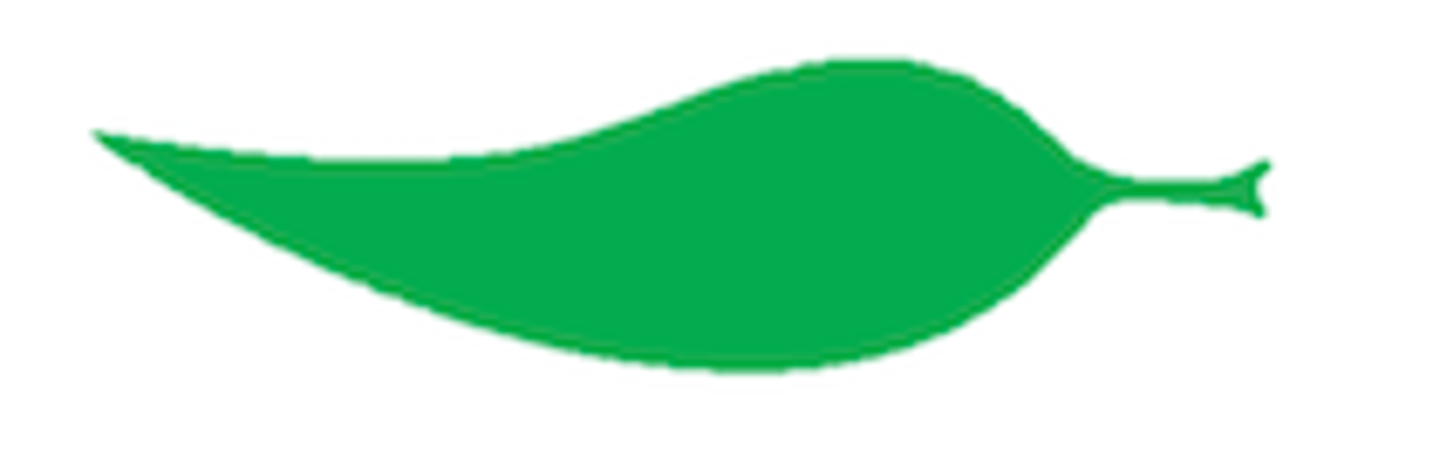

7
Mastered
Acuminate: long with tapering point at tip
What shape is this leaf?
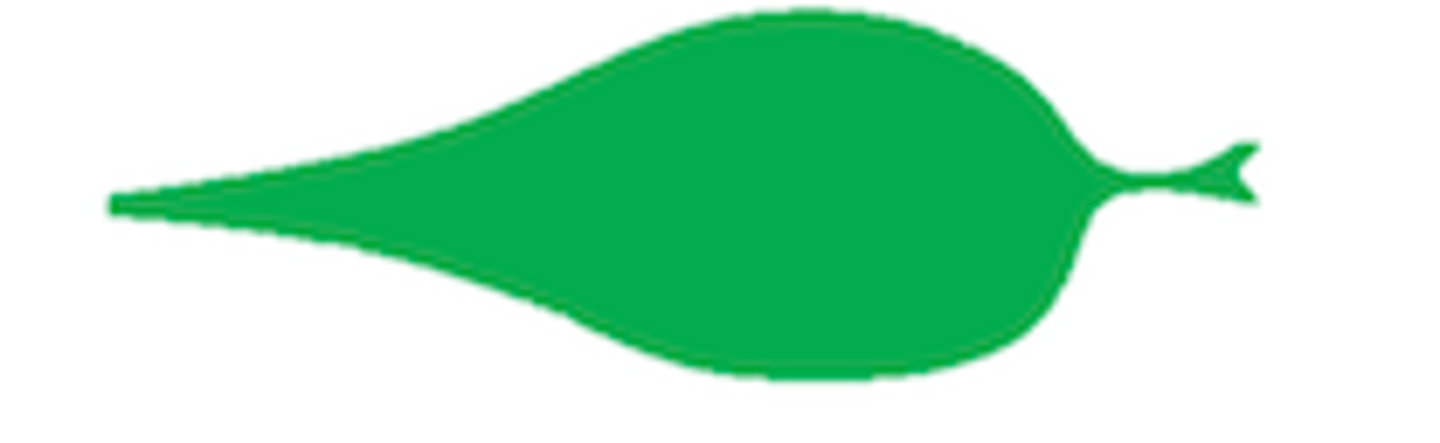

8
Mastered
Ovate: egg-shaped and wide at base
What shape is this leaf?

9
Mastered
Lanceolate: pointed at base
What shape is this leaf?
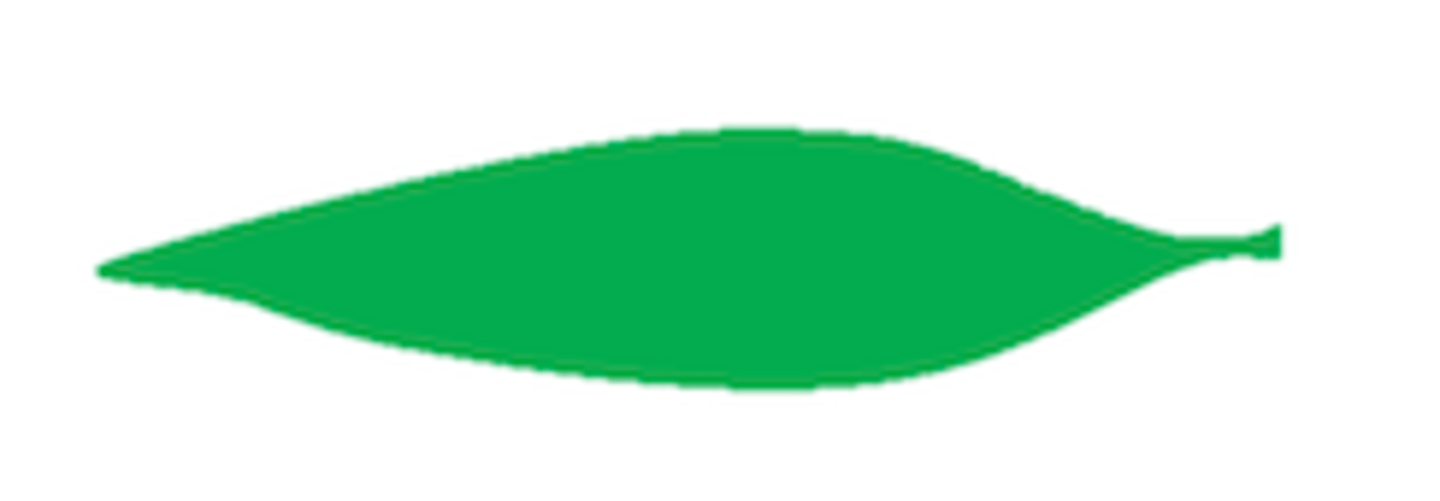

10
Mastered
Cordate: heart-shaped
What shape is this leaf?
