Geology test #3
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
What are 3 ways to melt the mantle?
decrease temperature
Increase temperature
add violates
What is the geotherm?
The change in temperature with depth(red/ green line in diagrams)
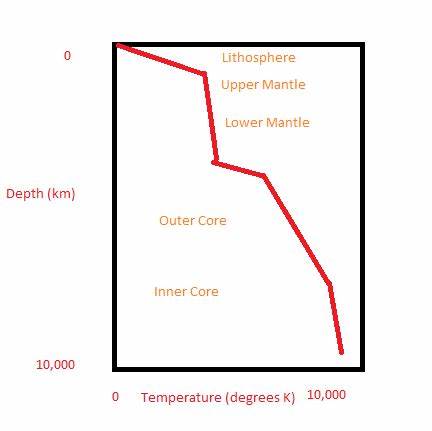
Lithospheric Geotherm
Conductive heat transvers
temperature changes significantly with depth
Asthenosphere geotherm
Convection heat transvers
Adiabatic Geotherm : pressure changes a lot, temperature changes very little
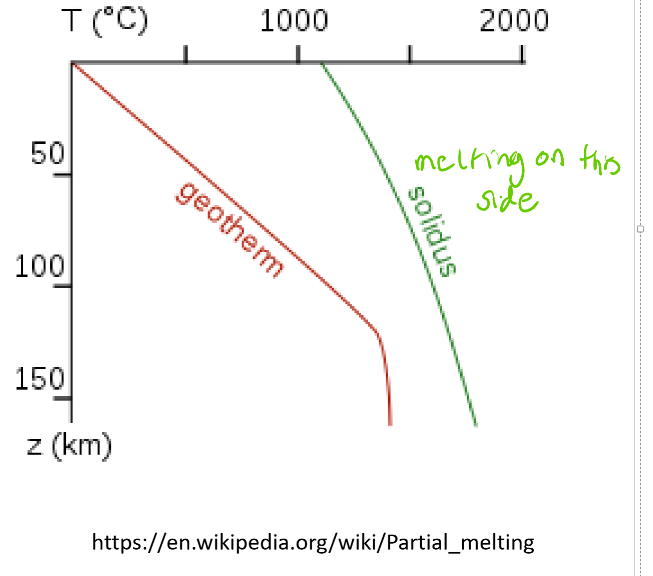
On What side of the curve does it remain solid or melt?
A mantle curves that resides at T and P to the left of the curve with remin solide
Where as to the right it will be at a high enough T and P to melt
Where does hot spot volcanism most occur
occurs within plates
away from plate boundaries
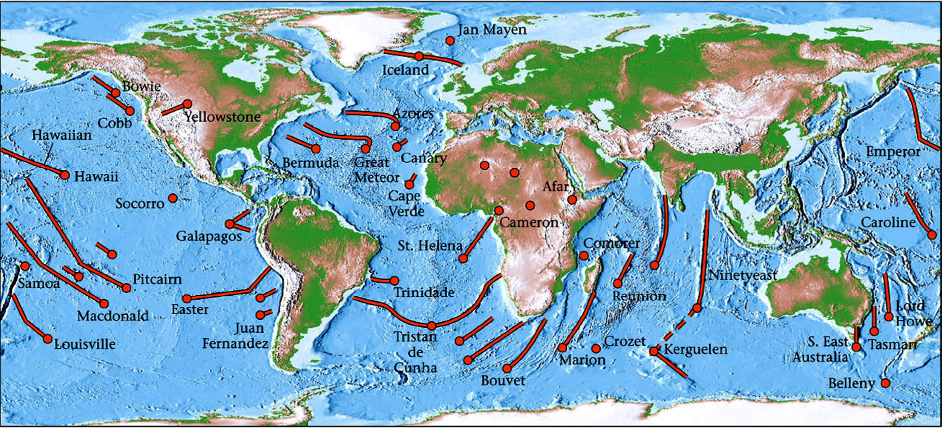
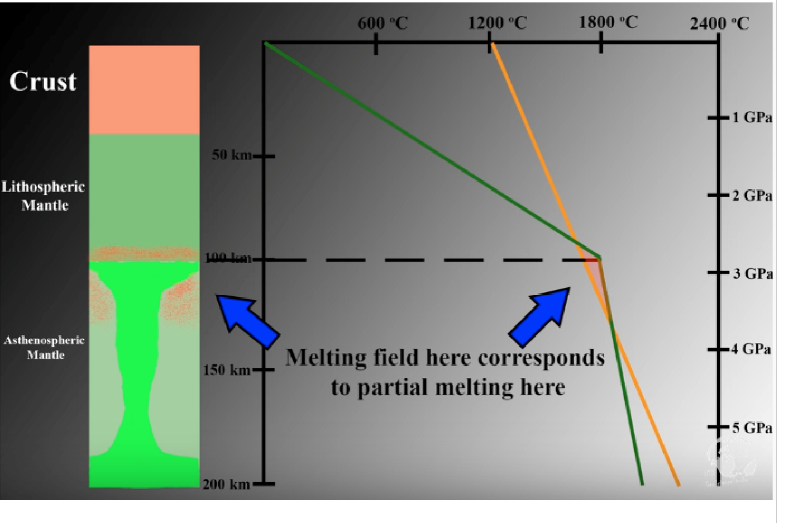
What is decomposition melting?
