Topic 5: Soil Systems and Terestrial Food Production Systems and Societies
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
subsistence farming
farmng to produce enough to feed their family
commercial farming
faarming on a large scale for busness
cash cropping
a crop that is grwon souly for commercial use and not the grower for profit
pastoral farming
farming based on rearing livestock
arable farmng
only crops are grown on that land
mixed farming
combining crops and livestock
monoculture
only growing one crop
malnutrition
lack of proper nutrition tht is damaging to health
food choices
the choice that people have with fod considering ecological conditions, cultures/religious restrictions, political restrictions, market forces
soil profile
the cross section of the soil that shows the layers that run parallel to the surface. it usually is 6 layerssoil
horizons
the individual layers with distinctive features
sandy soil
gritty and fall apart easily
good drainage
poor water retention
high porosity
low microbial diversity
poor nutrient retention
silty soil
smooth texture
high water retention
low aeration
low porosity
clay soil
poor drainage
high nutrient retention
poor aeration
high microbial diversity
LOAM soil
roughly 40:40:20 sand, silt, clay nd is best for agriculture
allows for adequate nutrient retention
good aration
good water retention
can supports a range of microbes and even invertebrates
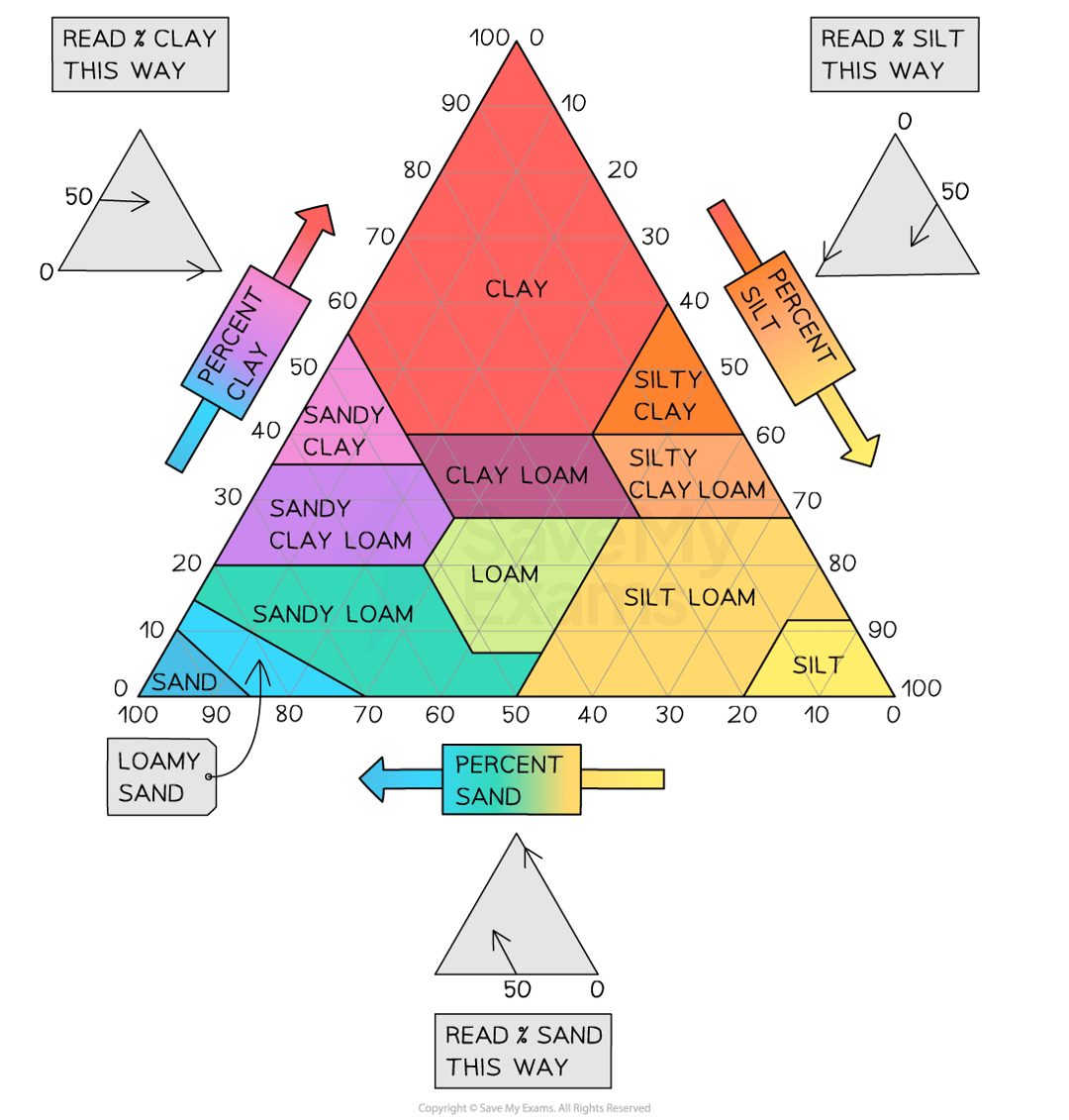
soil texture triangle
what are the soil horizons?