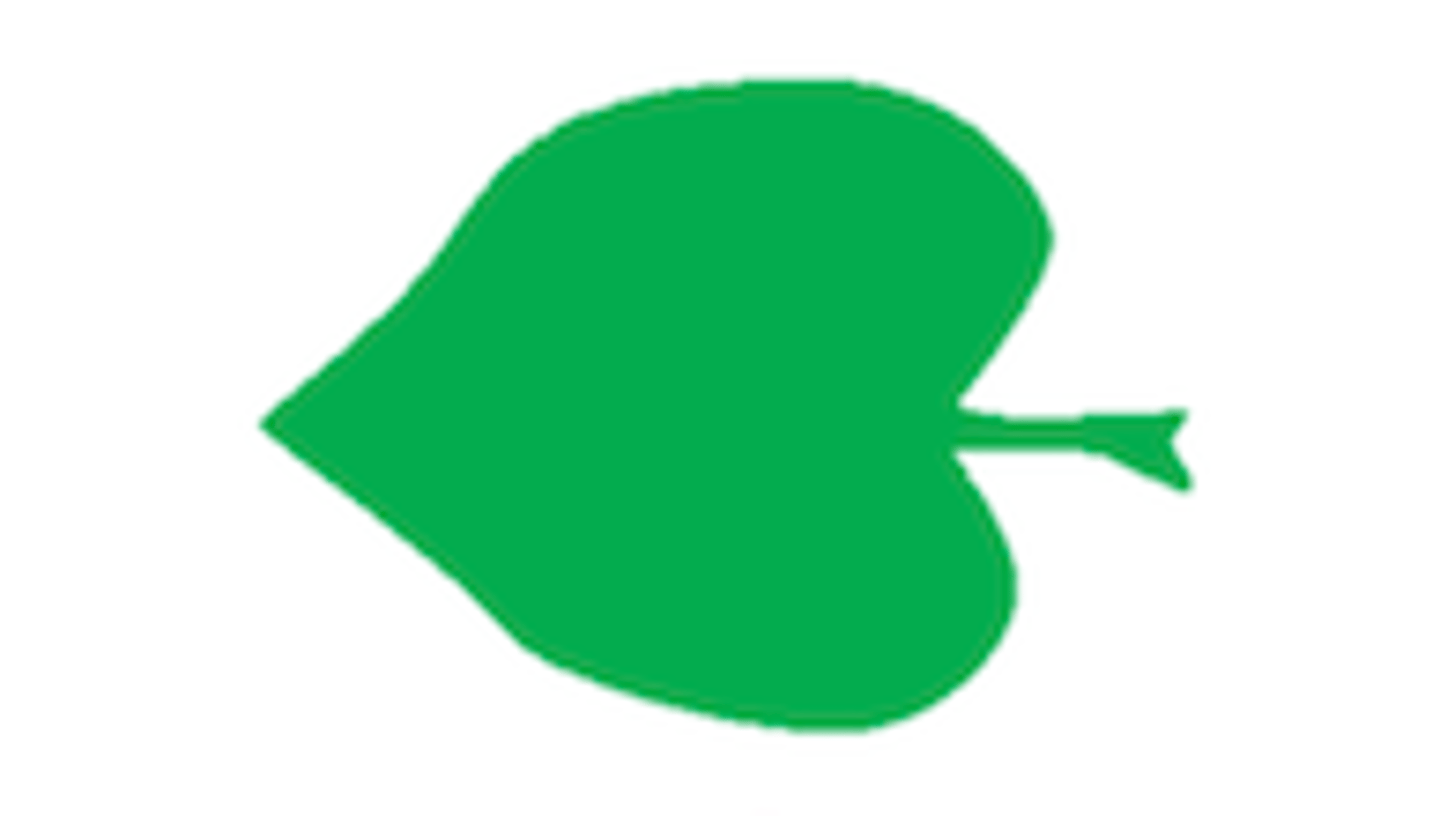

11
Mastered
Lobed: indented margins
What shape is this leaf?

12
Mastered
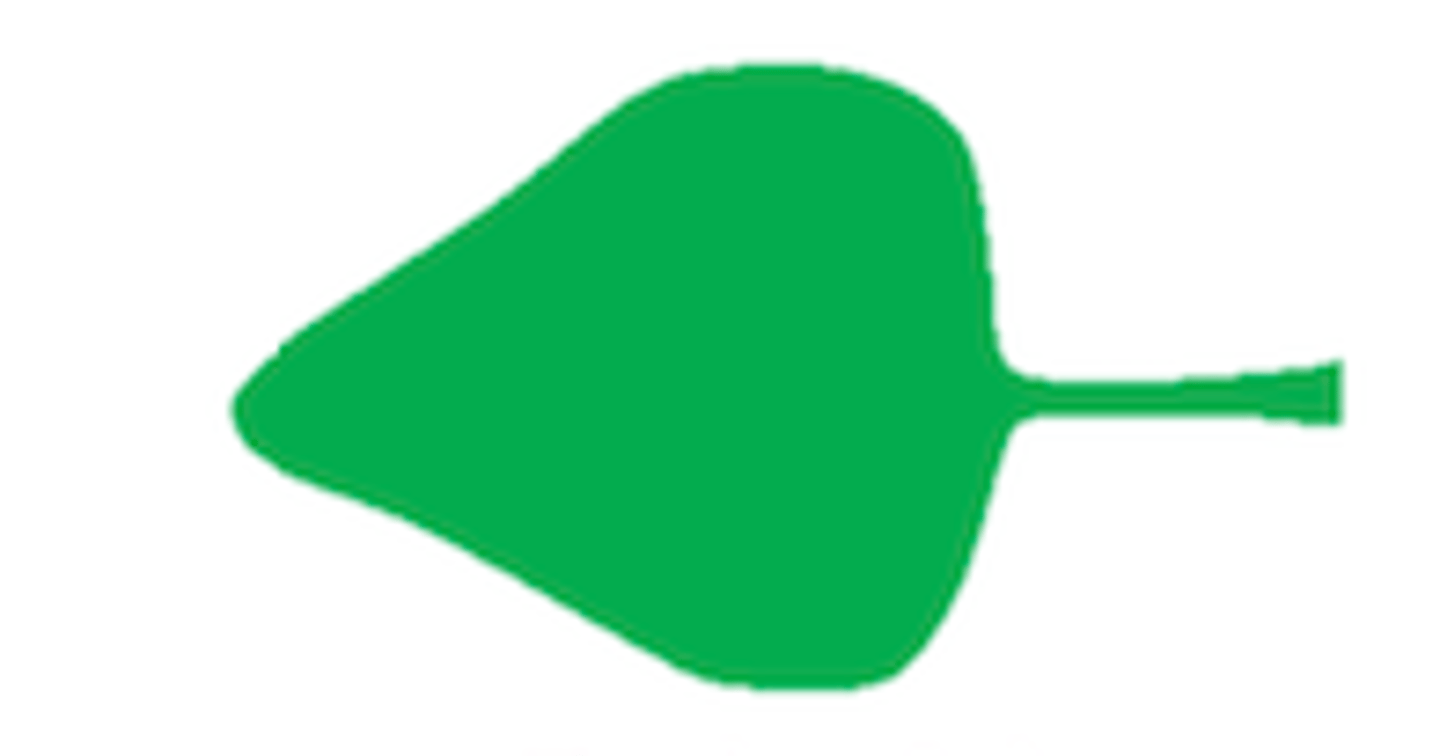
Deltoid: triangular
What shape is this leaf?
13
Mastered
Palmate: hand-shaped
What shape is this leaf?