Thinning of the lithosphere
which allows partial melting to occur where geotherm crosses the solidus
0987u5y4tfgn h
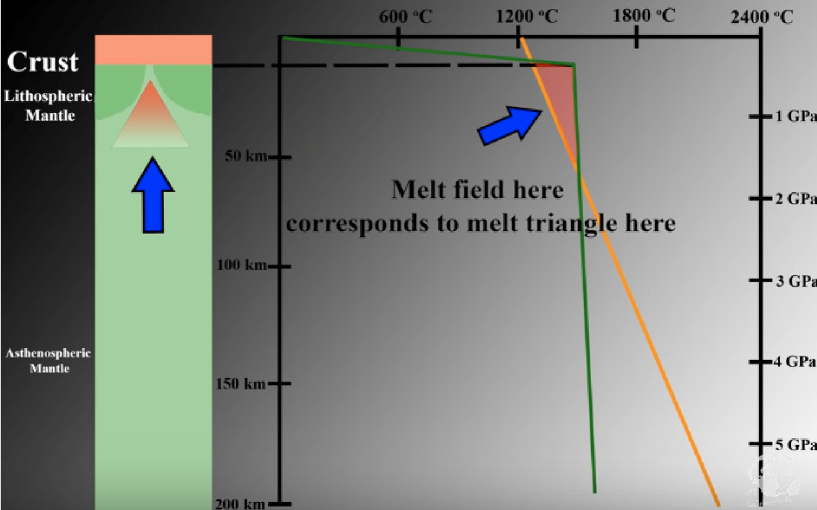
How is decomposition melting accomplished
Extension at midocean ridges
continental rifts
divergent boundaries
Adding volatics: Flux melting
changes the melting curve/ solidus/ liquidus such that it cross the geotherm
The blue lines is the wet solius
Cause by convergent margins
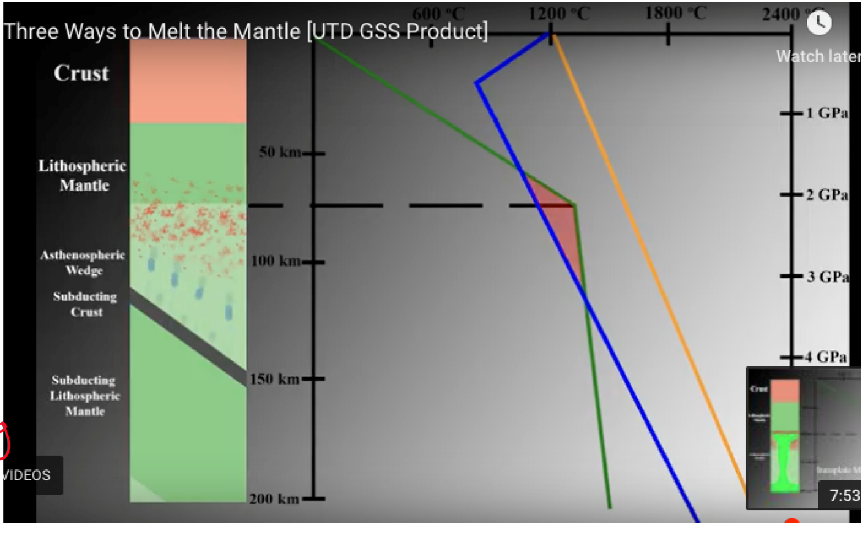
What is an example of adding volatiles
Ocean-continetial and ocean-ocean convergent plate boudries
The deceding slab contains wet sediment and hydrate minerals formed by alteration of the basalt on the seafloor
As the plate subducts is driven off the slub and into the overlaying mantle wedge
The hyrdate mantle melts at lower temp than dry mantle
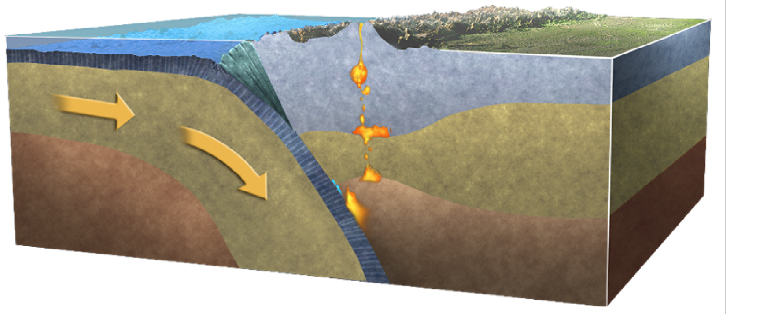
How can melts be created
Plates seperate and mantle rises at mid-ocean ridges ( decompostion melting)
Hot spot- localized plumes of melt
Fluid fluxing
Where is the only part of earth where the mantle can melt?
Outermost 200km of earth
How does the geotherm slope change?
the slope is a function of geotherm thickness