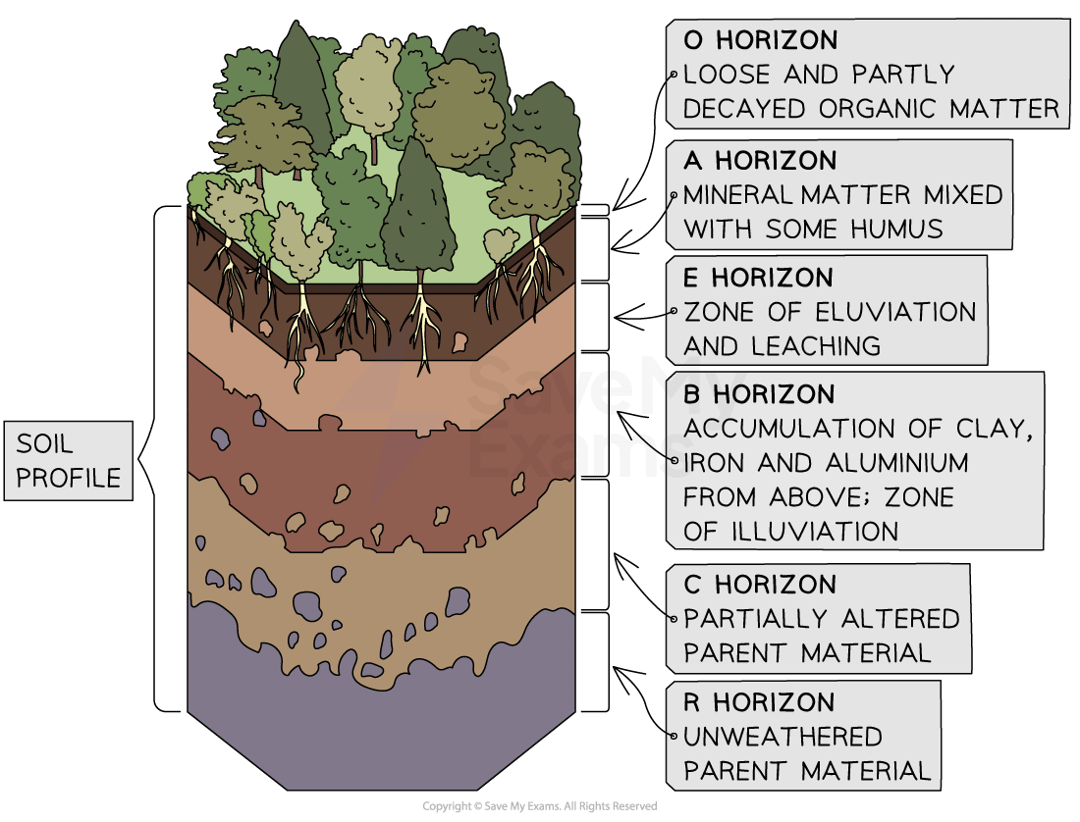
o - organic horizon that is newly deposited organic matter that s broken down by different organisms
a - eluvial, topsoil that is a build-up of humus (partially decomposed, fine material particles) it is dark in colour, waterlogged (gleying) with reduced decomposition
e - less humus and more inorganic material, lighter in colour
b - illuvial layer of clay and iron salts deposited in soluble minerals an organic matter
c - parent material (early bedrock) mainly weathered rock
r - unweathered parent material (late bedrock)
parent material
weathered rock that releases minerals into the soil
humus
decaying matter usually on the surface that is plant and animal matter
eluvial
material being displaced away from a soil layer
illuvial
material being displaced into a soil layer
describe the soil system
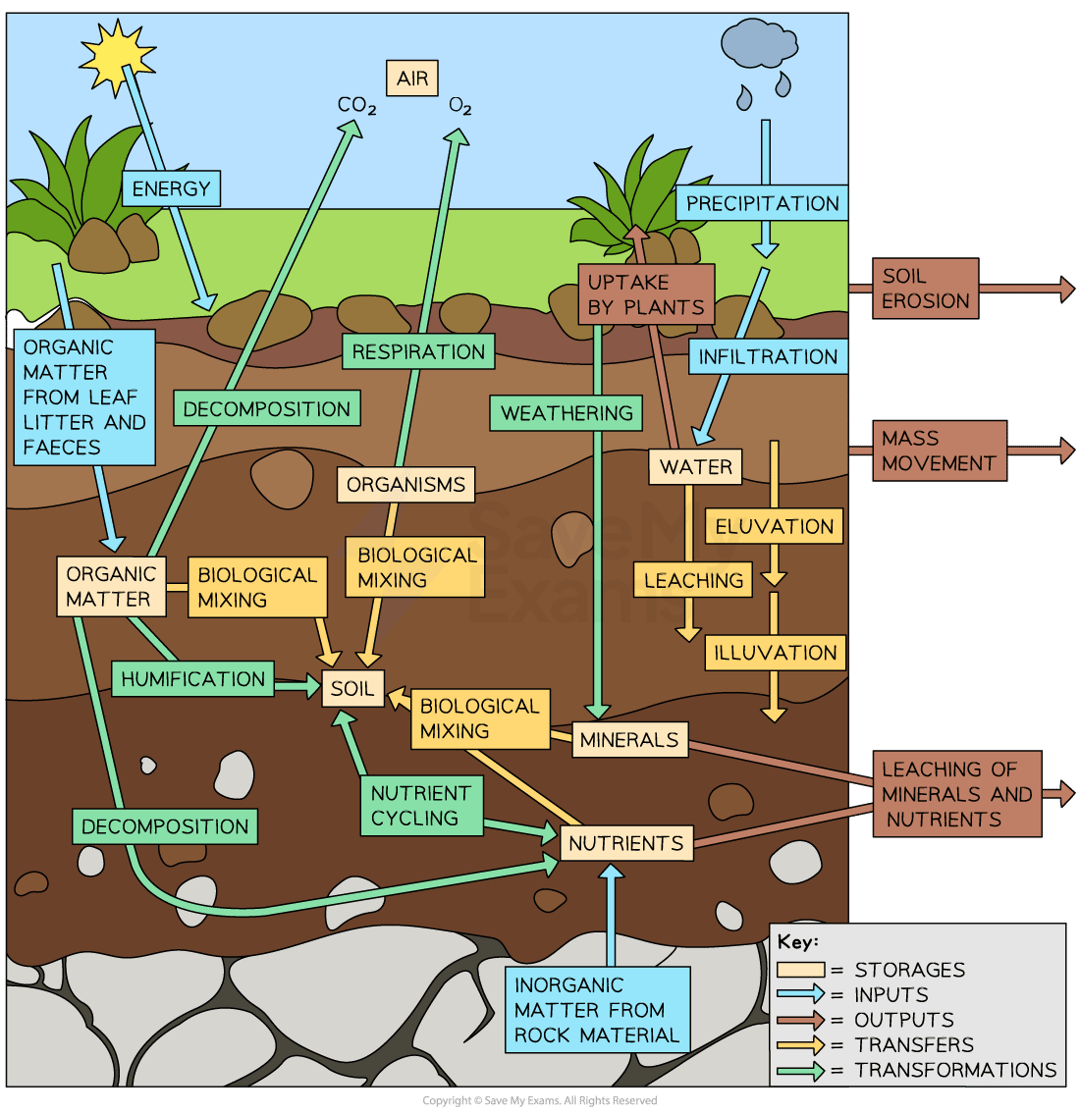
name the storages of soil systems
organic matter
organisms
nutrients
minerals
air
water
name the inputs of a soil system
organic matter
inorganic matter from rock material
precipitation
infiltration
energy
name the outputs of soil systems
leaching
uptake of plants
mass movement
soil erosion
name the transferes in soil systems
biological mixing
leaching
eluviation
illuviation
name the transformations in soil systems
decomposition
weathering
nutrient cycling
humification
mineralisation
intensive grazing
the grzing of livestock where the vegetation ad soil is damaged because there is more grazing than what the lan can keep up with
overcropping
the land is constantly being cultivated instead of being given time to lie fallow in between
soil erosion