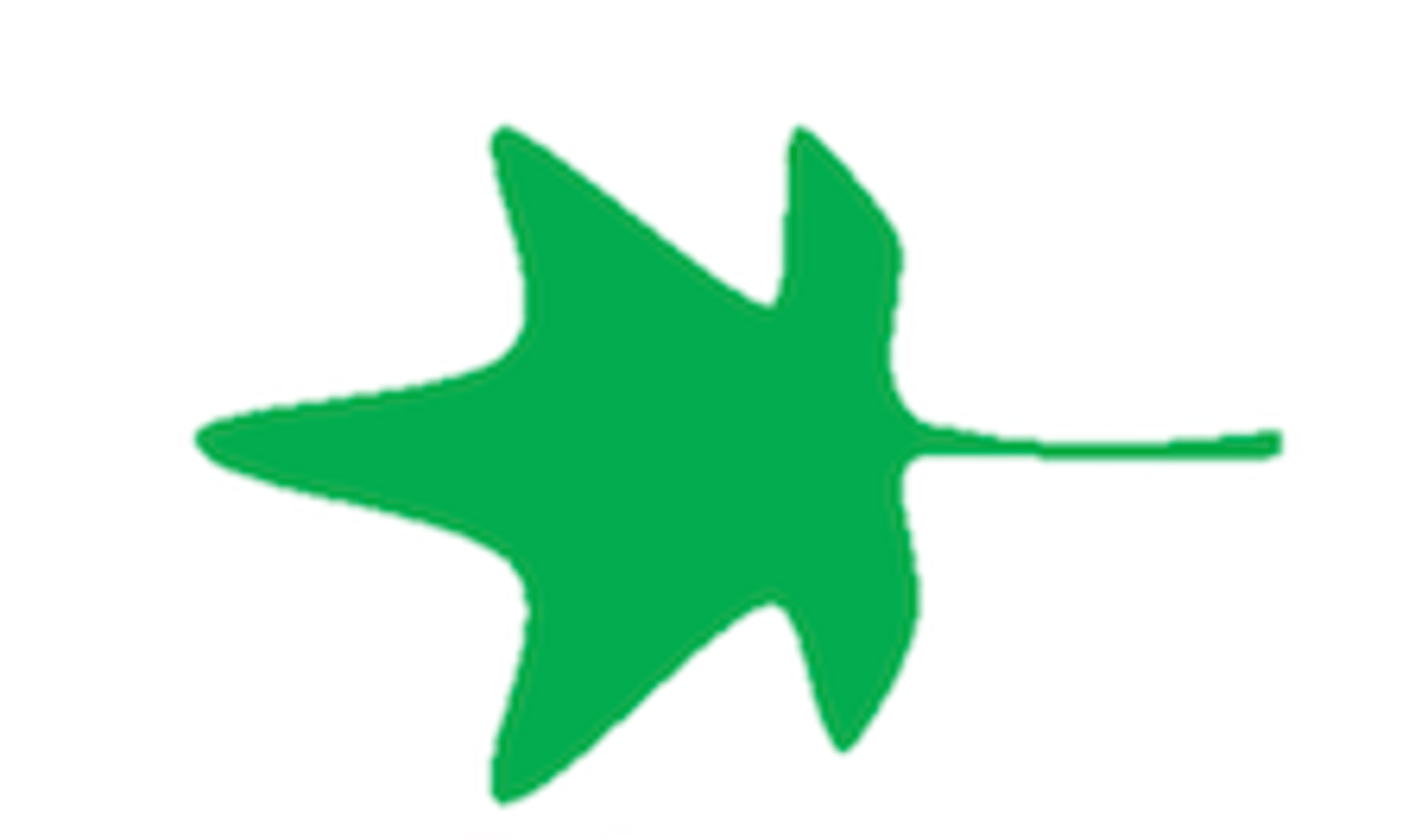

14
Mastered
Elliptic: oval-shaped with little to no point at tip
What shape is this leaf?
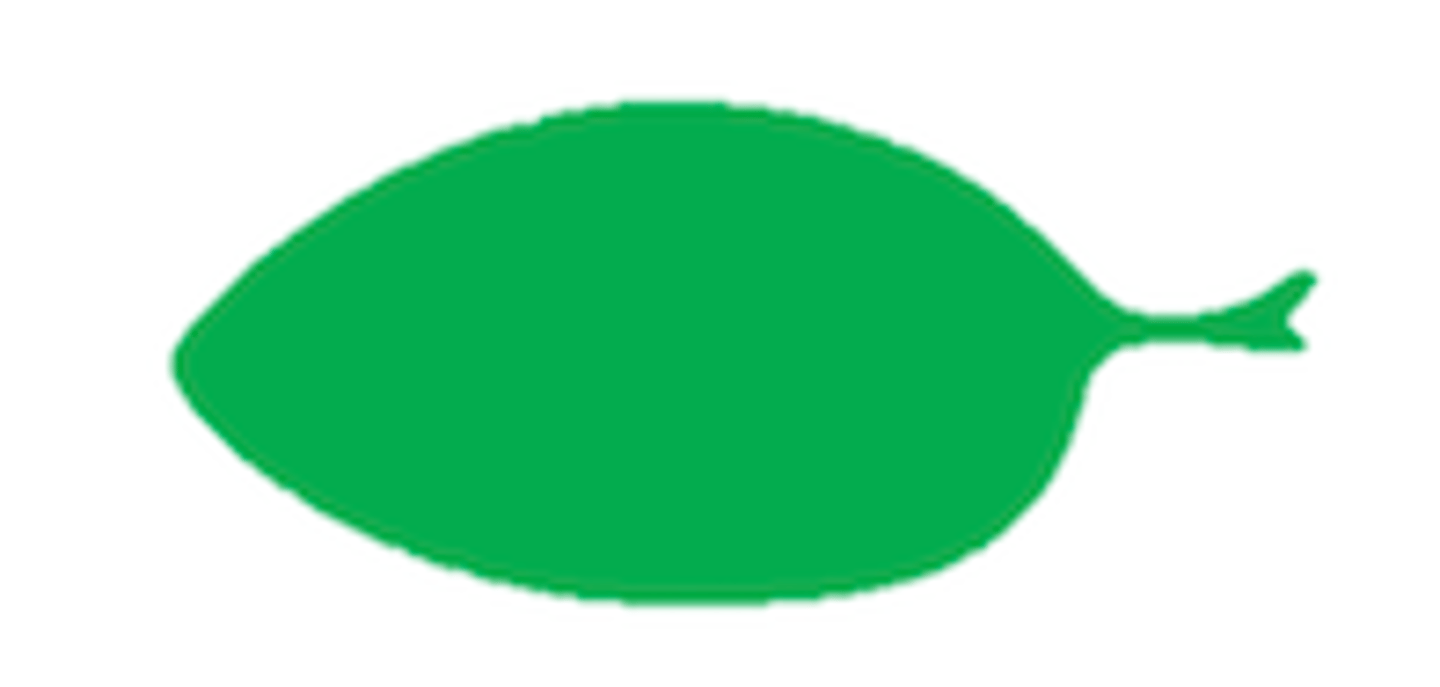

15
Mastered
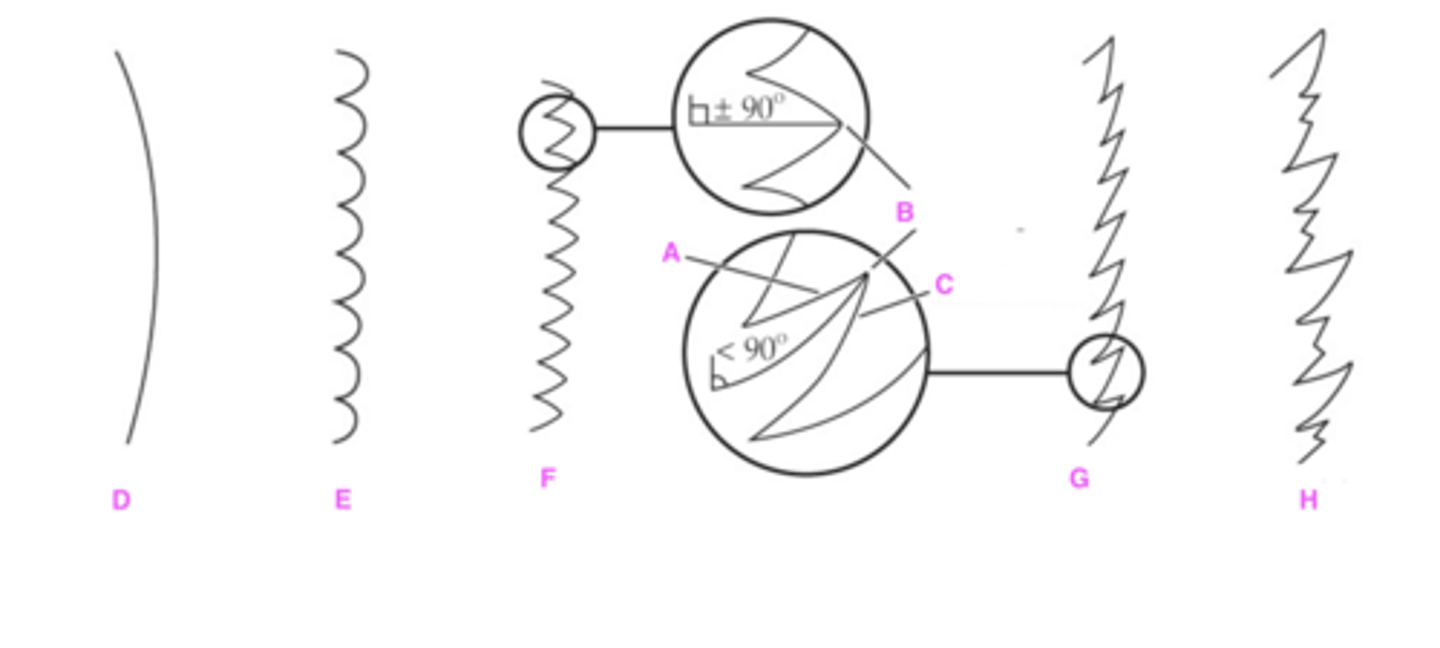
A. Apical side
B. Tooth apex
C. Basal side
D. Entire: leaf margin is smooth
E. Crenate: leaf margin is wavy
F: Dentate: teeth on leaf margin at 90 degree angles
G: Serrate: teeth on leaf margin LESS than 90 degree angles
H: Doubly serrate: serrate with small sub-teeth
Label structures A-H with proper leaf margin terminology.