lithopsheric geotherm increase as you move the curve up
astherospheric remains constant
Mantle plumes
increase the geotherm by the addition of heat from the mantle
allow melting to occur in the triangular region
happens at hot spots in Hawaii
1. What is the name given to the region surrounding the Pacific Ocean where most subaerial (land-based) volcanoes occur?
The ring of fire
cotnains 75% of planets voclanoes
1. Why do volcanoes occur here—what is the tectonic setting of this region?
Is is where multiple tectonic plates meet
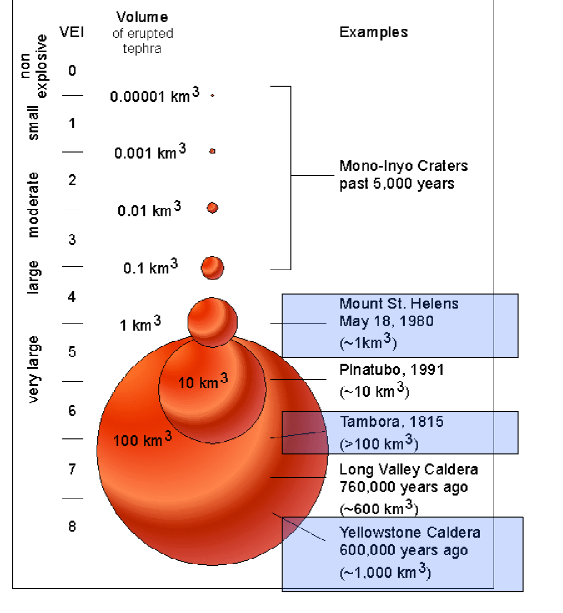
What is the Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI)
It measure and classify eruptions. It starts at zero and is a log scale. Does not have a upperlimit
1. What was the most explosive (higher VEI) volcano recorded?
VEI 8 which ocured thosands of millions of years ago
The most explosive volcanoe recorded was in Indonesia in 1815 which was a VEI of 7
1. List 2 benefits of volcanic eruptions
volcanic ash provide nutriest to nearby soil making the land fertile
when lava hardens into rock and creates new landforms
what characterists of an eruption are used to classify volcanoes according to this Index?