the nage in the coil characteristics that cause it to loose fertility. this can be from the removal of the land or leaching, ollution
soil conditioner
helps improve soil structure by increasing aeration, water holding capacity, nutrient content and help break up compacted clay soils
terracing
building flat crop fields on slopes of fields to slow down the flow of water and checking soil erosion
ploughing
breaking up the soil toe aerate it and also uproots plants such as weeds
contour farming
tillin sloped land along lines of consistent elevation to conserve water and reduce soil losses
crop rotation
planting a different crop after harvesting the previous one fully or season change
desertification
the destruction of a landscape from over farming that eventually leaves in a desert like state depleted of nutrients
wind breaks
lines of trees, shrubbery to protect winds from taking away the top layer of soil
strip cultivation
mixed cropping in systematic series of bands acts as a barrier to water or wind. staggered harvest reduces the amount of exposed soil
liming
lime is added to the soil o reduce its acidity to artificially make acidic soil more neutral or if there is excess acid deposition, then to adapt to these conditions
mulching
covering the soil with organic or inorganic material can protect it from erosion, prevent weed growth, and restore nutrient levelstrick
trickle drip
slow release of water from pipes under the surface can help reduce loss of water from evaporation and leaching
marginal lands
land that is avoided because it is difficult land to farm on but it has to be used sometimes to meet demand