(hint: A & C are asking for the term for these sides)
16
Mastered
parallel: veins run parallel to one another (monocots)
What type of venation does this leaf display?
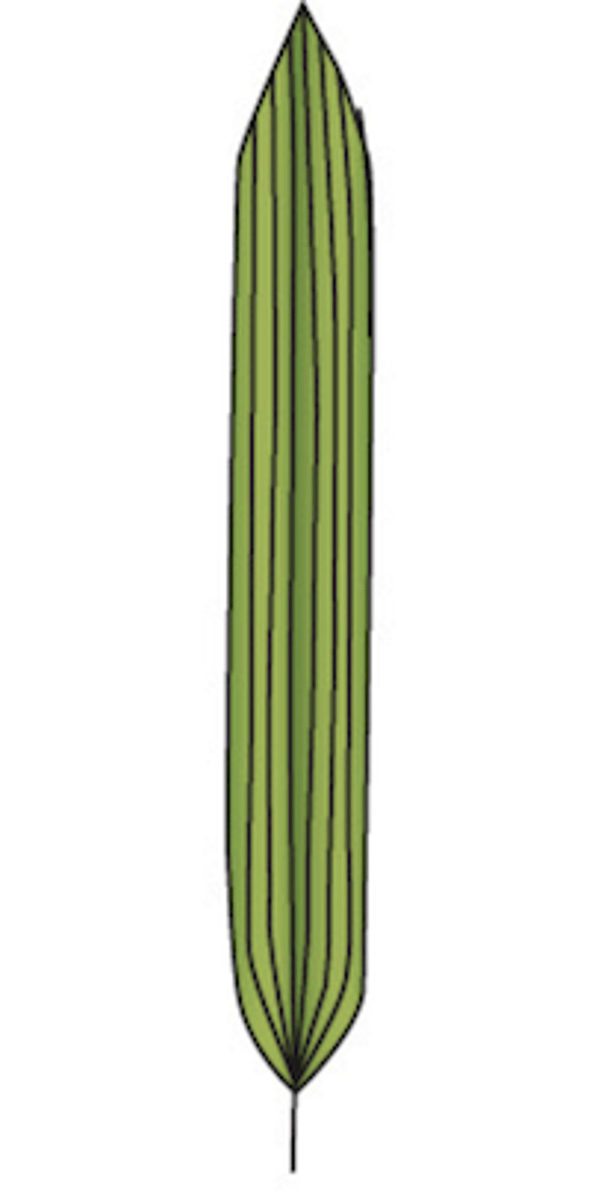
17
Mastered
arcuate (think that the veins are ARCING)
- veins arch to come into contact (or nearly) at the leaf apex
What type of venation does this leaf display?
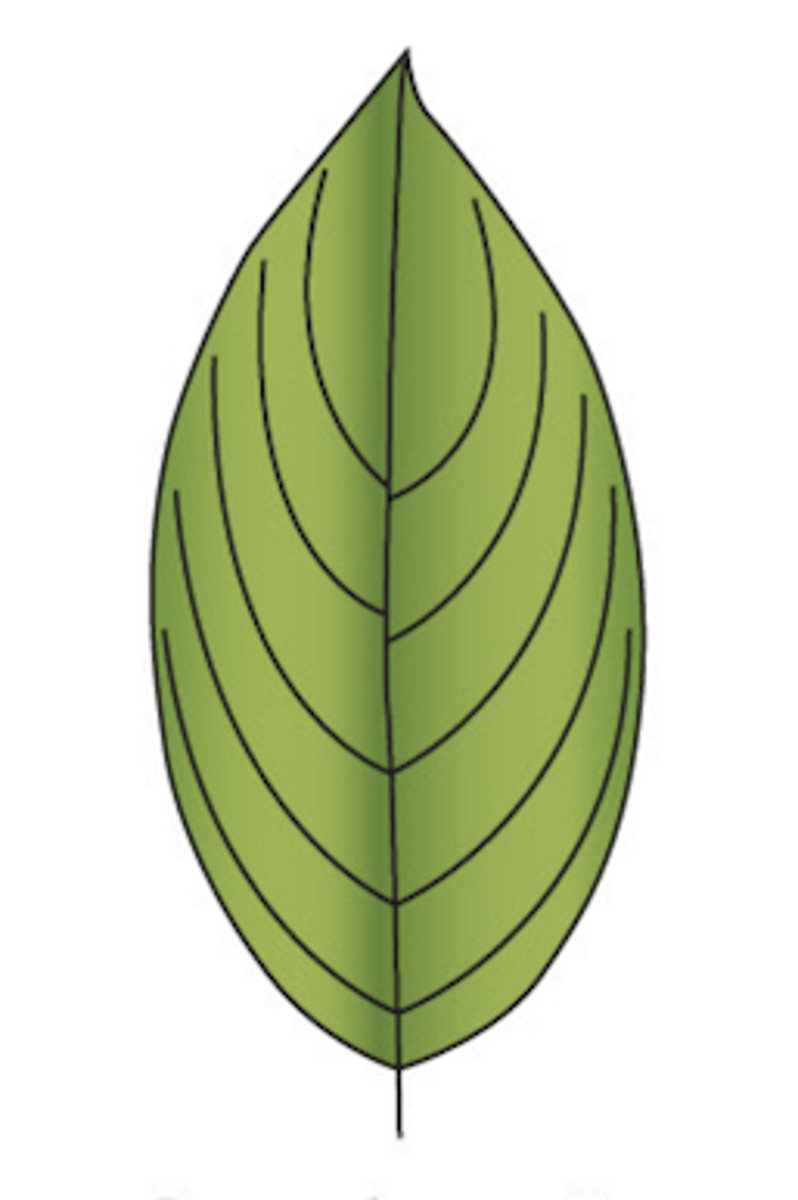
18
Mastered
dichotomous: veins branching in pairs, may or may not end in teeth
What type of venation does this leaf display?