volume of lava gas and other emmsions from the volcanoe
height of the eruption cloud above the summit
the degree of fragmentation
What produces the contrast in explosivity
melting viscosity (the main control)
Composition and temperature: felsic vs mafic
Volcaltiles- context of gasses
Interaction with external water
Melting Viscosity
The higher the silica content and the lower content of FE and MG, the more viscous the melt
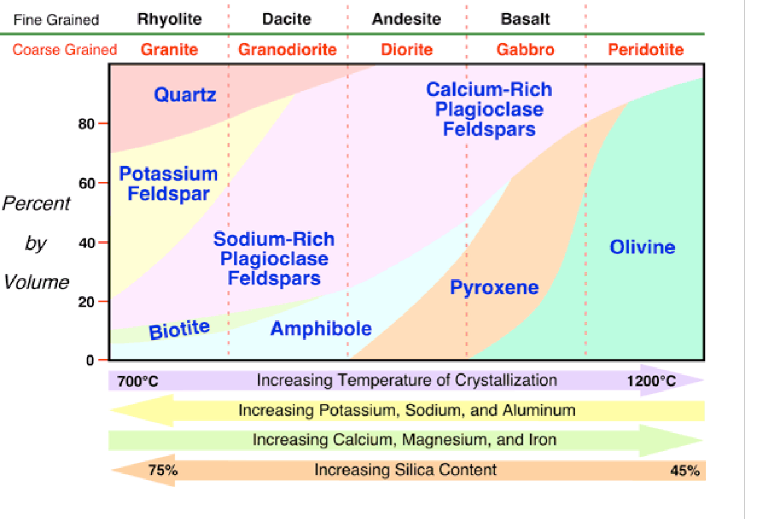
Which of the compositions would have the higher viscosity
this mean that these compsotions tend to be more explosive
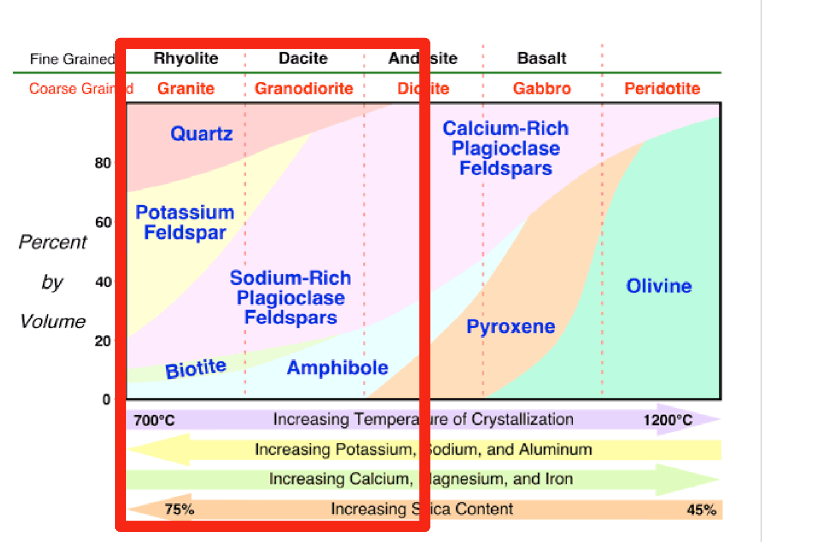
What type of characteristic have less viscous (less explosive)
more mafic/ bastlic melts
higher temerature
more fluid
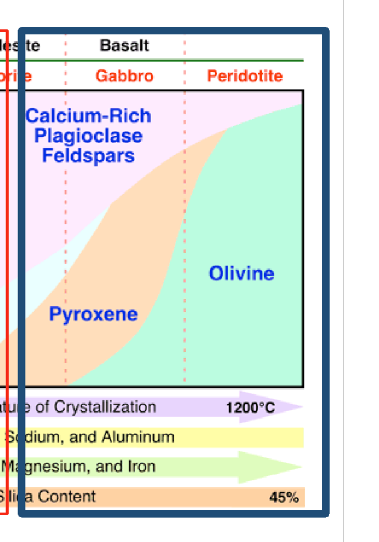
Where do you get partial melts of the matnle reaching the surface of the earth without getting throguh the crust?