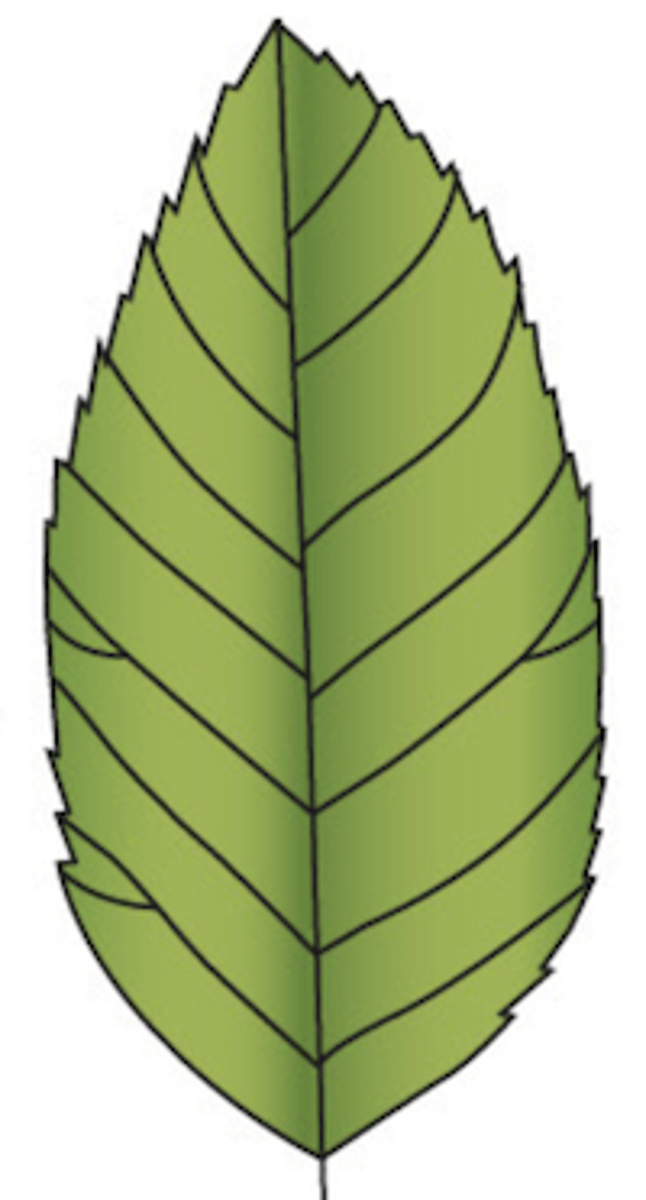
19
Mastered
dichotomous: veins branching in pairs, may or may not end in teeth
What type of venation does this leaf display?
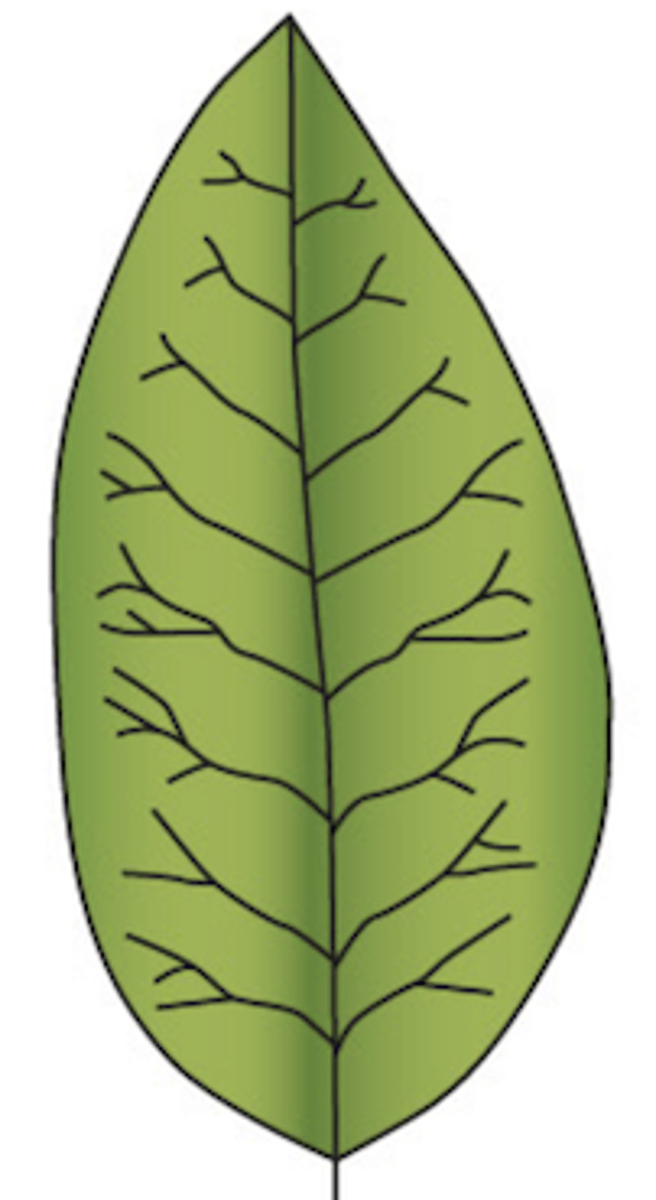
20
Mastered
alternate: 1 leaf per node
What type of leaf arrangement does this plant display?
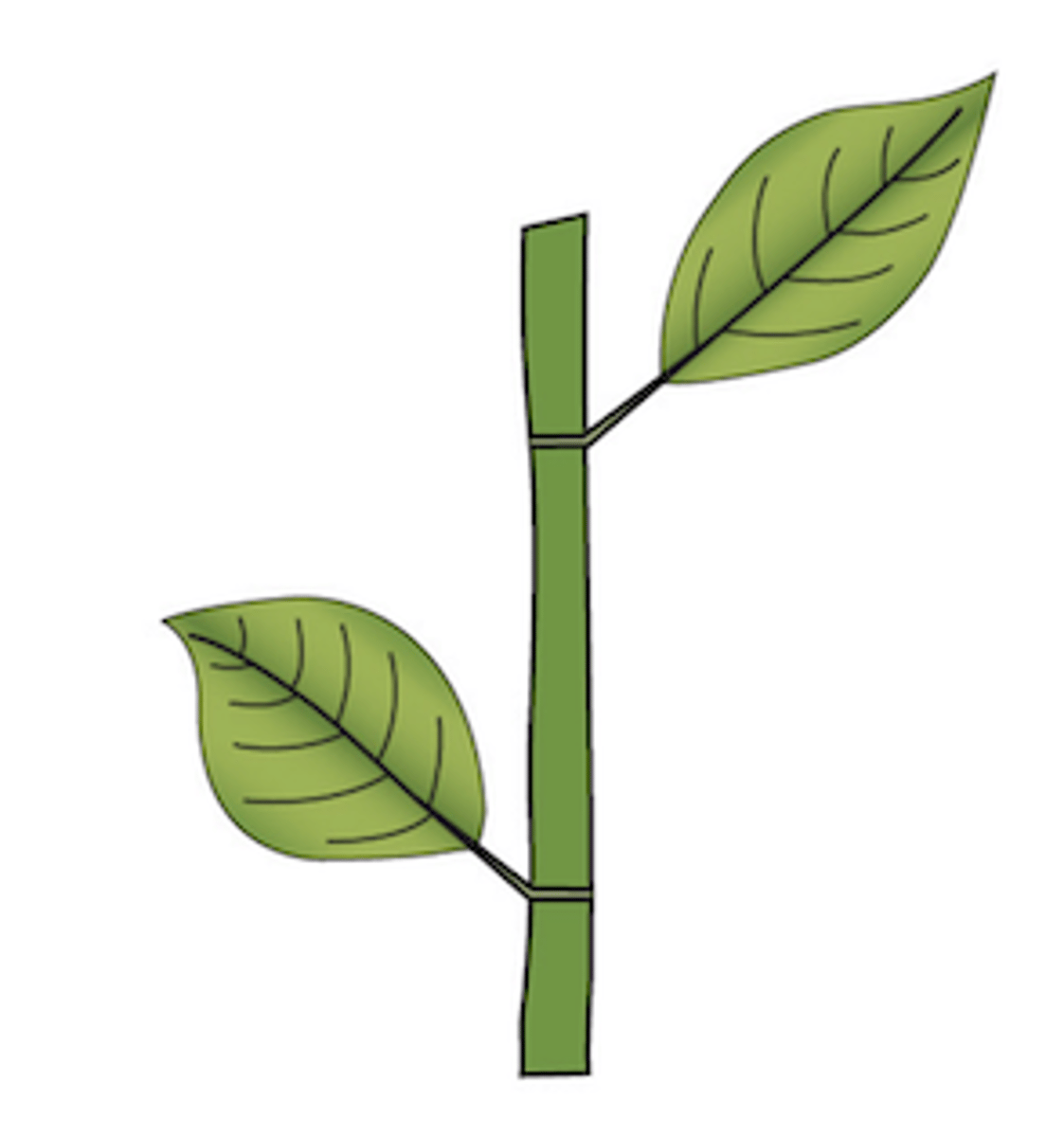

21
Mastered
opposite: 2 leaves per node opposite from one another on stem
What type of leaf arrangement does this plant display?
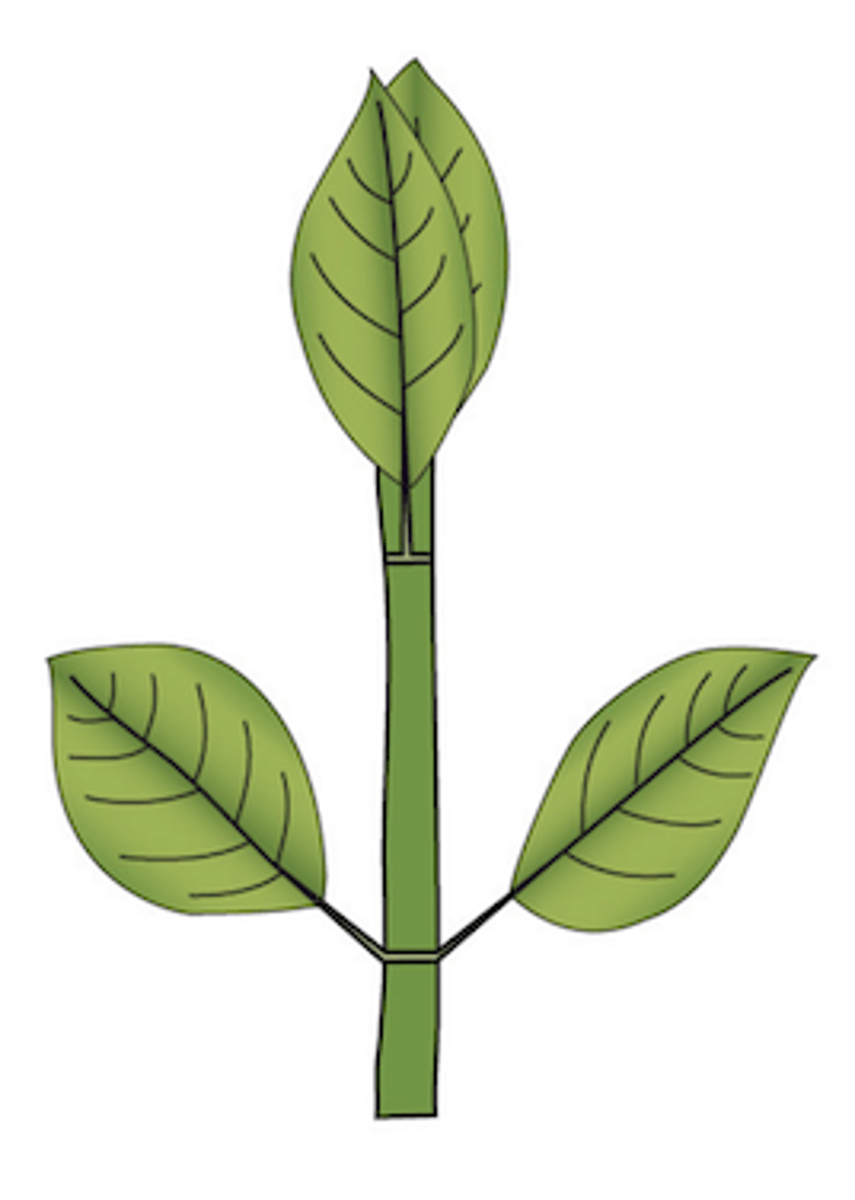

22
Mastered
whorled: 3 or more leaves per node
What type of leaf arrangement does this plant display?
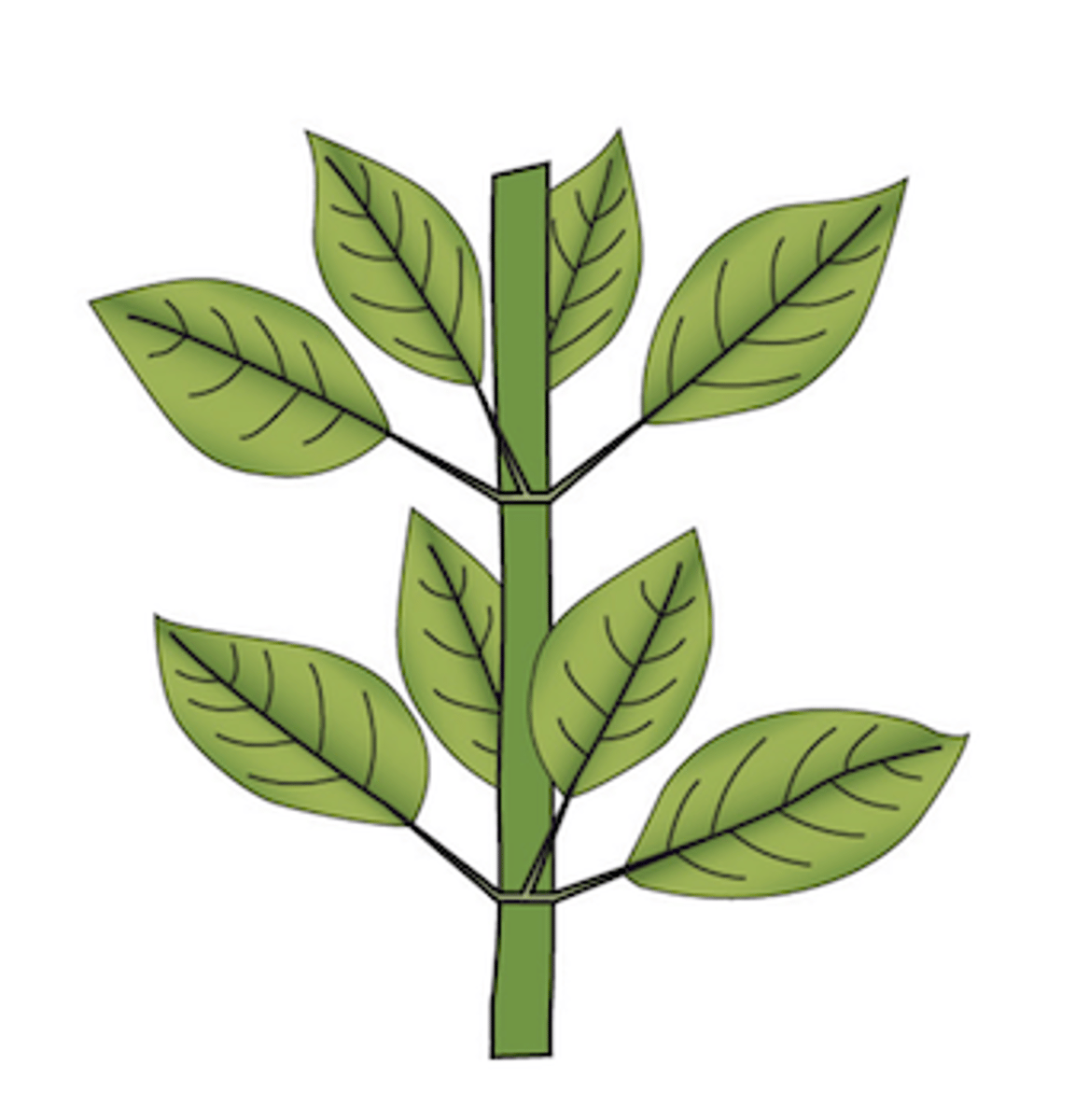

23
Mastered
Bud placement
What feature on a twig can you use to determine if its leaves are compound or not?