Oceanic divergent plate boudnries
oceanic hot spots
Where are more felsic melts produced
contiential divergent plate boundries
contienal hot spots
convergent plate boundries
What is the role of expanding gas on volcanic erruptions
they drive the volcanic erruptions
dissolved magmas under pressure
come out of solution and expand as magma rise
What are the mian magetic gas that are associated with expanding gases
H20, C02, so2
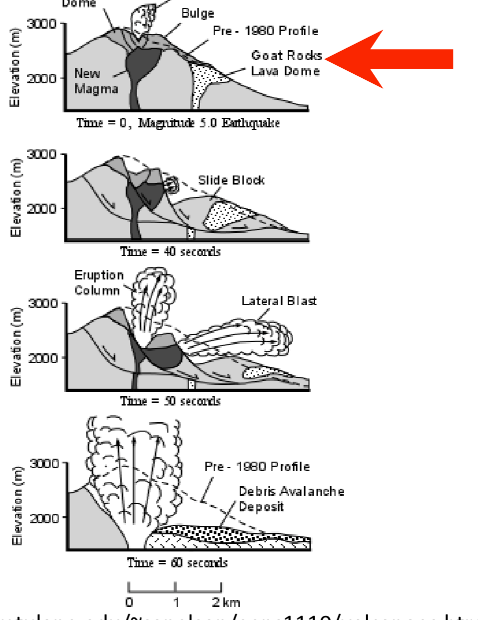
What is an example of expanding gases?
Mount St. Helens
magma rises in the chamber
at lower pressures the gases began to exsolve and the chamber expands
creates a bulge in the side of the mountain
What is the role of external water ?
If rising magma contacts water the water can vaporize
Intermingle with melt and cause an erruption
What is the classification of volcanic explosive index based of?
The volume of ejecta
What was the largest recored on the VEI
Tambora 1815
Do volcanoes always have the same classification during their life time ?
No, depends on composition and volatiles which change through the life of a volcano
Hawaiian
basaltic ( low viscosity magmas)
volatile bubble out quietly
not very explosive
Strombolian
bit more explosive
erruption chacterized by short term out put of pasty lava
results in scoria cones
example
MT etna Italy
Particun mexico

Plinian
much stronger
eruption columns reach 45 km into stratosphere
Examples
Naples, Italy
Vesuvius ( one of the most dangerous volcanoes in the world)
Surtseyan
results from basaltic eruption interacting with groundwater or surface water
wet equivalent of Strombolian eruption
water cause to be more explosive
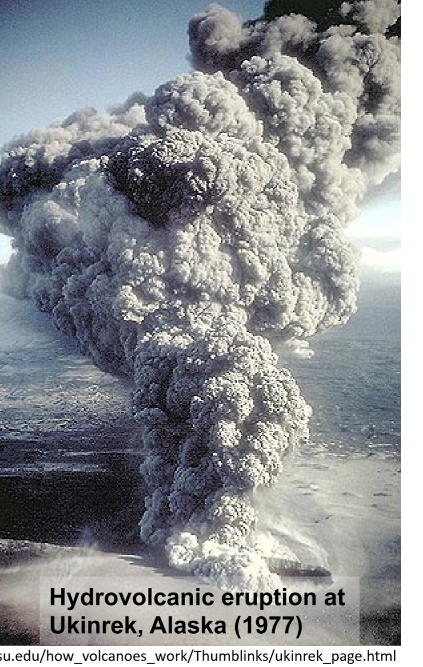

Vulcianian
more explosive that surtseyan
discrete canon like explosions
followed by sustained eruption

Phreatophian
What is a glacier
Mass of compressed ice on land that moves under its own wight
What are the different types of glacier
Alpine, conteinal ice sheets
Where are continental ice sheets only found
Antarctica and Greenland
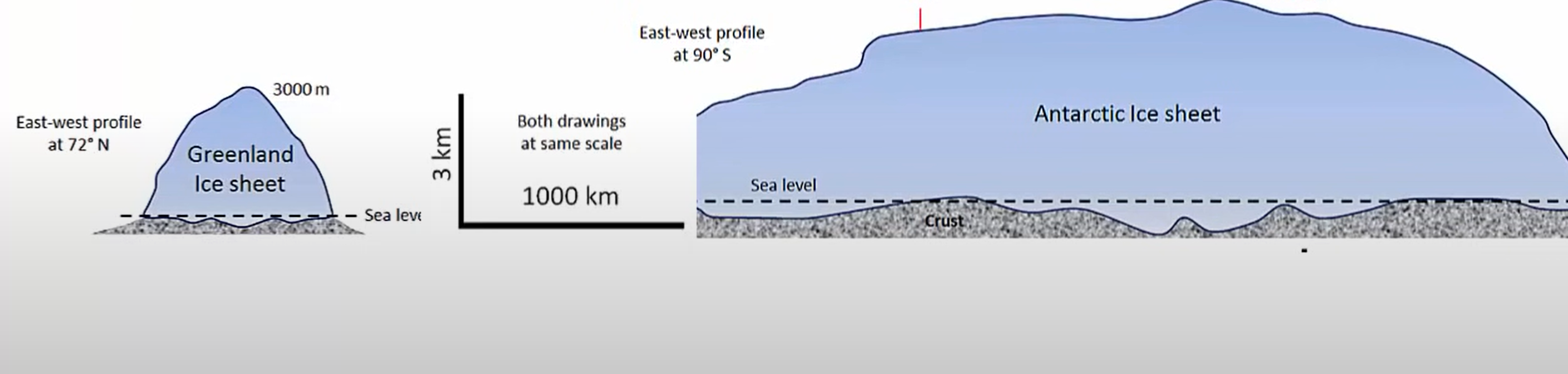
How do alphine glacier move ?