24
Mastered
Simple: single blade connected to a stem
Explain the type of leaf complexity this leaf possesses (simple, compound, etc.)
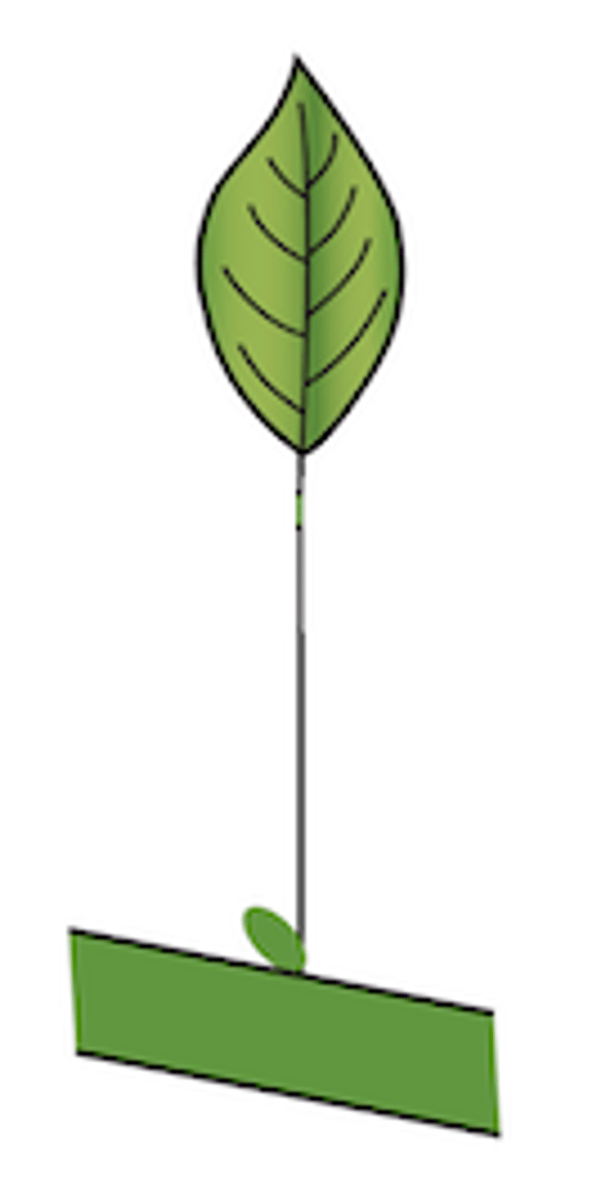

25
Mastered
Trifoliate: single blade with three lobes
Explain the type of leaf complexity this leaf possesses (simple, compound, etc.)
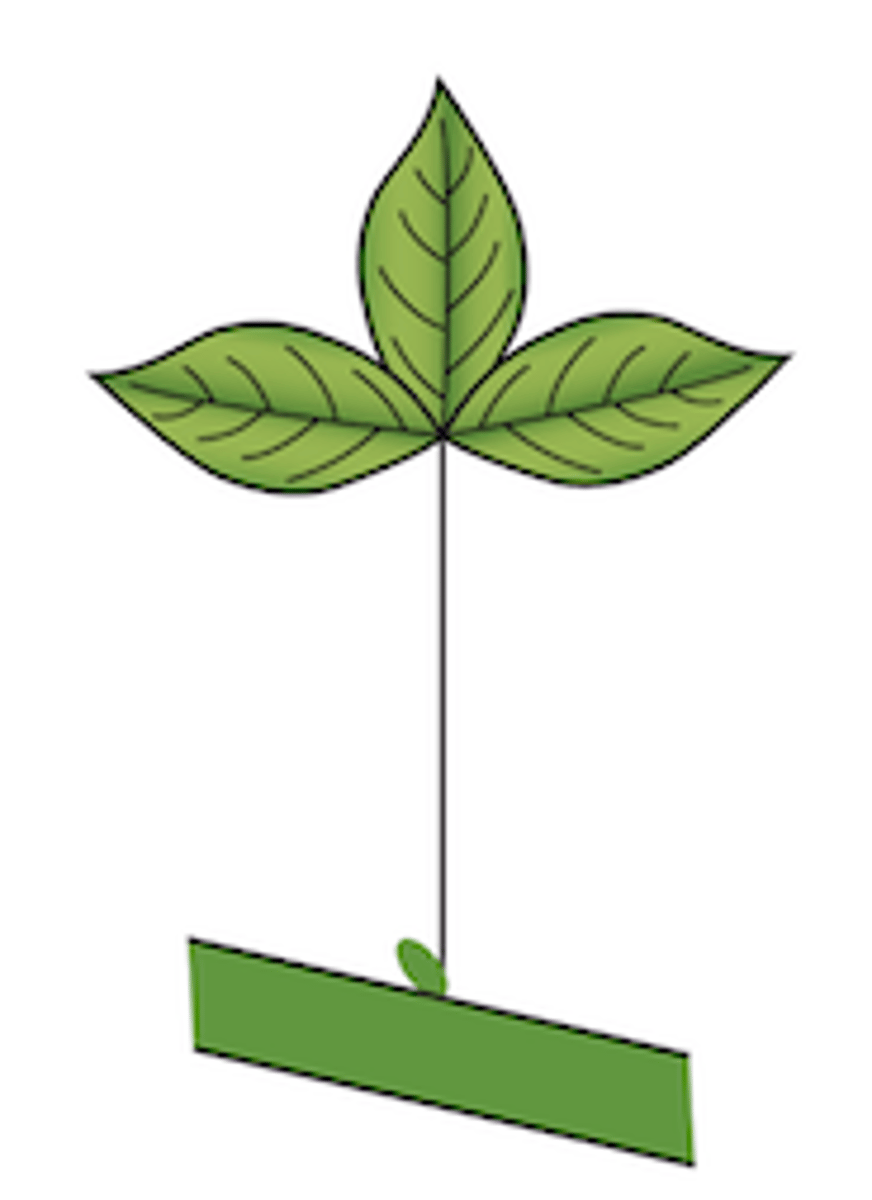

26
Mastered
Pinnately-compound: each leaf has multiple leaflets
A. Rachis (area of petiole between leaflets)
B. Petiolule (where leaflet meets rachis)
C. Petiole
D. Terminal leaflet
Explain the type of leaf complexity this leaf possesses (simple, compound, etc.) and label structures A-D.