downhill

How do continental icesheets?
move outward from the center where mass of ice is the greatest
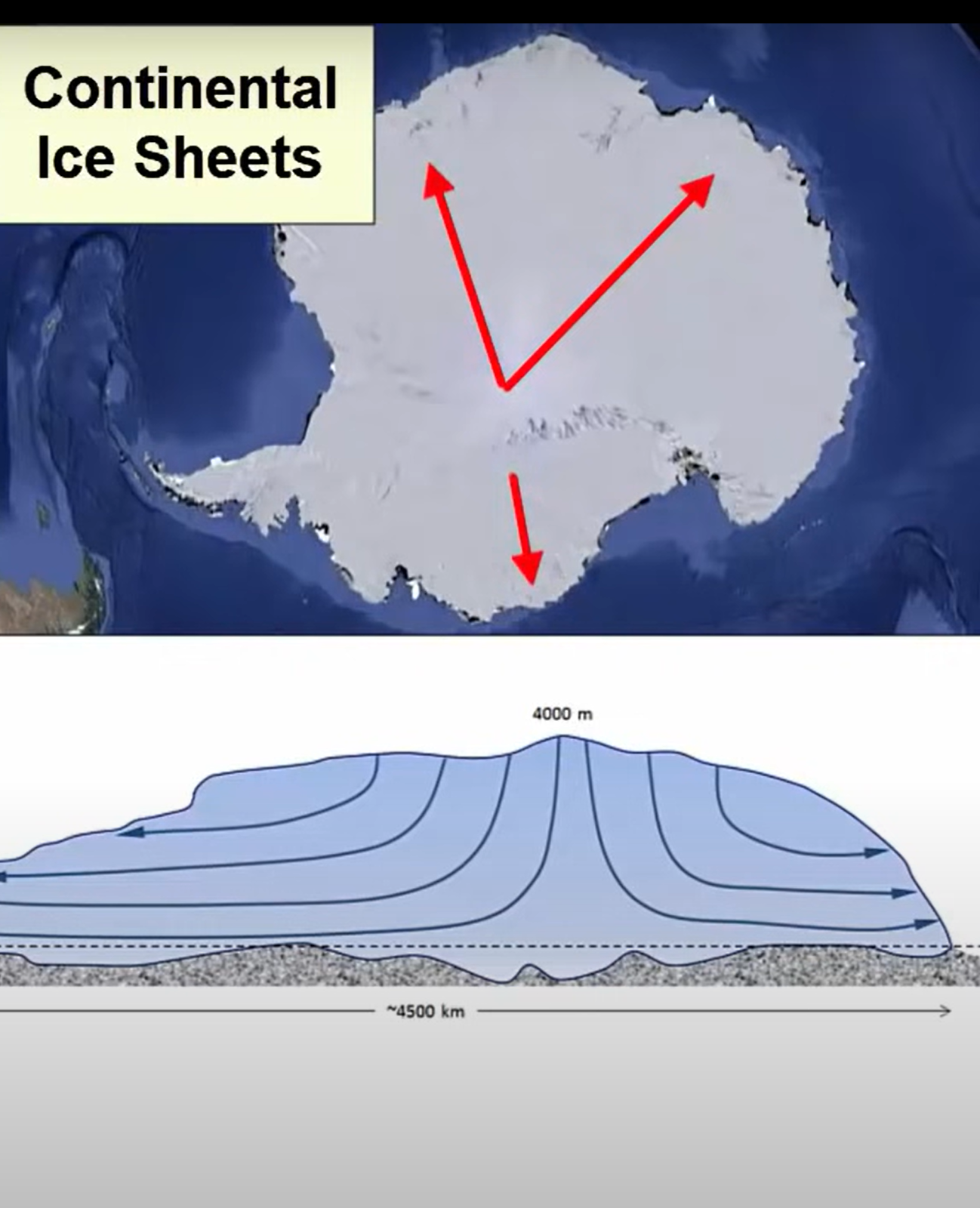
How do glaciers move?