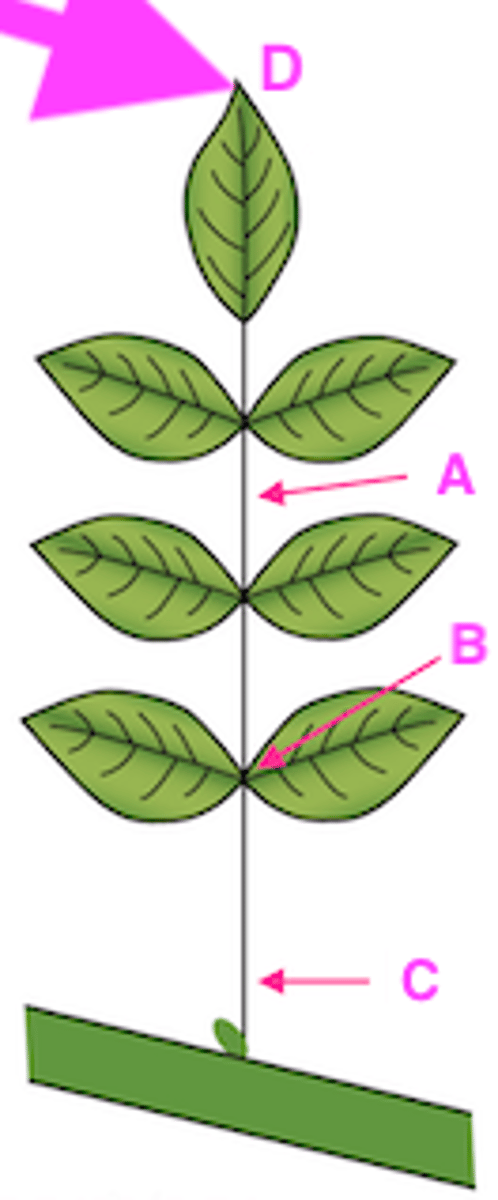
27
Mastered
Pinnately-compound: each leaf has multiple leaflets
A. Leaflet
Explain the type of leaf complexity this leaf possesses (simple, compound, etc.) and label structure A.
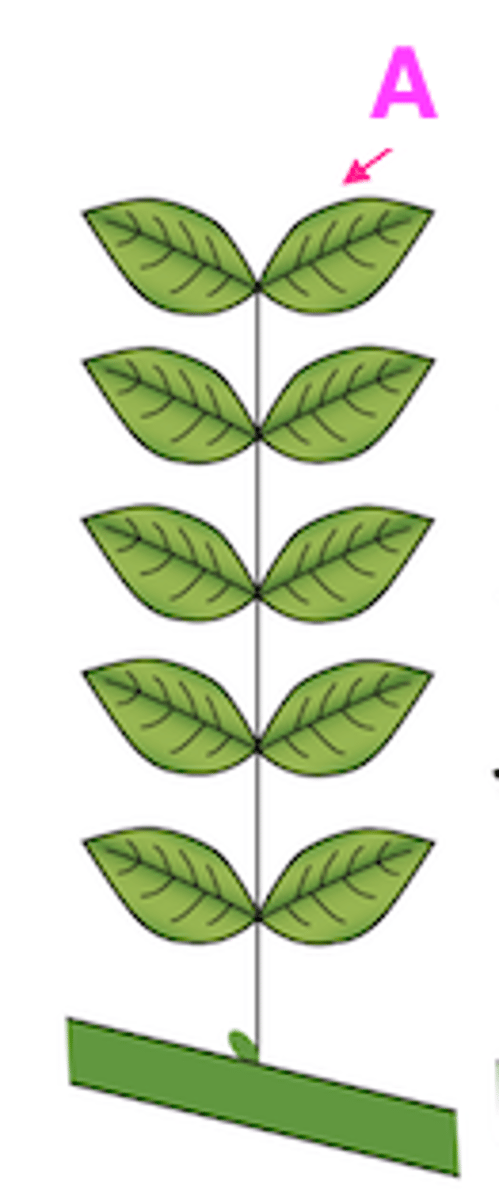
28
Mastered
Palmately-compound leaf: leaflets arranged to resemble a hand
Explain the type of leaf complexity this leaf possesses (simple, compound, etc.)
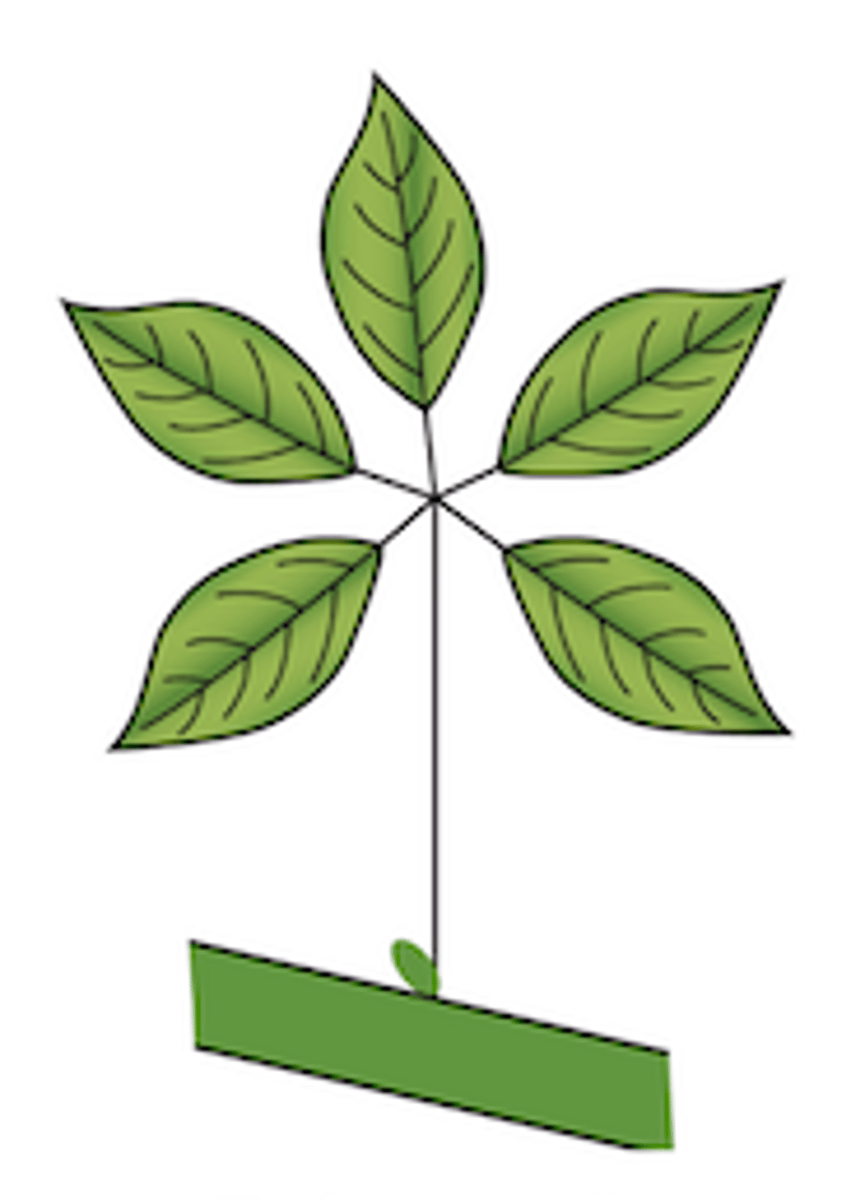

29
Mastered
Bipinnately-compound: two levels of division
A. Leaflet
B. Petiolule (where leaflet meets rachis)
C. Rachis (think baby stem on compound leaves)
D. Petiole
Explain the type of leaf complexity this leaf possesses (simple, compound, etc.) and label structures A-D.