plastic flow
basalt sliding
What happen when more snow is add than lost?
accumulation> ablation
Glacier advances (grows)
What happens when more snow is lost than gained
accumulation> ablation
Glacier retreats shrinks
What are the two forms of weathering for glacier?
Abrasion and frost wedging
Glacial deposits
angular poorly sorted grains
Glacial erratic
isolated large-grain remnants of glacial deposits
Moraine
piles of sediment dropped or spit out by glacier
Which landromed is produced through meltwater dissoposits from the toe of a glacier
outwash plain
The bigger the glacier, the bigger the valley and …
bigger the cirque
Glacier cover blank% of land surve todya and blank% 18,000 years ago(iceage)
10 and 30
Clastic
fragment of pre-existing rack (sandstone)
Chemical
precepted from solution Carbonate)
Biochemical
organisms play a role (shell material)
Organic
comprising large amounts of organic material
Weathering
The decomposition and disintegration of rocks and minerals at the earth’s surface by machinal and chemical processes
converts rock to gravel, sand, clay and soil
Erosion
The removal of weathered rocks and minerals for the place they were found
water
wind
glaciers
gravidity
Mechanical weathering
The physical disintegration rock into smaller pieces each retaining there original characteristics
Chemical weathering
decomposition of rock and minerals and as a result f chemical reactions (removal and/or addition of elements)
What are the main processes of chemical weather?
frost wedging
salt cracking
abrasion
biological activity
thermal expansion and contracting
pressure release fracturing
Frost wedging
when water freezes it expands and water migrates into cracks in rocks. Ice crystals growth puts tremendous pressure on surrounding rocks
Most effective in mountain areas where daily freeze/ thaw. Dangers to hikers

Salt cracking
salts crystallize in cracks puts pressure on surrounding rock
Important in
dry climate:
costal areas

Abrasion
breakdown of rock by fiction and impact
gilders(effective)
wind
running water(effective)
waves(effective)
Biological activity
plants growing in cracks in rocks
burrowing animals
human blasting for roads, development exploration
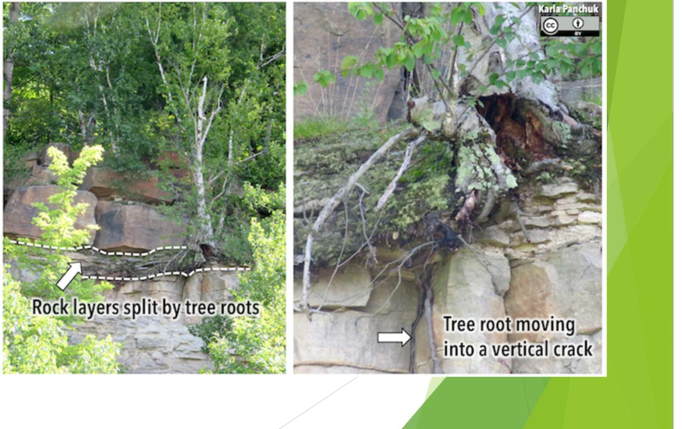

Pressure release fracturing
buried rocks are under confining pressure
when exposed they expand due to releasing
problem for miners
What is the main agent of chemical weathering
water
Dissolution
produces ions ( not minerals) and are reversable is the solvent is removed
Ex dissolving soluble materials in water, the salt is re-participated if the water evaporates
Salt deposits are creating with the drying of ancient seas

Example of dissolution
Natural rain water fall through the soil and reacts with C02 to form carbonic acid.
Carbonic acid reacts with calcite (Limestone) to produce it

Hydrolosis
where dissolution involves the release of ions from a mineral
is a reaction with water to form a hydrated mineral
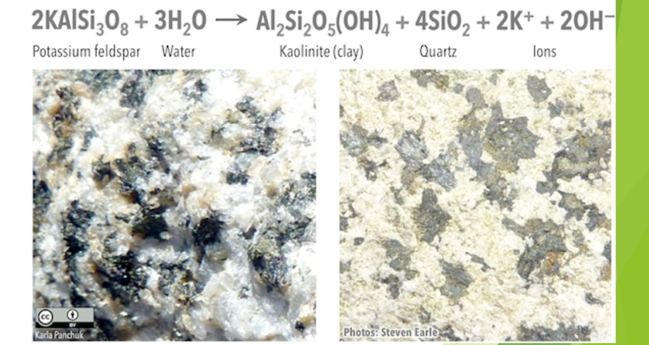
Oxidation
reaction with oxygen
ex iron bearing minerals oxdize to form rust

What are the control on rates and types of weathering
climate
Oxygen and C02 in the atmosphere and soil
Minerology
Surface area- how fragmented the rock is
What are characteristics of sedimentary rocks?
Clast textures:
Size
Shape
Sorting
What is the majour control on size, shape, and sorting?
Agents of transportation:
gravity
wind
water
ice
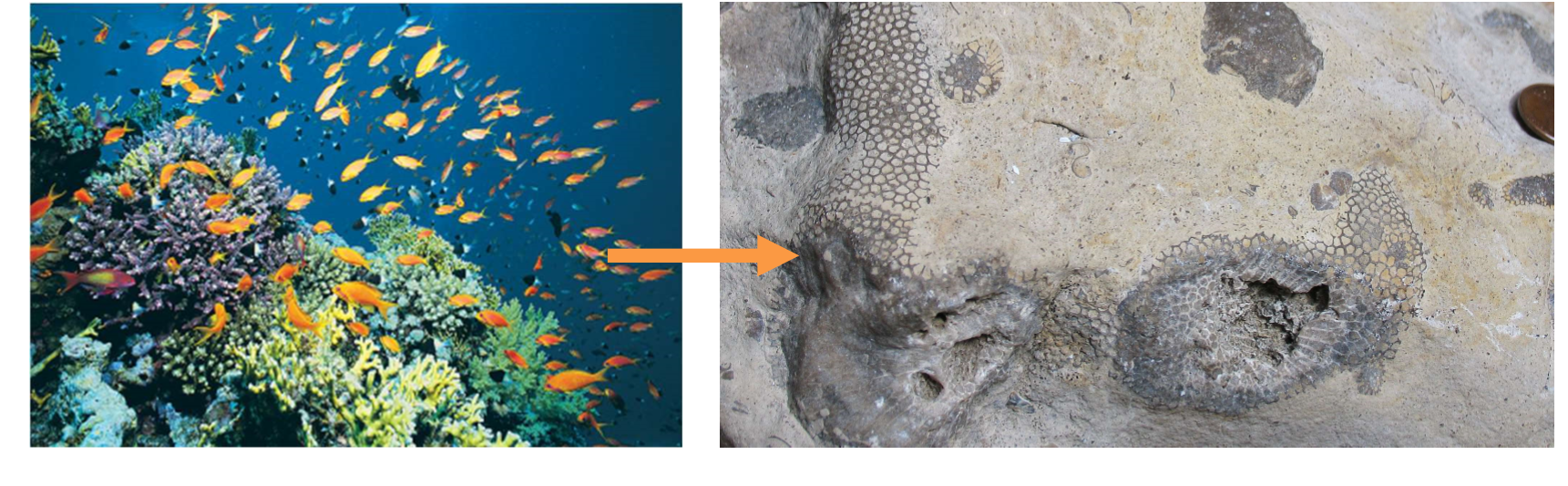
What is an example of chemical; and biochemical sediment
Limestone
formed from shell fragments and test (shells of microfossils)

What are the four general ways that produce volcanic rocks of different compositions